Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(11):561-565
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001100006
PURPOSE: to evaluate the influence of age on the quality of semen in men submitted to spermatic analysis in a human reproduction service, in cases of conjugal infertility. METHODS: a retrospective study in which the spermiograms of all men in process of investigation for conjugal infertility in a service of assisted reproduction in the Northeast of Brazil were evaluated from September 2002 to December 2004. A number of 531 individuals submitted to 531 spermatic evaluations were included in the study. The following parameters have been analyzed: spermatic volume, concentration, motility and morphology. The men under investigation have been divided in groups, according to the results obtained in each of the variables studied. Seminal volume groups were divided in: hypospermia, normospermia and hyperspermia. Spermatic concentration groups were divided in: azoospermia, oligospermia, normospermia and polyspermia. Motility groups were divided in: normal motility and asthenospermia. Morphology groups were divided in: normal morphology and teratospermia. The t test has been used to compare the average age of patients in groups with normal and in groups with altered parameters. The program XLSTAT (p<0.05) has been used for the statistical analysis. RESULTS: the individuals studied presented an average of 37±7.9 years old, with an average of seminal volume of 3±1.4 mL, a spermatic concentration of 61.4±66.4 spermatozoids by mL of semen, a progressive motility of 44.7±19.4% of the total of spermatozoids and normal morphology of 11.2±6.6% of the spermatozoids. Average age among groups were similar, except for that of individuals with hypospermia, which was significantly higher than the one from men with normospermia (39.6±10.3 versus 36.5±7.3, p=0.001). CONCLUSIONS: age interferes in an inversely proportional way on the ejaculated volume, but does not influence spermatic concentration, motility and morphology.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(11):556-560
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001100005
PURPOSE: to evaluate whether the sample adequacy influences the detection of precursor cervical cancer lesions. METHODS: a transversal study from January 2004 to December 2005. A number of 10,951 results of cervical cytotopathological exams from users of the National Health System (Sistema Único de Saúde, SUS) in Goiânia, Goiás , Brazil, was studied. These women had spontaneously looked for the services from the Family Health Program or from the Basic Units of Health. Samples were collected by medical doctors and nurses, through the conventional technique to detect cervical cancer. The analyzed smears were classified by the Bethesda System, the sample adequacy being defined along the routine screening and categorized as: satisfactory, satisfactory but presenting factors that might partially jeopardize the analysis, and unsatisfactory. Results were stored in the Epi-Info 3.3.2 program. The χ2 test was used to compare altered results with the adequacy of the samples from cytopathological smears. Differences with probability of rejection of the null hypothesis lower than 5% (p<0.05) were considered as significant. RESULTS: From 10,951 smears, 51.1% were classified as having satisfactory adequacy for analysis, 46.6% as satisfactory, but presenting some limiting factors, and 2.3%, as unsatisfactory. The main factors which have partially jeopardized the analysis were: lack of endocervical cells (52.2%), dried smears (22.8%), purulence (14.9%), or smears with some thick areas (9.5%). There was a higher rate of altered smears when the sample had been classified as satisfactory for analysis and with representation of endocervical cells ASC-US (2.3%), ASC-H (0.6%), LSIL (3.2%), HSIL (1.7%) and 0.3% of AGC. Differences were significant when p=0.001. The rate of low and high grade lesions was higher when the smears were satisfactory for analysis. CONCLUSIONS: the rate of precursor uterine cervix cancer lesions varies according to the sample adequacy, and the main adequacy limitations of the sample are mainly related to the collection condition.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(11):544-549
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001100003
PURPOSE: to compare the efficacy of tinidazole and cephazolin on the febrile and infectious morbidity of post vaginal and abdominal hysterectomy antibiotic prophylaxis. METHODS: randomized clinical study, where women admitted to hospital for hysterectomy were randomly allocated in one of the following antibiotic prophylaxis groups: Group C (2 g of IV cephazolin in the anesthetic induction); Group T (2 g of tinidazole orally, 12 hours before the surgery); or Group C+T (2 g of tinidazole orally 12 hours before the surgery and 2g of IV cephazolin in the anesthetic induction). Cervicovaginal smears were collected for specific cultures and the diagnosis of bacterial vaginosis (BV) was based in Amsel and Nugent's criteria. The patients were reevaluated 7 and 30 days after the surgery for signs of febrile and/or infectious morbidity. The χ2 or the Fisher's exact test was used to assess differences among the three groups, with a significance level of 5%. The sample power (1-β) was calculated through the SAS program. RESULTS: seven days after the hysterectomy, infectious morbidity was diagnosed in 6.6% of the women, but with no significant difference among the three groups studied (p=0.12). There was no febrile or infectious morbidity at the immediate post-surgical period or after 30 days from the surgery. BV ratio at the pre-surgical period was significantly higher among the women submitted to vaginal hysterectomy, rather than among the ones submitted to abdominal hysterectomy (27 versus 7%, p=0.02). BV ratio was also higher after 30 days, among the women submitted to vaginal hysterectomy (20 versus 8%), though without statistical significance (p=0.19). CONCLUSIONS: the use of tinidazole, isolated or associated with cephazolin has not presented higher efficacy, than the use of cephazolin, alone to prevent febrile or infectious morbidity post hysterectomy. The high ratio of BV at the immediate pre-surgery period among the women submitted to vaginal hysterectomy suggests that this infection must be better investigated and properly treated before the surgery.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(11):537-543
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001100002
PURPOSE: to evaluate the effect of tibolone use on dopplervelocimetric parameters of ophthalmic and retinal arteries. METHODS: clinical, prospective, longitudinal, randomized, placebo-controlled, triple-blind study, in which among 100 menopausal women, 50 have used 2.5 mg of the active principle tibolone (Tib Group) and 50, placebo as a means to form the control-group (Plac Group). In the Tib Group, 44 of the 50 women returned after 84 days to finish the exams, and in the Plac Group, 47. The ophthalmic and retinal arteries were studied to determine the resistance index (RI), the pulsatility index (PI) and the systole/diastole ratio (S/D). Assessments have been done before and 84 days after medication. The t-Student test has been used for the comparison of means between the groups in independent samples, as well as for within-group comparisons in dependent samples. RESULTS: in both groups, the women's characteristics were similar in age, menopause duration, body mass index, arterial blood pressure, deliveries and cardiac rate. The Tib Group presented the following values in the ophthalmic artery: RI(pre)=0.71±0.05, RI(post)0.72±0.08 (p=0.43); PI(pre)=1.29±0.22, PI(post)=1.30±0.25 (p=0.4) and S/D(pre)=3.49±0.77, SD(post)=3.65±0.94 (p=0.32). In the retinal artery, the following values have been found: RI(pre)=0.67±0.09, RI(post)=0.69±0.10 (p=0.7); PI(pre)=1.20±0.29, PI(post)=1.22±0.3 (p=0.2) and SD(pre)=3.29±0.95, SD(post)=3.30±1.07 (p=0.3). Also, the tibolone and control groups did not show any significant difference in regard to the above indexes in the end of the study. CONCLUSIONS: the 2.5 mg dose of tibolone had no effect on the Doppler velocimetry indexes of the ophthalmic and retinal arteries.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(10):504-510
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001000005
PURPOSE: to translate from English into Portuguese, adapt culturally and validate the Female Sexual Function Index (FSFI). METHODS: knowing the objectives of this research, two Brazilian translators have prepared a version each from the FSFI into Portuguese. Both versions have then been retro-translated into English by two English translators. After harmonizing the differences, they have been pre-tested in a pilot study. The final versions from the FSFI and from another questionnaire, the Short-Form Health Survey, which had already been translated and published in Portuguese, have then been simultaneously administered to one hundred patients, to test the FSFI psychometric proprieties concerning reliability (internal consistency and testing-retesting) and construct validity. Retesting was done after four weeks from the first interview. RESULTS: the process of cultural adaptation has not altered the Portuguese version of the FSFI, as compared to the original. The FSFI standardized Cronbach alpha was 0.96, and the evaluation by domains has varied from 0.31 to 0.97. As a measure of test-retest confidentiality, it was applied the intra-class coefficient, which has been considered strong and identical (1.0). Pearson's correlation coefficient between the FSFI and the Short-Form Health Survey was positive, but weak in most of the interrelated domains, varying from 0.017 to 0.036. CONCLUSIONS: the FSFI English version has been translated into Portuguese and culturally adapted, being reliable to evaluate the sexual response of Brazilian women.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(10):518-523
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001000007
Ectopic pregnancy in a cesarean scar is the rarest form of ectopic pregnancy and probably the most dangerous one because of the risk of uterine rupture and massive hemorrhage. This condition must be distinguished from cervical pregnancy and spontaneous abortion in progress, so that the appropriate treatment can be immediately offered. Since the advent of endovaginal ultrasonography, ectopic pregnancy in a cesarean scar can be diagnosed early in pregnancy if the sonographer is familiarized with the diagnostic criteria of this situation, especially in women with previous cesarean scar. Here we describe a case of ectopic pregnancy in a cesarean scar in which the diagnosis was considerably late, with presentation of spontaneous regression.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(10):511-517
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001000006
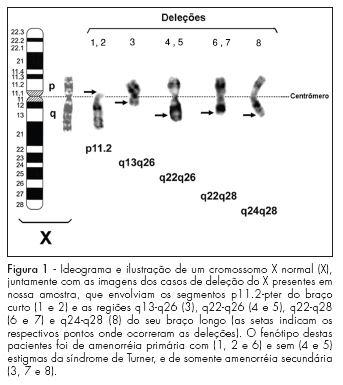
PURPOSE: to correlate the clinical manifestations of patients with amenorrhea and X chromosome abnormalities. METHODS: a retrospective analysis of the clinical and laboratorial findings of patients with amenorrhea and abnormalities of X chromosome, attended between January 1975 and November 2007 was performed. Their anthropometric measures were evaluated through standard growth tables, and, when present, minor and major anomalies were noted. The chromosomal study was performed through the GTG banded karyotype. RESULTS: from the total of 141 patients with amenorrhea, 16% presented numerical and 13% structural abnormalities of X chromosome. From these patients with X chromosome abnormalities (n=41), 35 had a complete clinical description. All presented hypergonadotrophic hypogonadism. Primary amenorrhea was observed in 24 patients, 91.7% of them with a Turner syndrome phenotype. Despite a case with Xq22-q28 deletion, all patients with this phenotype presented alterations involving Xp (one case with an additional cell lineage 46,XY). The two remaining patients with only primary amenorrhea had proximal deletions of Xq. Among the 11 patients with secondary amenorrhea, 54.5% presented a Turner phenotype (all with isolated or mosaic X chromosome monosomy). Patients with phenotype of isolated ovarian failure had only Xq deletions and X trisomy. CONCLUSIONS: the cytogenetic analysis must always be performed in women with ovarian failure of unknown cause, even in the absence of clinical dysmorphic features. This analysis is also extremely relevant in syndromic patients, because it can either confirm the diagnosis or identify patients in risk, like the cases involving a 46,XY lineage.