Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2020;42(8):501-507
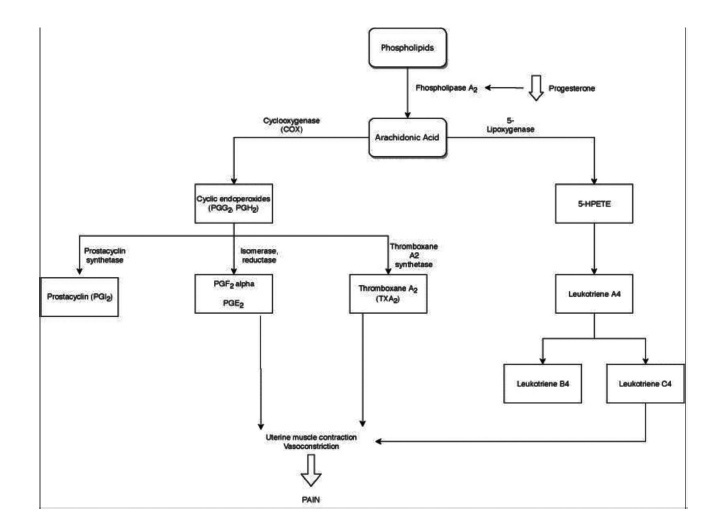
Primary dysmenorrhea is defined asmenstrual pain in the absence of pelvic disease. It is characterized by overproduction of prostaglandins by the endometrium, causing uterine hypercontractility that results in uterine muscle ischemia, hypoxia, and, subsequently, pain. It is the most common gynecological illness in women in their reproductive years and one of the most frequent causes of pelvic pain; however, it is underdiagnosed, undertreated, and even undervalued by women themselves, who accept it as part of themenstrual cycle. It hasmajor implications for quality of life, such as limitation of daily activities and psychological stress, being one of themain causes of school and work absenteeism. Its diagnosis is essentially clinical, based on the clinical history and normal physical examination. It is important to exclude secondary causes of dysmenorrhea. The treatment may have different approaches (pharmacological, nonpharmacological and surgical), but the first line of treatment is the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and, in cases of women who want contraception, the use of hormonal contraceptives. Alternative treatments, such as topical heat, lifestyle modification, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, dietary supplements, acupuncture, and acupressure, may be an option in cases of conventional treatments’ contraindication. Surgical treatment is only indicated in rare cases of women with severe dysmenorrhea refractory to treatment.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2018;40(4):196-202
To evaluate the association between hormonal contraception and the appearance of human papillomavirus HPV-induced lesions in the uterine cervix of patients assisted at a school outpatient clinic - ObGyn outpatient service of the Universidade do Sul de Santa Catarina.
A case-control study, with women in fertile age, performed between 2012 and 2015. A total of 101 patients with cervical lesions secondary to HPV were included in the case group, and 101 patients with normal oncotic colpocytology, in the control group. The data were analyzed through the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS, IBM Corp. Armonk, NY, US) software, version 24.0, using the 95% confidence interval. To test the homogeneity of the proportions, the chi-square (χ2) test was used for the qualitative variables, and the Student t-test, for the quantitative variables.
When comparing the occurrence of HPV lesions in users and non-users of combined oral contraceptives (COCs), the association with doses of 0.03 mg or higher of ethinylestradiol (EE) was observed. Thus, a higher probability of developing cervical lesions induced by HPV was identified (odds ratio [OR]: 1.9 p = 0.039); and when these cases were separated by the degree of the lesion, the probability of these patients presentingwith lowgrade squamous intraepithelial lesion was 2.1 times higher (p = 0.036), but with no impact on high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions and the occurrence of invasive cancer. No significant differences were found in the other variables analyzed.
Although the results found in the present study suggest a higher probability of the users of combined hormonal contraceptives with a concentration higher than 0.03 mg of EE to develop low-grade intraepithelial lesions, more studies are needed to conclude causality.
Search
Search in:
breast (42) breast cancer (42) breast neoplasms (95) Cesarean section (72) endometriosis (66) infertility (56) Maternal mortality (43) menopause (82) obesity (58) postpartum period (40) pregnancy (225) Pregnancy complications (99) Prenatal care (68) prenatal diagnosis (50) Prevalence (41) Quality of life (51) risk factors (94) ultrasonography (79) urinary incontinence (40) women's health (48)