About the journal
The Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia is a scientific publication of the Brazilian Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics Associations (FEBRASGO). It is aimed at gynecologists, obstetricians and professionals in related areas with the purpose to publish research results on relevant topics in the field of Gynecology, Obstetrics and related areas.
-
Febrasgo Position Statement
Immunization in women’s lives: present and future
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS10
Summary
Febrasgo Position StatementImmunization in women’s lives: present and future
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS10
Views25See moreKey points
•The negative impact of infectious diseases and their immunoprevention during the different stages of a woman’s life requires a broad approach including adolescence, adulthood, pregnancy and the postmenopausal phase.
•Immunization of pregnant women should be a priority for the protection of the maternal-fetal dyad, especially in regions with high rates of infections preventable by immunization.
•Brazil has one of the most comprehensive vaccination programs in the world – the National Immunization Program (Programa Nacional de Imunizações, PNI) – that serves all age groups: newborns, children, adolescents, adults, pregnant women and older adults, as well as groups with special needs, such as adolescents, pregnant and older adult women.
•However, vaccination coverage remains below ideal for all available vaccines, especially among adolescents and pregnant women, and Febrasgo is committed to collaborating with the PNI to combat vaccine hesitancy.
•The gynecologist/obstetrician is the reference physician for women, therefore the access to information and updates regarding all vaccines recommended for their patients is extremely important for this professional, aiming at the greatest possible protection.
•The objective of this Febrasgo Position Statement is to bring an update to women’s vaccination schedule, covering some vaccines that are available, including new approved vaccines and those in the commercialization phase.
•This work is a compilation of the First Febrasgo Scientific Immunization Forum held in the city of São Paulo in October 2023 with the objective to update recommendations for vaccines in use and new innovative vaccines soon to be available.
-
GUIDELINES
Brazilian Guideline on Menopausal Cardiovascular Health – 2024
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo100
Summary
GUIDELINESBrazilian Guideline on Menopausal Cardiovascular Health – 2024
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo100
Views371. IntroductionAfter the publication of the results from the Women’s Health Initiative (WHI) clinical trial in 2002 showing more risks than benefits to female health with estrogen (alone or combined with progestin) use to control menopausal signs and symptoms, there has been a progressive and sustained decline in the prescription of those drugs.–In the United […]See more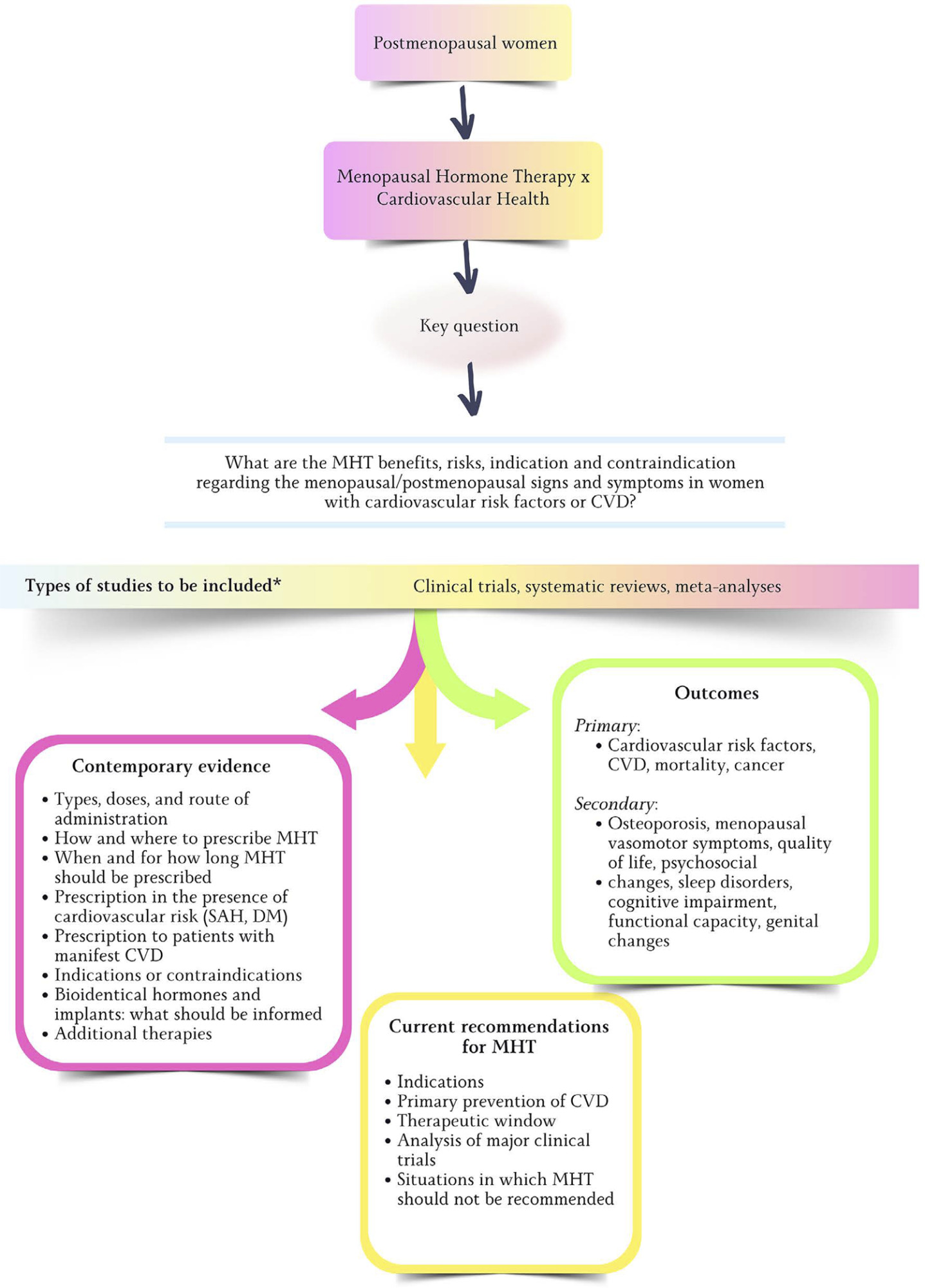
-
Febrasgo Position Statement
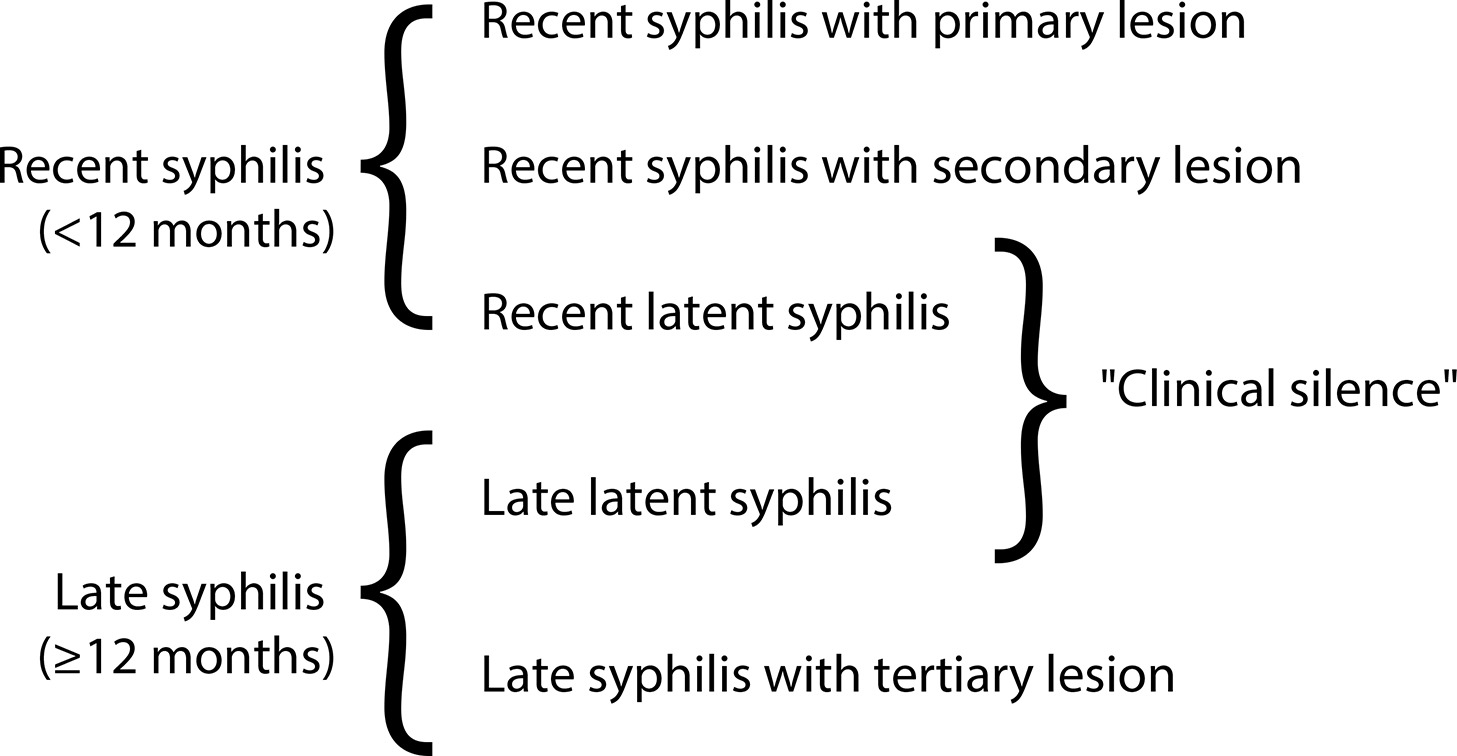
Syphilis and pregnancy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS09
Summary
Febrasgo Position StatementSyphilis and pregnancy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS09
Views66See moreKey points
•Although congenital syphilis has a known etiological agent, accessible diagnosis and low-cost, effective treatment with low fetal toxicity, it continues to challenge obstetric and antenatal care services.
•The increasing rates of syphilis in the general population have direct repercussions on the increase in cases of congenital syphilis, a situation of objective interest for public health.
•Although transforming the recording of syphilis and congenital syphilis into notifiable diseases improved the records and has made it possible to measure the occurrence of these diseases and create solutions, no effects on reducing their frequency have been reached yet.
•The failure to control syphilis/congenital syphilis is multifactorial, and associates variables that range from the deficiency in teaching about these diseases in schools and in the training system of the various health professional segments, as well as the lack of rigid policies for quality control from antenatal care until the clinical follow-up of children exposed to Treponema pallidum during pregnancy.
•To date, benzathine penicillin is the only antimicrobial accepted as effective by the main health authorities on the planet for the treatment of syphilis in pregnant women.
•The fear of anaphylaxis in response to the treatment of syphilis with benzathine penicillin is an important factor hindering the prompt and correct treatment of pregnant women with syphilis, even though health authorities have made efforts to face the problem with solid arguments, still insufficient to resolve the question.
•Although specific protocols are published, the failure to control the treatment of syphilis in pregnant women is still observed with high frequency, indicating and reinforcing a failure in the quality control of these care principles.
The National Specialized Commission on Infectious Diseases of the Brazilian Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics Associations (Febrasgo) endorses this document. Content production is based on scientific evidence on the proposed topic and the results presented contribute to clinical practice.
-
Review Article
Immunosuppressants in women with repeated implantation failure in assisted reproductive techniques: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo70
Summary
Review ArticleImmunosuppressants in women with repeated implantation failure in assisted reproductive techniques: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo70
Views137Abstract
Objective
To compare outcomes in patients with repeated implantation failure undergoing Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection/In vitro fertilization (IVF/ICSI) plus immunosuppressants such as prednisolone, prednisone, or cyclosporine A versus the use of IVF/ICSI alone.
Data source
Databases were systematically searched in PubMed, Cochrane, and Embase databases in September 2023.
Study Selection
Randomized clinical trials and observational studies with the outcomes of interest were included.
Data collect
We computed odds ratios (ORs) for binary endpoints, with 95% confidence intervals (CIs). Heterogeneity was assessed using I2 statistics. Data were analyzed using Review Manager 5.4.The main outcomes were live birth, miscarriage, implantation rate, clinical pregnancy, and biochemical pregnancy.
Data synthesis
Seven studies with 2,829 patients were included. Immunosuppressive treatments were used in 1,312 (46.37%). Cyclosporine A improved implantation rate (OR 1.48; 95% CI 1.01-2.18) and clinical pregnancy (1.89, 95% CI 1.14-3.14). Compared to non-immunosuppressive treatment, prednisolone and prednisone did not improve live birth (OR 1.13, 95% CI 0.88-1.46) and miscarriage (OR 1.49, 95% CI 1.07-2.09). Prednisolone showed no significant effect in patients undergoing IVF/ICSI, clinical pregnancy (OR 1.34; 95% CI 0.76-2.36), or implantation rate (OR 1.36; 95% CI 0.76-2.42).
Conclusion
Cyclosporine A may promote implantation and clinical pregnancy rates. However, given the limited sample size, it is important to approach these findings with caution. Our results indicate that prednisolone and prednisone do not have any beneficial effects on clinical outcomes of IVF/ICSI patients with repeated implantation failure.
PROSPERO
CRD42023449655
Key-words Cyclosporine APrednisolone Immunosupressive agentsPrednisoneRepeated implantation failureReproductionReproductive techniques, assistedSee more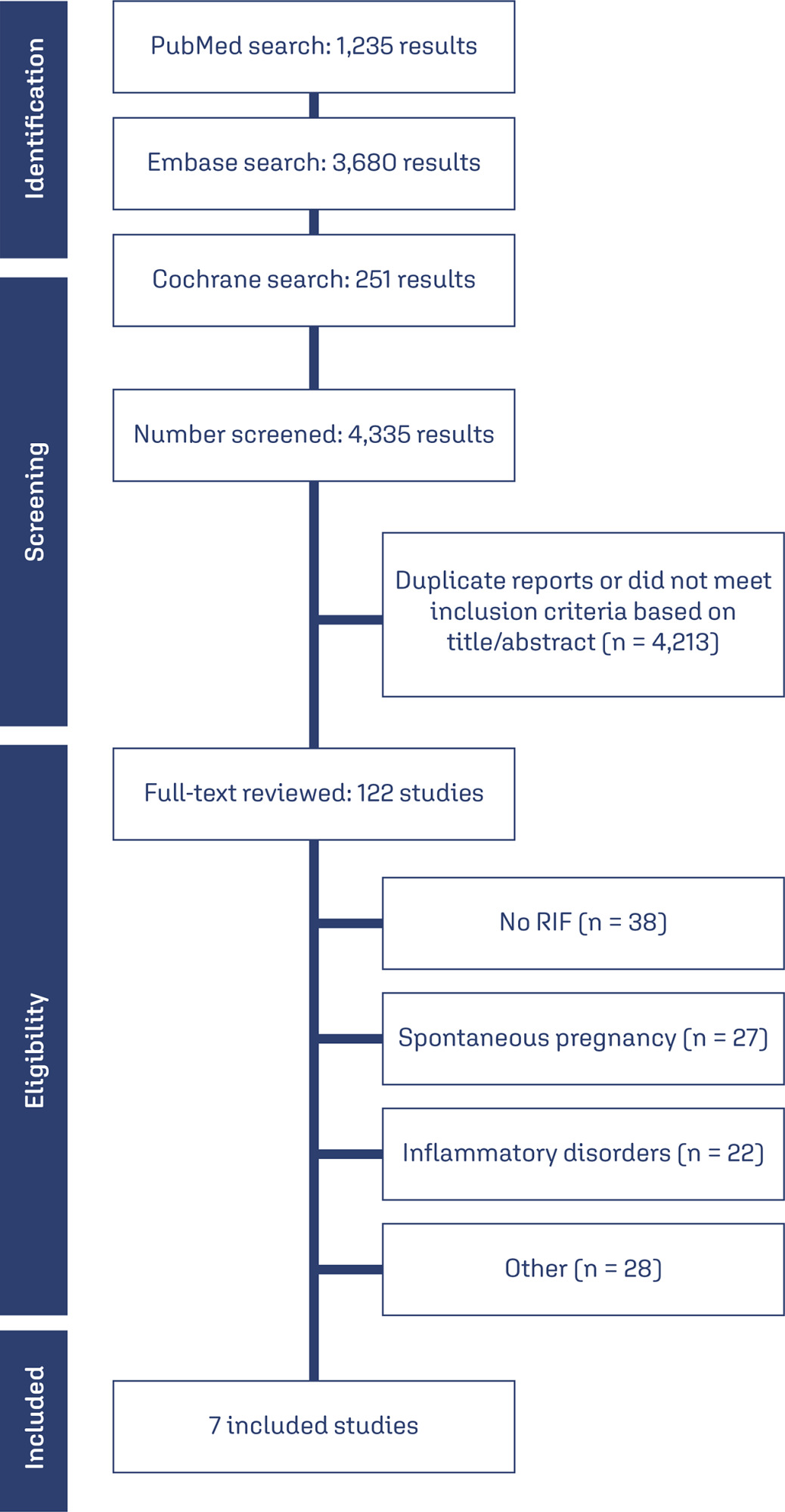
-
Original Article
Multidisciplinary team training in postpartum hemorrhage: impact on the use of blood products
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo67
Summary
Original ArticleMultidisciplinary team training in postpartum hemorrhage: impact on the use of blood products
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo67
Views38See moreAbstract
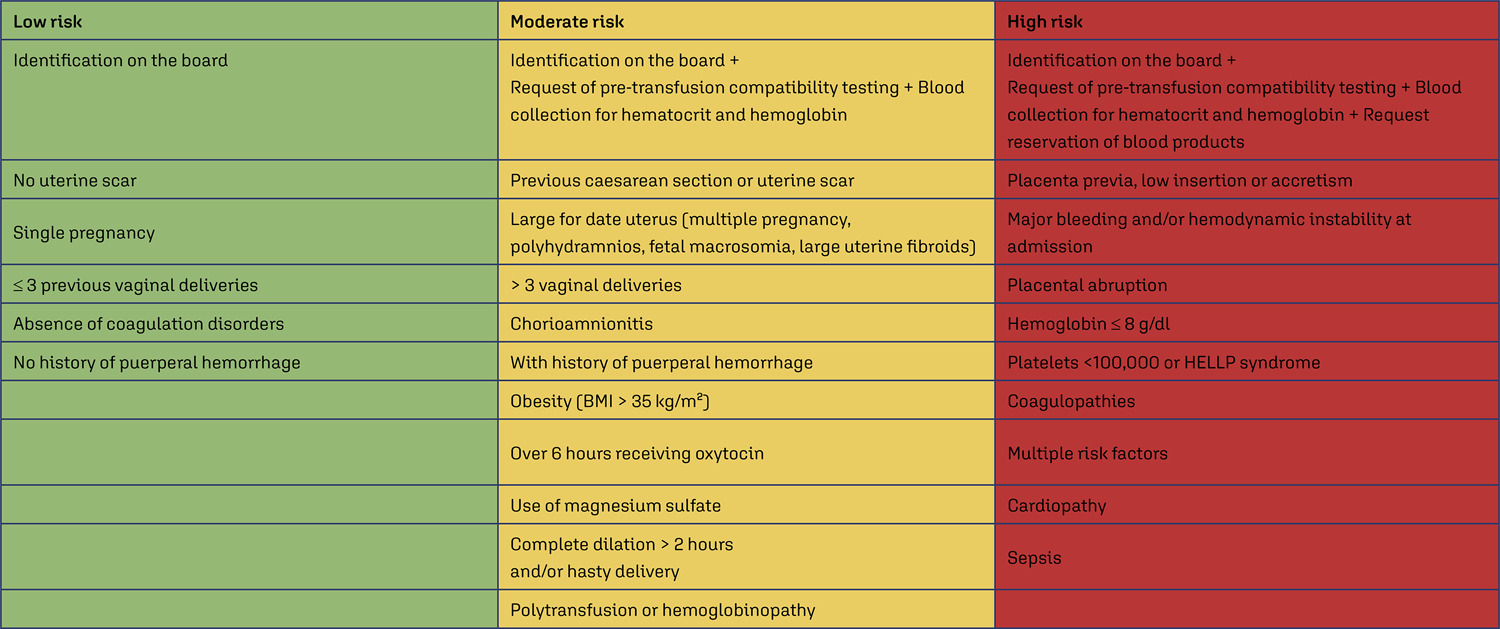
Objective
Compare the number of puerperal women submitted to blood transfusion before and after the implementation of a care protocol for postpartum hemorrhage (PPH) with multidisciplinary team training.
Methods
Cross-sectional study in a university hospital, analyzing births from 2015 to 2019, compared the use of blood products before and after the adoption of a PPH protocol with multidisciplinary training.
Results
Between 2015 and 2019, there were 17,731 births, with 299 (1.7%) postpartum women receiving blood products and 278 postpartum women were considered for this analysis, 128 (0.7%) at Time 1 and 150 (0.8%) at Time 2. After the multiprofessional team training (T2), there was a difference in the complete use of the PPH protocol (use of oxytocin, misoprostol and tranexamic acid) (T1 = 5.1% x T2 = 49.5%, p≤0.0001). An individual categorized analysis revealed that, in the T2 period, there was lower use of blood component units per patient compared to T1 (Mann-Whitney, p=0.006). It should be noted that at T1 and T2, 54% and 24% respectively received two units of blood products. It is important to highlight that after the multidisciplinary team training for the PPH protocol, the goal of zero maternal death due to hemorrhage was reached.
Conclusion
The adoption of a specific protocol for PPH, combined with the training of a multidisciplinary team, had an impact on the ability to identify women at high risk of hemorrhage, resulting in a decrease in the use of blood components.
-
Review Article
Neonatal and maternal outcomes of mRNA versus Non-mRNA COVID-19 vaccines in pregnant patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo69
Summary
Review ArticleNeonatal and maternal outcomes of mRNA versus Non-mRNA COVID-19 vaccines in pregnant patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo69
Views58Abstract
Objective
To compare the effectiveness and safety of non-mRNA versus mRNA COVID-19 vaccines on pregnant women and their newborns in a systematic review with meta-analysis.
Data sources
We searched PubMed, Embase, and Cochrane Central in May 2023.
Study selection
The search strategy yielded 4451 results, 16 studies were fully reviewed. We selected case-control studies analysing non-mRNA versus mRNA vaccines. Data collection and analysis: we assessed the risk of bias using the Cochrane Risk of Bias in Non-randomized Studies of Interventions (ROBINS-I) tool. Standardised mean differences were pooled using random-effect models.
Data synthesis
We identified 8 prospective and retrospective studies with a total of 32,153 patients. Non-mRNA vaccines were associated with a higher incidence of fever (OR 2.67; 95% CI 2.08-3.43; p<0.001), and a lower incidence of fetal or neonatal death (OR 0.16; 95% CI 0.08-0.33; p<0.001). In subgroup analyses, the Jansen vaccine (Ad26.COV2.S) was found to have a higher rate of premature labor/delivery (OR 4.48; 95% CI 1.45-13.83; p=0.009) and missed/spontaneous abortion (OR 1.90; 95% CI 1.09-3.30; p=0.02), as compared with the Pfizer (BNT162b2) vaccine.
Conclusion
non-mRNA vaccines are associated with a lower incidence of fetal or neonatal death among pregnant women who receive a Covid19 vaccine, although at an increased rate of pyrexia compared with mRNA vaccines. Other studies are required for better assessment.
PROSPERO
CRD42023421814
Key-words Coronavirus infectionsCOVID-19COVID-19 vaccinesInfant, newbornmRNA vaccinesPregnancy complicationsPregnant womenSARS-CoV-2See more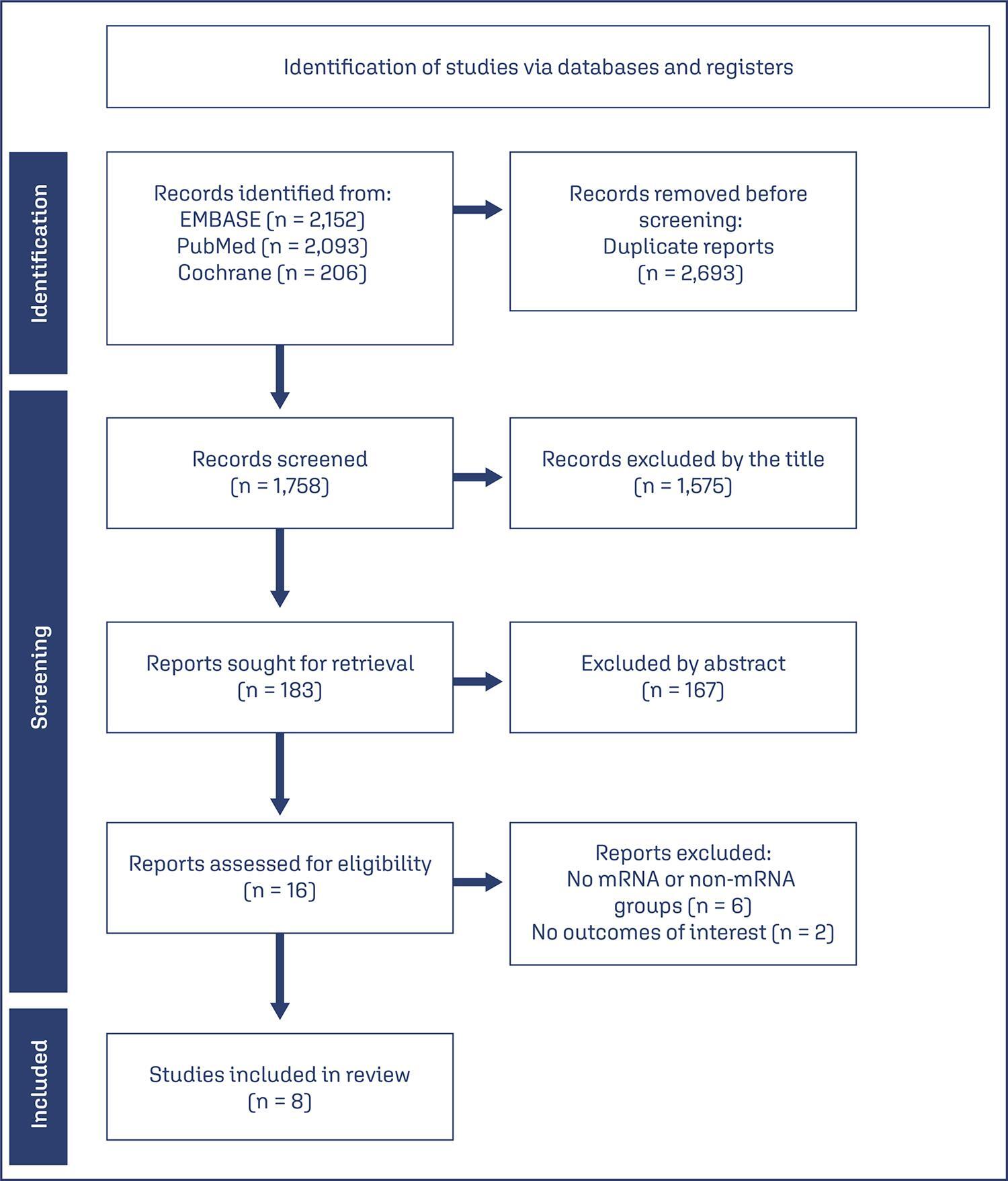
-
Original Article
A new screening of preterm birth in gestation with short cervix after pessary plus progesterone
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo39i
Summary
Original ArticleA new screening of preterm birth in gestation with short cervix after pessary plus progesterone
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo39i
Views95See moreAbstract
Objective
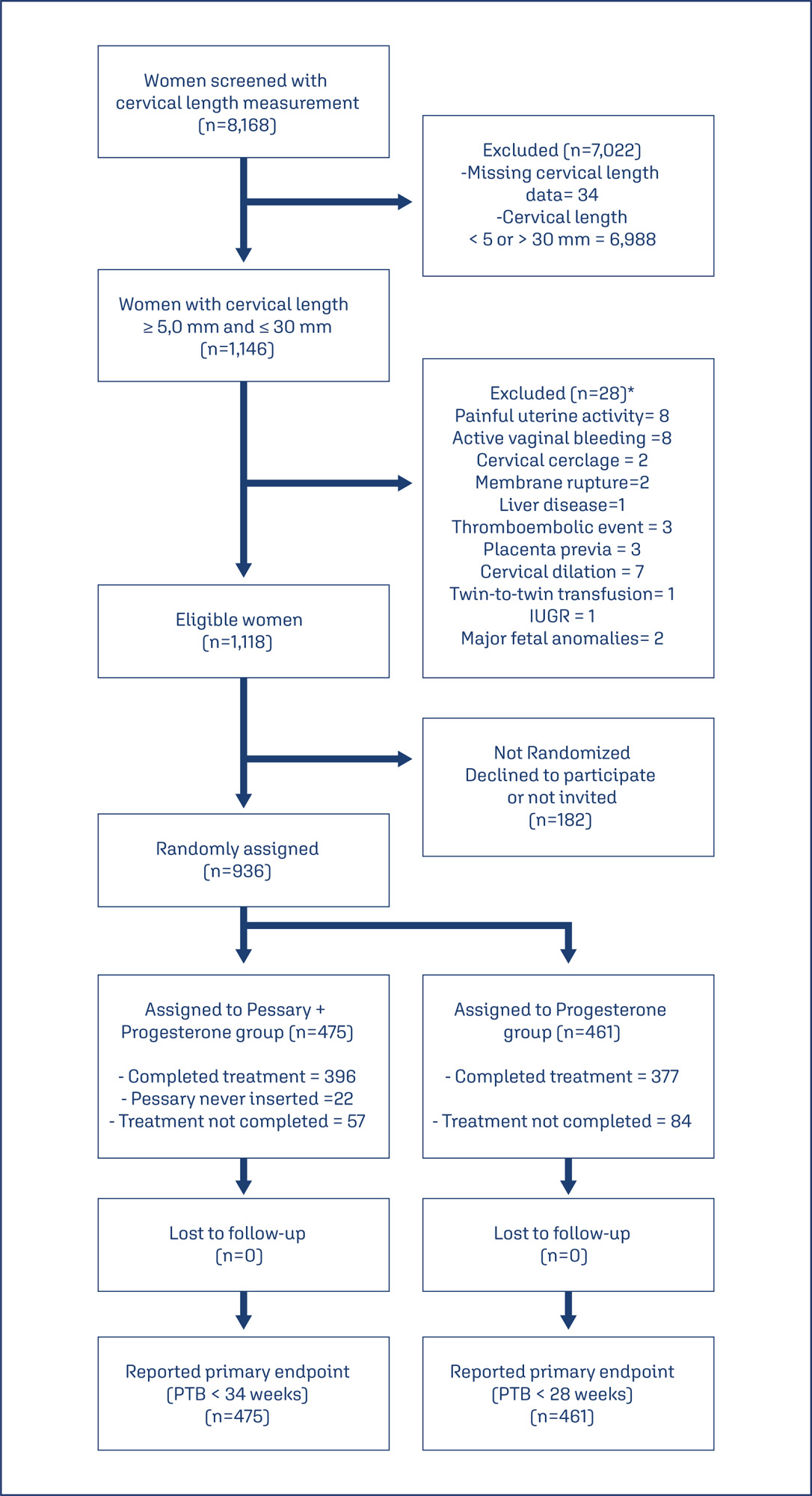
This study aims to create a new screening for preterm birth < 34 weeks after gestation with a cervical length (CL) ≤ 30 mm, based on clinical, demographic, and sonographic characteristics.
Methods
This is a post hoc analysis of a randomized clinical trial (RCT), which included pregnancies, in middle-gestation, screened with transvaginal ultrasound. After observing inclusion criteria, the patient was invited to compare pessary plus progesterone (PP) versus progesterone only (P) (1:1). The objective was to determine which variables were associated with severe preterm birth using logistic regression (LR). The area under the curve (AUC), sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) were calculated for both groups after applying LR, with a false positive rate (FPR) set at 10%.
Results
The RCT included 936 patients, 475 in PP and 461 in P. The LR selected: ethnics white, absence of previous curettage, previous preterm birth, singleton gestation, precocious identification of short cervix, CL < 14.7 mm, CL in curve > 21.0 mm. The AUC (CI95%), sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and PNV, with 10% of FPR, were respectively 0.978 (0.961-0.995), 83.4%, 98.1%, 83.4% and 98.1% for PP < 34 weeks; and 0.765 (0.665-0.864), 38.7%, 92.1%, 26.1% and 95.4%, for P < 28 weeks.
Conclusion
Logistic regression can be effective to screen preterm birth < 34 weeks in patients in the PP Group and all pregnancies with CL ≤ 30 mm.
-
Review Article
Relationship between early age at menarche, older age at menopause and subtypes of breast cancer: a scoping review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo50
Summary
Review ArticleRelationship between early age at menarche, older age at menopause and subtypes of breast cancer: a scoping review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo50
Views83See moreAbstract
Objective
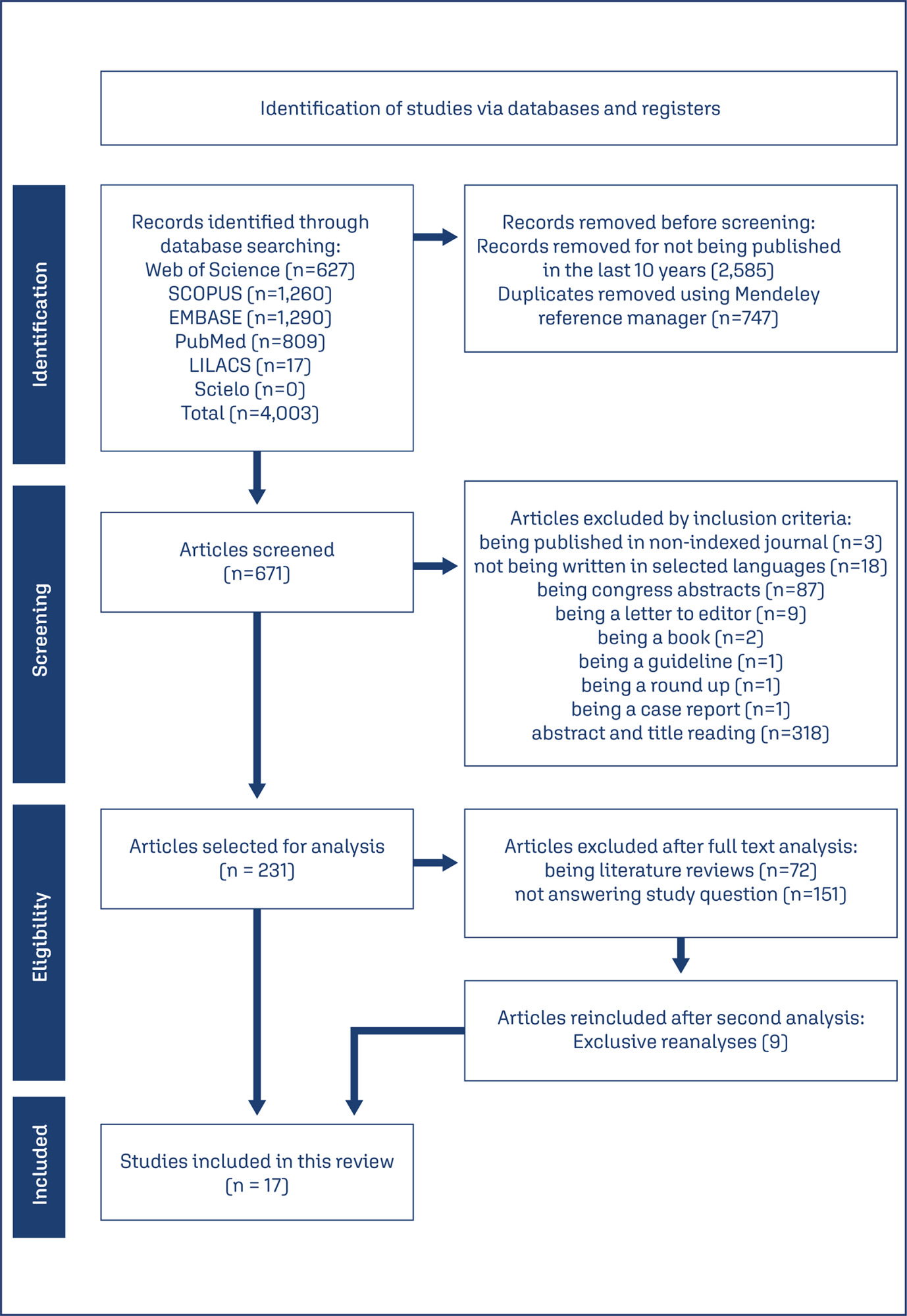
To determine the relationship between early age at menarche, late age at menopause with specific subtypes of breast cancer (BC).
Methods
A literature search was conducted in Embase, Lilacs, PubMed, Scopus, and Scielo databases, following the Joanna Briggs Institute scoping review protocol and answering the question “How early age at menarche or late age at menopause are related to different breast cancer subtypes?”.
Results
A number of 4,003 studies were identified, of which 17 were selected. Most of the included articles found a clear relationship between early menarche, late menopause and some subtypes of BC, mainly, PR+, ER+, luminal, and HER-2 tumors. However, some studies have found a contradictory relationship and one study didn’t find any relationship between them.
Conclusion
A relationship between early age at menarche and advanced age at menopause was observed with some subtypes of breast cancer, since other factors must be considered in its understanding.
-
Febrasgo Position Statement
Hyperprolactinemia in women: diagnostic approach
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS04
Summary
Febrasgo Position StatementHyperprolactinemia in women: diagnostic approach
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS04
-
Febrasgo Position Statement
Hyperprolactinemia in women: treatment
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS05
Summary
Febrasgo Position StatementHyperprolactinemia in women: treatment
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS05
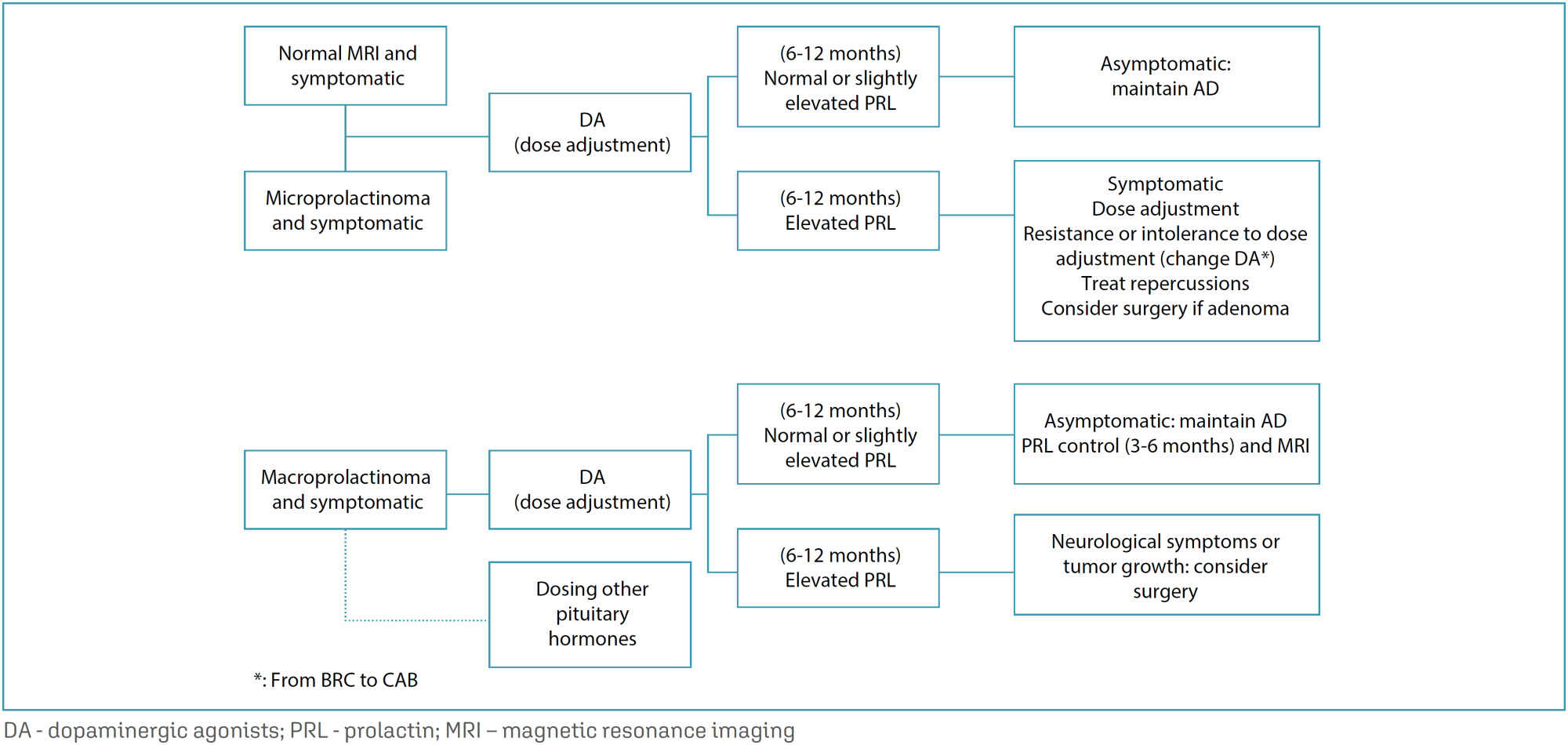
-
Febrasgo Position Statement
Breech birth care: Number 1 – 2024
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgofps1
Summary
Febrasgo Position StatementBreech birth care: Number 1 – 2024
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgofps1
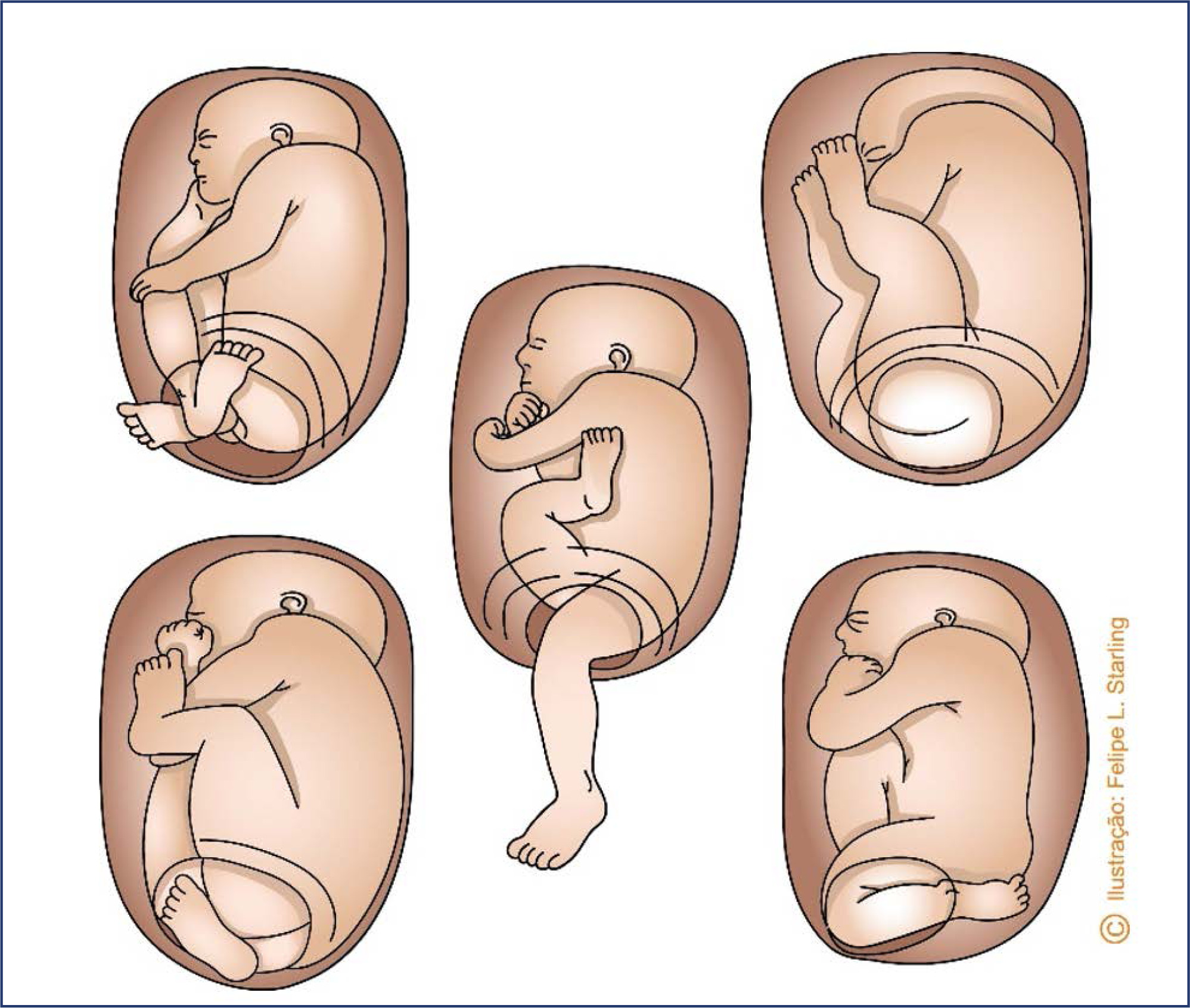
-
Letter to the Editor
Letter to Editor: In response to existence of SARS-CoV-2 in the peritoneal fluid
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo24
Summary
Letter to the EditorLetter to Editor: In response to existence of SARS-CoV-2 in the peritoneal fluid
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo24
-
Trabalhos Originais
Search for human papillomavirus in samples of normal endometrial tissue and tissue with carcinoma by the PCR technique
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(4):277-287
Summary
Trabalhos OriginaisSearch for human papillomavirus in samples of normal endometrial tissue and tissue with carcinoma by the PCR technique
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(4):277-287
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000400003
Views473See moreOBJECTIVE: to compare the prevalence of DNA of human papillomavirus (HPV), in samples of normal endometrial tissue, and tissue with endometrial carcinoma of women submitted to surgical treatment (hysterectomy), or between endometrial carcinoma and benign disease, through the PCR technique. METHODS: this is an observational control-case study where 100 women (50 with endometrial carcinoma and 50 with normal endometrial tissue) were analyzed for the detection of HPV DNA in samples of endometrial tissue kept in paraffin blocks by the PCR technique. The cases of endometrial carcinoma with uncertain primary site of the lesion as well as the cases with previous or current history of pre-neoplasic lesions or carcinoma of the lower genital tract were excluded. Variables as age, smoking habit, endometrial trophism, squamous differentiation and degree of tumor differentiation were also evaluated. RESULTS: the estimated relative risk of the presence of HPV in the endometrial carcinoma and in the normal endometrial tissue was the same. HPV was detected in 8% of the cases of carcinoma and 10% in the normal endometrial tissue. In spite of HPV having been 3.5 times more detected in women with smoking habit in the group without carcinoma, there was no statistical difference. The presence of HPV was also not correlated with the women’s age, endometrial trophism, squamous differentiation and degree of tumor differentiation. The HPV types 16 (5 cases) and 18 (4 cases) were the viruses most frequently found both in the normal endometrial tissue or in the tissue with carcinoma. No oncogenic low risk virus was detected in the samples. CONCLUSION: The same proportion of HPV is present in the endometrial tissue of women with endometrial cancer and with normal endometrium. It could not be demonstrated a possible correlation of DNA of HPV with the development of endometrial carcinoma.
-
Review Article
Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS®): a success history and particularities of its use in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo6
Summary
Review ArticleBreast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS®): a success history and particularities of its use in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo6
Views472See moreAbstract
BI-RADS® is a standardization system for breast imaging reports and results created by the American College of Radiology to initially address the lack of uniformity in mammography reporting. The system consists of a lexicon of descriptors, a reporting structure with final categories and recommended management, and a structure for data collection and auditing. It is accepted worldwide by all specialties involved in the care of breast diseases. Its implementation is related to the Mammography Quality Standards Act initiative in the United States (1992) and breast cancer screening. After its initial creation in 1993, four additional editions were published in 1995, 1998, 2003 and 2013. It is adopted in several countries around the world and has been translated into 6 languages. Successful breast cancer screening programs in high-income countries can be attributed in part to the widespread use of BI-RADS®. This success led to the development of similar classification systems for other organs (e.g., lung, liver, thyroid, ovaries, colon). In 1998, the structured report model was adopted in Brazil. This article highlights the pioneering and successful role of BI-RADS®, created by ACR 30 years ago, on the eve of publishing its sixth edition, which has evolved into a comprehensive quality assurance tool for multiple imaging modalities. And, especially, it contextualizes the importance of recognizing how we are using BI-RADS® in Brazil, from its implementation to the present day, with a focus on breast cancer screening.
-
Editorial
The path to elimination: FEBRASGO 2023’s targeted strategies against cervical cancer in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgoedt2
Summary
EditorialThe path to elimination: FEBRASGO 2023’s targeted strategies against cervical cancer in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgoedt2
-
Febrasgo Position Statement
Vulvovaginitis in pregnant women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS03
Summary
Febrasgo Position StatementVulvovaginitis in pregnant women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS03
Views336See moreKey points
• The balanced vaginal microbiome is the main factor defending the vaginal environment against infections. Lactobacilli play a key role in this regard, maintaining the vaginal pH within the normal range (3.8 to 4.5).
•Hormonal and immune adaptations resulting from pregnancy influence changes in the vaginal microbiome during pregnancy.
•An altered vaginal microbiome predisposes to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection.
•Bacterial vaginosis is the main clinical expression of an imbalanced vaginal microbiome.
•Vulvovaginal candidiasis depends more on the host’s conditions than on the etiological agent.
•Trichomonas vaginalis is a protozoan transmitted during sexual intercourse.
•The use of probiotics is not approved for use in pregnant women.
-
Review Article
Breastfeeding and the Benefits of Lactation for Women’s Health
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):354-359
Summary
Review ArticleBreastfeeding and the Benefits of Lactation for Women’s Health
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):354-359
Views125See moreAbstract
The offer of the maternal breast to the baby is an unquestionable right of mothers and their children, and all efforts should bemade to promote, follow and maintain exclusive breastfeeding for up to 6months and supplement it until the child completes 2 years of age. Many publications are available in the literature about the qualities of breast milk, its benefits and health repercussions, stimulating the practice of breastfeeding and supporting campaigns for its implementation. However, although it is widely known that breastfeeding is an important step in the reproductive process of women and its practice offers benefits to both mother and child, most of the available information highlights the benefits of breast milk for children, while mention of the effects of breastfeeding on the health of the mother is usually neglected. Thus, the objective of the present study is to highlight the multiple benefits of breastfeeding for the physical and emotional health of the nursing mother. The authors consulted articles published in the databases PubMed, Virtual Health Library andWeb of Science using the keywords breastfeeding, breast milk, lactation and maternal health.
-
Artigos Originais
Translation into Portuguese, cross-national adaptation and validation of the Female Sexual Function Index
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(10):504-510
Summary
Artigos OriginaisTranslation into Portuguese, cross-national adaptation and validation of the Female Sexual Function Index
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(10):504-510
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001000005
Views6PURPOSE: to translate from English into Portuguese, adapt culturally and validate the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI). METHODS: knowing the objectives of this research, two Brazilian translators have prepared a version each from the FSFI into Portuguese. Both versions have then been retro-translated into English by two English translators. After harmonizing the differences, they have been pre-tested in a pilot study. The final versions from the FSFI and from another questionnaire, the Short-Form Health Survey, which had already been translated and published in Portuguese, have then been simultaneously administered to one hundred patients, to test the FSFI psychometric proprieties concerning reliability (internal consistency and testing-retesting) and construct validity. Retesting was done after four weeks from the first interview. RESULTS: the process of cultural adaptation has not altered the Portuguese version of the FSFI, as compared to the original. The FSFI standardized Cronbach alpha was 0.96, and the evaluation by domains has varied from 0.31 to 0.97. As a measure of test-retest confidentiality, it was applied the intra-class coefficient, which has been considered strong and identical (1.0). Pearson’s correlation coefficient between the FSFI and the Short-Form Health Survey was positive, but weak in most of the interrelated domains, varying from 0.017 to 0.036. CONCLUSIONS: the FSFI English version has been translated into Portuguese and culturally adapted, being reliable to evaluate the sexual response of Brazilian women.
Key-words QuestionnairesReproducibility of resultsSexual dysfunctions, psychologicalTranslationsValidation studiesWomen’s healthSee more -
Review Article
Preeclampsia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(9):496-512
Summary
Review ArticlePreeclampsia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(9):496-512
Views50Abstract
The authors review hypertensive disease during pregnancy with an academic and practical view, and using the best evidence available. This disease, which is the most important clinical disease in Brazilian pregnant women, may have its incidence reduced with prevention through the use of calcium and aspirin in pregnant women at risk. Previously, it was a disease that presented with hypertension with proteinuria, but it has now been classified with new clinical parameters besides proteinuria. Morbidity and mortality should be reduced in a continental country such as Brazil using protocols for the early treatment of complications by calculating severe outcomes in preeclampsia. The early treatment of acute hypertension, use of magnesium sulfate and early hospitalization in cases of preeclampsia are concepts to pursue the reduction of our pregnant women’s mortality.
Key-words HELLP syndromeHigh-risk pregnancyPreeclampsiapregnancy arterial hypertensionPregnancy complicationsSee more
-
Review Article
Primary Dysmenorrhea: Assessment and Treatment
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(8):501-507
Summary
Review ArticlePrimary Dysmenorrhea: Assessment and Treatment
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(8):501-507
Views88See moreAbstract
Primary dysmenorrhea is defined asmenstrual pain in the absence of pelvic disease. It is characterized by overproduction of prostaglandins by the endometrium, causing uterine hypercontractility that results in uterine muscle ischemia, hypoxia, and, subsequently, pain. It is the most common gynecological illness in women in their reproductive years and one of the most frequent causes of pelvic pain; however, it is underdiagnosed, undertreated, and even undervalued by women themselves, who accept it as part of themenstrual cycle. It hasmajor implications for quality of life, such as limitation of daily activities and psychological stress, being one of themain causes of school and work absenteeism. Its diagnosis is essentially clinical, based on the clinical history and normal physical examination. It is important to exclude secondary causes of dysmenorrhea. The treatment may have different approaches (pharmacological, nonpharmacological and surgical), but the first line of treatment is the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and, in cases of women who want contraception, the use of hormonal contraceptives. Alternative treatments, such as topical heat, lifestyle modification, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, dietary supplements, acupuncture, and acupressure, may be an option in cases of conventional treatments’ contraindication. Surgical treatment is only indicated in rare cases of women with severe dysmenorrhea refractory to treatment.
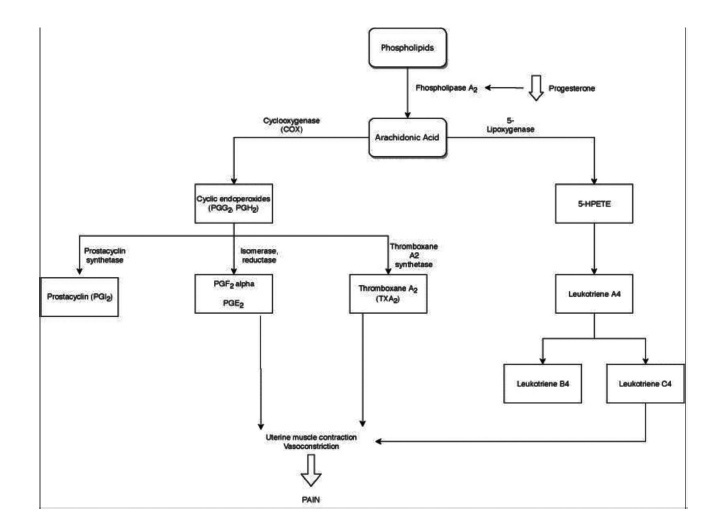
-
Artigos Originais
Coverage of the Pap smear in Brazil and its determining factors: a systematic literature review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(8):485-492
Summary
Artigos OriginaisCoverage of the Pap smear in Brazil and its determining factors: a systematic literature review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(8):485-492
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000800009
Views3See morePURPOSE: to present an overview of the coverage of the Pap smear in Brazil, emphasizing the determinant factors associated with failure of women to submit to the test. METHODS: the literature was reviewed using the LILACS (Latin-American and Caribbean Literature in Sciences of the Health), MEDLINE – 1966 to 2004 (International Literature in Sciences of the Health), PAHO (Collection of the Library of the Pan-American Organization of Health), and WHOLIS (System of Information of the Library of OMS) databases. The review was enlarged through the search of bibliographical references of relevant studies, request for published and unpublished studies by specialists, and other sources. Articles that fulfilled the following criteria were selected: to be a cross-sectional study, carried out in Brazil, including information about periodicity of the Pap test (some time in life or in the last three years) and/or containing information about factors associated with failure of women to submit to the test. Duplicates and articles without summary were excluded. A total of 13 articles fulfilling these criteria were selected. RESULTS: there are few studies on the coverage of Pap smear in Brazil. Most of them are concentrated in the big cities of the South and Southeast regions of the country. Besides the shortage, little methodological standardization exists in relation to the sampling and profile of the investigated women, which turns difficult the comparison among them. These methodological differences must have contributed to the great variability found in the coverage. However, in spite of all of the problems, a trend of time series increase is observed in the percentage of women who had at least one Pap smear in life. The two studies accomplished in the eighties showed coverage of 55.0 and 68.9% some time in life, while a household survey carried out in 2002 and 2003 presented values that varied from 73.4 to 92.9%; however, two studies of national inclusion presented estimates below 70.0% in the last three years. On the other hand, some variables were associated with the women’s failure to submit to the Pap smear: low socioeconomic level, low education, low family income, and to belong to the younger age groups. CONCLUSION: the data here presented point to regional inequalities in the coverage of the Pap smear in the Brazilian female population and to the need of intervention targeted to those factors associated with women’s failure to submit to the Pap smear.
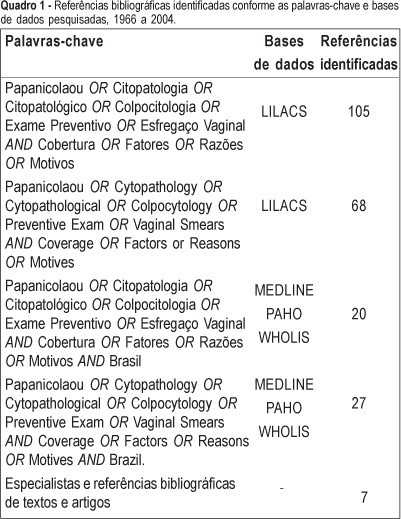
-
Review Article
Multiple Pregnancy: Epidemiology and Association with Maternal and Perinatal Morbidity
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):554-562
Summary
Review ArticleMultiple Pregnancy: Epidemiology and Association with Maternal and Perinatal Morbidity
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):554-562
Views30See moreAbstract
Twin pregnancy accounts for 2 to 4% of total births, with a prevalence ranging from 0.9 to 2.4% in Brazil. It is associated with worse maternal and perinatal outcomes. Many conditions, such as severe maternal morbidity (SMM) (potentially life-threatening conditions and maternal near-miss) and neonatal near-miss (NNM) still have not been properly investigated in the literature. The difficulty in determining the conditions associated with twin pregnancy probably lies in its relatively low occurrence and the need for larger population studies. The use of the whole population and of databases from large multicenter studies, therefore, may provide unprecedented results. Since it is a rare condition, it ismore easily evaluated using vital statistics from birth e-registries. Therefore, we have performed a literature review to identify the characteristics of twin pregnancy in Brazil and worldwide. Twin pregnancy has consistently been associated with SMM, maternal near-miss (MNM) and perinatal morbidity, with still worse results for the second twin, possibly due to some characteristics of the delivery, including safety and availability of appropriate obstetric care to women at a high risk of perinatal complications.
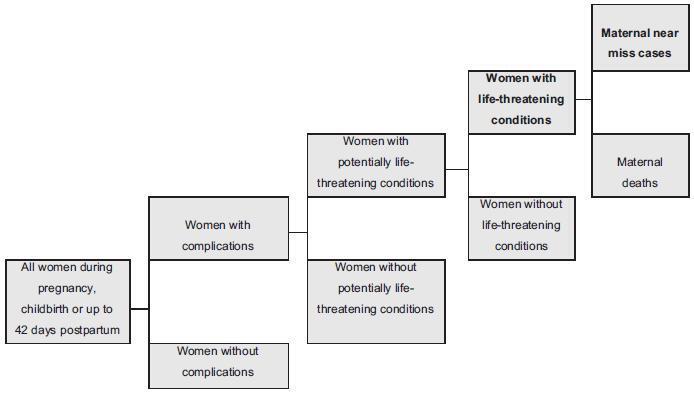
-
Trabalhos Originais
Pré-natal Care Profile among Public Health Service (“Sistema Único de Saúde”) Users from Caxias do Sul
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(5):293-299
Summary
Trabalhos OriginaisPré-natal Care Profile among Public Health Service (“Sistema Único de Saúde”) Users from Caxias do Sul
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2002;24(5):293-299
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000500002
Views2See morePurpose: to study the prenatal care among Public Health Service (“Sistema Único de Saúde”) users from Caxias do Sul – RS. Methods: a transversal study of 702 pregnancies attended at the Hospital Geral -Universidade de Caxias do Sul from March 2000 to March 2001 based on the criteria set by the “Programa Nacional de Humanização do Pré-natal e Nascimento (PNHPN)” of the Brazilian Ministry of Health. Results: the observed prenatal coverage was 95.4%, whereas the average of visits was 6.2. The main reported reason for not following prenatal care was the lack of information about its importance (65.6%). In 51.5% of the cases, prenatal care started in the third month of pregnancy, whereas 44.3% of the pregnant women carried out all the proposed complementary tests. Prenatal care was considered inappropriate in 64.8% and appropriate in 35.2% of the cases. The quality of prenatal attention was significantly associated with the mother’s education, as well as with the number of previous deliveries. The higher the educational level, the better the quality of observed prenatal care (p=0.0148). In addition, the higher number of previous deliveries showed to be associated with a later beginning of prenatal care and a lower number of visits (p=0.0008). Conclusions: the prenatal care available at Caxias do Sul in spite of its good coverage, should be reviewed in terms of quality. Special attention should be given to education in health along the prenatal assistance.
-
Artigos Originais
Validation of a quality of life questionnaire (King’s Health Questionnaire) in Brazilian women with urinary incontinence
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(5):235-242
Summary
Artigos OriginaisValidation of a quality of life questionnaire (King’s Health Questionnaire) in Brazilian women with urinary incontinence
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(5):235-242
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000500002
Views1See morePURPOSE: the proposal of the present study was to translate and to validate King’s Health Questionnaire (KHQ) for Brazilian women with urinary incontinence. METHODS: a hundred and thirty-four patients with urinary incontinence, confirmed by urodynamic study, were enrolled from the outpatient clinic of Uroginecology. Initially, we translated the KHQ into the Brazilian Portuguese language in agreement with international criteria. Due to language and cultural differences we performed a cultural, structural, conceptual, and semantic adaptation of the KHQ, in order to make sure that patients were able to fully understand the questions. All patients answered the KHQ twice on the same day, within an interval of 30 min, applied by two different interviewers. After 7 to 14 days, on a second visit, the questionnaire was applied again. Reliability (intra- and interobserver internal consistency), construct and discriminative validity were tested. RESULTS: several cultural adaptations were necessary until we reached the final version. The intra-observer internal consistency (alpha of Cronbach) of the several dimensions varied from moderate to high (0.77-0.90), and the interobserver internal consistency varied from 0.66 to 0.94. Moderate to strong correlation was detected among the specific KHQ urinary incontinence dominions and clinical urinary incontinence manifestations known to affect the quality of life of these patients. CONCLUSION: KHQ was adapted to the Portuguese language and to the Brazilian culture, showing great reliability and validity. It should be included and used in any Brazilian urinary incontinence clinical trial.

Search
Search in:
Tag Cloud
breast (42) breast cancer (42) Breast neoplasms (101) Cesarean section (76) Endometriosis (69) infertility (54) Maternal mortality (44) Menopause (86) Obesity (59) Polycystic ovary syndrome (41) Postpartum period (43) Pregnancy (243) Pregnancy complications (99) Pregnant women (41) Prenatal care (70) prenatal diagnosis (51) Quality of life (52) Risk factors (101) Ultrasonography (82) Women’s health (48)
Featured Articles
Aims and Vision
The Brazilian Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics (RBGO) aims to publish basic and clinical research in gynecology, obstetrics and other related specialties and be a reference to support and promote professional education for residents, researchers and university teachers. As a vision, RBGO aims to become an internationally recognized reference among the main world’s journals in Gynecology and Obstetrics.