-
Original Article
Gastrin-releasing peptide receptor: a promising new biomarker to identify cervical precursor lesions and cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo4
03-18-2025
Summary
Original ArticleGastrin-releasing peptide receptor: a promising new biomarker to identify cervical precursor lesions and cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo4
03-18-2025Views68Abstract
Objective:
This study aimed to verify the relation between gastrin-releasing peptide receptor (GRPR), oncogenic Human Papillomavirus (HPV) and cervical lesions severity.
Methods:
GRPR mRNA levels were evaluated in cervical cancer-derived cell lines and in primary keratinocytes expressing HPV16 oncogenes by RT-PCR. GRPR protein expression was assessed by immunohistochemistry in organotypic cell cultures derived from keratinocytes transduced with HPV16 oncogenes and in 208 cervical samples, including 59 non-neoplastic tissue, 28 cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 3 (CIN3), 44 squamous cell carcinomas (SCC) and 77 adenocarcinomas (ADC). Generic primers (GP5+/GP6+) were used to identify HPV infection in tissue samples. Experiments involving cell lines were analyzed through non-parametric tests (Kruskal Wallis), and Fisher's Exact Test for human tissues samples. All statistical tests were considered significant at p <0.05. Immunohistochemical evaluation was conducted independently and blindly by two observers (AD- LO). Any discordant findings were resolved through discussion to reach a consensus score.
Results:
GRPR mRNA levels were not increased in cells expressing HPV16 or HPV18 oncogenes. However, at the protein level, GRPR was upregulated in organotypic cell cultures containing HPV oncogenes. Besides, it was identified an association between GRPR expression and cervical lesion severity (p < 0.0001). The detection rate of high-risk HPV DNA was directly correlated with cervical disease. Nonetheless, HPV infection was not directly associated with GRPR in cervical samples.
Conclusion:
GRPR expression is highly predictive of cervical lesion severity, irrespective of HPV infection and might contribute to improving patient's therapeutic management as well as being used a marker of disease progression.
Key-words AdenocarcinomaCarcinoma, squamous cellGastrin-releasing peptide receptorHuman papillomavirusOncogenesPapillomavirus infectionsUterine cervical dysplasiaUterine cervical neoplasmsSee more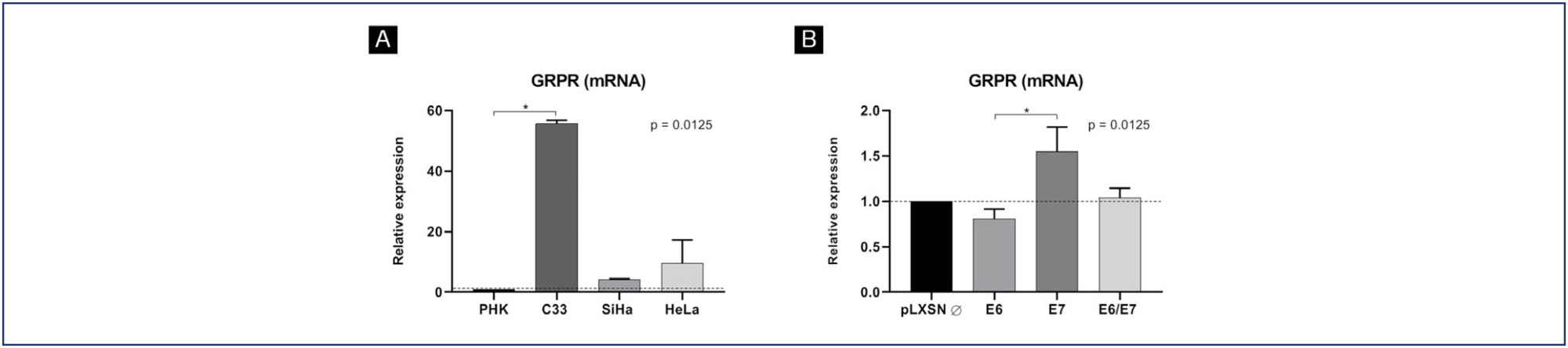
-
Original Article
A New Brazilian Device for Cervical Cancer Screening: Acceptability and Accuracy of Self-sampling
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(5):235-241
08-07-2023
Summary
Original ArticleA New Brazilian Device for Cervical Cancer Screening: Acceptability and Accuracy of Self-sampling
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(5):235-241
08-07-2023Views159Abstract
Objective
To evaluate the accuracy and patient acceptability toward self-sampling using a new device - SelfCervix® - for detecting HPV-DNA.
Methods
A total of 73 women aged 25–65 who underwent regular cervical cancer screening from March to October 2016 were included. Women performed self-sampling followed by a physician-sampling, and the samples were analyzed for HPV-DNA. After that, patients were surveyed about their acceptability of self-sampling.
Results
HPV-DNA detection rate of self-sampling presented high accuracy and was similar to physician-collection. Sixty-four (87.7%) patients answered the acceptability survey. Most patients (89%) considered the self-sampling comfortable, and 82.5% preferred self-sampling to physician-sampling. The reasons cited were time-saving and convenience. Fifty-one (79.7%) reported that they would recommend self-sampling.
Conclusion
Self-sampling using the new Brazilian device SelfCervix® is not inferior in HPV-DNA detection rate compared with physician-collection, and patients are supportive of the method. Therefore, it might be an option to reach under-screened populations in Brazil.
Key-words Cytologydiagnostic screening programsearly detection of cancerHuman papillomavirusUterine cervical neoplasmsSee more -
Original Article
Cytology-based Screening for Anal Intraepithelial Neoplasia in Immunocompetent Brazilian Women with a History of High-Grade Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia or Cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(7):678-685
08-29-2022
Summary
Original ArticleCytology-based Screening for Anal Intraepithelial Neoplasia in Immunocompetent Brazilian Women with a History of High-Grade Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia or Cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(7):678-685
08-29-2022Views107See moreAbstract
Objective
To determine the prevalence and possible variables associated with anal intraepithelial neoplasia and anal cancer in immunocompetent women with high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia.
Methods
A cross-sectional study involving immunocompetent women with a histological diagnosis of high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer, conducted between January 2016 and September 2020. All women underwent anal cytology and answered a questionnaire on characterization and potential risk factors. Women with altered cytology were submitted to anoscopy and biopsy.
Results
A total of 69 women were included in the study. Of these, 7 (10.1%) had abnormal anal cytology results: (high-grade lesion, atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance, and atypical squamous cells, cannot exclude high-grade lesions: 28,5% each; low grade lesion: 14,3%). Of the anoscopies, 3 (42.8%) showed alterations. Of the 2 (28,5% of all abnormal cytology results) biopsies performed, only 1 showed low-grade anal intraepithelial neoplasia. The average number of pregnancies, vaginal deliveries, and abortions was associated with abnormal anal cytology. However, the highest mean regarding the cesarean sections was associated with normal cytology.
Conclusion
The prevalence of anal intraepithelial neoplasia was compatible with data from recent studies, especially those conducted in Brazil. Opportunistic screening for anal intraepithelial neoplasia in this high-risk population should be considered. Anal cytology is suitable for this purpose, due to its low cost and feasibility in public health services.
-
Original Article
School-based HPV Vaccination: The Challenges in a Brazilian Initiative
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(12):926-931
01-24-2021
Summary
Original ArticleSchool-based HPV Vaccination: The Challenges in a Brazilian Initiative
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(12):926-931
01-24-2021Views204See moreAbstract
Objective
The present study assesses the implementation and the impact after 2 years of a school-based human papillomavirus (HPV) vaccination program in a Brazilian city.
Methods
A prospective study assessing the implementation of the program, offering quadrivalent HPV vaccine in two annual doses to girls and boys aged from 9 to 10 years old. The program was started in the city of Indaiatuba, state of São Paulo, Brazil, in 2018, and had authorization from the National Immunization Program. The number of HPV vaccine first doses applied and the coverage in 2018 was calculated and compared to the year 2017. There were described events that have influenced the results.
Results
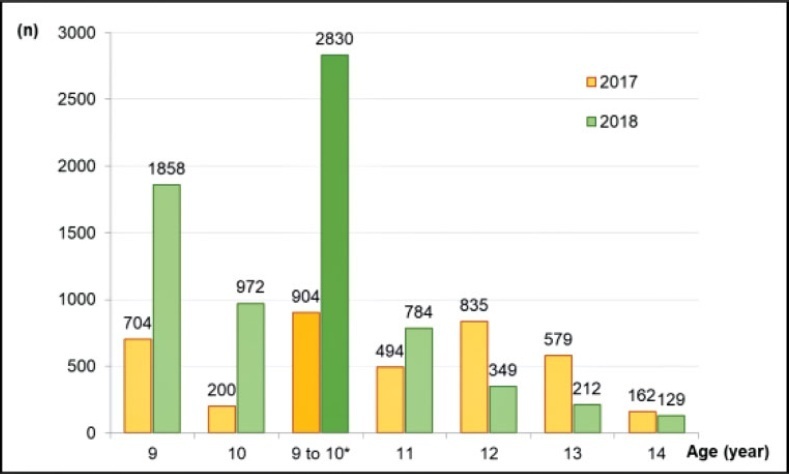
The program invited 4,878 children through schools (87.1% of the target population), and 7.5% refused vaccination. Several concurrent events required or competed for health professionals of the vaccination teams. The coverage of the first dose (between 9 and 10 years old) was 16.1% in 2017 and increased to 50.5% in 2018 (p < 0.0001). The first dose in all ages increased 78% in 2018 compared with 2017 (6,636/3,733). Competing demands over the program continued in 2019, and the first dose coverage dropped (26.9%). For 2020, a municipal law instituted school-based vaccination and the creation of dedicated teams for vaccination, and these strategies are waiting to be tested.
Conclusion
School-based annual HPV vaccination in children between 9 and 10 years old was feasible and increased vaccination coverage, regardless of gender, although the program was vulnerable to competing events.
-
Original Article
High-risk Human Papillomavirus Testing for Triage of Women with Previous Cytological Abnormalities from the Vale do Ribeira Region
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(6):340-348
07-17-2020
Summary
Original ArticleHigh-risk Human Papillomavirus Testing for Triage of Women with Previous Cytological Abnormalities from the Vale do Ribeira Region
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(6):340-348
07-17-2020Views130See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the performance of the hybrid capture 2 (HC2) high-risk papillomavirus (hrHPV) assay and cytological test in women with previous abnormalities, to detect cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2 or worse (≥ CIN 2).
Methods
A cytological test and HC2 (Qiagen, Gaithersburg, Maryland, EUA) for hrHPV were conducted in 359 liquid-based (Sure Path, Becton Dickinson, TriPath Imaging, Burlington, NC, USA) samples collected from women from the Vale do Ribeira Region, during July 2013 and September 2015 with previous cytology classified as atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASC-US), low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL), atypical squamous cells, cannot exclude high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (ASC-H), and atypical glandular cells (AGC). The histopathological examination was conducted in 179 women. The performance evaluations were calculated using the “exact” Clopper-Pearson 95% confidence interval (CI) test by MEDCALC (Medcalc Software Ltd, Ostend, Belgium).
Results
The ≥ CIN 2 frequency was 11.7% (21/179). The HC2 for hrHPV and repeat cytology to detect ≥ CIN 2 obtained, respectively, a sensitivity of 90.5% (95% CI = 69.6-98.8) and 90.5%, (95%CI = 69.6-98.8), a specificity of 65.8% (95% CI = 57.9-73.2) and 43.7% (95%CI = 35.8-51.8), a positive predictive value of 26.0% (95% CI = 21.4-31.3) and 17.6%, (95%CI = 14.9-20.6), and a negative predictive value of 98.1% (95%CI = 93.3-99.5) and 97.2% (95% CI = 90.1-99.2).
Conclusion
Hybrid capture 2 for hrHPV improves the performance of the detection of ≥ CIN 2, without compromising sensitivity, and provides a greater safety margin to return to the triennial screening of women undergoing follow-up due to previous abnormalities, without underlying ≥ CIN 2.
-
Original Articles
Influence of Gender and Undergraduate Course on the Knowledge about HPV and HPV Vaccine, and Vaccination Rate among Students of a Public University
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(2):96-105
04-17-2020
Summary
Original ArticlesInfluence of Gender and Undergraduate Course on the Knowledge about HPV and HPV Vaccine, and Vaccination Rate among Students of a Public University
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(2):96-105
04-17-2020Views168See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the knowledge related to human papillomavirus (HPV) infection and the rate of HPV vaccination among undergraduate freshmen and senior students of medicine, pharmacy, speech therapy, nursing and physical education in a Brazilian university.
Methods
A questionnaire concerning sociodemographic aspects, sexual background, and knowledge about HPV and its vaccine was filled out by 492 students. Three months later, a second questionnaire, concerning the new rate of vaccination, was applied to 233 students.
Results
Among the 290 women who answered the first questionnaire, 47% of the freshmen and 13% of the seniors stated they were not sexually active, as well as 11% of the 202 freshman and senior male students. Although the knowledge about HPV was higher among women, they reported a lower use of condoms. More than 83% of the women and 66% of the men knew that HPV can cause cervical cancer, but less than 30% of the students knew that HPV can cause vulvar, anal, penile and oropharyngeal cancer. Less than half of the students knew that HPV causes genital, anal and oropharyngeal warts. Comparing the students, the seniors had more knowledge of the fact that HPV is sexually transmitted, and that HPV infection can be asymptomatic. The rate of vaccination was of 26% for women, and of 8% for men, and it increased to 52% and 27% respectively among the 233 students evaluated in the second questionnaire.
Conclusion
As almost half of freshman women declared being sexually inactive, the investment in public health information programs and easier access to the HPV vaccine seem to be a useful strategy for undergraduate students.
-
Original Article
Estimation of the Costs of Invasive Cervical Cancer Treatment in Brazil: A Micro-Costing Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(6):387-393
07-22-2019
Summary
Original ArticleEstimation of the Costs of Invasive Cervical Cancer Treatment in Brazil: A Micro-Costing Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(6):387-393
07-22-2019Views119See moreAbstract
Objective
Themain objective of the present study was to estimate the annual treatment costs of invasive cervical cancer (ICC) per patient at an oncology center in Brazil from a societal perspective by considering direct medical, direct nonmedical, and indirect costs.
Methods
A cost analysis descriptive study, in which direct medical, direct nonmedical, and indirect costs were collected using a microcosting approach, was conducted between May 2014 and July 2016 from a societal perspective. The study population consisted of women diagnosed with ICC admitted to a tertiary hospital in Recife, state of Pernambuco, Brazil. The annual cost per patient was estimated in terms of the value of American Dollars (US$) in 2016.
Results
From a societal perspective, the annual ICC treatment cost per patient was US $ 2,219.73. Direct medical costs were responsible for 81.2% of the total value, of which radiotherapy and outpatient chemotherapy had the largest share. Under the base-case assumption, the estimated cost to the national budget of a year of ICC treatment in the Brazilian population was US$ 25,954,195.04.
Conclusion
We found a high economic impact of health care systems treating ICC in a poor region of Brazil. These estimates could be applicable to further evaluations of the cost-effectiveness of preventing and treating ICC.
-
Original Article
Knowledge of Pregnant Adolescents about Human Papillomavirus
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(5):291-297
06-27-2019
Summary
Original ArticleKnowledge of Pregnant Adolescents about Human Papillomavirus
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(5):291-297
06-27-2019Views128See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the level of information possessed by pregnant adolescents regarding the human papillomavirus (HPV).
Methods
Descriptive study developed in the adolescent prenatal outpatient clinic of a tertiary hospital fromthe state of São Paulo, Brazil. Data were collected between June and December 2017 following approval from the ethics and research committee (CAAE: 1.887.892/2017). Pregnant adolescents, ≤18 years old, who attended the abovementioned outpatient section, composed the sample. Those diagnosed with a psychiatric disorder and those with hearing or cognitive disabilities were excluded. After acceptance to participate in the present study, the pregnant adolescents signed an Informed Consent Form. Regarding the statistical analysis, the chi-squared test and the Fisher exact test were used.
Results
Regarding the knowledge about HPV, 123 (80.92%) of the participants had already heard about the subject; for 77 (50.66%), their schools had been the source of the information; 101 (66.45%) did not know how they could be infected by the virus. Age variation did not influence their knowledge on how to prevent themselves from HPV (p = 0.2562). The variable vaccine is associated with HPV prevention (p < 0.0001).
Conclusion
The pregnant adolescents composing the sample have shown to have knowledge about HPV. However, they do not prevent themselves from it appropriately, given that little more than half of the sample was vaccinated, had not reported an understanding that the use of preservatives and vaccination are effective means of prevention, and did not correlate HPV with uterine cervical cancer.


