Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2024;46:e-rbgo16
Dysmenorrhea is the pain related to menstruation; to screen for the symptoms, a working ability, location, intensity of days of pain, and dysmenorrhea (WaLIDD) score was created. The purpose of this work was to culturally adapt and assess the measurement properties of the WaLIDD score for dysmenorrhea in Brazilian women.
In this cross-sectional online study, we evaluated women with and without dysmenorrhea. Criterion validity and construct validity were assessed, respectively, by the Receiver Operator Characteristic (ROC) curve and correlations with the bodily pain and social functioning domains of medical outcomes study 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36), self-report of absenteeism and Stanford Presenteeism Scale for presenteeism. Test-retest reliability and measurement errors were assessed, respectively, by intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) and Bland and Altman Graph.
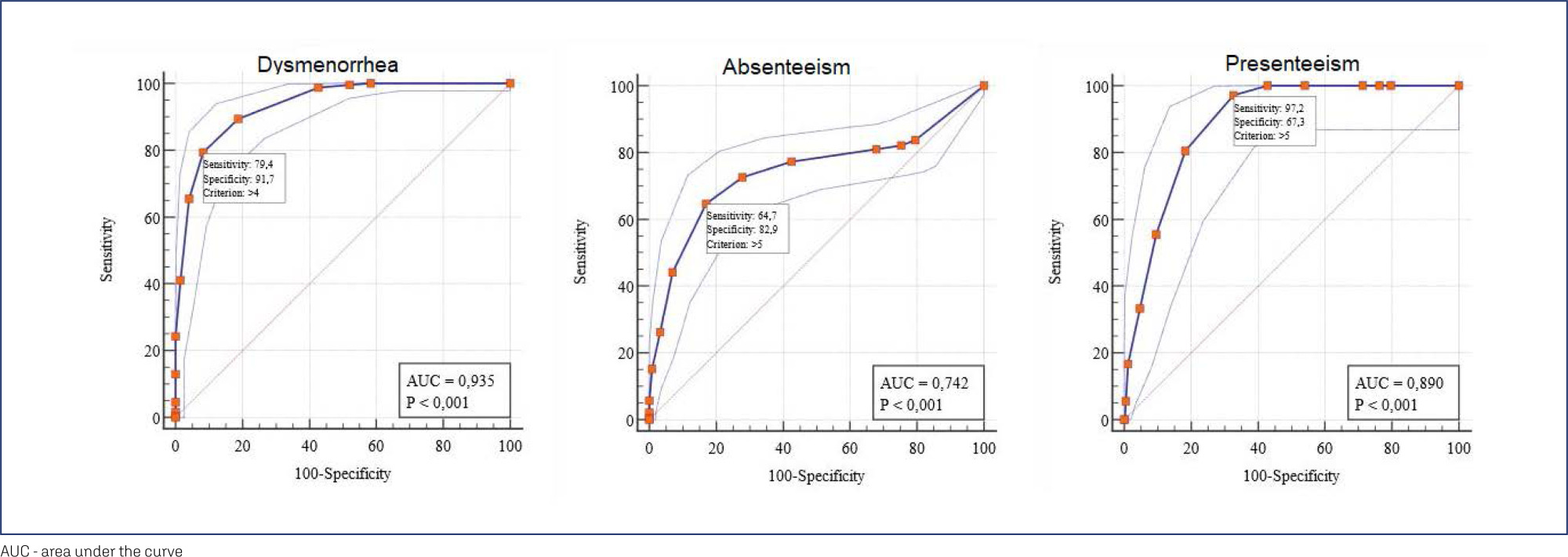
430 women completed the test, 238 (55.4%) women had dysmenorrhea, and 199 (46.3%) answered the questionnaire twice for the retest. The cutoff points ≥4, ≥5, and ≥5 could discriminate between women with and without dysmenorrhea, absenteeism, and presenteeism related to dysmenorrhea, respectively. Correlations between SF-36 – pain and social functioning domains and WaLIDD score were weak to strong and negative. For WaLIDD total Score, ICC was 0.95 and the limits of agreement were −1.54 and 1.62.
WaLIDD score is a short, valid and reliable instrument to screen and predict dysmenorrhea and could predict absenteeism and presenteeism related to dysmenorrhea in Brazilian women.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2021;43(12):968-979
The aim of the present systematic review meta-analysis is to assess the effect of olfactory stimulation on reducing dysmenorrhea.
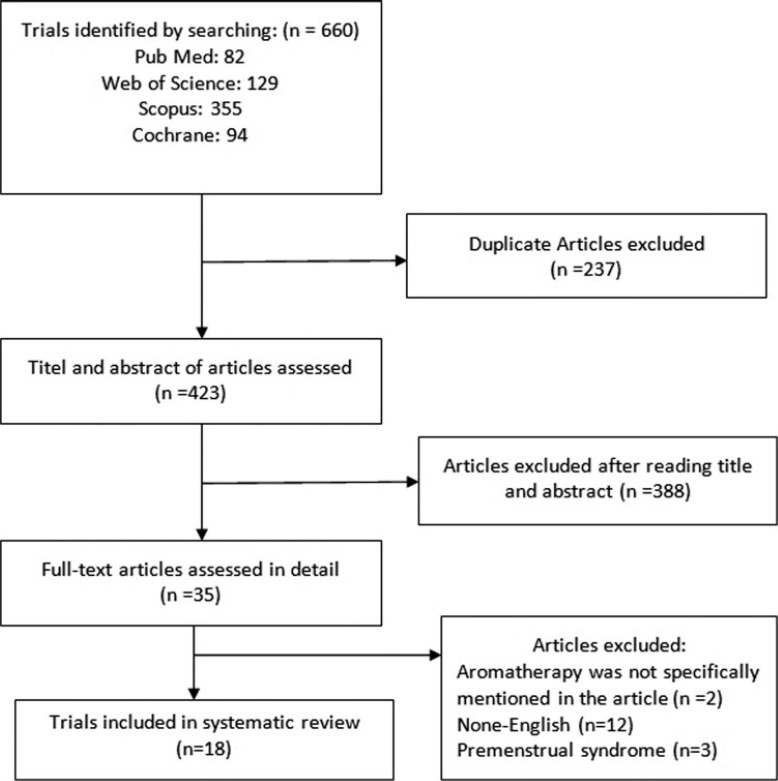
Systematic search was conducted in several databases, such as PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane, and Scopus, to identify relevant research up to October 26, 2019. The identified studies were evaluated based on a modified Jadad scale. The intervention involves aromatherapy alone or in combination with essential oils. There was no restriction for the control group such as a placebo group or other common treatments. The Comprehensive Meta-Analysis Version 2 (Bio stat, Englewood, NJ, USA) was used for meta-analysis. Cochran’s Q and I2 tests were utilized.
The findings of our meta-analysis, which contained 13 trials (15 data), showed that dysmenorrhea decreased significantly in the group receiving aromatherapy with herbal compared with the control group (standardized mean difference [SMD] =-0.795; 95% confidence interval [CI]: -0.922 to- 0.667; 17 trials O < 0.001); heterogeneity; I2 = 19.47%; p = 0.236). In addition, four studies with insufficient data were not included in our meta-analysis. The results of all studies suggested that aromatherapy with herbal medicine group compared with control group is effective.
Aromatherapy with herbal medicine decreased dysmenorrhea. This treatment was particularly effective when aroma oil was combined with massage or when a mixture of aroma oil was used for the treatment of dysmenorrhea.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2020;42(8):501-507
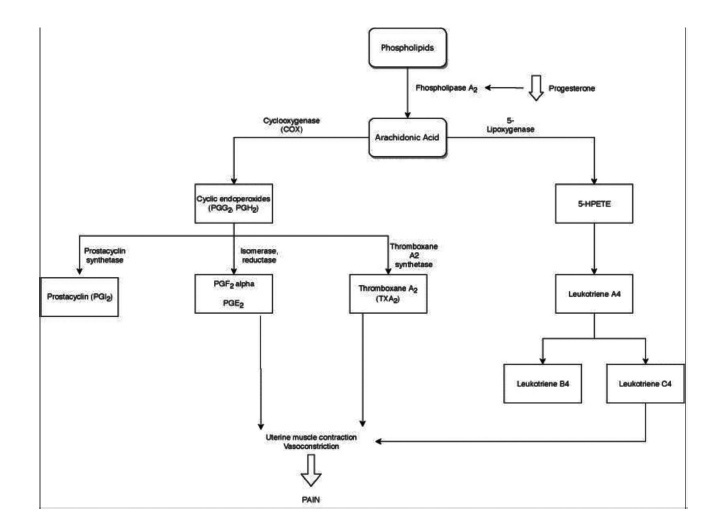
Primary dysmenorrhea is defined asmenstrual pain in the absence of pelvic disease. It is characterized by overproduction of prostaglandins by the endometrium, causing uterine hypercontractility that results in uterine muscle ischemia, hypoxia, and, subsequently, pain. It is the most common gynecological illness in women in their reproductive years and one of the most frequent causes of pelvic pain; however, it is underdiagnosed, undertreated, and even undervalued by women themselves, who accept it as part of themenstrual cycle. It hasmajor implications for quality of life, such as limitation of daily activities and psychological stress, being one of themain causes of school and work absenteeism. Its diagnosis is essentially clinical, based on the clinical history and normal physical examination. It is important to exclude secondary causes of dysmenorrhea. The treatment may have different approaches (pharmacological, nonpharmacological and surgical), but the first line of treatment is the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and, in cases of women who want contraception, the use of hormonal contraceptives. Alternative treatments, such as topical heat, lifestyle modification, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, dietary supplements, acupuncture, and acupressure, may be an option in cases of conventional treatments’ contraindication. Surgical treatment is only indicated in rare cases of women with severe dysmenorrhea refractory to treatment.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2020;42(2):90-95
To describe clinical and sociodemographic characteristics of women with deep infiltrating endometriosis (DIE) and assess their quality of life (QOL) during 6 months of medical treatment.
A descriptive cross-sectional study of 60 women diagnosed with DIE either by surgery or image methods (ultrasound or magnetic resonance), who received clinical treatment for at least 6 months in the Universidade de Campinas, Campinas, state of São Paulo, Brazil. Both the SF-36 and the EHP-30 questionnaires were used to assess the quality of life.
The mean age of the patients was 37.7 ± 6.0 years old, with 50% presenting dysmenorrhea; 57% dyspareunia; and 50% chronic pelvic pain. The SF-36 and the EHP-30 revealed impaired quality of life. In the SF-36, the worst domains were limitation due to emotional aspects (40.2 ± 43.1) and self-esteem and disposition (46.1 ± 24.8), whereas in the EHP-30 they were social well-being (50.3 ± 30.6); infertility (48.0 ± 36.3); and sexual intercourse (54.0 ± 32.1).
Although clinically treated, women with deep endometriosis present impairment in different domains of quality of life regardless of the questionnaire used for evaluation.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2019;41(9):548-554
To evaluate the existence of an association between ultrasound findings and epidemiological and clinical factors using results obtained from the EHP-30 questionnaire in women with ovarian endometriosis.
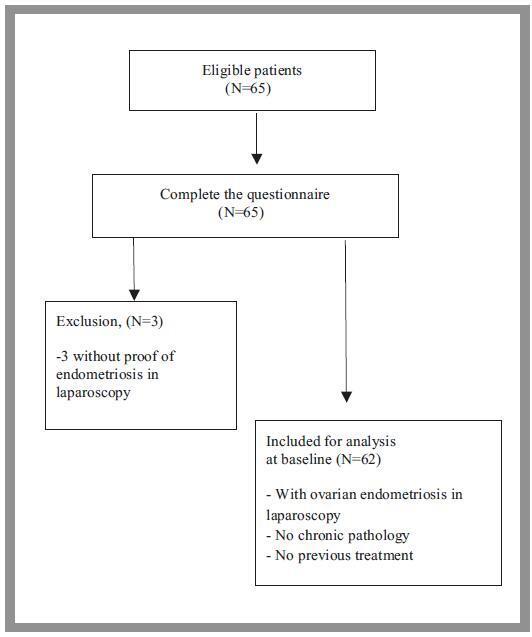
A cross-sectional observational study was performed between July 2012 and May 2015, in which patients with chronic pelvic pain suggestive of endometrioma, as indicated by the results from a transvaginal pelvic ultrasonography, completed the standardized Endometriosis Health Profile - 30 (EHP-30) questionnaire to access quality-of-life scores before beginning treatment for endometriosis. A total of 65 patients were included. The data was analyzed in the statistical program IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 22.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA) for the comparison of data through linear multiple regression.
The suitability of the linear regression model was confirmed by the histogram of the dependent variable and the residue distribution plot, confirming the trend of linearity as well as the homogeneous dispersion of the residues. The mean age of the patients was 39.7 ± 7.1 years old. Themajority was Caucasian (64.5%), had completed higher education (56.5%) and was nulligravida (40.3%). Infertility was present in 48.4% of the patients studied. Out of the total sample, 80.6% of the cases were symptomatic and complained mainly of acyclic pain, 79% of dysmenorrhea, and 61.3% of dyspareunia. This reflects the negative influence of endometriosis on the quality of life of patients with this disease.
Dyspareunia and acyclic pain were independent factors of correlation with high scores in the EHP-30 questionnaire, reflecting a worse quality of life.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2019;41(3):170-175
Endometriosis is a complex disease, and pain is an important component of the syndrome. One of the most used methods to assess pain is the visual analogue scale (VAS). The aim of the present research was to study the pain experienced by patients who referred to our unit for endometriosis, using the VAS to understand the variables that could influence it.
We have conducted a prospective study from February 2012 to December 2016, enrolling 388 patients who referred to a university hospital, in Florence, Italy. We have included in the present study patients during their follow-up for endometriosis; we have also included patients who underwent surgery with a histological diagnosis of endometriosis. We have collected sociodemographic and clinical information regarding age, body mass index (BMI), smoking habit, number of pregnancies, and endometriosis staging. Finally, we have administered the VAS for several symptoms.
Dysmenorrhea was the symptom associated with the highest perception of pain (mean VAS score of 5.76). The logistic regression showed that the stage of endometriosis could influence the pain associated to constipation and to dysuria. The linear regression showed that age couldinfluencethe pain associated to constipation, to dyspareunia,and to dysmenorrhea. A positive correlation was found between dysmenorrhea and chronic pelvic pain(CPP), between dysmenorrhea and dyspareunia, and between constipation and dysuria.
Using a validated method, the VAS, we have studied the pain experienced by a group of patients with a history of endometriosis and observed that smoking habit and BMI did not influence the VAS scores, and that dysmenorrhea was associated with the highest perception of pain.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2009;31(6):305-310
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000600007
PURPOSE: to present a series of cases of membranous dysmenorrhea. METHODS: all the patients selected were under diagnostic suspicion, after being clinically attended in a private medical office due to the report of painful dysmenorrhea associated with spontaneous elimination of elastic material with uterine shape. Only relevant facts about the pain condition have been described, together with the present and previous medical history and life habits. The material eliminated was forwarded to the pathology laboratory, where the macro and microscopic analyses were done. Cases with no confirmation of membranous material elimination were not selected. After the diagnostic confirmation, literature up to 2008 was carried out using the MeSH method, with the words "membranous dysmenorrheal". RESULTS: three cases of dysmenorrhea were transcribed. Besides the characteristic picture of pain and vaginal elimination of elastic material, all the cases were associated with the use of hormonal contraceptive methods. CONCLUSIONS: despite the fact that there are only sporadic reports of cases of membranous dysmenorrhea in the scientific literature, this etiology must be considered in cases of pain associated with vaginal bleeding plus elimination of elastic or solid material. The final diagnosis depends on anatomopathological exam, which should not be dismissed. We highlight the need for more discussion about this pathology, to keep the professionals updated with the aim of exerting adequate diagnosis and therapeutics.
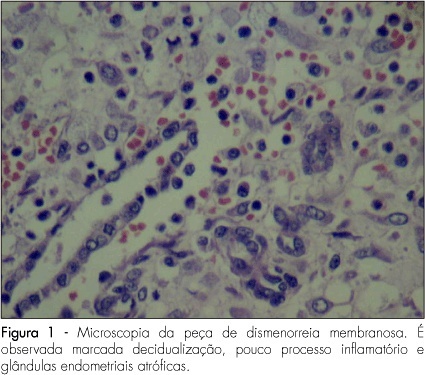
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2007;29(2):74-79
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032007000200003
PURPOSE: to evaluate the association between women's menstrual experience and preferred changes in their menstrual cycles. METHODS: a cross-sectional study design was used. A total of 420 women were interviewed. Participants complied with the following criteria: age (18 to 20, 25 to 34 and 45 to 49 years); schooling (<8 years and >12 years); having menstruated during the three months previous to the study. Subjects were selected in the city of Campinas (SP), in nine private and seven public health services. For data collection, a questionnaire was prepared on the basis of the results of a previous pilot study that consisted of small groups. A data bank was prepared with the information registered in the questionnaires and the analysis was carried out with SAS, version 8.2. For the statistical analysis, the Pearson chi2 test and the Fisher exact test were used to evaluate the association between variables (p<0.05). RESULTS: most subjects preferred greater than once a month intervals between menstruations. There was an association of the typical menstrual intervals experienced by women (p=0.0248) and the degree of interference of menstruation with daily activities (p=0.048) with the preferred interval between menses. However, there was no association between preferred intervals by women and the following characteristics of pain: duration, intensity and use of medication. CONCLUSIONS: the results suggest that women would like intervals longer than one month or to never menstruate.
Search
Search in:
breast (42) breast cancer (42) breast neoplasms (95) Cesarean section (72) endometriosis (66) infertility (56) Maternal mortality (43) menopause (82) obesity (58) postpartum period (40) pregnancy (225) Pregnancy complications (99) Prenatal care (68) prenatal diagnosis (50) Prevalence (41) Quality of life (51) risk factors (94) ultrasonography (79) urinary incontinence (40) women's health (48)