Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2024;46:e-rbgo6
BI-RADS® is a standardization system for breast imaging reports and results created by the American College of Radiology to initially address the lack of uniformity in mammography reporting. The system consists of a lexicon of descriptors, a reporting structure with final categories and recommended management, and a structure for data collection and auditing. It is accepted worldwide by all specialties involved in the care of breast diseases. Its implementation is related to the Mammography Quality Standards Act initiative in the United States (1992) and breast cancer screening. After its initial creation in 1993, four additional editions were published in 1995, 1998, 2003 and 2013. It is adopted in several countries around the world and has been translated into 6 languages. Successful breast cancer screening programs in high-income countries can be attributed in part to the widespread use of BI-RADS®. This success led to the development of similar classification systems for other organs (e.g., lung, liver, thyroid, ovaries, colon). In 1998, the structured report model was adopted in Brazil. This article highlights the pioneering and successful role of BI-RADS®, created by ACR 30 years ago, on the eve of publishing its sixth edition, which has evolved into a comprehensive quality assurance tool for multiple imaging modalities. And, especially, it contextualizes the importance of recognizing how we are using BI-RADS® in Brazil, from its implementation to the present day, with a focus on breast cancer screening.

Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2024;46:e-rbgo13
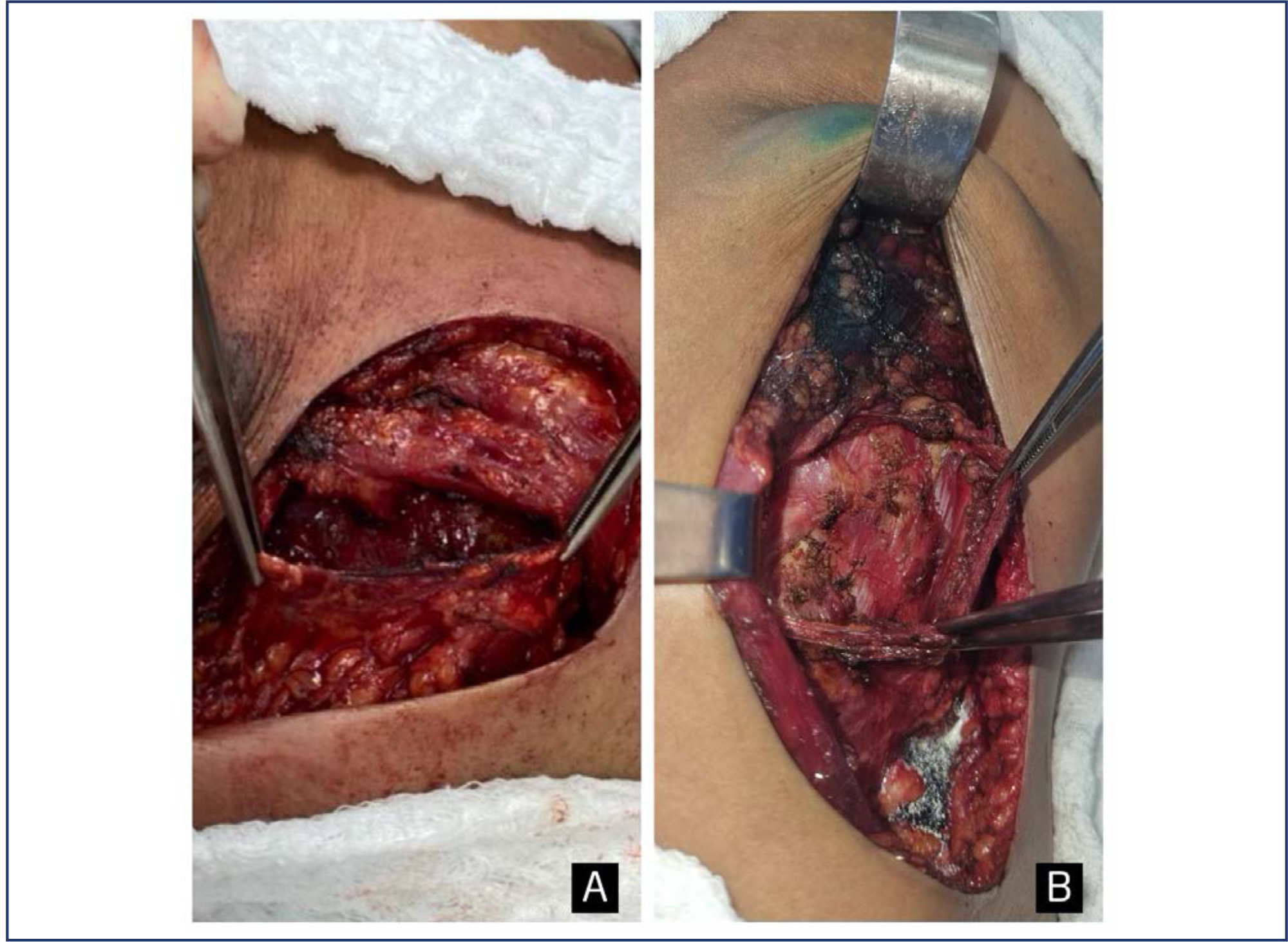
The purpose of this study was to compare postoperative pain between SF flap and serratus anterior muscle (SM) in direct-to-implant breast reconstruction.
This is a prospective cohort study that included 53 women diagnosed with breast cancer who underwent mastectomy and one-stage implant-based breast reconstruction from January 2020 to March 2021. Twenty-nine patients (54.7%) had SF elevation, and 24 patients (45.3%) underwent SM elevation. We evaluated patient-reported early postoperative pain on the first day after surgery. Also, it was reported that all surgical complications in the first month and patient reported outcomes (PROs) were measured with the BRECON 23 questionnaire.
The serratus fascia group used implants with larger volumes, 407.6 ± 98.9 cc (p < 0.01). There was no significant difference between the fascial and muscular groups regarding the postoperative pain score reported by the patients (2 versus 3; p = 0.30). Also, there was no difference between the groups regarding early surgical complications and PROs after breast reconstruction.
The use of SF seems to cause less morbidity, which makes the technique an alternative to be considered in breast reconstruction. Although there was no statistical difference in postoperative pain scores between the fascia and serratus muscle groups.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2024;46:e-rbgo15
To compare the medical image interpretation's time between the conventional and automated methods of breast ultrasound in patients with breast lesions. Secondarily, to evaluate the agreement between the two methods and interobservers.
This is a cross-sectional study with prospective data collection. The agreement's degrees were established in relation to the breast lesions's ultrasound descriptors. To determine the accuracy of each method, a biopsy of suspicious lesions was performed, considering the histopathological result as the diagnostic gold standard.
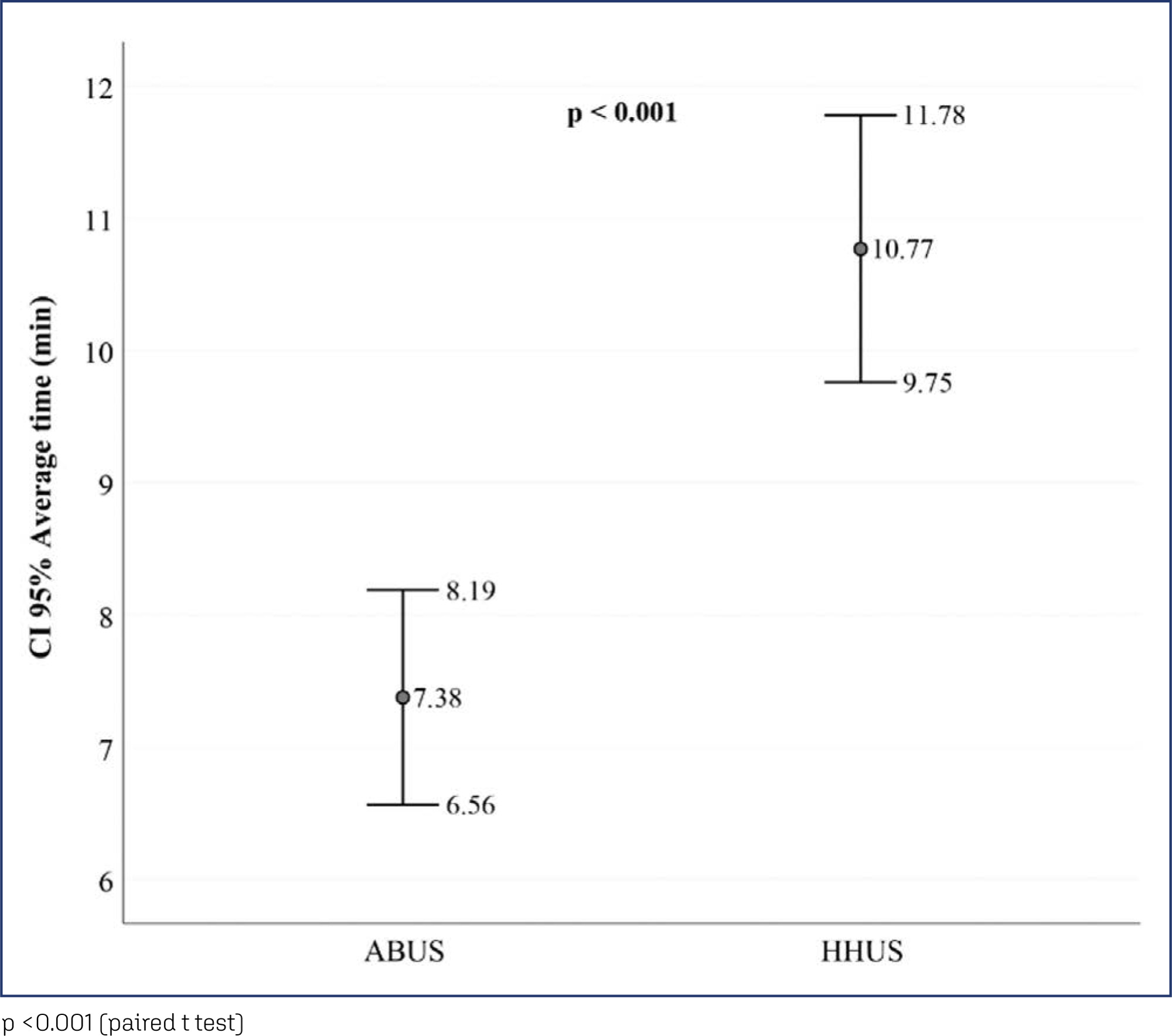
We evaluated 27 women. Conventional ultrasound used an average medical time of 10.77 minutes (± 2.55) greater than the average of 7.38 minutes (± 2.06) for automated ultrasound (p<0.001). The degrees of agreement between the methods ranged from 0.75 to 0.95 for researcher 1 and from 0.71 to 0.98 for researcher 2. Among the researchers, the degrees of agreement were between 0.63 and 1 for automated ultrasound and between 0.68 and 1 for conventional ultrasound. The area of the ROC curve for the conventional method was 0.67 (p=0.003) for researcher 1 and 0.72 (p<0.001) for researcher 2. The area of the ROC curve for the automated method was 0. 69 (p=0.001) for researcher 1 and 0.78 (p<0.001) for researcher 2.
We observed less time devoted by the physician to automated ultrasound compared to conventional ultrasound, maintaining accuracy. There was substantial or strong to perfect interobserver agreement and substantial or strong to almost perfect agreement between the methods.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2023;45(10):609-619
To investigate the clinicopathological significance and prognosis of the expression of the anterior gradient 3 (AGR3) protein in women with breast cancer.
The PubMed, CINAHL, EMBASE, Scopus, and Web of Science databases were searched for studies published in English and without restrictions regarding the year of publication. The search terms were: breast cancer AND anterior gradient 3 OR AGR3 expression.
We included observational or interventional studies, studies on AGR3 protein expression by immunohistochemistry, and studies on invasive breast cancer. Case reports, studies with animals, and reviews were excluded. In total, 4 studies were included, containing 713 cases of breast cancer.
Data were extracted on clinicopathological characteristics and survival. A meta-analysis of the prevalence of AGR3 expression was performed according to the clinicopathological characteristics, hazard ratios (HRs), and overall survival and disease-free survival.
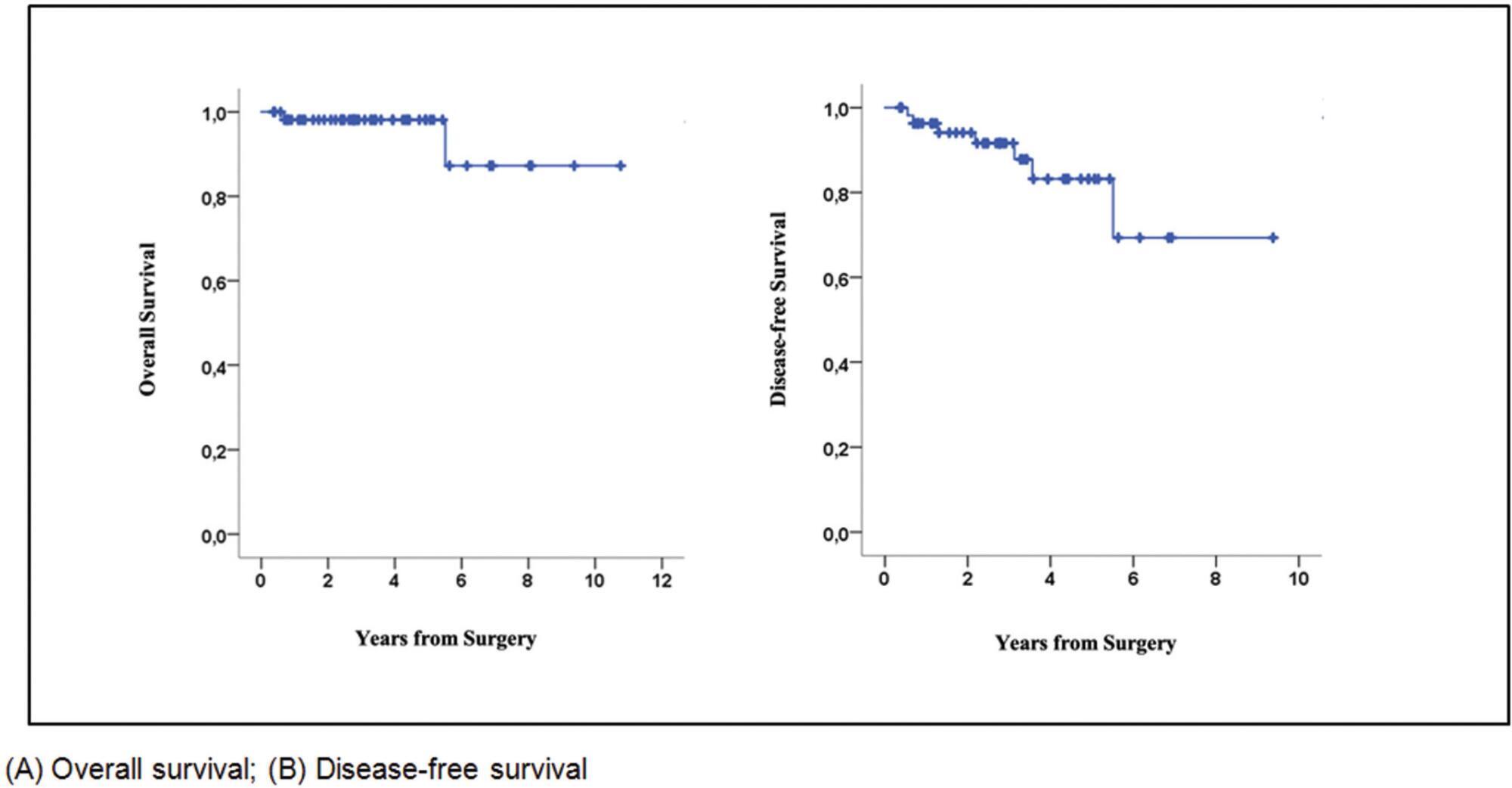
The expression of AGR3 was found in 62% of the cases, and it was associated with histological grade II, positivity of estrogen and progesterone receptors, low expression of ki67, recurrence or distant metastasis, and lumen subtypes. In patients with low and intermediate histological grades, AGR3 expression was associated with worse overall survival (HR: 2.39; 95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 0.628–4.159; p = 0.008) and worse disease-free survival (HR: 3.856; 95%CI: 1.026–6.686; p = 0.008).
The AGR3 protein may be a biomarker for the early detection of breast cancer and predict prognosis in luminal subtypes. In addition, in patients with low and intermediate histological grades, AGR3 protein expression may indicate an unfavorable prognosis in relation to survival.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2023;45(7):409-414
In this integrative review, we aimed to describe the records of time devoted by physicians to breast ultrasound in a review of articles in the literature, in order to observe whether the automation of the method enabled a reduction in these values. We selected articles from the Latin American and Caribbean Literature in Health Sciences (LILACS) and MEDLINE databases, through Virtual Health Library (BVS), SciELO (Scientific Electronic Library Online), PubMed, and Scopus. We obtained 561 articles, and, after excluding duplicates and screening procedures, 9 were selected, whose main information related to the guiding question of the research was synthesized and analyzed. It was concluded that the automation of breast ultrasound represents a possible strategy for optimization of the medical time dedicated to the method, but this needs to be better evaluated in comparative studies between both methods (traditional and automated), with methodology directed to the specific investigation of this potentiality.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2023;45(5):242-252
Evaluate the effect of combined training on body image (BI), body composition and functional capacity in patients with breast cancer. As also the relationship of BI with body composition and functional capacity.
This was a Controlled Clinical Trial study, this study including 26 patients with breast cancer (30 to 59 years). The training group (n = 13) underwent 12 weeks of training, including three 60-min sessions of aerobic exercise and resistance training, and two sessions of flexibility training per week; each flexibility exercise lasted 20s. The Control Group (n = 13) received only the standard hospital treatment. Participants were evaluated at baseline and after 12 weeks. BI (primary outcomes) was assessed using the Body Image After Breast Cancer Questionnaire; Body composition was estimated with the indicators: Body mass index; Weight, Waist hip Ratio; Waist height ratio; Conicity index; Reciprocal ponderal index; Percentage of fat; Circumference of the abdomen and waist; Functional capacity by cardiorespiratory fitness (cycle ergometer) and strength (manual dynamometer). The statistic was performed in the Biostatistics and Stata 14.0 (α = 5%).
The patients in the training group showed a reduction in the limitation dimension (p = 0.036) on BI, However, an increase in waist circumference was observed in both groups. In addition an increase in VO2max (p < 0.001) and strength in the right (p = 0.005) and left arms (p = 0.033).
Combined training demonstrates to be an effective and non-pharmacological strategy to patients with breast cancer, with improvement on BI and functional capacity, changing related variables negatively when there is no physical training.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(11):1052-1058
Nipple-sparing mastectomy (NSM) has been traditionally used in selected cases with tumor-to-nipple distance > 2 cm and negative frozen section of the base of the nipple. Recommending NSM in unselected populations remains controversial. The present study evaluated the oncological outcomes of patients submitted to NSM in an unselected population seen at a single center.
This retrospective cohort study included unselected patients with invasive carcinoma or ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) who underwent NSM in 2010 to 2020. The endpoints were locoregional recurrence, disease-free survival (DFS), and overall survival (OS), irrespective of tumor size or tumor-to-nipple distance.
Seventy-six patients (mean age 46.1 years) (58 invasive carcinomas/18 DCIS) were included. The most invasive carcinomas were hormone-positive (60%) (HER2 overexpression: 24%; triple-negative: 16%), while 39% of DCIS were high-grade. Invasive carcinomas were T2 in 66% of cases, with axillary metastases in 38%. Surgical margins were all negative. All patients with invasive carcinoma received systemic treatment and 38% underwent radiotherapy. After a mean of 34.8 months, 3 patients with invasive carcinoma (5.1%) and 1 with DCIS (5.5%) had local recurrence. Two patients had distant metastasis and died during follow-up. The 5-year OS and DFS rates for invasive carcinoma were 98% and 83%, respectively.
In unselected cases, the 5-year oncological outcomes following NSM were found to be acceptable and comparable to previous reports. Further studies are required.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(9):871-877
This study aimed to evaluate the diagnostic profile of breast cancer cases during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic compared with the previous year.
It is a retrospective study of cases diagnosed by a reference service in the public health system of Campinas, SP, Brazil. Two periods were analyzed: March to October 2019 (preCOVID period) and March to October 2020 (COVID-period). All women diagnosed during the periods were included. The Chi-Squared or Fisher exact and Mann-Whitney tests were used.
In the preCOVID and COVID periods, breast cancers were diagnosed, respectively, in 115 vs 59 women, and the mean ages at diagnosis were 55 and 57 years (p = 0.339). In the COVID period, the family history of breast cancer was more observed (9.6% vs 29.8%, p < 0.001), cases were more frequently symptomatic (50.4% vs 79.7%, p < 0.001) and had more frequently palpable masses (56.5% vs 79.7%, p = 0.003). In symptomatic women, the mean number of days from symptom to mammography were 233.6 (458.3) in 2019 and 152.1 (151.5) in 2020 (p = 0.871). Among invasive tumors, the proportion of breast cancers in stages I and II was slightly higher in the COVID period, although not significantly (76.7% vs 82.4%, p = 0.428). Also in the COVID period, the frequency of luminal A-like tumors was lower (29.2% vs 11.8%, p = 0.018), of triple-negative tumors was twice as high (10.1% vs 21.6%, p = 0.062), and of estrogen receptor-positive tumors was lower (82.2% vs 66.0%, p = 0.030).
During the COVID-19 pandemic, breast cancer diagnoses were reduced. Cases detected were suggestive of a worse prognosis: symptomatic women with palpable masses and more aggressive subtypes. Indolent tumors were those more sensitive to the interruption in screening.
Search
Search in:
breast (42) breast cancer (42) breast neoplasms (95) Cesarean section (72) endometriosis (66) infertility (56) Maternal mortality (43) menopause (82) obesity (58) postpartum period (40) pregnancy (225) Pregnancy complications (99) Prenatal care (68) prenatal diagnosis (50) Prevalence (41) Quality of life (51) risk factors (94) ultrasonography (79) urinary incontinence (40) women's health (48)