Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2023;45(10):594-602
Adhesive capsulitis is a condition characterized by shoulder pain and stiffness. Breast cancer treatment has been linked to the development of this condition, but its mechanisms are still little known. This study's objective was to identify predictors factors associated with the development of adhesive capsulitis in breast cancer patients.
A case control study was performed with women undergoing treatment for breast cancer in a single center. The sampling was nonprobabilistic and consecutive. Adhesive capsulitis was defined as constant pain associated with decreased active and passive shoulder movement in anterior elevation, external rotation at 0°/90° abduction, and internal rotation at 90° abduction. The study group consisted of patients with shoulder pain and range of motion limitations, while the control group consisted of women without any shoulder abnormalities. Sociodemographic and clinical variables were collected. A univariate logistic regression was used to assess the influence of variables on the studied outcome. For p< 0.20, a multivariate logistic regression was used. The probability of null hypothesis rejection was 5%.
A total of 145 women were assessed, with 39 (26.9%) on the study group and 106 (73.1%) on the control group. The majority was under 60 years old. In the multivariate analysis, variables correlated to the outcome under study were shoulder immobilization (OR = 3.09; 95% CI: 1.33–7.18; p = 0.009), lymphedema (OR = 5.09; 95% CI: 1.81–14.35; p = 0.002), and obesity (OR = 3.91; 95% CI: 1.27–12.01; p = 0.017).
Lymphedema, postsurgery immobilization, and obesity are predictive factors for the development of adhesive capsulitis in breast cancer patients.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2023;45(9):535-541
Breast cancer (BC) biomarkers, such as hormone receptors expression, are crucial to guide therapy in BC patients. Antiandrogens have been studied in BC; however, limited data are available on androgen receptor (AR) expression test methodology. We aim to report the core needle biopsy (CNB) accuracy for AR expression in BC.
Patients diagnosed with stage I-III invasive BC from a single institution were included. Androgen receptor expression was evaluated by immunohistochemistry (IHC) using 1 and 10% cutoff and the AR expression in surgical specimens (SS) was the gold standard. Kappa coefficients were used to evaluate the intraprocedural agreement.
A total of 72 patients were included, with a mean age of 61 years old and 84% were Luminal A or B tumors. The prevalence of AR expression in all BC samples was 87.5% using a cutoff ≥ 10% in SS. With a cutoff value ≥ 1%, CNB had an accuracy of 95.8% (Kappa value = 0.645; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.272–1.000; p < 0.001) and 86.1% (Kappa value = 0.365; 95% CI: 0.052–0.679; p < 0.001) when ≥ 10% cutoff was used for AR positivity. Androgen receptor expression in CNB (cutoff ≥ 1%) had a sensitivity of 98.5%, specificity of 60%, positive predictive value of 97.0%, and a negative predictive value of 76.9% in the detection of AR expression in SS.
Core needle biopsy has good accuracy in evaluating AR expression in BC. The accuracy of CNB decreases with higher cutoff values for AR positivity.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(8):761-770
The study aimed to characterize the clinical, histological, and immunohistochemical profile of women with invasive breast cancer, according to the risk for Hereditary Predisposition Breast and Ovarian Cancer Syndrome in a Brazilian population.
This is a retrospective study performed from a hospital-based cohort of 522 women, diagnosed with breast cancer treated at an oncology referral center in the Southeast region of Brazil, between 2014 and 2016.
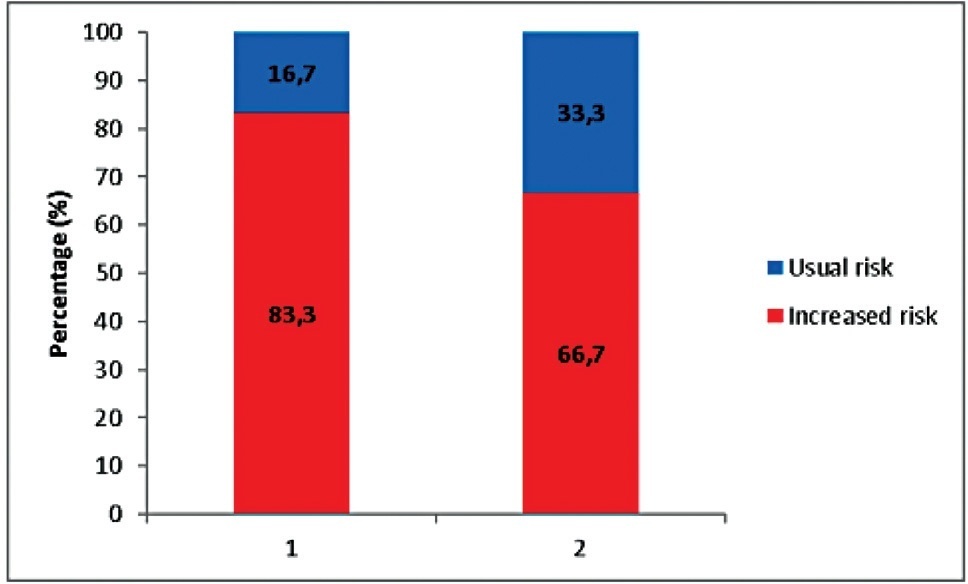
Among the 430 women diagnosed with invasive breast cancer who composed the study population, 127 (29.5%) were classified as at increased risk for hereditary predisposition to breast and ovarian cancer syndrome. There was a lower level of education in patients at increased risk (34.6%) when compared with those at usual risk (46.0%). Regarding tumor characteristics, women at increased risk had higher percentages of the disease diagnosed at an advanced stage (32.3%), and with tumors > 2cm (63.0%), with increased prevalence for both characteristics, when compared with those at usual risk. Furthermore, we found higher percentages of HG3 (43.3%) and Ki-67 ≥ 25% (64.6%) in women at increased risk, with prevalence being about twice as high in this group. The presence of triple-negative tumors was observed as 25.2% in women at increased risk and 6.0% in women at usual risk, with the prevalence of absence of biomarkers being 2.5 times higher among women in the increased risk group.
From the clinical criteria routinely used in the diagnosis of breast cancer, the care practice of genetic counseling for patients at increased risk of hereditary breast cancer in contexts such as Brazil is still scarce.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2021;43(11):840-846
The present study aims to assess the feasibility and patient satisfaction of teleoncology orientation in a vulnerable population of breast cancer patients assessed in a government health system during the coronavirus pandemic in 2020.
Eligible patients received an invitation to receive remote care to minimize exposure to an environment in which the risk of respiratory infection was present. The means of communication was telephone through an application that allows free conversation with no charge. An anonymous-response questionnaire based on a Likert-type scale was sent through a cell phone application or e-mail directly to each patient or close relative of the patient immediately after teleconsultation. Responses to the questions, which addressed utility, facility, interface quality, interaction quality, reliability, satisfaction, and interest in future evaluation, were compiled and analyzed.
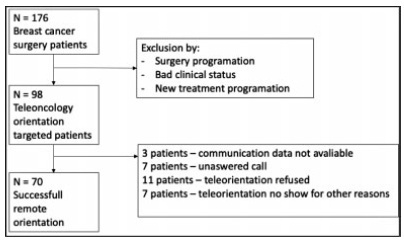
A total of 176 eligible patients scheduled for consultation were evaluated and 98 were included. Seventy (71.4%) successfully undertook the teleorientation. The questionnaire was submitted by 43 (61.4%) patients. The overall teleoncology orientation was classified as very positive by 41 (95.3%) patients. Specifically, regarding the questionnaire items, 43 (100%) patients scored 4 or 5 (agreed that the teleconsultation was beneficial) concerning the facility, followed by 42 (97.2%) for the interface quality, 41 (95.3%) for both utility and interaction quality, 40 (93%) for satisfaction and interest in future evaluation, and, finally, 39 (90.6%) for reliability.
Teleoncology orientation of low-income breast cancer patients is most feasible and leads to high patient satisfaction.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2021;43(8):616-621
This study evaluated the risk of the hereditary breast and ovarian cancer (HBOC) syndrome in patients with breast cancer by using the Family History Screening 7 (FHS-7) tool, a validated low-cost questionnaire with high sensitivity able to screen the HBOC risk in the population.
Women diagnosed with breast cancer (n=101) assisted by the Unified Health System at the 8th Regional Health Municipal Office of the state of Paraná answered the FHS-7, and the results were analyzed using IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 25.0. software (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA).
The risk of HBOC was 19.80% (n=20). Patients at risk exhibited aggressive tumor characteristics, such as high-grade tumors (30%), presence of angiolymphatic emboli (35%), and premenopausal at diagnosis (50%). Significant associations between the prevalence of high-grade tumors were observed inwomen younger than 50 years at diagnosis with HBOC (p=0.003).
Our findings suggest a possible family inheritance associated with worse clinical features in women with breast cancer in this population, indicating that HBOC investigation can be initially performed with low-cost instruments such as FHS-7.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2021;43(4):297-303
To evaluate the number of patients with early-stage breast cancer who could benefit from the omission of axillary surgery following the application of the Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology (ACOSOG) Z0011 trial criteria.
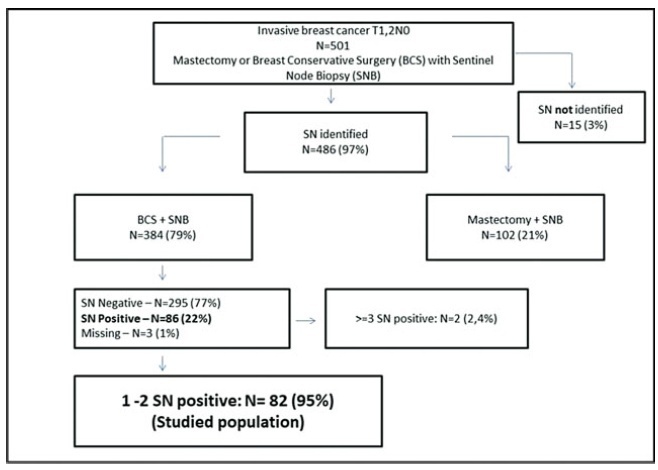
A retrospective cohort study conducted in the Hospital da Mulher da Universidade Estadual de Campinas. The study population included 384 women diagnosed with early-stage invasive breast cancer, clinically negative axilla, treated with breast-conserving surgery and sentinel lymph node biopsy, radiation therapy, chemotherapy and/or endocrine therapy, from January 2005 to December 2010. The ACOSOG Z0011 trial criteria were applied to this population and a statistical analysis was performed to make a comparison between populations.
A total of 384 patients underwent breast-conserving surgery and sentinel lymph node biopsy. Of the total number of patients, 86 women underwent axillary lymph node dissection for metastatic sentinel lymph nodes (SNLs). One patient underwent axillary node dissection due to a suspicious SLN intraoperatively, thus, she was excluded fromthe study. Among these patients, 82/86 (95.3%) had one to two involved sentinel lymph nodes andmet the criteria for the ACOSOG Z0011 trial with the omission of axillary lymph node dissection. Among the 82 eligible women, there were only 13 cases (15.9%) of lymphovascular invasion and 62 cases (75.6%) of tumors measuring up to 2 cm in diameter (T1).
The ACOSOG Z0011 trial criteria can be applied to a select group of SLNpositive patients, reducing the costs and morbidities of breast cancer surgery.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2021;43(3):185-189
The objective of the present study was to analyze the reasons that led to hormone therapies (HTs) regimen changes in women with breast cancer.
This was a retrospective cross-sectional study from a single-institution Brazilian cancer center with patient records diagnosed with breast cancer between January 2012 and January 2017.
From 1,555 women who were in treatment with HT, 213 (13.7%) women had HT switched, either tamoxifen to anastrozole or vice-versa. Most women included in the present study who switched HT were > 50 years old, postmenopausal, Caucasian, and had at least one comorbidity. From the group with therapy change, ‘disease progression’ was reason of change in 124 (58.2%) cases, and in 65 (30.5%) patients, ‘presence of side effects’ was the reason. From those women who suffered with side effects, 24 (36.9%) had comorbidities.
The present study demonstrated a low rate of HT switch of tamoxifen to anastrozole. Among the reasons for changing therapy, the most common was disease progression, which includes cancer recurrence, metastasis or increased tumor. Side effects were second; furthermore, age and comorbidities are risk factors for side effects.
Search
Search in:
breast (42) breast cancer (42) breast neoplasms (95) Cesarean section (72) endometriosis (66) infertility (56) Maternal mortality (43) menopause (82) obesity (58) postpartum period (40) pregnancy (225) Pregnancy complications (99) Prenatal care (68) prenatal diagnosis (50) Prevalence (41) Quality of life (51) risk factors (94) ultrasonography (79) urinary incontinence (40) women's health (48)