Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2024;46:e-rbgo7
To validate the 10-item Cervantes Scale (CS-10) among Brazilian women.
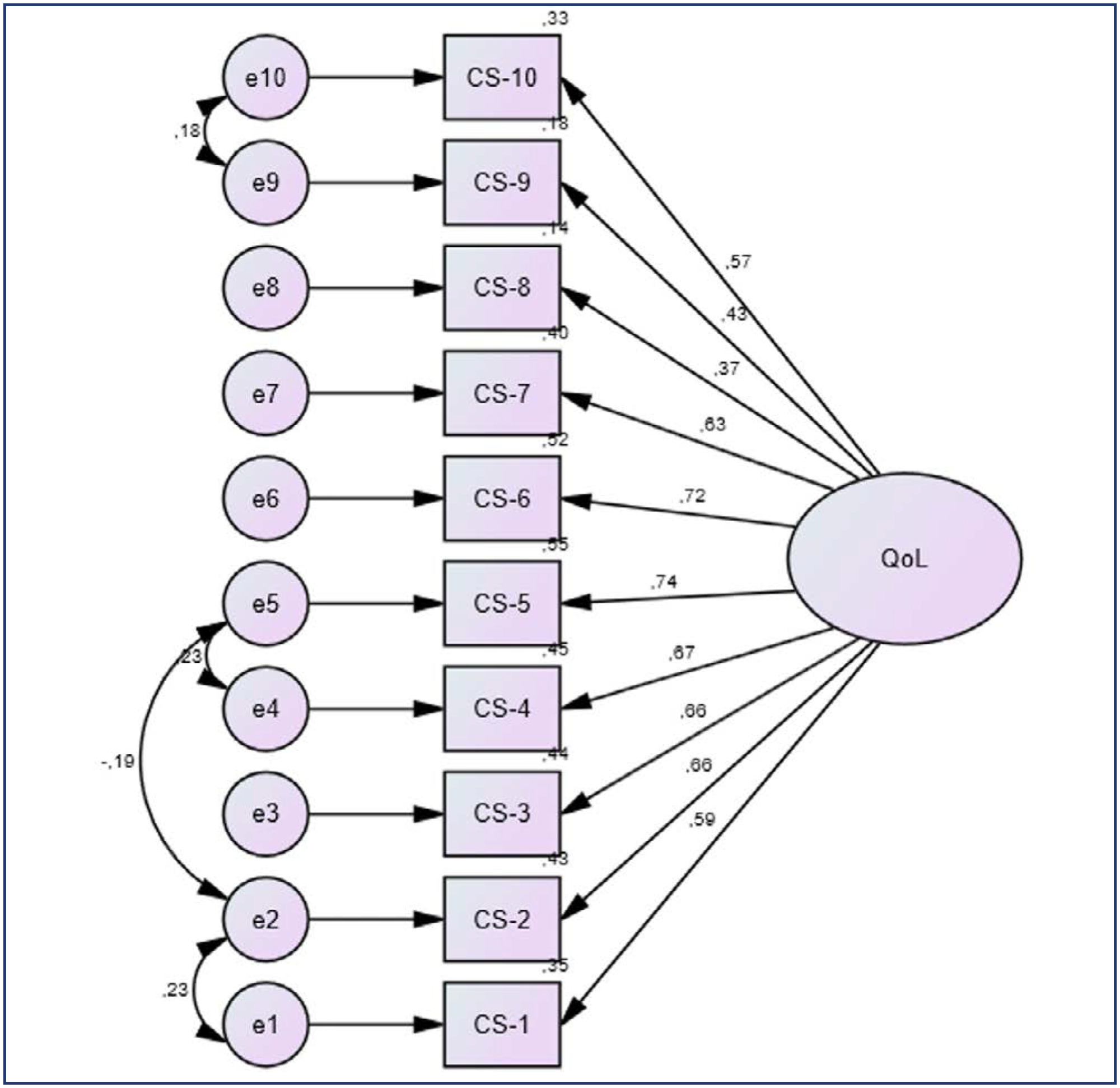
This is a cross-sectional observational study involving women in the community aged 40–55 years in the Southern region of Brazil. They completed a general health, habits and socio-demographic questionnaire, the CS-10 and the Women’s Health Questionnaire (WHQ). Women unable to understand the survey, not consenting to participate, or having incapacity imposing difficulties during the completion of the questionnaire were excluded. A Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) was conducted with the AMOS 16.0 software. Chi-square of degrees of freedom (χ2/df), the Comparative Fit Index (CFI), the Tucker-Lewis Index (TLI) and the Root-Mean-Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) were used as indices of goodness of fit. Cronbach’s alpha coefficient was used for internal consistency.
A total of 422 women were included (premenopausal n=35, perimenopausal n=172, postmenopausal n=215). The CFA for the CS-10 showed a good fit (χ²/df=1.454, CFI=0.989; TLI=0.985; RMSEA=0.033; CI 90%=0.002-0.052; PCLOSE=0.921; Model p=0.049). Good reliability was established in CS-10 and WHQ (Cronbach’s alpha=0.724). Postmenopausal women had higher total CS-10 scores (p≤0.0001), reflecting worse quality of life (QoL) related to menopause symptoms and confirming the greater symptomatology evaluated by high total scores for WHQ found in this population when compared to those in the premenopausal period (p=0.041).
The CS-10 is a consistent tool for health-related QoL in Brazilian mid-aged women.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2024;46:e-rbgo10
To analyze data of patients with symptomatic pelvic organ prolapse evaluated with PFDI20 and its subscales to report the prevalence of lower gastrointestinal symptoms and anal incontinence in the population of a public hospital and analyze its impact on quality of life.
Cross-sectional study of patients with symptomatic POP. Patients were evaluated with demographic data, POP-Q, pelvic floor ultrasonography, urological parameters, and pelvic floor symptoms (PFDI-20), and quality of life (P-QoL) surveys. Patients were classified as CRADI-8 "positive" for colorectal symptoms, with responses "moderate" in at least 3 and/or "severe" in at least 2 of the items in the CRADI-8 questionnaires.
One hundred thirteen patients were included. 42.5% (48) were considered positive for colorectal symptoms on CRADI-8. 53.4% presented anal incontinence. No significant differences were found in sociodemographic variables, POP-Q stage, ultrasound parameters, or urological parameters. Positive patients had a significantly worse result in PFDI-20, POPDI (48 vs 28; p<0.001), UDI6 (51 vs 24; p<0.001), and in the areas of social limitation (44.4 vs 22.2; p = 0.045), sleep- energy (61.5 vs 44.4; p = 0.08), and severity (56.8 vs 43.7, p=0.015) according to P-QoL.
Moderate or severe colorectal symptoms are seen in 40% of patients with symptomatic POP in our unit. Full evaluation of pelvic floor dysfunction symptoms should be performed routinely in urogynecology units.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2023;45(10):575-583
In the present study, our aim was to translate, adapt, and validate the Pelvic Health History Form (a quality of life [QoL] questionnaire) of the International Pelvic Pain Society (IPPS) from English to Portuguese.
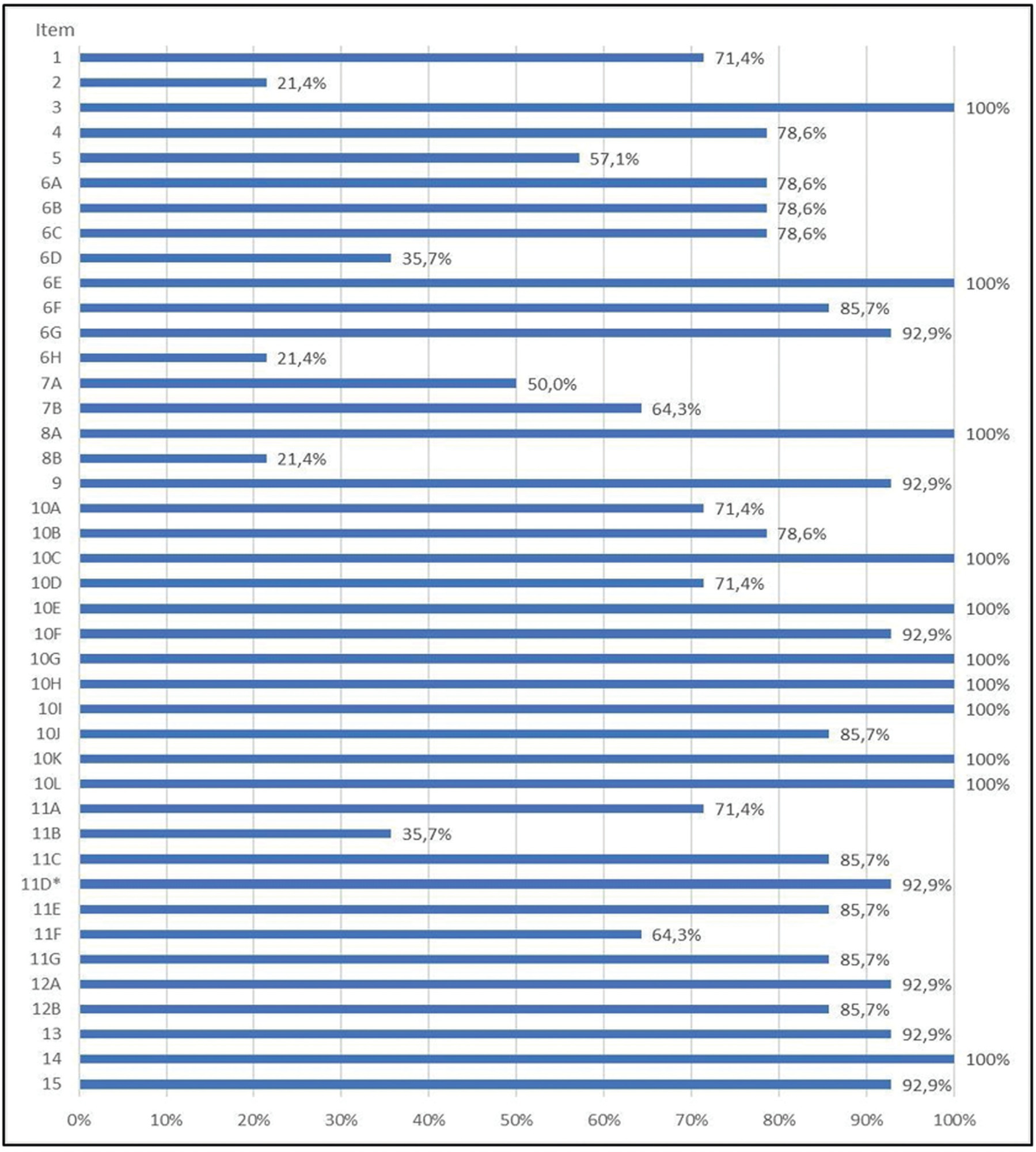
The study was approved by the Ethics and Research Committee (CEP, in the Portuguese acronym) and the IPPS. The "Transcultural Adaptation" method comprised 5 stages: translation, synthesis, backtranslation, expert review, and pretest. Cultural adaptation and validation included cognitive interviews and statistical analysis of unanswered items (> 15%) in 14 clinic patients from CPP and endometriosis clinic at Santa Casa de São Paulo.
Strong equivalences were established between the USA and Brazil questionnaires in terms of semantics, idioms, experiences, and concepts. Eighteen culturally inappropriate items were identified and adjusted using the revised response rate index. The subjective form underwent rigorous assessments, confirming its accurate measurement of intended targets.
The methodology showed efficiency and equivalence, confirming its validity. The user-friendly format and inclusion of translated, adapted, and validated instruments in Portuguese make the form valuable for evaluating pelvic health, with potential for future research.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2023;45(2):065-073
The study was conducted to determine the quality of life and depression of women with gestational diabetes during pregnancy and the postpartum period.
100 pregnant women with gestational diabetes and 100 healthy pregnant women were included in the present study. Data were obtained from pregnant women in their third trimester who agreed to take part in the study. The data was collected during the third trimester and six to eight weeks after the baby was born. The data were obtained by socio-demographic characteristics form, postpartum data collection form, the MOS 36 Item Short Form Health Survey and Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CESD).
The mean age of pregnant women with gestational diabetes in the study was the same as the average age of healthy pregnant women. The CESD score of pregnant women with gestational diabetes was 26,77 ± 4,85 while the corresponding score was 25,19 ± 4,43 for healthy women. Additionally, the score in the postpartum period was 32.47 ± 5.94 for pregnant women with gestational diabetes and 35.47 ± 8.33 for healthy pregnant women. CESD scores were found to be higher than the cut-off score of 16 in both groups, and the mean scores increased during the postpartum period.
During the postpartum period, the quality of life of pregnant women with gestational diabetes was affected more negatively than healthy pregnant women. Depressive symptoms of women with both gestational diabetes and healthy pregnancy were found to be high in pregnancy and postpartum periods.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(5):475-482
To assess the quality of life (QoL) of pregnant women with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) treated at a high-risk prenatal outpatient clinic during the third trimester of gestation.
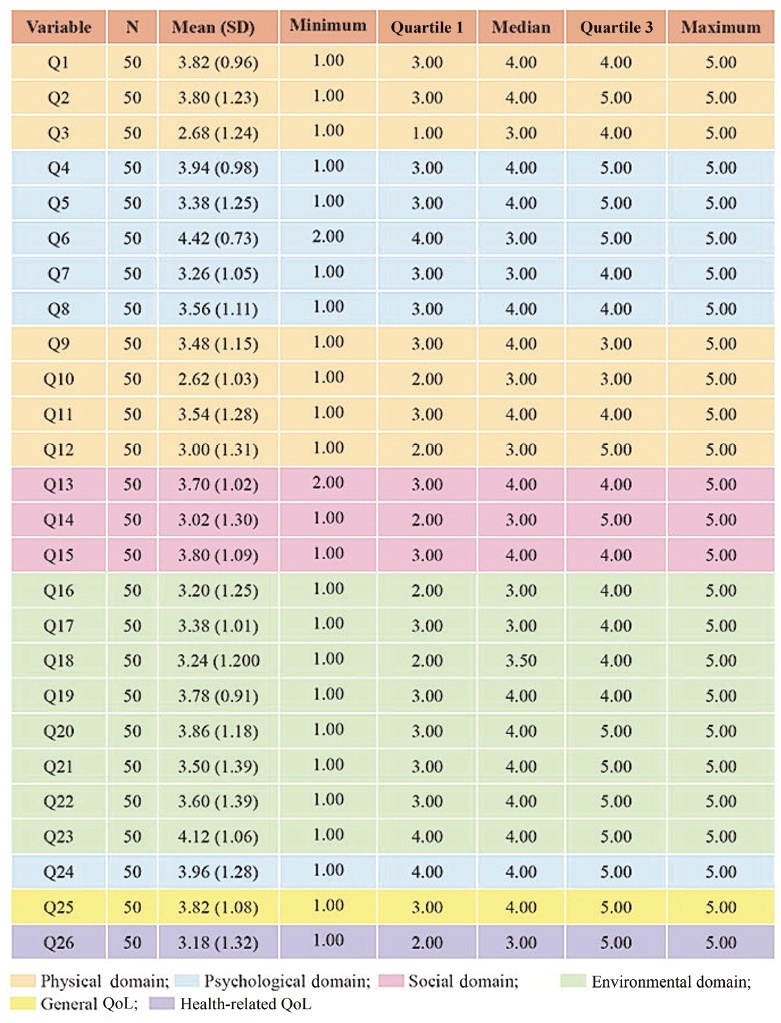
An observational descriptive study was performed in a high-risk prenatal outpatient clinic. Women in the third trimester of pregnancy and undergoing antenatal care between July 2017 and July 2019 answered the abbreviated World Health Organization Quality of Life (WHOQOL-BREF) questionnaire, consisting of 26 questions divided into 4 domains (physical, psychological, social and environmental).
We interviewed 50 pregnant women with a mean gestational age of 30 weeks (standard deviation [SD]: 10 weeks) who were diagnosed with SLE. The average age of the participants was 30 years (SD: 14.85), and the average time since the diagnosis of SLE was of 9.06 years (SD: 6.8 years). Most participants had a partner, did not plan their pregnancy (76%), and did not use contraception prior to pregnancy (80%). The score of each domain ranges from 0 (the worst score) to 100 (the best score). The means ± SDs of the scores of the participants on each domain were: physical - 52.21 ± 18.44); psychological - 64.17 ± 18.56); social - 66.33 ± 27.09); and environmental - 64.56 (18.53). The means ± SDs of the general QoL, and health-related QoL items were of 70.50 ± 24.06 and 70.00 ± 30.72 respectively.
The physical domain presented the lowest scores compared with the other three domains. Pregnant women with SLE had high overall QoL scores, and their health-related QoL scores were also relatively high.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(3):295-303
Endometriosis is an inflammatory disease that affects women of reproductive age, causing pain and the possibility of infertility. Endometriosis was associated to low life quality and research shows the impact of endometriosis in several areas of life, justifying how these patients are more likely to develop depression, anxiety, and stress.
The aim of the present systematic review was to explore the field of psychology in endometriosis, identifying studies that used the cognitive behavioral therapy technique as a treatment for endometriosis and chronic pelvic pain.
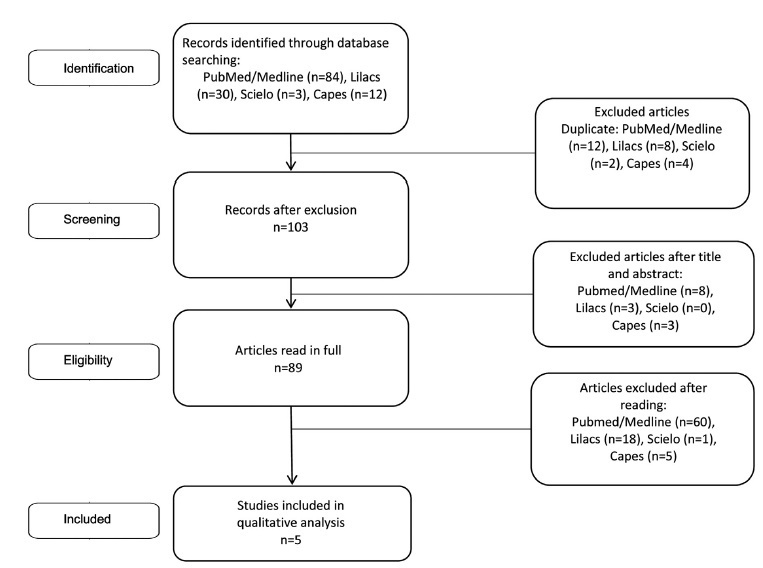
The keywords used were Endometriosis and Behavioral Therapy; Behavioral Disciplines and Activities; Cognitive Behavioral Therapy; Mental Health; Psychological Techniques; Psychology; Psychotherapy; Mental Health Services; and the search was performed in the following databases: PubMed/Medline, Scielo, Lilacs, and Capes. The study followed the PRISMA guidelines and all studies whose intervention strategy used was related to cognitive-behavioral therapy were considered.
Of the 129 articles found, only 5 were selected, and it was possible to identify that the psychological intervention whose approach brought cognitive-behavioral therapy techniques promoted a decrease in the sensation of pain, improvements in the scores of depression and stress, and significant changes in aspects of quality of life such as vitality, physical and social functioning, emotional well-being, control, and autonomy.
Cognitive-behavioral therapy can be very promising to take care of the emotional side of those who have endometriosis However, the present systematic review highlights the need to develop more structured studies with consistent, clear and replicablemethods to reach a psychological intervention protocol for patients who live with this gynecological-physical-emotional condition.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2020;42(4):211-217
To reveal the changes in the quality of life reported by women with Human papillomavirus (HPV)-induced lesions.
This is a cross-sectional, descriptive-exploratory study of a qualitative approach performed from June to August 2016. Semi-structured face-to-face interviews based on five questions on the concept of quality of life were used. The data were submitted to thematic analysis. All ethical aspects have been contemplated.
A total of 20 women aged between 25 and 59 years old were interviewed. From the analysis of the data, the following thematic units emerged: physical and emotional changes, especially complaints of pruritus, discharge and pain, worry, fear, shame and sadness; changes in sexual and affective relationships with decreased libido, dyspareunia and interruption of sexual activity; changes in social relationships resulting in absenteeism at work.
Human papillomavirus infection impairs the quality of life of women as it significantly affects sexual, affective, physical, emotional, and everyday habits. Therefore, HPV infection can lead to exponential changes in the quality of life of women, which can be mitigated by the availability of sources of support such as family, friends and the multi-professional team, helping to improve knowledge and cope with HPV.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2020;42(2):90-95
To describe clinical and sociodemographic characteristics of women with deep infiltrating endometriosis (DIE) and assess their quality of life (QOL) during 6 months of medical treatment.
A descriptive cross-sectional study of 60 women diagnosed with DIE either by surgery or image methods (ultrasound or magnetic resonance), who received clinical treatment for at least 6 months in the Universidade de Campinas, Campinas, state of São Paulo, Brazil. Both the SF-36 and the EHP-30 questionnaires were used to assess the quality of life.
The mean age of the patients was 37.7 ± 6.0 years old, with 50% presenting dysmenorrhea; 57% dyspareunia; and 50% chronic pelvic pain. The SF-36 and the EHP-30 revealed impaired quality of life. In the SF-36, the worst domains were limitation due to emotional aspects (40.2 ± 43.1) and self-esteem and disposition (46.1 ± 24.8), whereas in the EHP-30 they were social well-being (50.3 ± 30.6); infertility (48.0 ± 36.3); and sexual intercourse (54.0 ± 32.1).
Although clinically treated, women with deep endometriosis present impairment in different domains of quality of life regardless of the questionnaire used for evaluation.
Search
Search in:
breast (42) breast cancer (42) breast neoplasms (95) Cesarean section (72) endometriosis (66) infertility (56) Maternal mortality (43) menopause (82) obesity (58) postpartum period (40) pregnancy (225) Pregnancy complications (99) Prenatal care (68) prenatal diagnosis (50) Prevalence (41) Quality of life (51) risk factors (94) ultrasonography (79) urinary incontinence (40) women's health (48)