Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2024;46:e-rbgo17
To determine the prevalence of anxiety, depression and burnout in residents of Gynecology and Obstetrics during COVID-19 pandemic in Brazil and its associated factors.
Cross-sectional study involving all regions of Brazil, through the application of a sociodemographic questionnaire, the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HAD) and the Maslach Burnout Inventory (MBI-HSS) instrument. Multivariate analysis was performed after adjusting the Poisson model.
Among the 719 participating medical residents, screening was positive for anxiety in 75.7% and for depression in 49.8% of cases. Burnout syndrome was evidenced in 41.3% of the physicians studied. Those with depression are more likely to have anxiety (OR 0.797; 95%CI 0.687 - 0.925) and burnout syndrome (OR 0.847 95%CI 0.74 - 0.97). Residents with anxiety (OR 0.805; 95%CI 0.699 - 0.928) and burnout (OR 0.841; 95%CI 0.734 - 0.963) are more likely to have depression.
High prevalence of anxiety, depression and burnout were found in residents of Gynecology and Obstetrics in Brazil, in addition to important correlations between anxiety-depression and depression-burnout.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(9):854-865
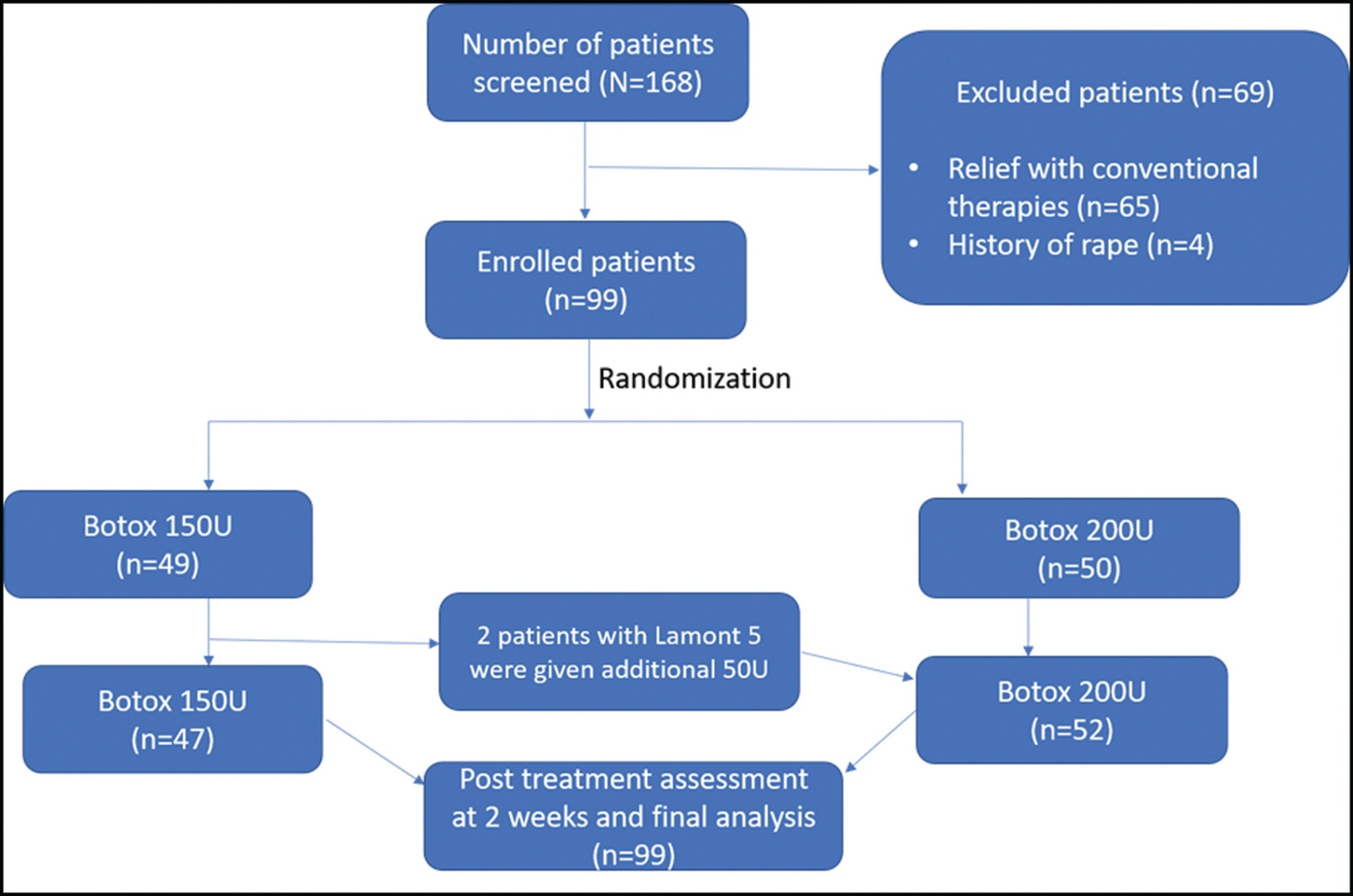
To comparatively evaluate the outcome of treatment with 150 versus 200 units (U) of botulinum toxin in achieving pain-free intercourse and relieving muscle contraction in order to allow gynecological examination.
In this comparative prospective observational study, 99 patients with vaginismus were treated with botulinum toxin injections from September 2016 to August 2021. Diagnosis and grading of vaginismus severity were assessed using a Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI) questionnaire. Under local or general anesthesia, botulinum toxin diluted with preservative-free saline (150 U and 200 U) was injected into, above, and below the right and left bulbospongiosus muscle and the lateral submucosal areas of the introitus and perineal body using an insulin syringe. Patients were recalled after 2 weeks, and the postoperative outcome was recorded using a similar preoperative questionnaire.
Overall, the mean age of patients was 30.2 years. The baseline and clinical characteristics were comparable between the 2 groups (p > 0.05). Significant improvements were seen in the pain and anxiety scores of finger penetration, dilator use, intercourse, and cotton swab in individual groups. The intergroup comparisons between 150 U and 200 U of Botox were not statistically significant (p > 0.05).
Low-dose Botox (150 U) is equally effective as high dose Botox injections (200 U) in vaginismus patients. Therefore, Botox-150 U can be used to treat vaginismus as an alternative to high doses of the same substance.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(2):100-108
In addition to being a medical phenomenon, pandemics affect the individual and society on several levels and lead to disruptions. In the pandemic process, different groups in the population, including pregnant women as a defenseless group, are subjected to psychological threat. The present study aimed to determine the levels of anxiety and depression and related factors in pregnant women during the the coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) pandemic.
The present cross-sectional study was conducted with 269 pregnant women through face-to-face interviews held in Istanbul, Turkey. Regarding the data collection tools, the Cronbach α reliability coefficient was of 0.90 for the Beck Anxiety Inventory, and of 0.85 for the Beck Depression Inventory.
Among the participating pregnant women, 30.5% had mild, 17.5% had moderate, and 5.9% had severe anxiety symptoms, whereas 35.3% had mild, 16.7% had moderate, and 2.2% had severe depression symptoms. We found that those who were concerned about their health had 5.36 times (p=0.04) more risk of developing anxiety, and 4.82 times (p=0.01) more risk of developing depression than those who were not concerned. Those who had a history of psychiatric disease had 3.92 times (p=0.02) more risk of developing anxiety than those without it.
We determined that about half of the pregnant women included in the study had some degree of anxiety and depression during the COVID-19 pandemic. The risk factors for anxiety and depression among the pregnant women were determined as smoking, concerns about health and getting infectedwith the coronavirus, history of psychiatric disease, and undergoing regular antenatal care.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2020;42(11):739-745
To evaluate factors associated with anxiety and the effect of simulation-based training (SBT) on student anxiety, self-confidence and learning satisfaction in relation to pelvic and breast examination.
A longitudinal study was conducted with 4th year medical students at the Universidade José do Rosário Vellano. A 12-item, self-report questionnaire on student anxiety at performing gynecological examinations was applied before and after SBT, with answers being given on a Likert-type scale. After training, the self-confidence levels and satisfaction of the students related to the learning process were also evaluated.
Eighty students with a mean age of 24.1 ± 4.2 years were included in the study. Of these, 62.5% were women. Pre-SBT evaluation showed that students were more anxious at performing a pelvic examination than a breast examination (2.4 ± 1.0 versus 1.7 ± 0.8, respectively; p < 0.001). The primary reason for anxiety regarding both pelvic and breast examination was fear of hurting the patient. SBT significantly reduced student anxiety (2.0 ± 0.8 versus 1.5 ± 0.5, respectively; p < 0.001). The satisfaction and self-confidence of the students were found to be high (6.8 ± 0.3 and 6.0 ± 0.9, respectively), with no difference between genders.
The use of SBT in teaching students to perform pelvic and breast examinations resulted in reduced anxiety and increased self-confidence in a group of medical students of both genders, with high levels of satisfaction in relation to the training.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2020;42(8):486-492
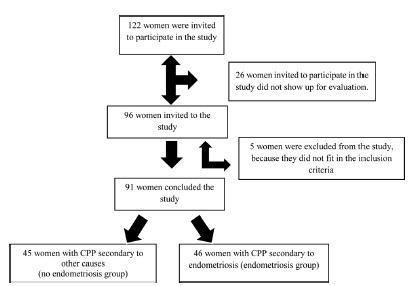
To determine the average body composition (percentage of body fat), the anthropometric markers, and the intensity of clinical pain in women with a clinical diagnosis of chronic pelvic pain (CPP) secondary to endometriosis.
A case-control study performed with 91 women, 46 of whom with CPP secondary to endometriosis and 45 of whom with CPP secondary to other causes. They underwent an evaluation of the anthropometric parameters by means of the body mass index (BMI), the perimeters (waist, abdomen, hip), and the percentage of body fat (%BF), which were assessed on a body composition monitor by bioimpedance; the intensity of the clinical pain was evaluated using the visual analog scale (VAS), and the symptoms of anxiety and depression, using the hospital’s anxiety and depression scale (HAD).
The groups did not differ in terms of mean age, BMI, %BF or regarding the available waist-to-hip ratio (WHR). The mean intensity of the clinical pain by the VAS was of 7.2 ± 2.06 in the group with CPP secondary to endometriosis, and of 5.93 ± 2.64 in the group with CPP secondary to other causes (p = 0.03), revealing significant differences between the groups.
We concluded that, despite the difference in the pain score assessed between the two groups, there was no difference regarding body composition and anthropometry.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2018;40(12):771-778
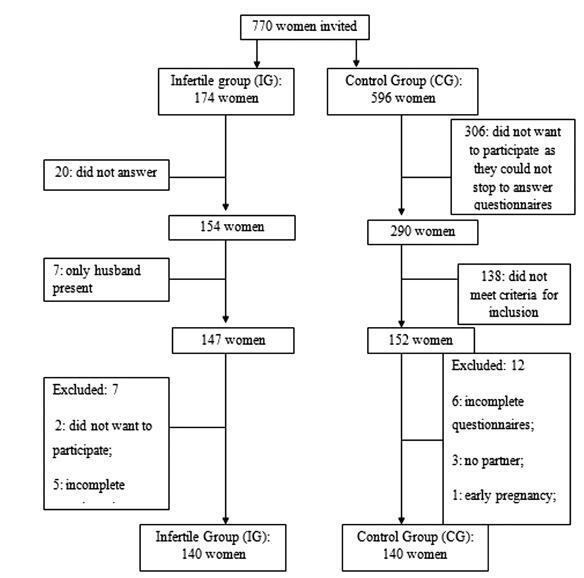
To assess the sexual function, anxiety, and depression of infertile women relative to a control group.
Infertile women (infertile group, IG) of reproductive age were invited to participate in this controlled study. A control group (CG) of women was recruited from the general population of the same city. Sexual function was assessed by the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI), and anxiety and depression were measured by the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS).
A total of 280 women participated in the present study, 140 in the IG and 140 in the CG. The analysis of the FSFI scores showed that 47 women (33.57%) in the IG and 49 women (35%) in the CG had sexual dysfunction (FSFI ≤ 26.55; p = 0.90). Women with anxiety or depression had a greater risk of sexual dysfunction, and sexual dysfunction increased the risk of anxiety and depression. Married women had a lower risk of depression than single women who were living with their partners.
Infertilewomenhadno increased riskof sexual dysfunction relativetocontrols. Anxiety and depression increased the risk of sexual dysfunction in the studied population.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2017;39(10):545-551
To assess the clinical characteristics of subjects with gender dysphoria (GD).
A cross-sectional study of adults with GD. Symptoms of anxiety and depression were measured using the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS). Sociodemographic data, clinical data and life habits were recorded.
Total of 44 subjects participated in the study: 36 (82%) trans women and 8 (18%) trans men. Forty-three (98%) of the GD patients had anxiety (36 [100%] trans women and 7 [87.5%] trans men), and 36 (82%) had depression (29 [80.5%] trans women and 7 [87.5%] trans men). Suicide had been attempted by 32 (73%) subjects. The rates of depression were lower among the subjects living with partners, parents, or other people than among those living alone (p = 0.03), and it was also lower among the subjects who were married compared to those who were dating or single (p = 0.03).
Improving the relationship status may reduce the prevalence of depressive symptoms in GD patients. There was a high rate of attempted suicide in this sample.
Search
Search in:
breast (42) breast cancer (42) breast neoplasms (95) Cesarean section (72) endometriosis (66) infertility (56) Maternal mortality (43) menopause (82) obesity (58) postpartum period (40) pregnancy (225) Pregnancy complications (99) Prenatal care (68) prenatal diagnosis (50) Prevalence (41) Quality of life (51) risk factors (94) ultrasonography (79) urinary incontinence (40) women's health (48)