Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2024;46:e-rbgo19
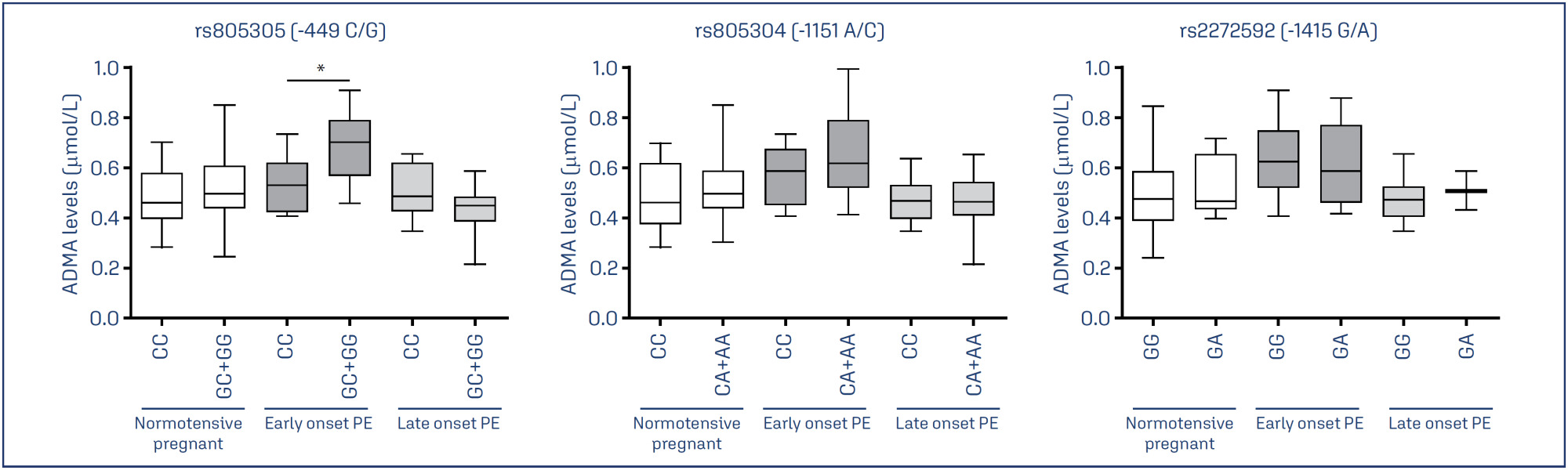
To examine whether the DDAH2 promoter polymorphisms -1415G/A (rs2272592), -1151A/C (rs805304) and -449G/C (rs805305), and their haplotypes, are associated with PE compared with normotensive pregnant women, and whether they affect ADMA levels in these groups.
A total of 208 pregnant women were included in the study and classified as early-onset (N=57) or late-onset PE (N =49), and as normotensive pregnant women (N = 102).
Pregnant with early-onset PE carrying the GC and GG genotypes for the DDAH2 -449G/C polymorphism had increased ADMA levels (P=0.01). No association of DDAH2 polymorphisms with PE in single-locus analysis was found. However, the G-C-G haplotype was associated with the risk for late-onset PE.
It is suggested that DDAH2 polymorphisms could affect ADMA levels in PE, and that DDAH2 haplotypes may affect the risk for PE.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2015;37(11):516-519
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005454
To investigate the frequencies of polymorphic allele and genotypes for the LT-α gene, position +252 (rs909253), in Brazilian women with preeclampsia.
This is a case-control study, in which 30 women with preeclampsia, classified according to the criteria of the National High Blood Pressure Education Program, and 115 women in the control group, with at least two healthy pregnancies, were selected. Peripheral blood was collected, and DNA was extracted, followed by genotyping, using specific primers and restriction analysis. The genotypes obtained were AA, AG and GG. Statistical analysis was performed using the χ2 association test. The Hardy-Weinberg Equilibrium was tested using the Haploview Program.
The results showed no association between genotypes and preeclampsia development (χ2=2.0; p=0.4). When the AG and GG genotypes were grouped according to allele G presence or absence (genotype AA), the data showed that the presence of allele G was not significantly different between cases (women with preeclampsia) and controls (χ2=0.0; p=1.0). The LT-α gene polymorphism, position +252 (rs909253), seems not to be an important candidate for the development of preeclampsia. Other inflammatory genes should be researched, and studies involving gene-environment interactions should be performed, in order to reach a better understanding of the etiology of the preeclampsia.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2011;33(7):158-163
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000700007
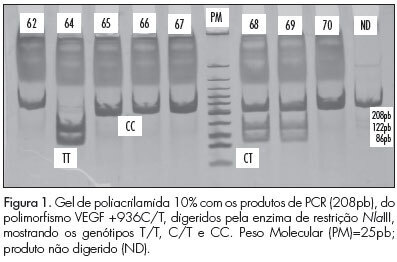
PURPOSE: To identify genetic polymorphisms of endothelial growth factor (VEGF), positions +936C/T and -2578C/A, in women with pre-eclampsia. METHODS: This was a cross-sectional study conducted on 80 women divided into two groups: pre-eclampsia and control. The sample was characterized using a pre-structured interview and data transcribed from the medical records. DNA extraction, amplification of sequences by the Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR) with specific primers and polymorphism analysis of Restriction Fragment Length Polymorphism (RFLP) were performed to identify polymorphisms. The statistical analysis was performedin a descriptive manner and using the ![]() test. The multiple logistic regression model was used to determine the effect of polymorphisms on pre-eclampsia. RESULTS:Ahigher frequency of the T allele of theVEGF +936C/T polymorphism was observedin patients with pre-eclampsia, but with no significant difference. The presence of allele A of the VEGF -2578C/A was significantly higher in the control group. CONCLUSIONS:No significant association was observed between VEGF +936C/Tpolymorphism andpre-eclampsia. For the VEGF -2578C/A polymorphism a significant differencewas observed between thecontrol and pre-eclampsia group, with allele A being the most frequent in the control, suggesting the possibility that carriers of allele A have lower susceptibility to the development of pre-eclampsia.
test. The multiple logistic regression model was used to determine the effect of polymorphisms on pre-eclampsia. RESULTS:Ahigher frequency of the T allele of theVEGF +936C/T polymorphism was observedin patients with pre-eclampsia, but with no significant difference. The presence of allele A of the VEGF -2578C/A was significantly higher in the control group. CONCLUSIONS:No significant association was observed between VEGF +936C/Tpolymorphism andpre-eclampsia. For the VEGF -2578C/A polymorphism a significant differencewas observed between thecontrol and pre-eclampsia group, with allele A being the most frequent in the control, suggesting the possibility that carriers of allele A have lower susceptibility to the development of pre-eclampsia.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2011;33(6):271-275
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000600002
PURPOSE: to investigate the association between gene polymorphism of the progesterone receptor (PROGINS) and the risk of premature birth. METHODS: In this case-control study, 57 women with previous premature delivery (Case Group) and 57 patients with delivery at term in the current pregnancy and no history of preterm delivery (Control Group) were selected. A 10 mL amount of peripheral blood was collected by venipuncture and genomic DNA was extracted followed by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) under specific conditions for this polymorphism and 2% agarose gel electrophoresis. The bands were visualized with an ultraviolet light transilluminator. Genotype and allele PROGINS frequencies were compared between the two groups by the χ2 test, with the level of significance set at value p<0.05. The Odds Ratio (OR) was also used, with 95% confidence intervals. RESULTS: PROGINS genotypic frequencies were 75.4% T1/T1, 22.8% T1/T2 and 1.8% T2/T2 in the Group with Preterm Delivery and 80.7% T1/T1, 19.3% T1/T2 and 0% T2/T2 in the term Delivery Group. There were no differences between groups when genotype and allele frequencies were analyzed: p=0.4 (OR=0.7) and p=0.4 (OR=0.7). CONCLUSIONS: the present study suggests that the presence of PROGINS polymorphism in our population does not constitute a risk factor for premature birth.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2011;33(2):65-69
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000200002
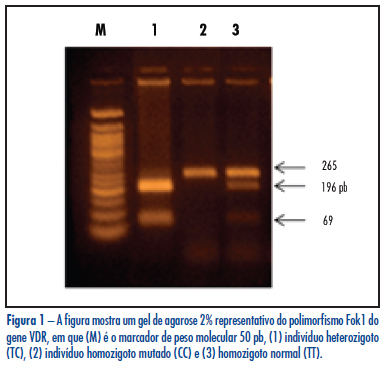
PURPOSE: to evaluate the frequency of VDR gene polymorphism Fok1 in infertile women with endometriosis and Control and its relation to the disease. METHODS: a case-control study that included 147 infertile women with endometriosis and 154 fertile women without endometriosis as Control. Fok1 polymorphism (rs10735810, T2C), which promotes a T/C exchange in exon 2 of the VDR gene, was identified by the polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP), that involves the combination of amplification by PCR and digestion with restriction endonuclease. The χ2 test was used to compare allele and genotype frequencies between groups. All p-values were two-tailed and a p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. RESULTS: the TT, TC and CC genotype frequencies of VDR Fok1 polymorphism were 44.2%, 46.9% and 8.9% in infertile women with endometriosis and 41.6%, 50% and 8.4% in the Control Group. No significant difference was found (p=0.8), even when the patients were subdivided according to the stage of endometriosis (p=0.3 for minimal and mild endometriosis and p=0.2 for moderate and severe endometriosis). Alleles T and C were present, respectively, in 67.6% and 32.3% of infertile women with endometriosis (p=0.8), in 63.5% and 36.5% of women with minimal/mild endometriosis (p=0.5), in 72.5% and 27.5% of women with moderate/severe endometriosis (p=0.2), and in 66.6% and 33.4% of the Control Group. No statistically significant difference was found among any groups and the Control. CONCLUSION: the results suggest that VDR gene polymorphism Fok1 does not confer genetic susceptibility to endometriosis-associated infertility in the Brazilian population.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2011;33(1):37-42
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000100006
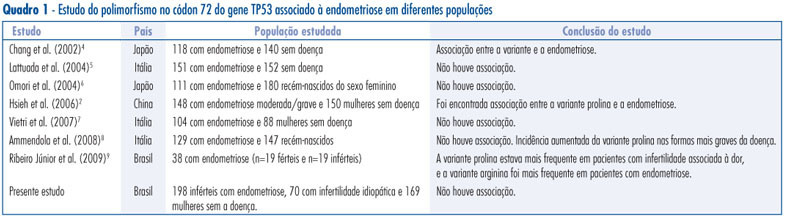
PURPOSE: to evaluate the frequency of TP53 codon 72 polymorphism in infertile women with endometriosis, women with idiopathic infertility, controls and its relation to the disease. METHODS: a case-control study that included 198 infertile women with endometriosis, 70 women with idiopathic infertility and 169 fertile women without endometriosis as control. Detection of TP53 codon 72 gene polymorphism (rs1042522, Arg/C:Pro/G), that promotes a C/G exchange in the coding region of the gene, was performed by real time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), using the TaqMan system of primers, that flank the implicated region and probes labeled with different fluorescent dyes, one for allele C and other for allele G. When two dyes were observed, the patient was considered to be heterozygous CG. In the presence of only one dye, the individual was considered to be homozygous CC or GG. The χ2 test was used to compare allele and genotype frequencies between groups. All p-values were two-tailed and a p-value <0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. RESULTS: we found no statistically significant difference in the distribution of TP53 codon 72 polymorphism genotypes CC, CG or GG (p=0.7) and alleles C or G (p=0.4) between infertile patients with endometriosis and controls (p=0.4), regardless of the stage of the disease. In relation to infertility, no statistically significant difference in the genotype or allele distribution (p=1.0 and p=0.9, respectively) was observed between idiopathic infertile women and controls. Considering the dominant inheritance model, again, no statistically significant difference was found even in the endometriosis (p=0.5) or the idiopathic infertility group (p=0.9) when compared to controls. Regarding the recessive inheritance model no statistically significant difference was found, with p=0.6 and p=1.0, respectively, for the endometriosis and idiopathic infertility groups. CONCLUSION: the results suggest that the TP53 codon 72 polymorphism does not confer genetic susceptibility to endometriosis and/or infertility in the Brazilian population, not even the severe form of the disease.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2010;32(7):327-333
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000700004
PURPOSE: to evaluate the clinical and epidemiological risk factors for endometrial cancer in postmenopausal women with endometrial polyps, as well as the genetic polymorphism of the progesterone receptor (PROGINS). METHODS: a case-control study was designed with 160 postmenopausal women with endometrial polyps, compared to a normal Control Group of 400 postmenopausal women. The genotyping of PROGINS polymorphism was determined by the polymerase chain reaction. Clinical and epidemiological data were compared between benign endometrial polyps and 118 of the control subjects. Variables were also compared with regard to benign and malignant endometrial polyps. RESULTS: comparison of the epidemiological variables between groups showed a significant difference for age, ethnicity, time since menopause, parity, tamoxifen use, hypertension and breast cancer, all of them more prevalent in the polyp group. After adjustment for age, statistical significance remained only for parity (OR=1.1), hypertension (OR=2.2) and breast cancer (OR=14.4). There were six cases of malignant polyps (3.7%). The frequency of bleeding was 23.4% for benign polyps and 100% for malignant polyps, with large polyps being detected in 54.6% of the benign cases and in 100 of the malignnat ones. The frequency of arterial hypertension was 54.5% for benign polyps and 83.3% for the malignant ones. The frequency of PROGINS T1/T1, T1/T2 and T2/T2 polymorphism was 79.9%, 19.5% and 0.6%, respectively, for the polyp group, and 78.8%, 20.8% and 0.5% for the Control Group. CONCLUSIONS: elderly age, hypertension, and breast cancer were significantly associated with endometrial polyps. The presence of PROGINS polymorphism was not significantly associated with endometrial polyps. The incidence of malignant polyps was low and strongly associated with bleeding, large-sized polyp and arterial hypertension.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2010;32(5):229-233
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000500005
PURPOSE: to assess a possible association between polymorphism of the progesterone receptor gene (PROGINS) and recurrent spontaneous abortion (RSA). METHODS: in this case-control study, 85 women with at least three previous spontaneous abortions without an identifiable cause (RSA Group) and 157 women with at least two previous term pregnancies without pathologies and no previous miscarriage (Control Group) were selected. An amount of 10 mL of peripheral blood was collected by venipuncture and genomic DNA was extracted by the DTAB/CTAB method, followed by the polymerase chain reaction (PCR) under specific conditions for this polymorphism and by amplification by 2% agarose gel electrophoresis. The bands were visualized with an ultraviolet light transilluminator and the gels were photographed. Differences in the PROGINS genotype and allele frequencies between groups were analyzed by the χ2 test, with the level of significance set at p<0.05. The Odds Ratio (OR) was also used, with 95% confidence intervals 95%CI. RESULTS: PROGINS genotypic frequencies were 72.3% T1T1 and 27.7% T1T2 for the RSA group and 764% T1T1, 22.3% T1T2 and 1.3% T2T2 for the control group. There were no differecnes between groups when the genotype and allele frequencies were analyzed: respectively p=0.48 (OR: 0.8) and p=0.65 (OR: 0.9). CONCLUSIONS: our results suggest that PROGINS polymorphism is not associated with RSA.
Search
Search in:
breast (42) breast cancer (42) breast neoplasms (95) Cesarean section (72) endometriosis (66) infertility (56) Maternal mortality (43) menopause (82) obesity (58) postpartum period (40) pregnancy (225) Pregnancy complications (99) Prenatal care (68) prenatal diagnosis (50) Prevalence (41) Quality of life (51) risk factors (94) ultrasonography (79) urinary incontinence (40) women's health (48)