Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2024;46:e-rbgo35
We aimed to translate and determine cultural validity of the Vaginal Changes Sexual and Body Esteem Scale (VSBE) for Brazilian Portuguese language in postpartum women who underwent vaginal delivery with or without perineal laceration and cesarean section.
A cross-sectional study conducted virtually, with online data collection through a survey with 234 postpartum women of 975 that were invited. Clinical, sociodemographic, and psychometric variables from the VSBE questionnaire were analyzed (content validity index, internal consistency, test-retest reliability, construct/structural and discriminant validity). Multivariate analysis was performed to explore associated factors with the presence of perineal laceration.
One-hundred fifty-eight women experienced vaginal delivery, of which 24.79% had an intact perineum, 33.33% had perineal laceration, and 9.4% underwent episiotomy; and 76 participants had cesarean sections. Women with perineal laceration were older, presented dyspareunia and previous surgeries than women without perineal laceration (p<0.05). For VSBE, a high internal consistency (Cronbach's α > 0.7) was observed, but it did not correlate with Body Attractiveness Questionnaire and Female Sexual Function Index; however, it correlated with the presence of women sutured for perineal laceration. Moreover, VSBE presented good structural validity with two loading factors after exploratory factor analysis. VSBE also demonstrated discriminant validity between the presence or absence of perineal laceration. The presence of urinary incontinence (UI) (OR=2.716[1.015-4.667];p=0.046) and a higher VSBE total score (OR=1.056[1.037-1.075];p<0.001) were the only factors associated with perineal laceration.
Vaginal Changes Sexual and Body Esteem Scale demonstrated appropriate translation and good internal consistency, discriminant/construct validity and reliability. Vaginal Changes Sexual and Body Esteem Scale total score and presence of UI were associated with women that underwent perineal laceration.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2023;45(3):121-126
To evaluate and compare peripheral, pelvic floor, respiratory muscle strength, and functionality in the immediate puerperium of normal delivery and cesarean section.
This is a cross-sectional study that verified respiratory, pelvic floor, peripheral, and functional muscle strength through manovacuometry, pelvic floor functional assessment (PFF), dynamometry, and the Time Up and Go (TUG) test, respectively. The groups were divided according to the type of delivery, into a cesarean section group and a normal parturition group.
The sample was composed of 72 postpartum puerperae, 36 of normal parturition, and 36 of cesarean section, evaluated before hospital discharge, mean age ranged from 25.56 ± 6.28 and 28.57 ± 6.47 years in puerperae of normal parturition and cesarean section respectively. Cesarean showed higher pelvic floor strength (PFF) compared to normal parturition (p < 0.002), but puerperae from normal delivery showed better functionality (p < 0.001). As for peripheral muscle strength and respiratory muscle strength, there was no significance when comparing the types of parturirion.
There is a reduction in pelvic muscle strength in puerperae of normal delivery and a decrease in functionality in puerperae of cesarean section.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(12):1083-1089
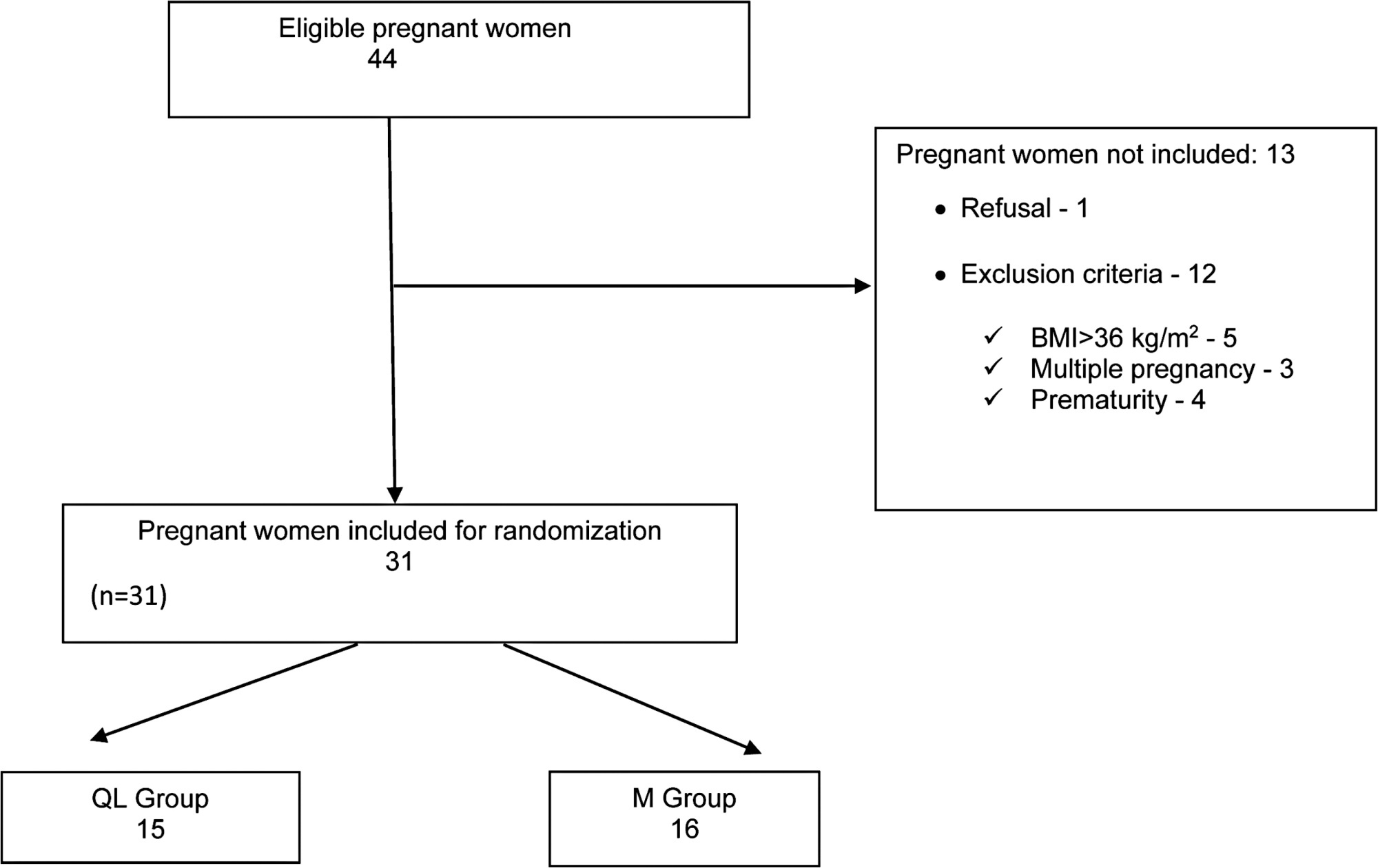
To compare the efficacy of quadratus lumborum (QL) block and intrathecal morphine (M) for postcesarean delivery analgesia.
Thirty-one pregnant women with ≥ 37 weeks of gestation submitted to elective cesarean section were included in the study. They were randomly allocated to either the QL group (12.5 mg 0.5% bupivacaine for spinal anesthesia and 0.3 ml/kg 0.2% bupivacaine for QL block) or the M group (12.5 mg bupivacaine 0.5% and 100 mcg of morphine in spinal anesthesia). The visual analog scale of pain, consumption of morphine and tramadol for pain relief in 48 hours, and side effects were recorded.
Median pain score and/or pain variation were higher in the morphine group than in the QL group (p = 0.02). There was no significant difference in the consumption of morphine or tramadol between groups over time. Side effects such as pruritus, nausea, and vomiting were observed only in the morphine group.
Quadratus lumborum block and intrathecal morphine are effective for analgesia after cesarean section. Patients undergoing QL block had lower postoperative pain scores without the undesirable side effects of opioids such as nausea, vomiting, and pruritus.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(9):830-837
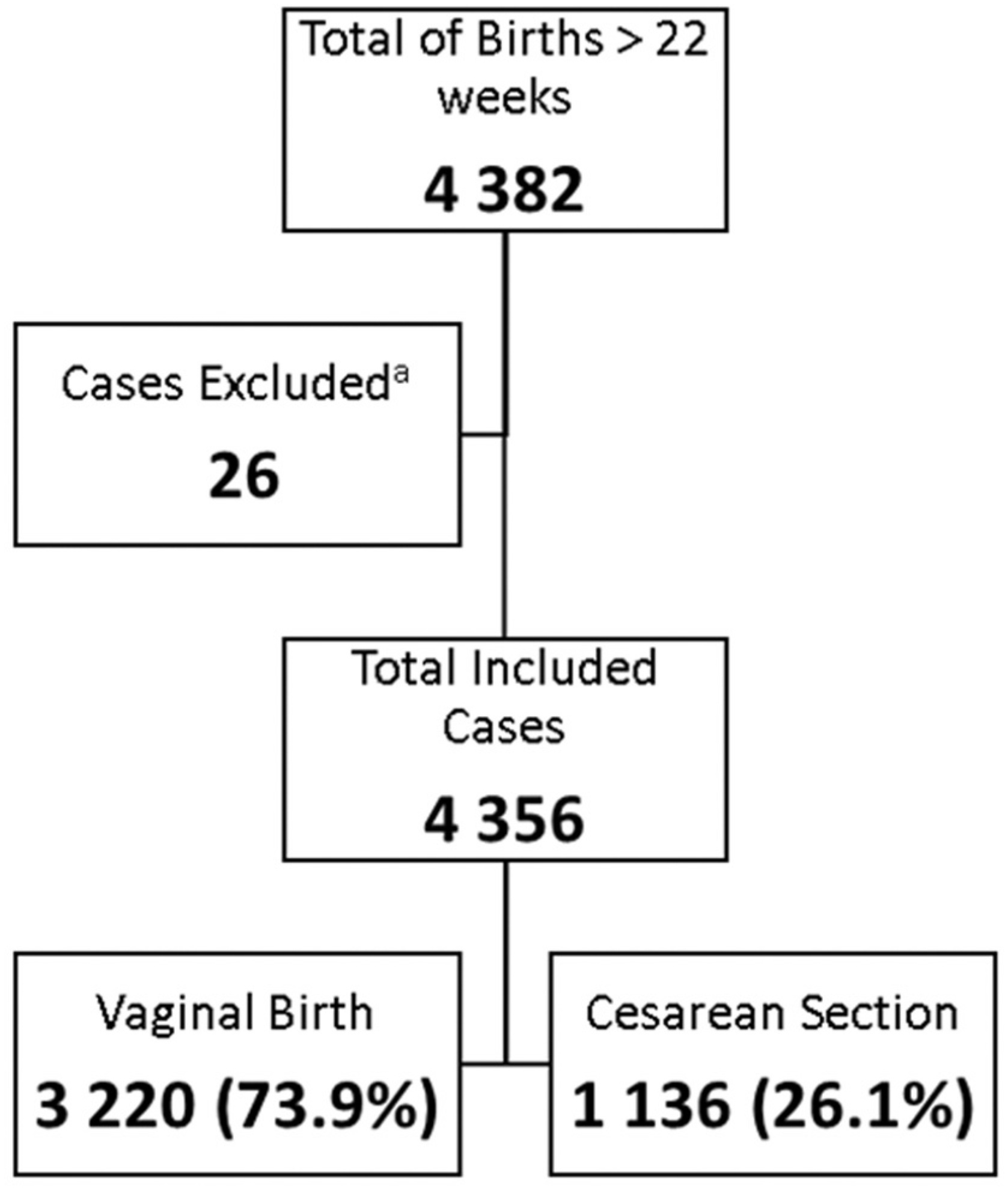
To use the Robson Ten Group Classification (RTGC) to analyze cesarean section (CS) rates in a Honduran maternity hospital, with focus in groups that consider induction of labor.
Cross-sectional study. Women admitted for childbirth (August 2017 to October 2018) were classified according to the RTGC. The CS rate for each group and the contribution to the overall CS rate was calculated, with further analyses of the induction of labor among term primiparous (group 2a), term multiparous (group 4a), and cases with one previous CS (group 5.1).
A total of 4,356 women were considered, with an overall CS rate of 26.1%. Group 3 was the largest group, with 38.6% (1,682/4,356) of the cases, followed by Group 1, with 30.8% (1,342/4,356), and Group 5, with 10.3% (450/4,356). Considering the contribution to overall CS rates per group, Group 5 contributed with 30.4% (345/1,136) of the CSs and within this group, 286/345 (82.9%) had 1 previous CS, with a CS rate > 70%. Groups 1 and 3, with 26.6% (291/1,136) and 13.5% (153/1,136), respectively, were the second and third larger contributors to the CS rate. Groups 2a and 4a had high induction success, with low CS rates (18.4 and 16.9%, respectively).
The RTGC is a useful tool to assess CS rates in different healthcare facilities. Groups 5, 1, and 3 were the main contributors to the CS rate, and groups 2 and 4 showed the impact and importance of induction of labor. These findings may support future interventions to reduce unnecessary CS, especially among primiparous and in women with previous CS.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(7):640-645
The present study seeks to identify the associated factors that increased primary cesarean delivery rates.
This was a cross-sectional study that evaluated the number of primary cesarean sections performed in the years 2006 and 2018 at the Hospital de Clínicas de Porto Alegre (HCPA, in the Portuguese acronym), through the collection of data from the medical records of the patients.
Advanced maternal age, twin pregnancy, and higher body mass index (BMI) became more frequent in 2018 in comparison with 2006. To mitigate the impact of confounding in comparisons among groups, we made an adjustment by propensity scores and detected significant differences when comparing both age groups on twin pregnancy rates, gestational diabetes mellitus, and thyroid disease.
Data from the present study can be used to prevent and improve the management of morbidities, impacting on better outcomes in obstetrical practice.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2021;43(10):728-735
The role of breast milk in the physical and mental health of infants and in the prevention of infant death is widely known. The benefits of breastfeeding for mothers and infants have been proven, but several factors can affect breastfeeding. Childbirth is one of the most influential factors. The present study aimed to investigate the effect of the type of delivery (natural childbirth and cesarean section) on breastfeeding based on the latch, audible swallowing, type of nipple, comfort, hold (LATCH) scoring system.
The present cross-sectional observational study was performed using the census method among women who referred to Afzalipour Hospital for delivery in May 2020; the breastfeeding pattern was completed by observation and the in-case information, by LATCH checklist. Data were analyzed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, United States) software, version 19.0, analysis of variance (ANOVA), and the Chi-squared statistical test.
Out of a total of 254 deliveries (127 natural childbirths and 127 cesarean deliveries), there was no statistically significant difference between the 2 study groups in terms of age, maternal employment status, and infant weight, but there was a statistically significant relationship between the type of delivery, the maternal level of schooling, and the appearance, pulse, grimace, activity, and respiration (Apgar) score in the first minute. The mean score of breastfeeding patterns among the natural childbirth group (9.33) was higher than that of the cesarean section group (7.21).
The type of delivery affects the mother’s performance during breastfeeding, and mothers submitted to cesarean sections need more support and help in breastfeeding.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2021;43(5):374-376
To analyze effects of the COVID-19 pandemic on the consumption of personal protective equipment and products (PPEP), as well as the frequency of surgical site infection (SSI) among non-COVID-19 patients submitted to cesarean sections.
A retrospective study was conducted in a maternity unity of a public teaching hospital which was not part of the reference service for COVID-19 treatment. It compared PPEP consumption and the occurrence of SSI after cesarean sections in monthly periods before and after the occurrence of the first case of COVID-19 in Porto Alegre, state of Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Personal protective equipment and products consumption was measured as units of masks, gloves, gowns, and caps, and use of alcohol-based products or soap for hand sanitation asml/patient/day. The SSI index was calculated as the proportion of cases of SSI over the number of cesarean sections performed monthly during the study period.
There was an increase in all measured items of PPEP, with consumption of disposable masks with a median of 1,450 units in the pre-COVID period, and of 2550 in the post-COVID period (a 75.9% increase). A decrease of 49% in SSI was detected, with a median of 1.74 in the pre-COVID period and of 0.89 in the post-COVID period.
The increase in consumption of PPEP could be a result of safer practices adopted by healthcare workers with the advent of COVID-19, of which the following reduction in the occurrence of SSI could be a direct consequence. Despite the severity of the crisis, one could state that extreme situations can lead to valuable reflections and opportunities for improvement.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2021;43(2):84-90
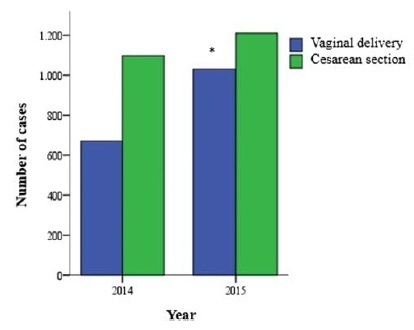
To analyze and compare the frequency of cesarean sections and vaginal deliveries through the Robson Classification in pregnant women attended at a tertiary hospital in two different periods.
Cross-sectional, retrospective study of birth records, comprising 4,010 women, conducted from January 2014 to December 2015 in the only public regional referral hospital for the care of high- risk pregnancies, located in Southern Brazil.
The overall cesarean section rate reached 57.5% and the main indication was the existence of a previous uterine cesarean scar. Based on the Robson Classification, groups 5 (26.3%) and 10 (17.4%) were the most frequent ones. In 2015, there was a significant increase in the frequency of groups 1 and 3 (p < 0.001), when compared with the previous year, resulting in an increase in the number of vaginal deliveries (p < 0.0001) and a reduction in cesarean section rates.
The Robson Classification proved to be a useful tool to identify the profile of parturients and the groups with the highest risk of cesarean sections in different periods in the same service. Thus, it allowsmonitoring in a dynamic way the indications and delivery routes and developing actions to reduce cesarean rates according to the characteristics of the pregnant women attended.
Search
Search in:
breast (42) breast cancer (42) breast neoplasms (95) Cesarean section (72) endometriosis (66) infertility (56) Maternal mortality (43) menopause (82) obesity (58) postpartum period (40) pregnancy (225) Pregnancy complications (99) Prenatal care (68) prenatal diagnosis (50) Prevalence (41) Quality of life (51) risk factors (94) ultrasonography (79) urinary incontinence (40) women's health (48)