Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2024;46:e-rbgo23
To assess the rate of missed postpartum appointments at a referral center for high-risk pregnancy and compare puerperal women who did and did not attend these appointments to identify related factors.
This was a retrospective cross-sectional study with all women scheduled for postpartum consultations at a high-risk obstetrics service in 2018. The variables selected to compare women were personal, obstetric, and perinatal. The variables of interest were obtained from the hospital's electronic medical records. Statistical analyses were performed using the Chi-square, Fisher's exact, or Mann–Whitney tests. For the variable of the interbirth interval, a receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) was used to best discriminate whether or not patients attended the postpartum consultation. The significance level for the statistical tests was 5%.
A total of 1,629 women scheduled for postpartum consultations in 2018 were included. The rate of missing the postpartum consultation was 34.8%. A shorter interbirth interval (p = 0.039), previous use of psychoactive substances (p = 0.027), current or former smoking (p = 0.003), and multiparity (p < 0.001) were associated with non-attendance.
This study showed a high rate of postpartum appointment non-attendance. This is particularly relevant because it was demonstrated in a high-risk obstetric service linked to clinical severity or social vulnerability cases. This highlights the need for new approaches to puerperal women before hospital discharge and new tools to increase adherence to postpartum consultations, especially for multiparous women.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2024;46:e-rbgo27
To evaluate whether the continuous support provided by doulas influences the endogenous release of serotonin in parturients.
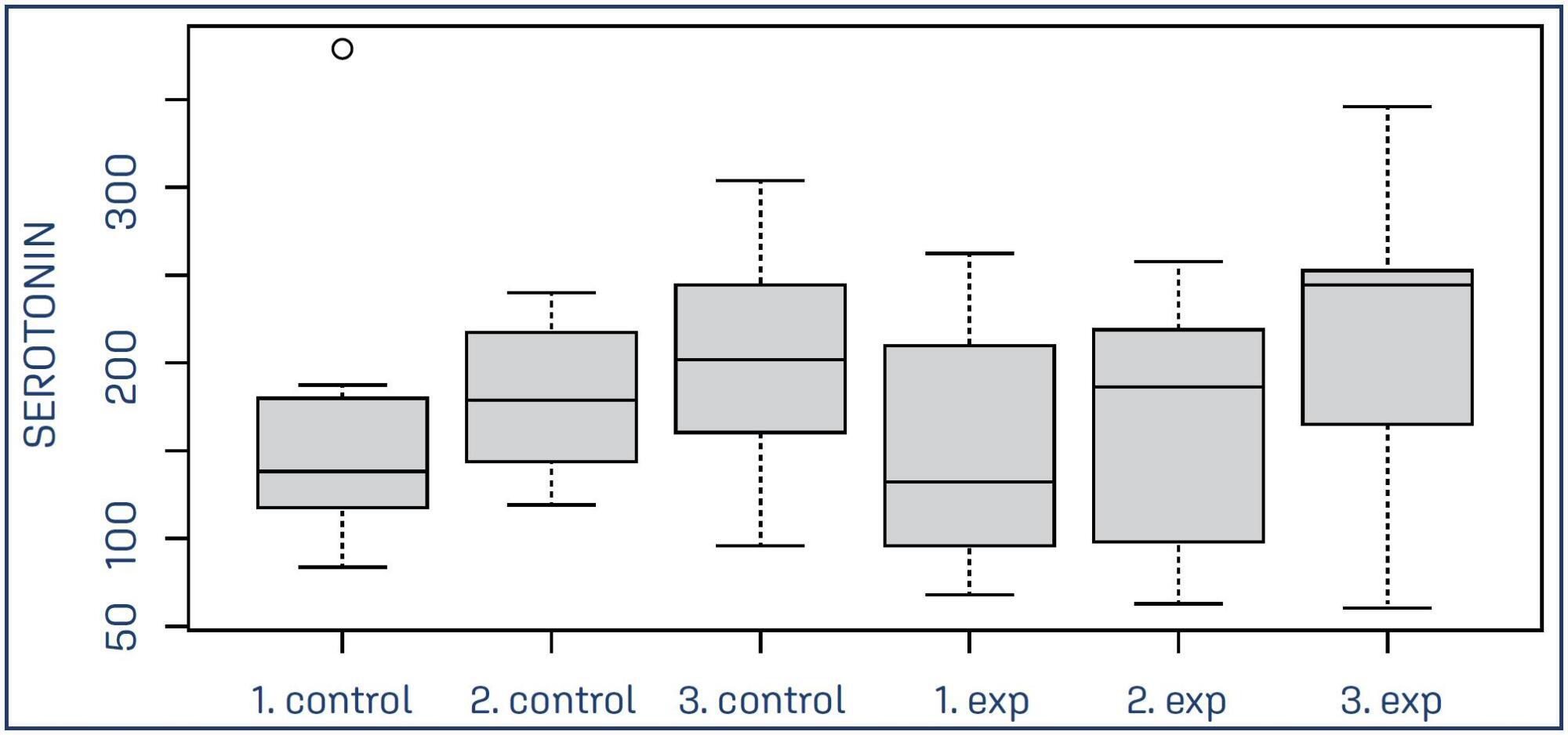
This pilot study included 24 primigravidae at term. Of these, 12 women received continuous doula support (Experimental Group), whereas the other 12 received the usual assistance without doula support (Control Group). Blood samples were collected from all the women at the active and expulsion stages of labor and at the fourth period of labor (Greenberg period) for evaluation of their serotonin levels using high-performance liquid chromatography.
The average serotonin concentrations in the control and experimental groups were respectively 159.33 and 150.02 ng/mL at the active stage, 179.13 and 162.65 ng/mL at the expulsion stage, and 198.94 and 221.21 ng/mL at the Greenberg period. There were no statistically significant differences in serotonin concentrations between the two groups at the active and expulsion stages of labor. By contrast, within the experimental group, a significant increase in serotonin concentration was observed in the Greenberg period compared with the levels in the active and expulsion stages (p < 0.05).
The novelty of this study relies on the ability to correlate the influence of the continuous support offered by doulas with the release of serotonin in parturients, with the results suggesting that the assistance received during labor can modulate the levels of hormone release in the Greenberg period.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2024;46:e-rbgo19
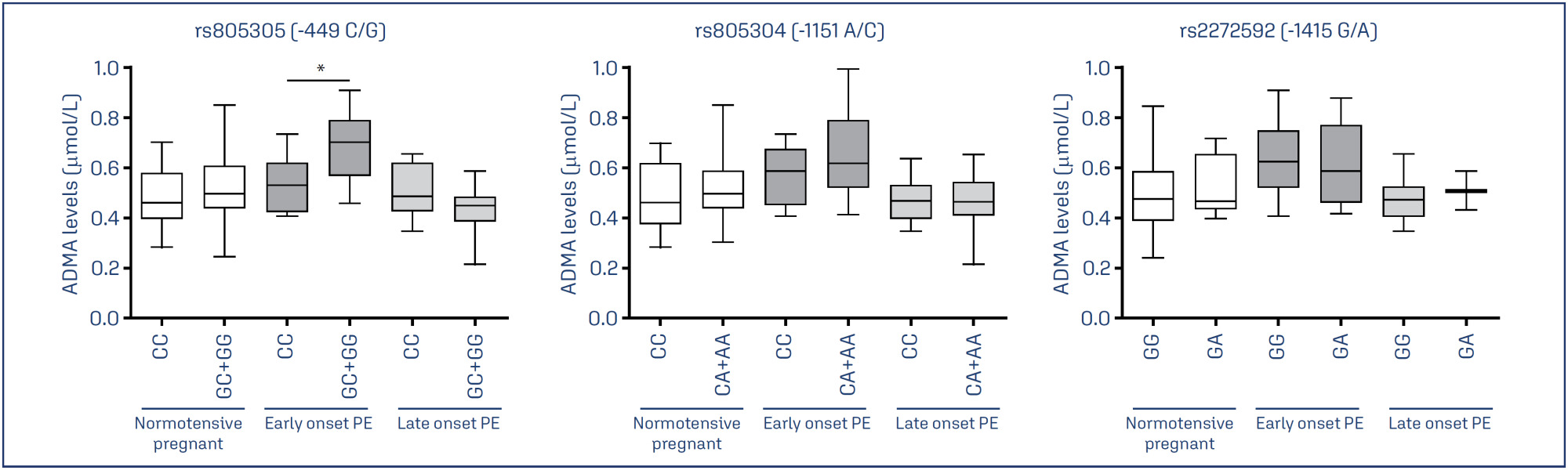
To examine whether the DDAH2 promoter polymorphisms -1415G/A (rs2272592), -1151A/C (rs805304) and -449G/C (rs805305), and their haplotypes, are associated with PE compared with normotensive pregnant women, and whether they affect ADMA levels in these groups.
A total of 208 pregnant women were included in the study and classified as early-onset (N=57) or late-onset PE (N =49), and as normotensive pregnant women (N = 102).
Pregnant with early-onset PE carrying the GC and GG genotypes for the DDAH2 -449G/C polymorphism had increased ADMA levels (P=0.01). No association of DDAH2 polymorphisms with PE in single-locus analysis was found. However, the G-C-G haplotype was associated with the risk for late-onset PE.
It is suggested that DDAH2 polymorphisms could affect ADMA levels in PE, and that DDAH2 haplotypes may affect the risk for PE.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(9):821-829
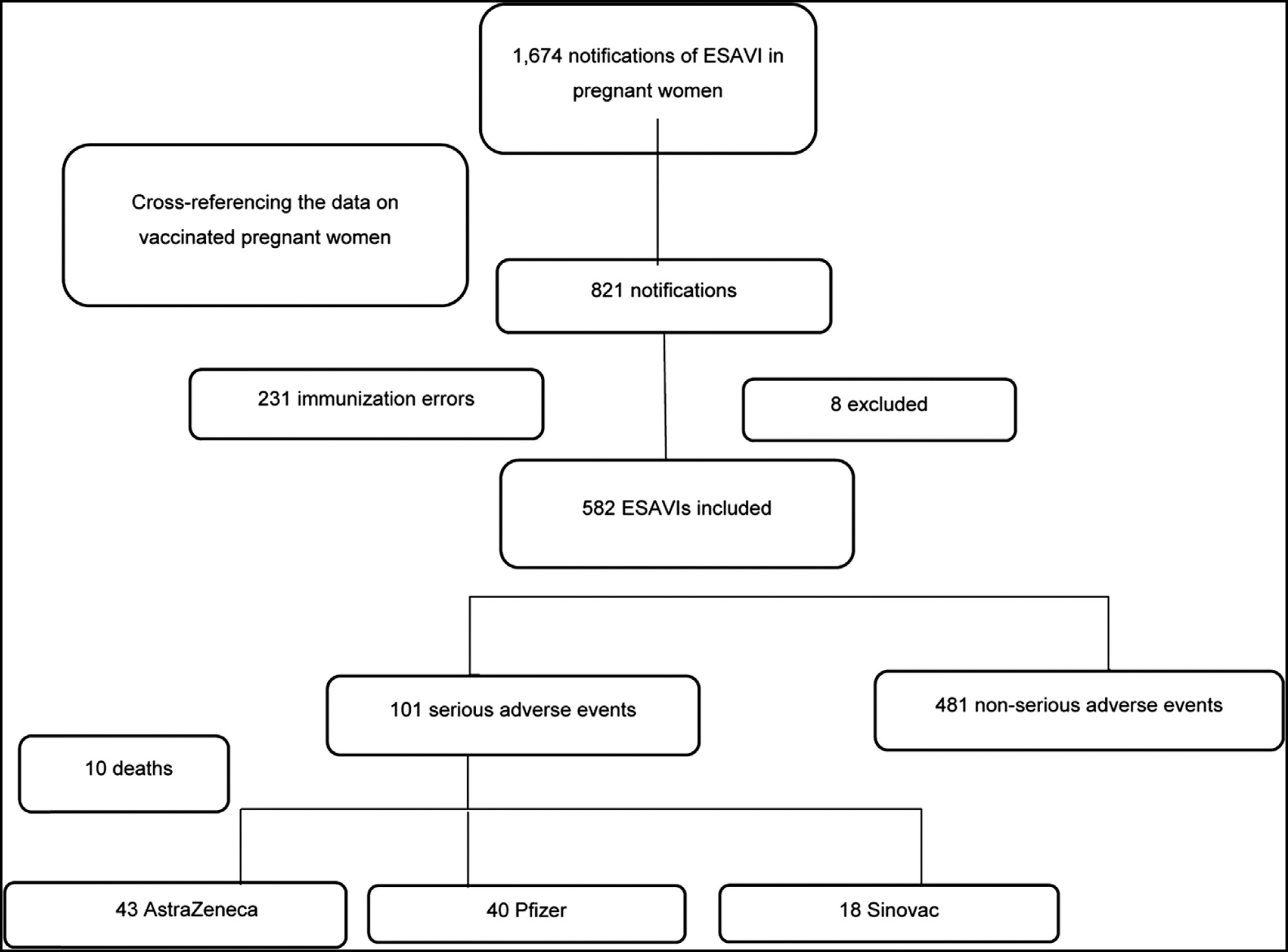
Regulations for the vaccination of pregnant women in Brazil occurred in March 2021. Despite the absence of robust data in the literature on the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) vaccinations in pregnant women, it is understood that the benefit-risk ratio tends to be favorable when considering the pandemic and the high burden of the disease. However, it is still important to monitor for Events Supposedly Attributable to Vaccination or Immunization (ESAVI) and to draw safety profiles of the different platforms used in pregnant and postpartum women. The present study aims to describe the main characteristics of ESAVIs related to COVID-19 vaccines occurring in pregnant women in the first months of the vaccination campaign in Brazil. During the evaluation period, 1,674 notifications of ESAVIs in pregnant women were recorded, and 582 notifications were included for the analysis. Of the 582 ESAVIs identified, 481 (82%) were classified as non-serious adverse events and 101 (17%) as serious adverse events. Ten deaths were identified, including one death which was considered to be causally related to the vaccine. The other nine maternal deaths had causality C, that is, without causal relationship with the vaccine, and most were due to complications inherent to pregnancy, such as pregnancy-specific hypertensive disorder (PSHD) in 4 cases and 3 due to COVID-19. Despite some limitations in our study, we believe it brings new insights into COVID-19 vaccines in this group and will add to the available evidence.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(5):540-547
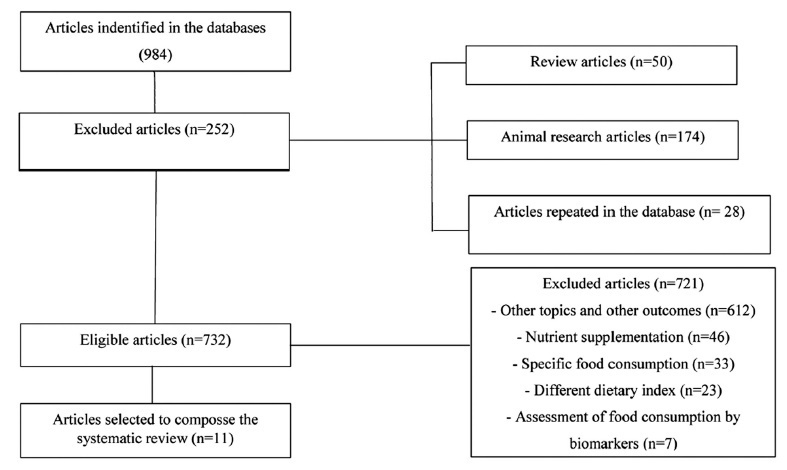
The present systematic review (PROSPERO: CRD42020148630) hypothesizes the association of excessive weight gain during pregnancywith dietary patterns composed of ultraprocessed foods. Thus, the objective was to investigate the association between dietary patterns after analysis and weight gain during pregnancy. The search for articles was performed in nine databases. Two reviewers selected the articles in the databases and extracted from them the data used in the review. Two scales were used to evaluate the quality of the selected studies: New Castle-Ottawa Quality Assessment for cohort-based studies and Appraisal tool for Cross-Sectional Studies (AXIS) for cross-sectional-based studies. In total, 11 studies were identified with sample size variation (n=173-5,733). Women presenting more adherence to healthy and traditional patterns (fruits, vegetables, salads, nuts, and dairy) recorded less excessive gestational weight gain (GWG). Higher intake ofmixed patterns and western patterns rich in ultraprocessed foods were associated with a higher prevalence of excessive GWG (24.48- 55.20%). Gestational dietary patterns a posteriori-derived that have presented ultraprocessed components rich in fat and sugars presented association with high GWG; healthy and traditional dietary patterns were related to better mother-child health conditions, such as adequate GWG.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(2):100-108
In addition to being a medical phenomenon, pandemics affect the individual and society on several levels and lead to disruptions. In the pandemic process, different groups in the population, including pregnant women as a defenseless group, are subjected to psychological threat. The present study aimed to determine the levels of anxiety and depression and related factors in pregnant women during the the coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) pandemic.
The present cross-sectional study was conducted with 269 pregnant women through face-to-face interviews held in Istanbul, Turkey. Regarding the data collection tools, the Cronbach α reliability coefficient was of 0.90 for the Beck Anxiety Inventory, and of 0.85 for the Beck Depression Inventory.
Among the participating pregnant women, 30.5% had mild, 17.5% had moderate, and 5.9% had severe anxiety symptoms, whereas 35.3% had mild, 16.7% had moderate, and 2.2% had severe depression symptoms. We found that those who were concerned about their health had 5.36 times (p=0.04) more risk of developing anxiety, and 4.82 times (p=0.01) more risk of developing depression than those who were not concerned. Those who had a history of psychiatric disease had 3.92 times (p=0.02) more risk of developing anxiety than those without it.
We determined that about half of the pregnant women included in the study had some degree of anxiety and depression during the COVID-19 pandemic. The risk factors for anxiety and depression among the pregnant women were determined as smoking, concerns about health and getting infectedwith the coronavirus, history of psychiatric disease, and undergoing regular antenatal care.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2020;42(10):659-668
To identify the most effective procedures recommended for the prevention of preeclampsia.
A systematic review was performed in the following databases: Pubmed/MEDLINE, CINAHL, Web of Science, Cochrane and LILACS via the Virtual Health Library (VHL). A manual search was also performed to find additional references. The risk of bias, the quality of the evidence, and the classification of the strength of the recommendations were evaluated using the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluations (GRADE) approach.
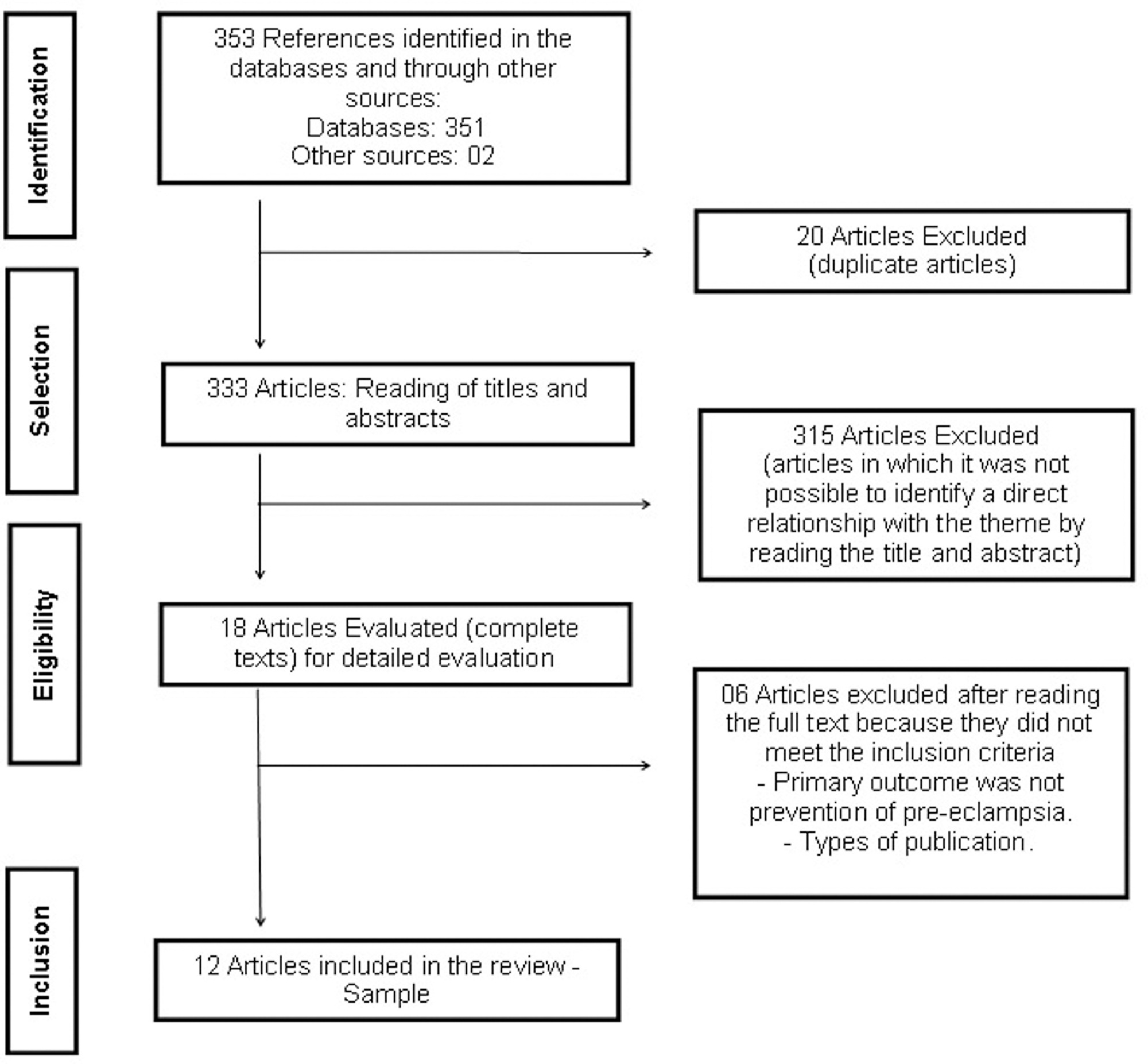
In the initial search in the databases, the total number of articles retrieved was 351, and 2 were retrieved through the manual search; after duplicate articles were removed, 333 citations remained. After a thorough review of the titles and abstracts, 315 references were excluded. Accordingly, 18 articles were maintained for selection of the complete text (phase 2). This process led to the exclusion of 6 studies. In total, 12 articles were selected for data extraction and qualitative synthesis.
The articles selected for the study were analyzed, and we inserted the synthesis of the evidence in the online software GRADEpro Guideline Development Tool (GDT) (McMaster University and Evidence Prime Inc. All right reserved. McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontário, Canada); thus, it was possible to develop a table of evidence, with the quality of the evidence and the classification of the strength of the recommendations.
In total, seven studies recommended the individual use of aspirin, or aspirin combined with calcium, heparin or dipyridamole. The use of calcium alone or in combination with phytonutrients was also highlighted. All of the studies were with women at a high risk of developing preeclampsia.
According to the studies evaluated, the administration of aspirin is still the best procedure to be used in the clinical practice to prevent preeclampsia.
Search
Search in:
breast (42) breast cancer (42) breast neoplasms (95) Cesarean section (72) endometriosis (66) infertility (56) Maternal mortality (43) menopause (82) obesity (58) postpartum period (40) pregnancy (225) Pregnancy complications (99) Prenatal care (68) prenatal diagnosis (50) Prevalence (41) Quality of life (51) risk factors (94) ultrasonography (79) urinary incontinence (40) women's health (48)