Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2023;45(12):790-795
To compare cytological and histological results from women > 64 years old who followed the Brazilian national cervical cancer screening guidelines with those who did not.
The present observational retrospective study analyzed 207 abnormal cervical smear results from women > 64 years old in a mid-sized city in Brazil over 14 years. All results were reported according to the Bethesda System. The women were divided into those who followed the screening guidelines and those who did not.
Atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance and low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion cytology results were found in 128 (62.2%) cases. Of these, 112 (87.5%) had repeated cytology with positive results. The other 79 (38.1%) with abnormal results should have been referred to colposcopy and biopsy. Out of 41 (51.9%) biopsied women, 23 (29.1%) had a confirmed diagnosis of neoplasia or precursor lesion. In contrast, among the 78 (37.7%) biopsied patients, 40 (51.3%) followed the guideline recommendations, with 9 (22.5%) positive biopsies. Of the 38 (48.7%) women who did not follow the guidelines, there were 24 (63.1%) positive results. Women who did not follow the guidelines demonstrated higher chances of cancer and precursor lesions (odds ratio [OR]: 5.904; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 2.188–15.932; p = 0.0002).
Women > 64 years old who did not follow the national screening protocol showed significant differences in the frequency of abnormal results and severity of diagnosis compared with those who followed the protocol.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2022;44(1):40-46
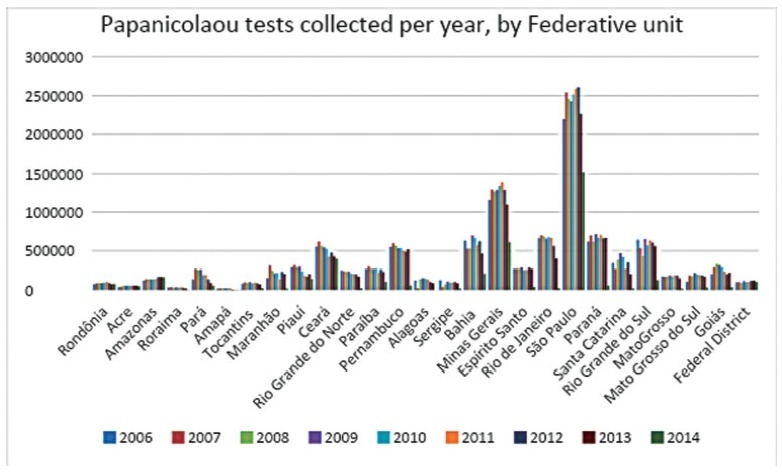
To analyze the quantity of cervical smears, also designated Papanicolaou tests, between 2006 and 2015 in all the Federal units of Brazil, as well as to verify the quantity of exams collected outside the recommended age range and the economic impact of such excess.
The data was collected from the Ministry of Health’s database called Sistema de Informação do Câncer do Colo de Útero (SISCOLO), which contains all the test results collected nationwide by the Unified Health System (SUS, in the Portuguese acronym). From that, the number of exams and the age range of thewomen who underwent them were analyzed; besides, these numbers were stratified according to the state of where the exam was performed. The quantity of exams collected outside the recommended age range was verified, and, so, the economic impact generated was noted.
Between 2006and2015, 87,425,549Papanicolaoutestswere collected in Brazil. Of these, 20,215,052 testswere collected outside the age range recommended by the Brazilian Ministry of Health; this number corresponded to 23.12% of all exams. From such data, considering that each Pap smear collected by SUS generates a cost of BRL 7.30 to the government, according to the information in the Tabela SUS dated September 2018, there was a total charge of BRL 147,569,880 for tests collected outside the protocol.
In Brazil, according to the Ministry of Health’s protocol about the recommended practices on collecting Pap smears, whose newest edition dates of 2016, it is recommended that Pap smears are collected inwomen from a specific age range, inwhom the potential diagnosing advantages overcome the onus of overdiagnosis or of a lesion with great regression potential. However, such protocols have not been correctly followed, promoting more than 20 million tests in excess, and an exorbitant cost for the Brazilian public health system. It is relevant to take measures to correctly use the official protocol, reducing the patients risks, as well as the economic impact for SUS.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2020;42(6):340-348
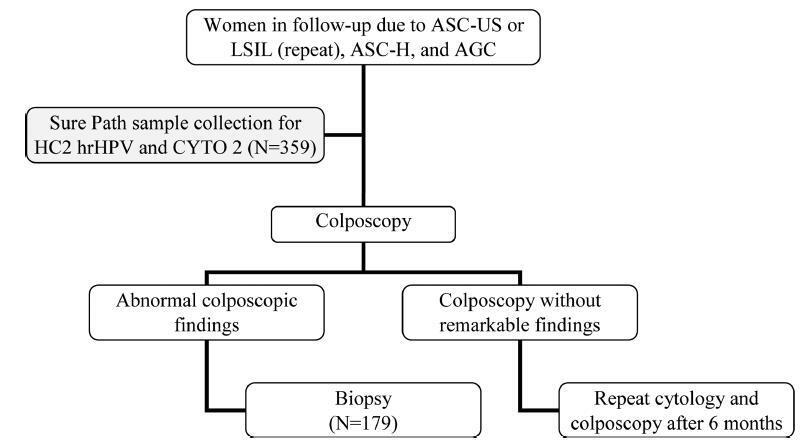
To evaluate the performance of the hybrid capture 2 (HC2) high-risk papillomavirus (hrHPV) assay and cytological test in women with previous abnormalities, to detect cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2 or worse (≥ CIN 2).
A cytological test and HC2 (Qiagen, Gaithersburg, Maryland, EUA) for hrHPV were conducted in 359 liquid-based (Sure Path, Becton Dickinson, TriPath Imaging, Burlington, NC, USA) samples collected from women from the Vale do Ribeira Region, during July 2013 and September 2015 with previous cytology classified as atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASC-US), low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL), atypical squamous cells, cannot exclude high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (ASC-H), and atypical glandular cells (AGC). The histopathological examination was conducted in 179 women. The performance evaluations were calculated using the “exact” Clopper-Pearson 95% confidence interval (CI) test by MEDCALC (Medcalc Software Ltd, Ostend, Belgium).
The ≥ CIN 2 frequency was 11.7% (21/179). The HC2 for hrHPV and repeat cytology to detect ≥ CIN 2 obtained, respectively, a sensitivity of 90.5% (95% CI = 69.6-98.8) and 90.5%, (95%CI = 69.6-98.8), a specificity of 65.8% (95% CI = 57.9-73.2) and 43.7% (95%CI = 35.8-51.8), a positive predictive value of 26.0% (95% CI = 21.4-31.3) and 17.6%, (95%CI = 14.9-20.6), and a negative predictive value of 98.1% (95%CI = 93.3-99.5) and 97.2% (95% CI = 90.1-99.2).
Hybrid capture 2 for hrHPV improves the performance of the detection of ≥ CIN 2, without compromising sensitivity, and provides a greater safety margin to return to the triennial screening of women undergoing follow-up due to previous abnormalities, without underlying ≥ CIN 2.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2018;40(7):410-416
To estimate the cytological and colposcopic performances for the diagnosis of cervical neoplasias.
Cross-sectional retrospective study with data from patients’ charts. The participants underwent colposcopy, guided biopsies, and excision when needed. The cytological and colposcopic categorization followed the Bethesda System and the international colposcopic terminologies. The cytology and colposcopy performances were evaluated by sensitivity (SE), specificity (SP), positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) analyses with 95% confidence interval (95% CI).
From 1,571 participants, a total of 1,154 (73.4%) were diagnosed with cervical squamous intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2 or worse (CIN 2+), 114 (7.2%) with adenocarcinoma in situ or worse (AIS+), 615 (39.2%) presented atypical squamous cells, cannot exclude high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion or worse (ASC-H+) cytology, and 934 (59.4%) presented major or suspicious for invasion colposcopic abnormalities. The SE, SP, PPV, and NPV of ASC-H+ for diagnoses of CIN 2+ and AIS+ were, respectively: 44% (95% CI: 41-47) and 72% (95% CI: 67-76), 79% (95% CI: 77-81) and 79% (95% CI: 75-83), 88% (95% CI: 87-90) and 55% (95% CI: 50-60), and 28% (95% CI: 26-31) and 88% (95% CI: 85-91). The SE, SP, PPV, and NPV of major or suspicious for invasion colposcopic abnormalities for diagnoses of CIN 2+ and AIS+were, respectively: 62% (95% CI: 60-65) and 86% (95% CI: 83-89), 59% (95% CI: 57-62) and 59% (95% CI: 55-64), 85% (95% CI: 83-87) and 44% (95% CI: 40-49), and 29% (95% CI: 27-32) and 92% (95% CI: 89-94).
The SE analyses results of ASC-H+ and major or suspicious for invasion colposcopic abnormalities were higher for diagnoses of glandular neoplasias. These results confirm the role of cytology in identifying women at risk who will have their final diagnoses settled by colposcopy and histology.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2018;40(3):121-126
To assess the management chosen by gynecologists after atypical squamous cells (ASCs) cytology results, and to evaluate the outcomes of these cases in Brazilian women.
A prospective observational study evaluated the initial management offered by the gynecologist in the case of 2,458 ASCs cytology results collected between January of 2010 and July of 2016. The outcomes of the cytology, high-risk human papilloma virus (HR-HPV) test and histology were compared in two subgroups: atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASC-US) and atypical squamous cells-cannot exclude high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (ASC-H).
In many cases of ASC-US (36.97%) and ASC-H (40.50%), no clinical actions were taken. Cytology was the most frequent follow-up chosen, including for cases of ASC-H, which goes against the conduct recommended in the national guideline. In women over 30 years of age, the period of time elapsed between an ASC-US result and a new cytology was in 13.03 months, in disagreement with the national guideline recommendations (p< 0.0001). Negative for intraepithelial lesions or malignancy (NILM) cytologic (p = 0.0026) and histologic (p = 0.0017) results in the follow-up were associated with prior ASC-US, while negative results for ASC-H were cytologically (p< 0.0001) and histologically associated with high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) (p< 0.0001). Two invasive cervical carcinomas (ICCs) were found in the follow-up for ASC-H, and there was a statistically significant association (p = 0.0341). A positive HR-HPV test was associated with ASC-H (p = 0.0075).
The data suggest that even for a population of Brazilian women assisted at private clinics, the national guidelines recommendations for ASCs results are not followed.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2017;39(9):480-487
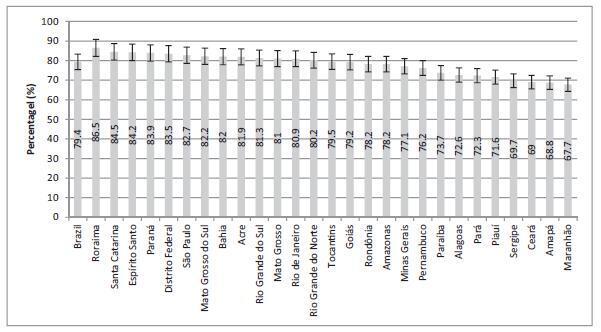
To evaluate the coverage of the Papanicolaou test in Brazil and the associated factors.
Cross-sectional study based on data from the Brazilian Health Survey 2013 comprising the proportion of 25- to 64-year-old women who had undergone a Papanicolaou test within the previous 3 years, categorized by sociodemographic variables and access to healthcare services.
The screening coverage in Brazil was of 79.4% (95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 78.4-80.3), showing significant differences between the different states of the country, with the highest rate in the state of Roraima (86.5; 95%CI: 83.5-89.4), and the lowestone in the state ofMaranhão (67.7; 95%CI: 61.3-74.0).Undergoing the test was significantlymore frequent amongmarriedwomen (83.6%; 95%CI: 82.4-84.8), those with higher educational levels (88.7%; 95%CI: 87.0-90.5), of white ethnicity (82.6%; 95%CI: 81.3-83.9) and who reside in urban areas (80.1%; 95%CI: 79.1-81.2). Those who had undergone the test more than three years prior to the survey and the ones who had never undergone it were associated with a lower level of education, being of black or brown ethnicity, single or divorced, and rural dwellers.
The coverage of cervical cancer screening in Brazil is below the recommended rate and presents regional and sociodemographic disparities.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2015;37(8):381-387
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005393
To evaluate the waiting times before obtaining the first colposcopic examination for women with abnormal Papanicolaou smears.
Retrospective cohort study conducted on patients who required a colposcopic examination to clarify an abnormal pap test, between 2002 January and 2008 August, in a metropolitan region of Brazil. The waiting times were defined as: Total Waiting Time (interval between the date of the pap test result and the date of the first colposcopic examination); Partial A Waiting Time (interval between the date of the pap test result and the date of referral); Partial B Waiting Time (interval between the date of referral and the date of the first colposcopic examination). Means, medians, relative and absolute frequencies were calculated. The Kruskal-Wallis test and Pearson's chi-square test were used to determine statistical significance.
A total of 1,544 women with mean of age of 34 years (SD=12.6 years) were analyzed. Most of them had access to colposcopic examination within 30 days (65.8%) or 60 days (92.8%) from referral. Mean Total Waiting Time, Partial A Waiting Time, and Partial B Waiting Time were 94.5 days (SD=96.8 days), 67.8 days (SD=95.3 days) and 29.2 days (SD=35.1 days), respectively.
A large part of the women studied had access to colposcopic examination within 60 days after referral, but Total waiting time was long. Measures to reduce the waiting time for obtaining the first colposcopic examination can help to improve the quality of care in the context of cervical cancer control in the region, and ought to be addressed at the phase between the date of the pap test results and the date of referral to the teaching hospital.
Summary
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2015;37(5):229-232
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320150005295
To compare the frequency of an ASCUS Pap Smear result in pregnant and
non-pregnant women, stratified by age group.
We analyzed the results of 1,336,180 cytopathologyc exams of Pap smears performed
between 2000 and 2009 (ten years) with the purpose of screening for cervical
carcinoma. Comparisons were made between pregnant and non-pregnant women, and the
sample was stratified into three age groups (20-24, 25-29 and 30-34 years). The
χ2 test was used and the magnitude of association was determined by
the by Odds Ratio (OR) with the 95% confidence interval (95%CI).
A Total of 447,489 samples were excluded on the basis of the criteria adopted,
for a total final sample of 37,137 pregnant women and 851,554 non-pregnant women.
An ASCUS result was detected in 1.2% of cases, with a significant difference
between pregnant and non-pregnant women in the age groups of 20-24 years (OR=0.85;
95%CI 0.75-0.97) and 25-29 years (OR=0.78; 95%CI 0.63-0.96). There was no
difference in the group between 30-34 years (OR=0.76; 95%CI 0.57-1.03).
This study suggested that non-pregnant women have a higher frequency of ASCUS,
most evident in the age group of 20 to 29 years. The collection of cervical cancer
screening should not be a compulsory part of the prenatal routine.
Search
Search in:
breast (42) breast cancer (42) breast neoplasms (95) Cesarean section (72) endometriosis (66) infertility (56) Maternal mortality (43) menopause (82) obesity (58) postpartum period (40) pregnancy (225) Pregnancy complications (99) Prenatal care (68) prenatal diagnosis (50) Prevalence (41) Quality of life (51) risk factors (94) ultrasonography (79) urinary incontinence (40) women's health (48)