Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2024;46:e-rbgo36
Seminal cryopreservation causes significant damage to the sperm; therefore, different methods of cryopreservation have been studied. The aim of the study was to compare the effects of density gradient processing and washing/centrifugation with seminal plasma removal for cryopreservation in semen parameters.
Seminal samples of 26 normozoospermic patients were divided into 3 parts: with seminal plasma; after washing/centrifugation; and after selection through density gradient. The samples were cryopreserved for at least two weeks. Motility, sperm count, morphology and viability were evaluated before cryopreservation and after thawing.
Density gradient processing selected motile and viable sperm with normal morphology in fresh samples (p<0.05). Cryopreservation negatively affected all sperm parameters regardless of the processing performed, and even if the sperm recovery was lower in the density gradient after the thawing, progressive motility, total motility, viability and morphology remained higher (p<0.05).
Cryopreservation significantly compromises sperm parameters (motility, morphology, viability). In normozoospermic patients, the density gradients select better quality spermatozoa compared to other processing methods; this benefit was kept after thawing.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2023;45(12):818-823
Cervical cancer (CC) is caused by persistent infection of human papillomavirus of high oncogenic risk (hr-HPV); however, several cofactors are important in its carcinogenesis, such as smoking, multiparity, and prolonged use of oral hormonal contraceptives (COCs). Worldwide, 16% of women use COCs, whereas in Brazil this rate is of ~ 30%. The safety and adverse effects of COCs are widely discussed in the literature, including the increase in carcinogenic risk. Due to the existence of several drugs, combinations, and dosages of COCs, it is hard to have uniform information in epidemiological studies. Our objective was to perform a narrative review on the role of COCs use in the carcinogenesis of cervical cancer. Several populational studies have suggested an increase in the incidence of cervical cancer for those who have used COCs for > 5 years, but other available studies reach controversial and contradictory results regarding the action of COCs in the development of CC.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2023;45(12):796-807
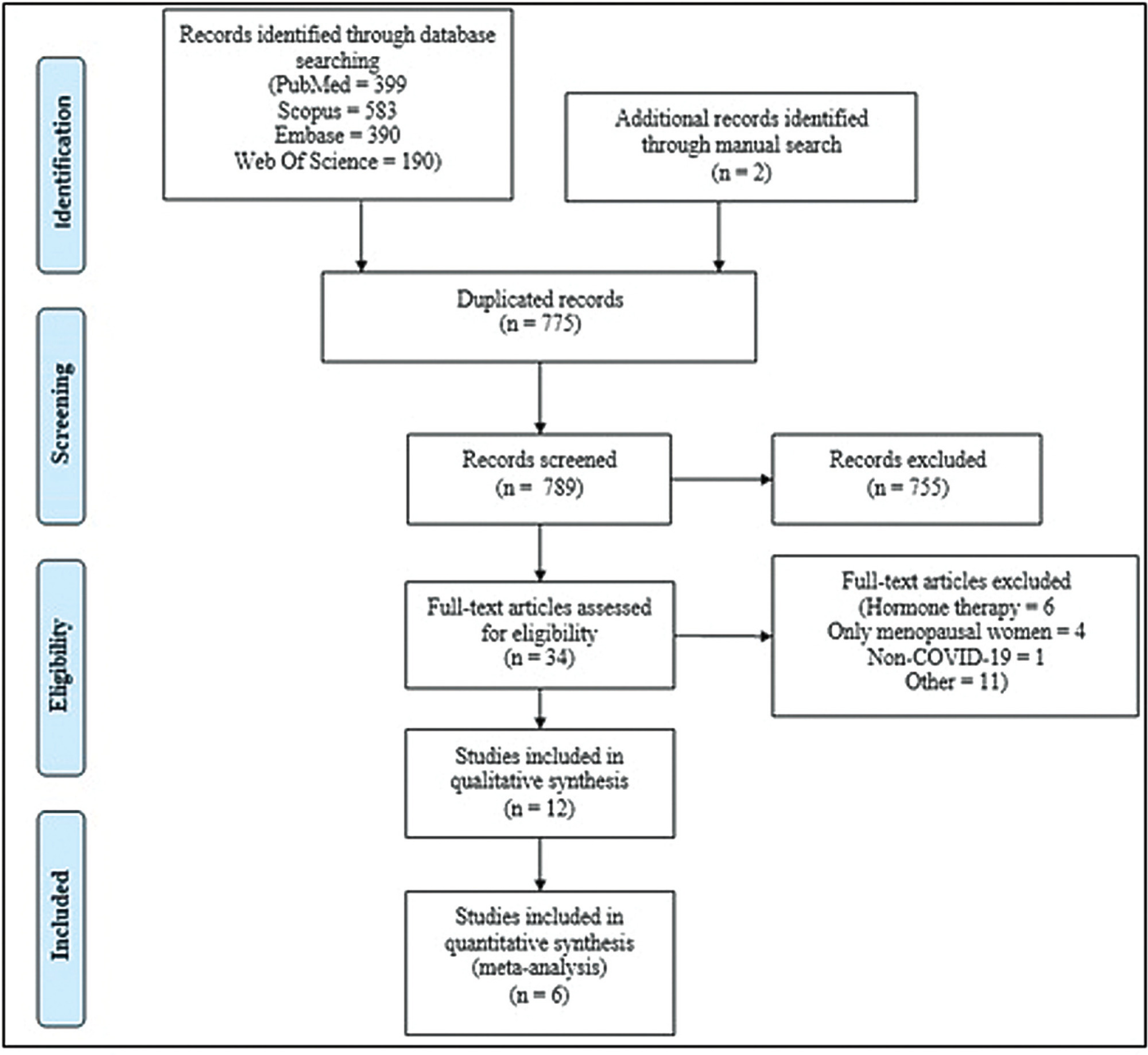
Menopause causes several changes in the body that may affect the response to COVID-19. We aimed to investigate the possible association between menopausal status and incidence and outcomes in COVID-19 patients.
Combinations of keywordsCOVID-19, menopause, and estrogen were used to search the PubMed, Embase, Web-of-Science, and Scopus databases for articles reporting the incidence and outcomes of COVID-19 (discharge, length-of-admission, intensive care, or mortality) in premenopausal women, available through December 29, 2022. Data from studies comparing the incidence of COVID-19 infection with the age-matched male population were pooled and meta-analyzed using a random-effects model.
Overall, 1,564 studies were retrieved, of which 12 were finally included in the systematic review to compare disease outcomes, and 6 were meta-analyzed for the incidence of COVID-19 in premenopausal and postmenopausal women. All studies reported better COVID-19-associated outcomes in premenopausal women compared with postmenopausal women. After adjusting for confounding factors, three studies found better outcomes in postmenopausal women, and two found no association between menopausal status and COVID-19 outcomes. Our meta-analysis found a higher incidence of COVID-19 infection among premenopausal women than postmenopausal women, when compared with age-matched men (odds ratio = 1.270; 95% confidence interval: 1.086–1.486; p = 0.003).
The incidence of COVID-19 was significantly higher in premenopausal women than in postmenopausal women when compared with age-matched men. Although premenopausal women may have more favorable COVID-19-associated outcomes, the presumed preventive effect of estrogens on the incidence and related outcomes of COVID-19 in premenopausal women cannot be proven at present. Further longitudinal studies comparing pre- and post-menopausal women are required to provide further insight into this matter.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2023;45(12):808-817
To assess the efficacy, safety, and acceptability of misoprostol in the treatment of incomplete miscarriage.
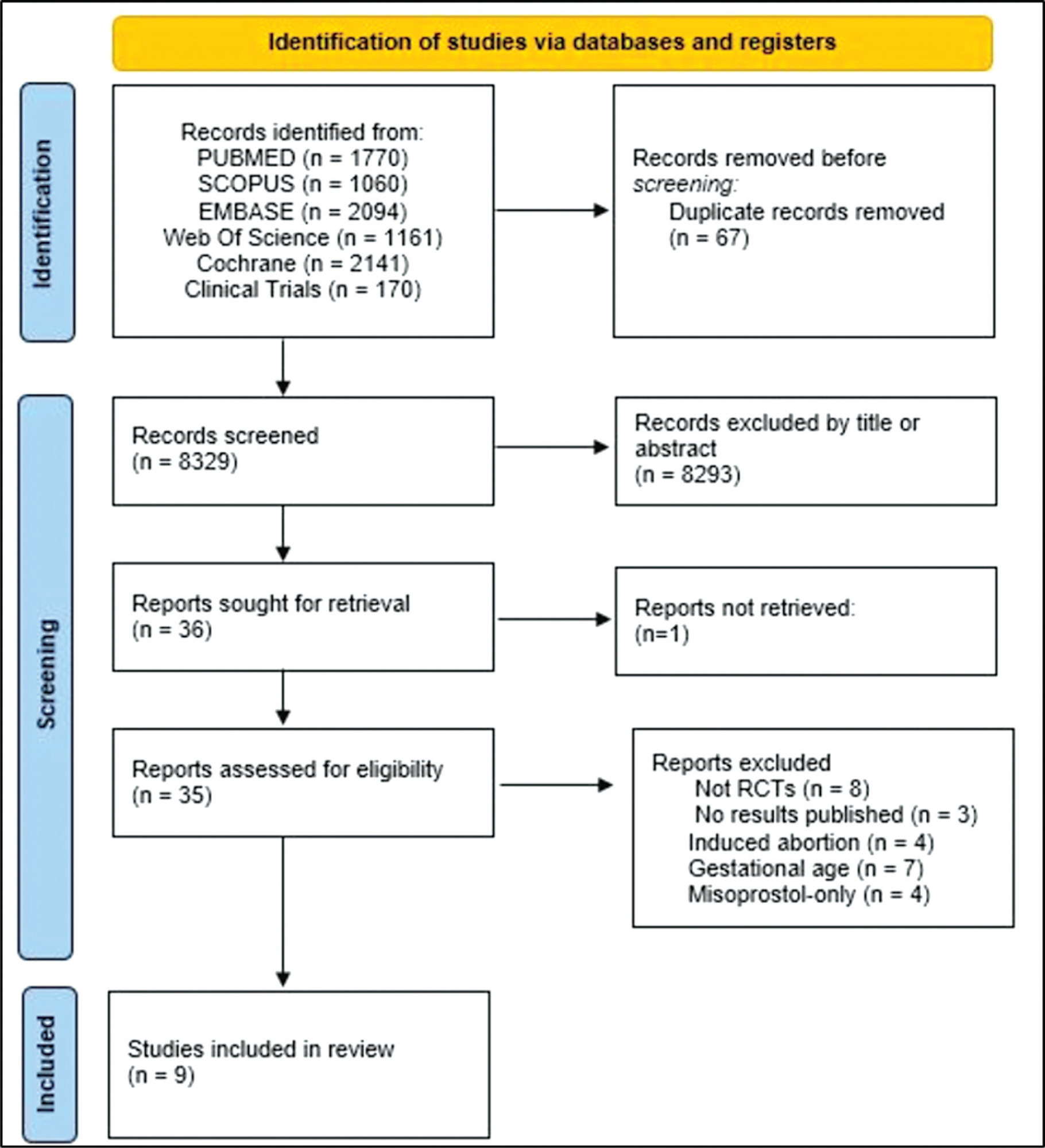
The PubMed, Scopus, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and Clinical Trials databases (clinicaltrials.gov) were searched for the relevant articles, and search strategies were developed using a combination of thematic Medical Subject Headings terms and text words. The last search was conducted on July 4, 2022. No language restrictions were applied.
Randomized clinical trials with patients of gestational age up to 6/7 weeks with a diagnosis of incomplete abortion and who were managed with at least 1 of the 3 types of treatment studied were included. A total of 8,087 studies were screened.
Data were synthesized using the statistical package Review Manager V.5.1 (The Cochrane Collaboration, Oxford, United Kingdom). For dichotomous outcomes, the odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were derived for each study. Heterogeneity between the trial results was evaluated using the standard test, I2 statistic.
When comparing misoprostol with medical vacuum aspiration (MVA), the rate of complete abortion was higher in the MVA group (OR = 0.16; 95%CI = 0.07–0.36). Hemorrhage or heavy bleeding was more common in the misoprostol group (OR = 3.00; 95%CI = 1.96–4.59), but pain after treatment was more common in patients treated with MVA (OR = 0.65; 95%CI = 0.52–0.80). No statistically significant differences were observed in the general acceptability of the treatments.
Misoprostol has been determined as a safe option with good acceptance by patients.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2023;45(10):609-619
To investigate the clinicopathological significance and prognosis of the expression of the anterior gradient 3 (AGR3) protein in women with breast cancer.
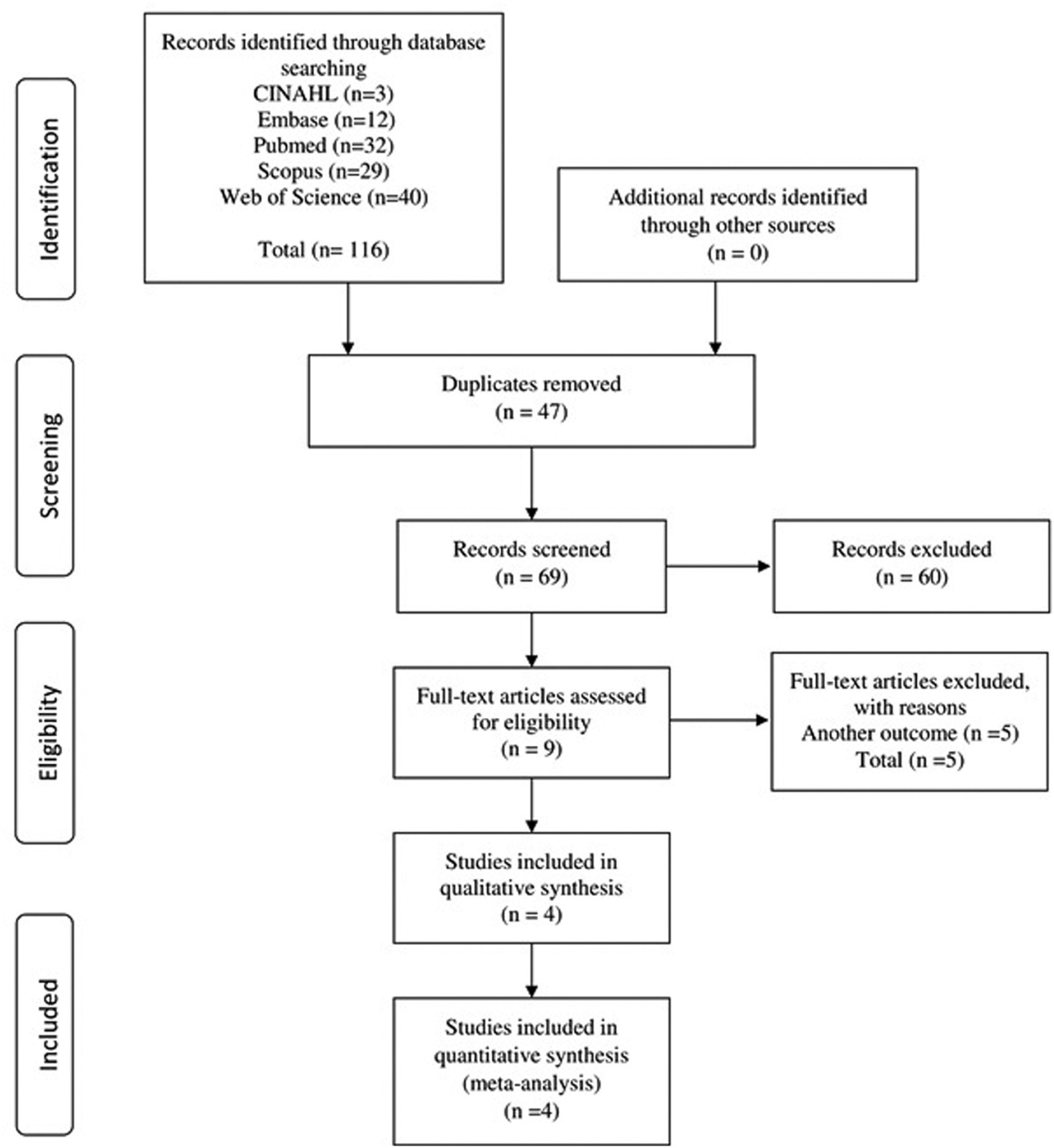
The PubMed, CINAHL, EMBASE, Scopus, and Web of Science databases were searched for studies published in English and without restrictions regarding the year of publication. The search terms were: breast cancer AND anterior gradient 3 OR AGR3 expression.
We included observational or interventional studies, studies on AGR3 protein expression by immunohistochemistry, and studies on invasive breast cancer. Case reports, studies with animals, and reviews were excluded. In total, 4 studies were included, containing 713 cases of breast cancer.
Data were extracted on clinicopathological characteristics and survival. A meta-analysis of the prevalence of AGR3 expression was performed according to the clinicopathological characteristics, hazard ratios (HRs), and overall survival and disease-free survival.
The expression of AGR3 was found in 62% of the cases, and it was associated with histological grade II, positivity of estrogen and progesterone receptors, low expression of ki67, recurrence or distant metastasis, and lumen subtypes. In patients with low and intermediate histological grades, AGR3 expression was associated with worse overall survival (HR: 2.39; 95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 0.628–4.159; p = 0.008) and worse disease-free survival (HR: 3.856; 95%CI: 1.026–6.686; p = 0.008).
The AGR3 protein may be a biomarker for the early detection of breast cancer and predict prognosis in luminal subtypes. In addition, in patients with low and intermediate histological grades, AGR3 protein expression may indicate an unfavorable prognosis in relation to survival.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2023;45(11):724-728
To determine if the use of lubricating gel on the speculum during the cervicovaginal cytology examination interferes with the results obtained, as well as whether it reduces reported discomfort in patients.
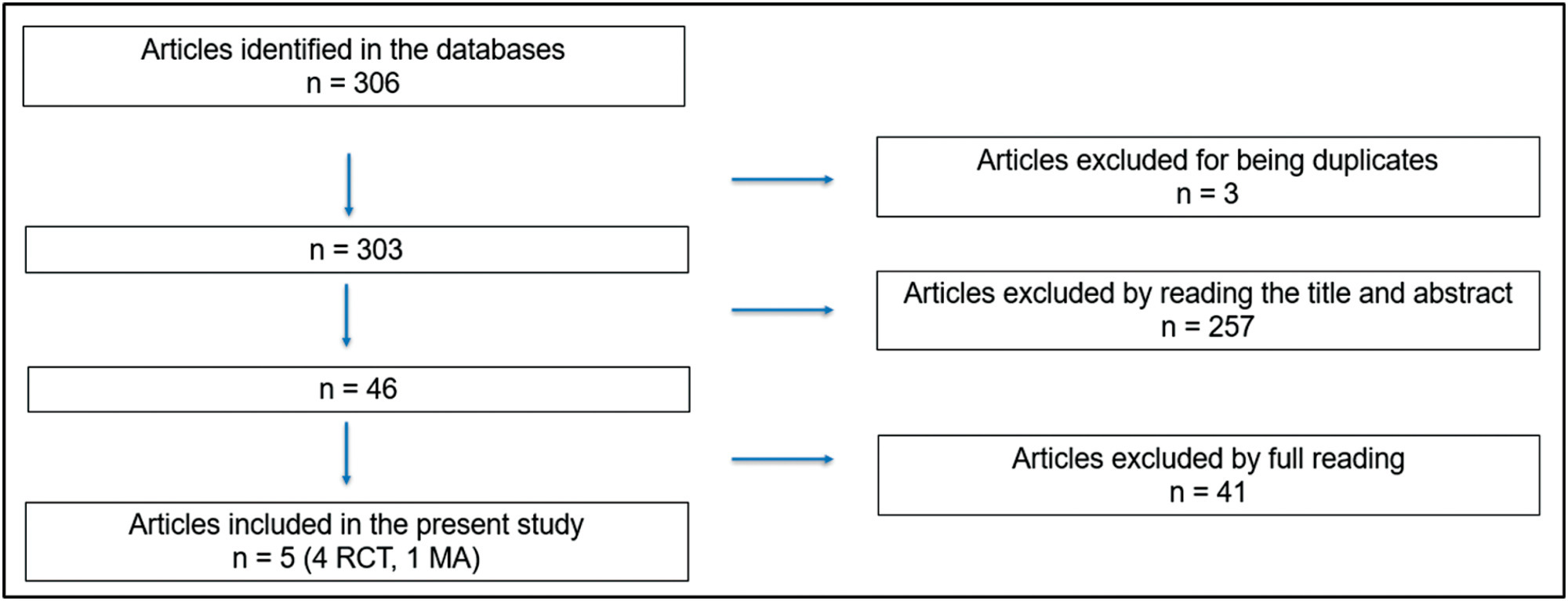
A systematic review was carried out according to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) recommendations, with a search in the Pubmed/Medline, Scielo, Cochrane Library, Embase databases of articles published between January 2011 and May 2022. The keywords used were cytology, speculum, lubricant, result, and pain.
The initial search resulted in 306 articles, of which were excluded three because they were duplicates, 257 after reading the title and abstract and 41 after reading the full text. Thus, five articles were selected for the study: four randomized clinical trials and one metanalysis.
The selection of articles was performed by two investigators. The 5 selected articles were read in full and submitted to a comparative analysis.
Screening through cervicovaginal cytology allows for early diagnosis and reduction of associated mortality, but the procedure can be associated with pain. A small amount of aqueous lubricating gel in the speculum can be used to reduce the discomfort associated with performing cervicovaginal cytology.
The use of lubricating gel in the speculum does not seem to be associated with a change in the cytology result and reduces the discomfort associated with its insertion into the vagina.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2023;45(11):729-744
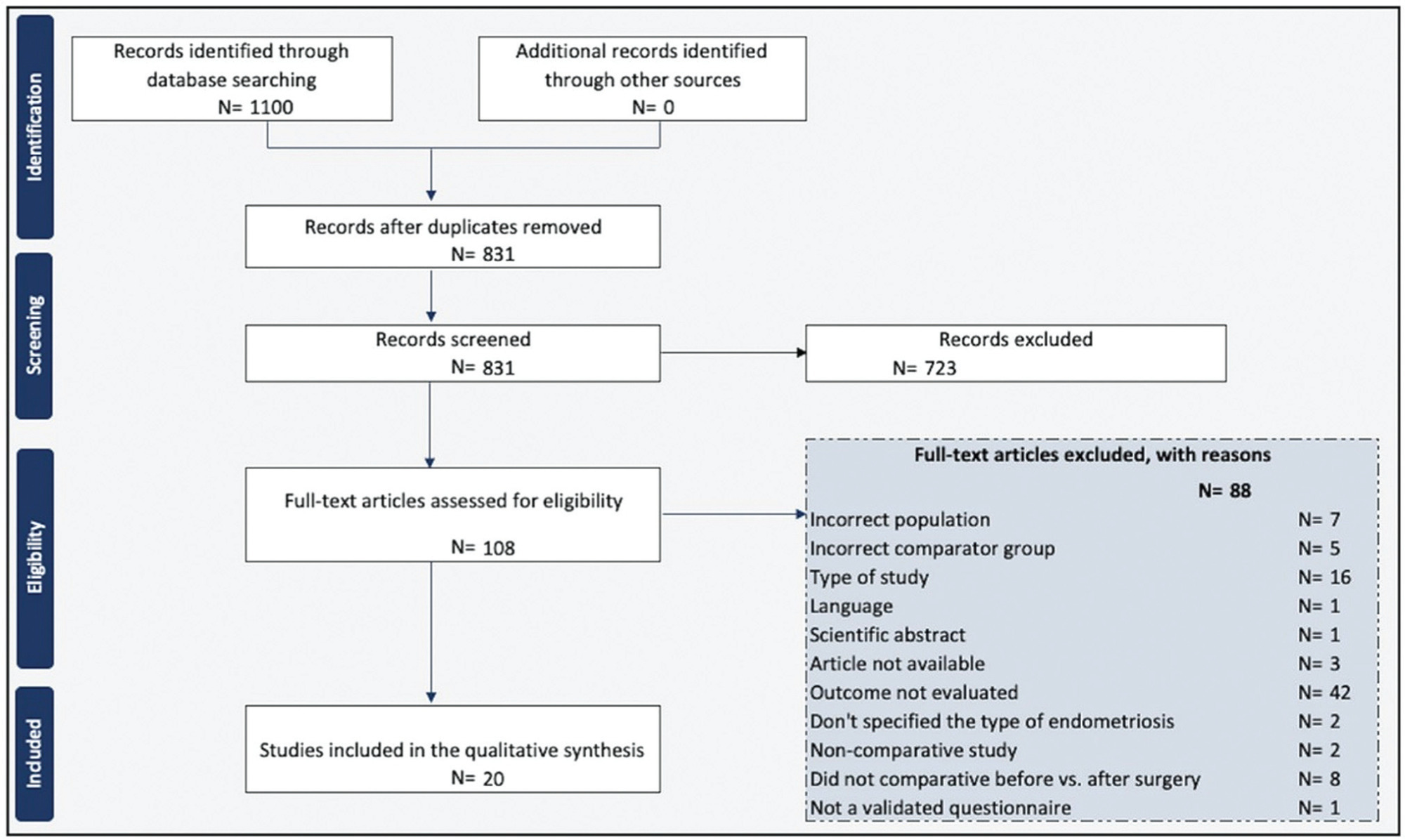
To review the current state of knowledge on the impact of the surgical treatment on the sexual function and dyspareunia of deep endometriosis patients.
A systematic review was conducted in accordance with the Meta-Analysis of Observational Studies in Epidemiology (MOOSE) guidelines. We conducted systematic searches in the PubMed, EMBASE, LILACS, and Web of Science databases from inception until December 2022. The eligibility criteria were studies including: preoperative and postoperative comparative analyses; patients with a diagnosis of deep endometriosis; and questionnaires to measure sexual quality of life.
Two reviewers screened and reviewed 1,100 full-text articles to analyze sexual function after the surgical treatment for deep endometriosis. The risk of bias was assessed using the Newcastle-Ottawa scale for observational studies and the Cochrane Collaboration's tool for randomized controlled trials. The present study was registered at the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO; registration CRD42021289742).
General variables about the studies, the surgical technique, complementary treatments, and questionnaires were inserted in an Microsoft Excel 2010 (Microsoft Corp., Redmond, WA, United States) spreadsheet.
We included 20 studies in which the videolaparoscopy technique was used for the excision of deep infiltrating endometriosis. A meta-analysis could not be performed due to the substantial heterogeneity among the studies. Classes III and IV of the revised American Fertility Society classification were predominant and multiple surgical techniques for the treatment of endometriosis were performed. Standardized and validated questionnaires were applied to evaluate sexual function.
Laparoscopic surgery is a complex procedure that involves multiple organs, and it has been proved to be effective in improving sexual function and dyspareunia in women with deep infiltrating endometriosis.
Search
Search in:
breast (42) breast cancer (42) breast neoplasms (95) Cesarean section (72) endometriosis (66) infertility (56) Maternal mortality (43) menopause (82) obesity (58) postpartum period (40) pregnancy (225) Pregnancy complications (99) Prenatal care (68) prenatal diagnosis (50) Prevalence (41) Quality of life (51) risk factors (94) ultrasonography (79) urinary incontinence (40) women's health (48)