Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2024;46:e-rbgo7
To validate the 10-item Cervantes Scale (CS-10) among Brazilian women.
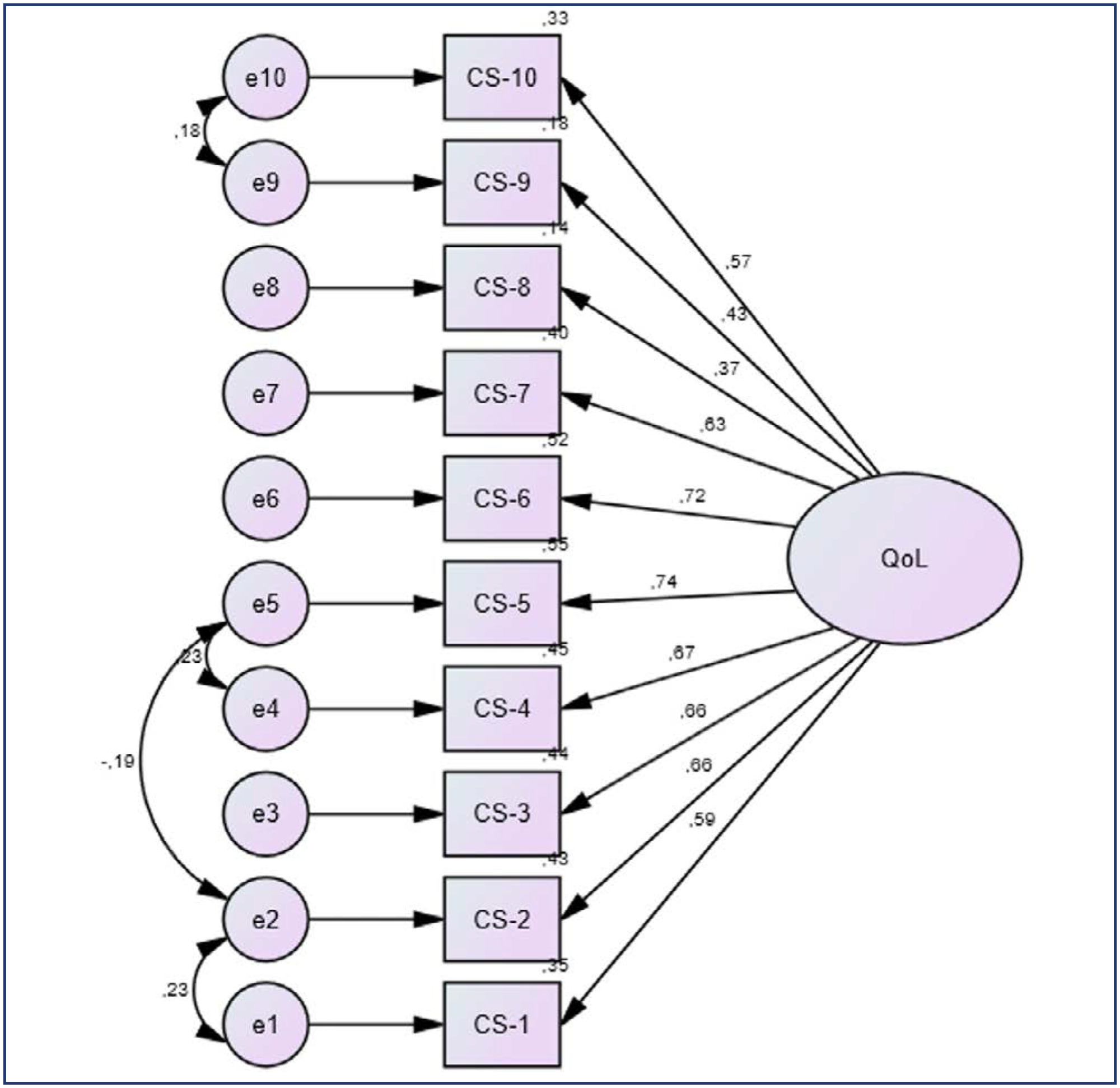
This is a cross-sectional observational study involving women in the community aged 40–55 years in the Southern region of Brazil. They completed a general health, habits and socio-demographic questionnaire, the CS-10 and the Women’s Health Questionnaire (WHQ). Women unable to understand the survey, not consenting to participate, or having incapacity imposing difficulties during the completion of the questionnaire were excluded. A Confirmatory Factor Analysis (CFA) was conducted with the AMOS 16.0 software. Chi-square of degrees of freedom (χ2/df), the Comparative Fit Index (CFI), the Tucker-Lewis Index (TLI) and the Root-Mean-Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) were used as indices of goodness of fit. Cronbach’s alpha coefficient was used for internal consistency.
A total of 422 women were included (premenopausal n=35, perimenopausal n=172, postmenopausal n=215). The CFA for the CS-10 showed a good fit (χ²/df=1.454, CFI=0.989; TLI=0.985; RMSEA=0.033; CI 90%=0.002-0.052; PCLOSE=0.921; Model p=0.049). Good reliability was established in CS-10 and WHQ (Cronbach’s alpha=0.724). Postmenopausal women had higher total CS-10 scores (p≤0.0001), reflecting worse quality of life (QoL) related to menopause symptoms and confirming the greater symptomatology evaluated by high total scores for WHQ found in this population when compared to those in the premenopausal period (p=0.041).
The CS-10 is a consistent tool for health-related QoL in Brazilian mid-aged women.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2024;46:e-rbgo16
Dysmenorrhea is the pain related to menstruation; to screen for the symptoms, a working ability, location, intensity of days of pain, and dysmenorrhea (WaLIDD) score was created. The purpose of this work was to culturally adapt and assess the measurement properties of the WaLIDD score for dysmenorrhea in Brazilian women.
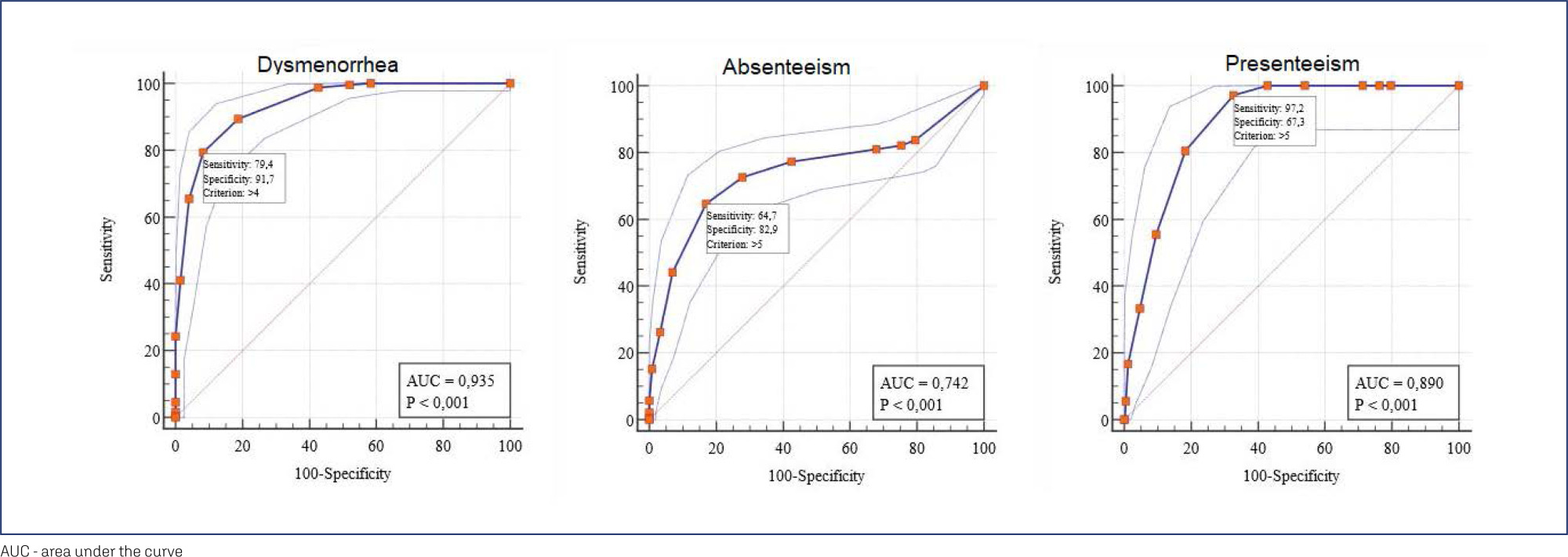
In this cross-sectional online study, we evaluated women with and without dysmenorrhea. Criterion validity and construct validity were assessed, respectively, by the Receiver Operator Characteristic (ROC) curve and correlations with the bodily pain and social functioning domains of medical outcomes study 36-item short-form health survey (SF-36), self-report of absenteeism and Stanford Presenteeism Scale for presenteeism. Test-retest reliability and measurement errors were assessed, respectively, by intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) and Bland and Altman Graph.
430 women completed the test, 238 (55.4%) women had dysmenorrhea, and 199 (46.3%) answered the questionnaire twice for the retest. The cutoff points ≥4, ≥5, and ≥5 could discriminate between women with and without dysmenorrhea, absenteeism, and presenteeism related to dysmenorrhea, respectively. Correlations between SF-36 – pain and social functioning domains and WaLIDD score were weak to strong and negative. For WaLIDD total Score, ICC was 0.95 and the limits of agreement were −1.54 and 1.62.
WaLIDD score is a short, valid and reliable instrument to screen and predict dysmenorrhea and could predict absenteeism and presenteeism related to dysmenorrhea in Brazilian women.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(10):945-952
To analyze the cases of all women who attend to a service of legal termination of pregnancy in cases of sexual violence in a public reference hospital and to identify the factors related to its execution.
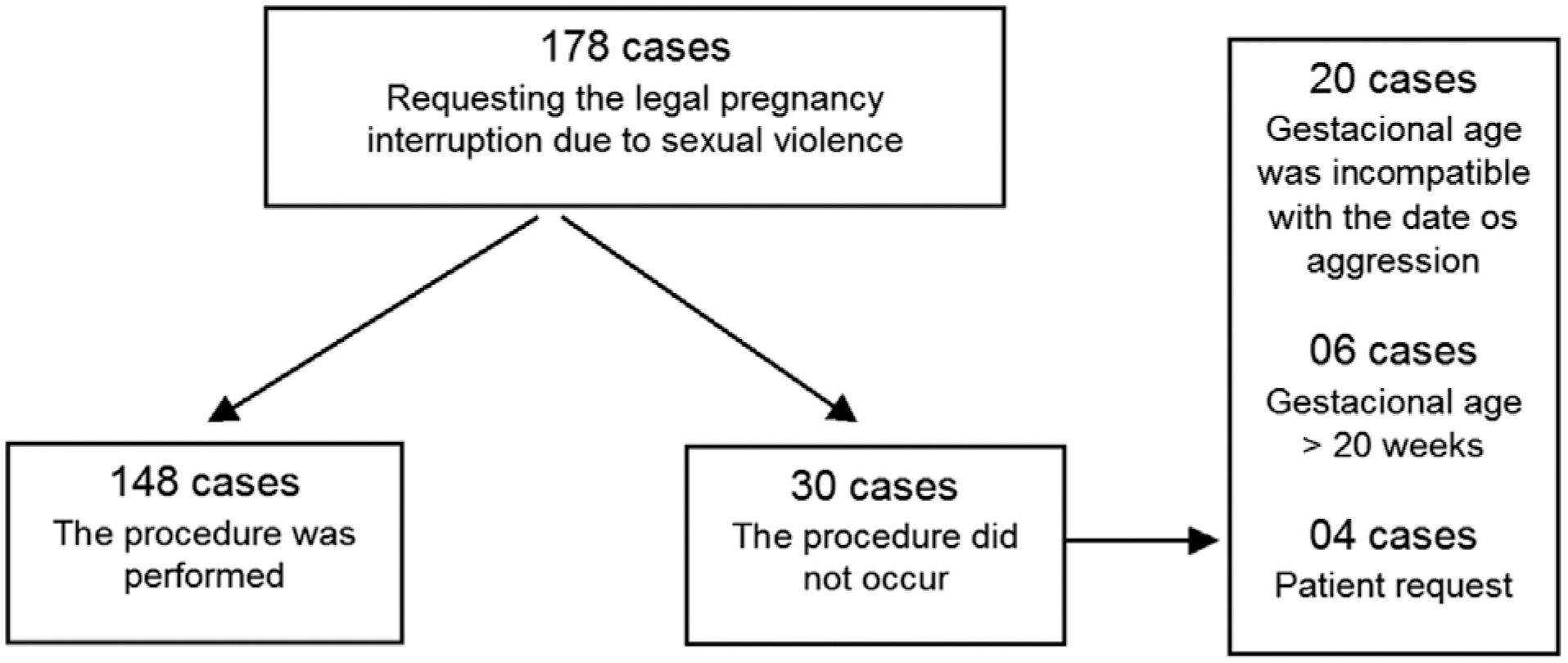
Cross-sectional observational study with information from medical records from January 2014 to December 2020. A total of 178 cases were included, with an evaluation of the data referring to the women who attended due to sexual violence, characteristics of sexual violence, hospital care, techniques used, and complications. The analysis was presented in relative and absolute frequencies, medians, means, and standard deviation. Factors related to the completion of the procedure were assessed using binary logistic regression.
Termination of pregnancy was performed in 83.2% of the cases; in 75.7% of the cases, the technique used was the association of transvaginal misoprostol and intrauterine manual aspiration. There were no deaths, and the rate of complications was 1.4%. Gestational age at the time the patient's sought assistance was the determining factor for the protocol not being completed. Pregnancies up to 12 weeks were associated with a lower chance of the interruption not occurring (odds ratio [OR]: 0.41; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.12–0.88), while cases with gestational age > 20 weeks were associated with a greater chance of the interruption not happening (OR: 29.93; 95%CI: 3.91–271.50).
The service studied was effective, with gestational age being the significant factor for resolution.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(7):710-718
To describe the effects of combined oral contraceptives (COC) on the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS).
The findings of this study suggest that the COC promotes greater activation of the RAAS. Supporting the idea that its use is related to an increased risk of cardiovascular events, including systemic arterial hypertension.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(4):409-424
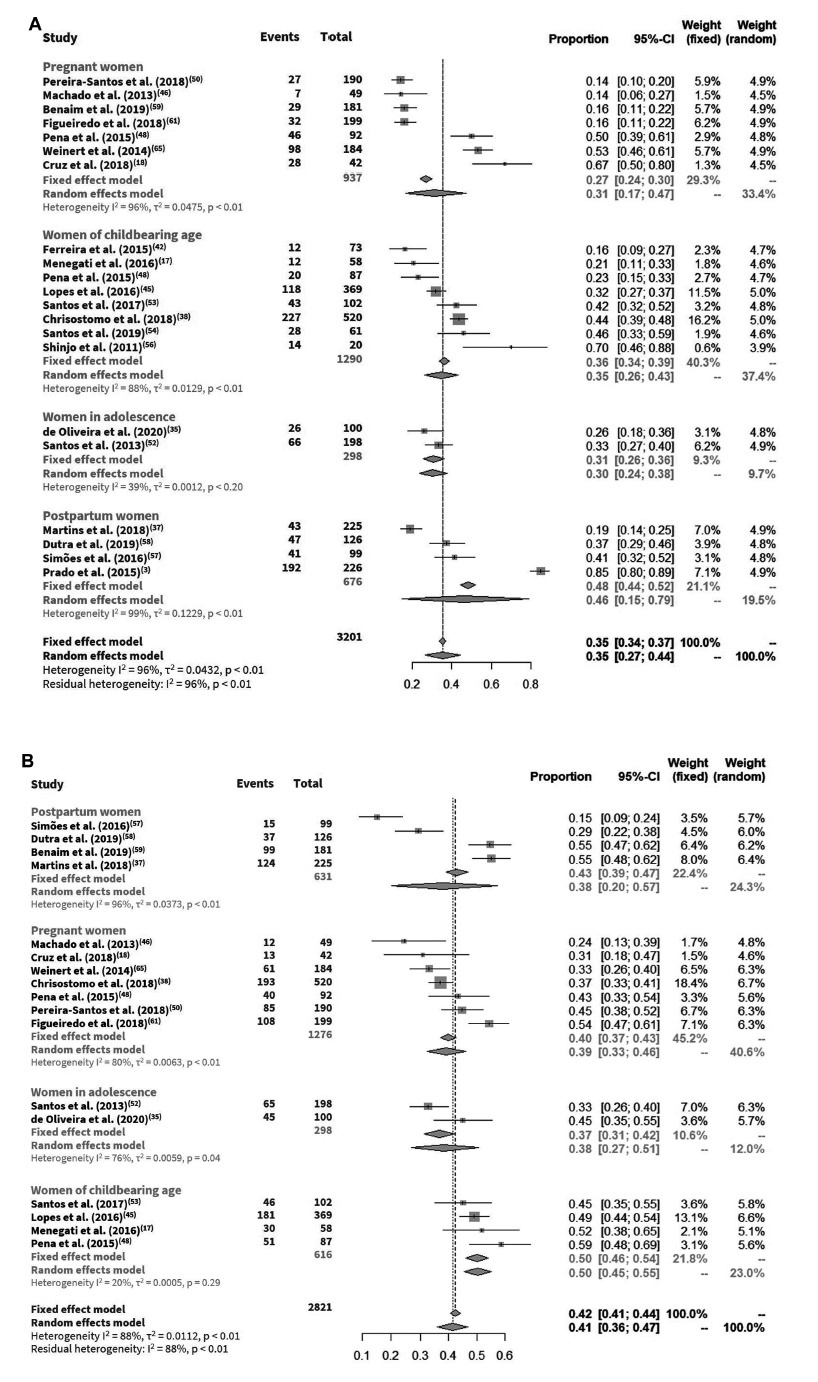
To estimate the prevalence of inadequate vitamin D level and its associated factors for women of childbearing age in Brazil.
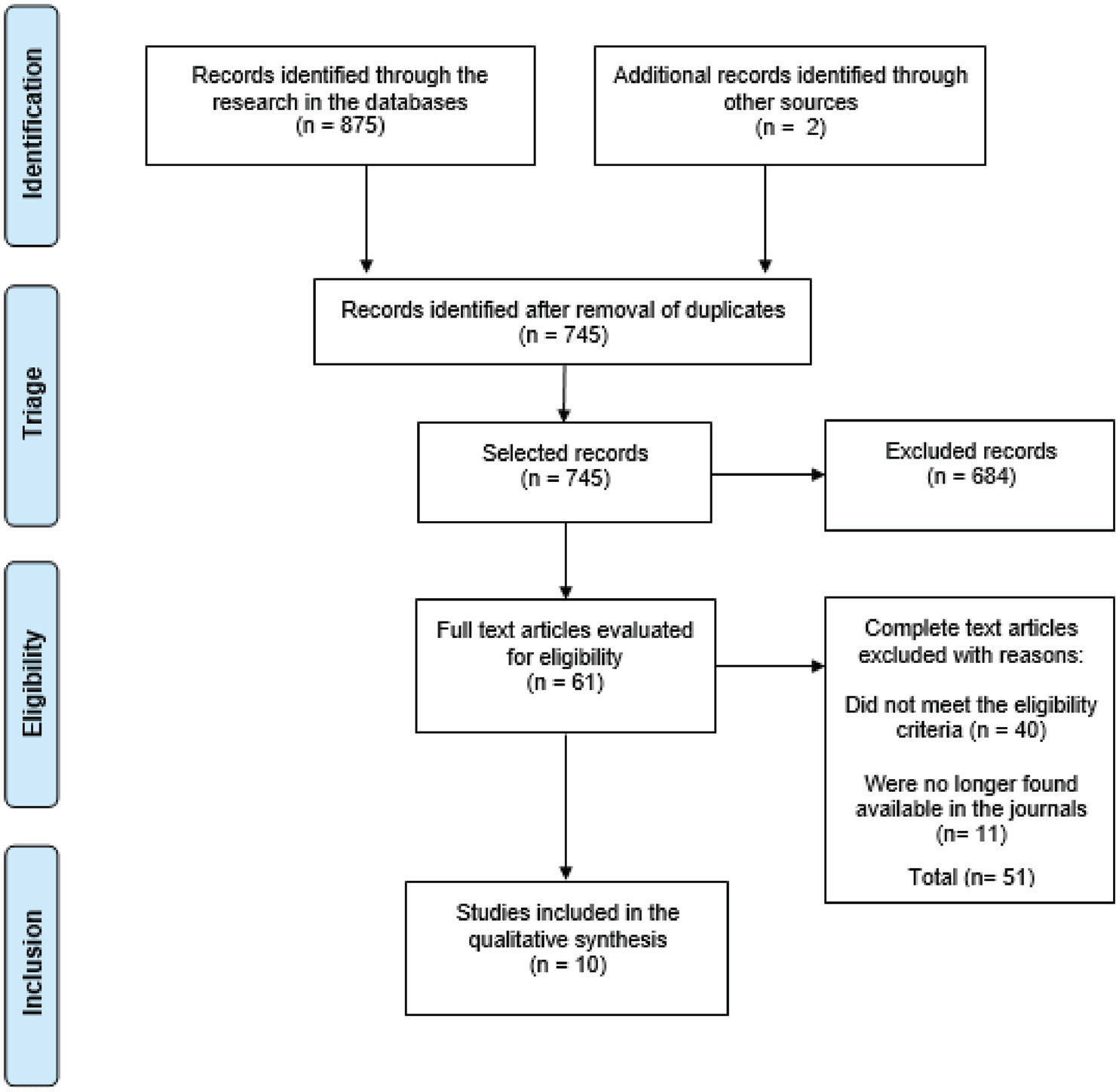
A systematic reviewwas conducted (last updatedMay 2020).Meta-analyses were performed using the inverse-variance for fixed models with summary proportion calculation by Freeman-Tukey double arcsine. Reporting and methodological quality were assessed using the Joanna Briggs Institute tool for prevalence studies.
Our review identified 31 studies, comprising 4,006 participants. All the studies had at least one weakness, mainly due to the use of convenience sampling and small sample size. The overall prevalence of vitamin D deficiency, insufficiency, and both deficiency and insufficiency were 35% (confidence interval, 95%CI: 34-37%), 42% (95%CI: 41-44%), and 72% (95%CI: 71-74%), respectively.
Although the magnitude of the prevalence of inadequate levels of vitamin D is uncertain, the evidence suggests that presence of vitamin D deficiency or insufficiency in women of reproductive age can cause moderate to severe problems.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2021;43(7):522-529
To assess the sexual function and associated factors in postmenopausal women.
This a descriptive, cross-sectional study with 380 women aged 40 to 65 years, users of public health services in 2019. Questionnaires were applied on demographic characteristics, on climacteric symptoms (menopause rating scale) and on sexual function (sexual quotient, female version). Bivariate andmultiple analyses by logistic regression were performed, with adjusted odds ratios (ORad) and 95% confidence intervals (95%CIs).
More than half (243/64%) of the participating women were at risk of sexual dysfunction, with lower scores in the domains of sexual desire and interest, comfort, orgasm, and satisfaction. Women with a partner (ORad 2.07; 95%CI 1.03-4.17) and those who reported sleep problems (ORad 2.72; 95%CI 1.77-4.19), depressed mood (ORad 2.03; 95%CI 1.32-3.10), sexual complaints (ORad 8.16; 95%CI 5.06-13.15), and vaginal dryness (ORad 3.44; 95%CI 2.22-5.32) showed greater chance of sexual dysfunction.
There was a high prevalence of sexual dysfunction, with the influence of conjugality and climacteric symptoms on sexual function.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2021;43(5):403-413
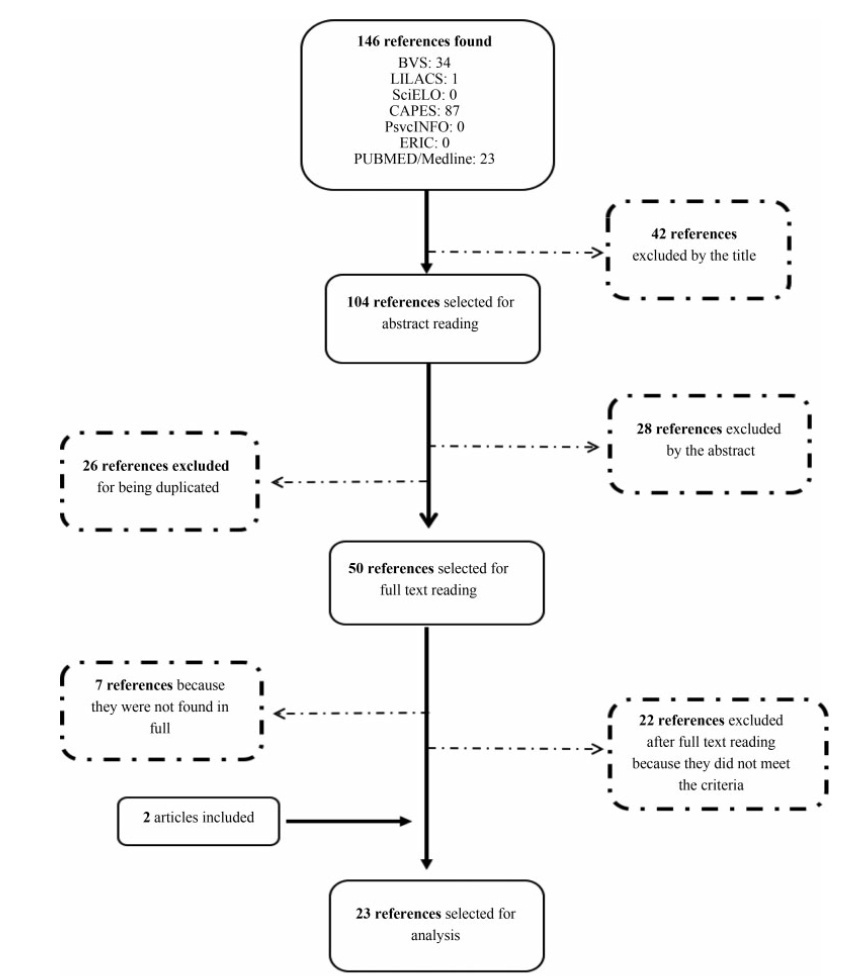
To investigate in the literature the studies on the benefits ofmusic therapy interventions among pregnant women in the prenatal, delivery and postpartum periods.
The search for articles was carried out in the following electronic databases: VHL, LILACS, SciELO, Portal CAPES, PsycINFO, ERIC, PubMed/Medline, and journals specialized in this field: Revista Brasileira de Musicoterapia (“Brazilian Journal of Music Therapy”) and Voices.
Descriptors in Portuguese (musicoterapia, gravidez, gestantes, revisão), English (music therapy, pregnancy, pregnant women, review) and Spanish (musicoterapia, embarazo, mujeres embarazadas, revisión) were used. The search was delimited between January 2009 and June 2019. The process of selection and evaluation of the articles was performed through peer review.
n The following data were extracted: article title, year of publication, journal, author(s), database, country and date of collection, purpose of the study, sample size, type of care, intervention, instruments used, results, and conclusion. The data were organized in chronological order based on the year of publication of thestudy.
In total, 146 articles were identified, and only 23 studies were included in this systematic review. The articles found indicate among their results relaxation, decreased levels of anxiety, psychosocial stress and depression, decreased pain, increase in the maternal bond, improvement in the quality of sleep, control of the fetal heart rate and maternal blood pressure, and decreased intake of drugs in the postoperative period.
Music therapy during the prenatal, delivery and postpartum periods can provide benefits to pregnant women and newborns, thus justifying its importance in this field.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2020;42(4):211-217
To reveal the changes in the quality of life reported by women with Human papillomavirus (HPV)-induced lesions.
This is a cross-sectional, descriptive-exploratory study of a qualitative approach performed from June to August 2016. Semi-structured face-to-face interviews based on five questions on the concept of quality of life were used. The data were submitted to thematic analysis. All ethical aspects have been contemplated.
A total of 20 women aged between 25 and 59 years old were interviewed. From the analysis of the data, the following thematic units emerged: physical and emotional changes, especially complaints of pruritus, discharge and pain, worry, fear, shame and sadness; changes in sexual and affective relationships with decreased libido, dyspareunia and interruption of sexual activity; changes in social relationships resulting in absenteeism at work.
Human papillomavirus infection impairs the quality of life of women as it significantly affects sexual, affective, physical, emotional, and everyday habits. Therefore, HPV infection can lead to exponential changes in the quality of life of women, which can be mitigated by the availability of sources of support such as family, friends and the multi-professional team, helping to improve knowledge and cope with HPV.
Search
Search in:
breast (42) breast cancer (42) breast neoplasms (95) Cesarean section (72) endometriosis (66) infertility (56) Maternal mortality (43) menopause (82) obesity (58) postpartum period (40) pregnancy (225) Pregnancy complications (99) Prenatal care (68) prenatal diagnosis (50) Prevalence (41) Quality of life (51) risk factors (94) ultrasonography (79) urinary incontinence (40) women's health (48)