Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(1):28-34
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000100006
PURPOSE: to determine the prevalence of depression and anxiety in climacteric women and the probable factors responsible for its occurrence. METHODS: a transversal study that has selected 93 women attended at a climacteric outpatient clinic, from May 2006 to August 2007. Inclusion criteria were: women from 40 to 65 years old who agreed with participating in the project. Exclusion criteria: patients in hormonal therapy, hormone-therapy by implant, DIUs and depo injections in the preceding six months, endocrinopathies leading to menstrual irregularities, hepatopathies, thrombopathies, use of drugs which interfere in the menstrual cycle, anxiolytics and antidepressants (as their use indicates previous diagnosis of mood disorders), hysterectomy, oophorectomy, cancer or psychiatric disease, and patients who had been submitted to radio or chemotherapy. During the interview, four questionnaires were applied: Anamnesis, containing socio-demographic, clinical and living habits data; Blatt-Kupperman's Menopausal Index for climacteric syndrome diagnosis; Anxiety sub-scale of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression scale (HADS-A) for anxiety diagnosis; and Beck's Depression Inventory for the diagnosis of depression. Descriptive and correlation analysis among the variables, χ2 and Hosmer-Lemeshow tests were performed using the Statistica Software program, version 6. RESULTS: the average depression prevalence among the patients was 36.8%, while that of anxiety was 53.7%. There was no significant difference between the prevalence of depression and anxiety in the three phases of climacterium. There was a significant relationship between the presence of moderate climacteric symptoms and the presence of mood alterations (p<0.001). Depression was more frequent in women with anxiety (OR=4.2) and insomnia (OR=4.9), having a job being a protection factor (OR=0.2). Risk factors related to anxiety were the presence of depression (OR=6.1) and antecedents of pre-menstrual tension (OR=7.0). CONCLUSIONS: the prevalence of depression and anxiety is high in climacterium, being possible to detect risk factors related to their occurrence.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(12):620-625
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001200006
PURPOSE: to compare delivery and pregnancy follow-up among adolescent and non-adolescent pregnant women whose delivery occurred in a tertiary hospital from Região de Lisboa (Portugal). METHODS: retrospective study with 10,656 deliveries. Pregnancy follow-up, delivery type, need of episiotomy and severe lacerations, Apgar index at the fifth minute and the delivery weight have been evaluated. The pregnant women were divided into two groups, over and under 20 years old. The group with women under 20 was further subdivided in pregnant women under or over 16. The χ2 test has been used for statistical analysis. RESULTS: adolescents presented worse follow-up: first appointment after 12 weeks (46.4 versus 26.3%) and less than four appointments (8.1 versus 3.1%), less dystocia (21.5 versus 35.1%), less caesarian sections (10.6 versus 20.7%), and lower need for inducing labor (16.5 versus 26.5%). There was no significant difference concerning gestational age at delivery and ratio of low weight newborns. Among adolescents, the ones under 16 had more low weight newborns (12 versus 7.4%) and more deliveries between 34 and 37 weeks (10.8 versus 4.2%). CONCLUSIONS: in a hospital attending adolescents with social and psychological support, the fact of them having had a worse follow-up in the pre-natal phase, their performance has not been worse. Nevertheless, special attention might be given to pregnant women under 16.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(12):614-619
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001200005
PURPOSE: This paper has aimed at estimating the prevalence of infections by Chlamydia trachomatis and by Neisseria gonorrhoeae in pregnant women from six Brazilian cities, identifying its association with socio-economical and demographic variables. METHODS: This study has been part of a multicentric nationwide transversal research, with samples of pregnant women attended from 2004 to 2005 in basic attention pre-natal services from six Brazilian cities (Manaus, Fortaleza, Goiânia, Rio de Janeiro, São Paulo and Porto Alegre). Cervico-vaginal samples have been collected from all the pregnant women, and have afterwards been submitted to the hybrid capture technique in order to identify chlamydia and gonococcus. Socio-demographic, medical, sexual and obstetric information have been collected through specific questionnaires. The Odds Ratio (OR) has been used to evaluate risk factors associated to infection by gonorrhea and chlamydia. Statistical analysis has been done with the t-Student, χ2 and Fisher's exact tests. RESULTS: Three thousand and three pregnant women with an average age of 23.8 years old (±6.9) took part in the study. Infection prevalence by chlamydia and gonococcus were 9.4 and 1.5, respectively. Ten per cent of the pregnant women with chlamydia have presented gonococcus simultaneously. The risk of presenting one of those infections was two times higher for the women under 20. The infection main predictors have been: age under 20, race/black, single/separated and report of over one partner in the previous year. CONCLUSIONS: This study has observed high prevalence of infection by Chlamydia trachomatis and by Neisseria gonorrhoeae in Brazilian pregnant women. The main risk factor for the infection has been to be under 20 years old.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(12):594-601
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001200002
PURPOSE: to evaluate factors associated with women's dyslipidemia during menopause. METHODS: case-control study of prevalent cases and controls selected from a dedicated outpatient clinic. From recent biochemical parameters found in patients' files, women have been grouped in 'case' and 'control'. Women who presented any alteration in the blood levels of total cholesterol, LDL-cholesterol, triglycerides and/or HDL-cholesterol were considered as case, and the ones who presented normal levels of them, as control. Data concerning socioeconomic situation, physical activity, etilism and tabagism, anthropometric measurements and food ingestion have been collected and then compared between the groups. Ratios have been compared by the χ2, Fisher's exact test and/or t-Student test, depending on the distribution type. The crude relationship between each factor and the presence of dyslipidemia has been estimated by logistic regression. RESULTS: data have been collected from 84 women aged from 42 to 59 years, as 45 of them were grouped as case (dyslipidemic) and 39 as control (non-dyslipidemic). Age average of cases and controls was 52.1±4.2 and 52.2±4.7 years old, respectively. The sample showed to be homogeneous for the socioeconomic characteristics (income, occupation and schooling), physical activity practice, etilism and tabagism, and food ingestion, with no significant correlation with dyslipidemia. The groups presented an income up to two minimal wages, low schooling level (up to the fourth grade of lower school), and the housewife occupation. Smoking and drinking alcohol was not very frequent. Practicing physical activity was non-existent, thus characterizing a sedentary population. Food ingestion was adequate for carbohydrates, protein, lipids, but not for cholesterol (excessive) and fibers (insufficient), in both groups. Concerning the anthropometric evaluation, there has been an association with dyslipidemia, as the body mass index (BMI) and the waist circumference (WC) were significantly larger in case than in control. The waist-hip ratio has been similar in both groups. Weight excess has been found in most of the cases (73.3%) as almost half of them (44%) presented WC >88 cm, which represents a very increased risk. CONCLUSIONS: it is possible to conclude that, in the studied sample, only the anthropometric measurements have been considered as risk factors associated with dyslipidemia, during post-menopause.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(12):609-613
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001200004
PURPOSE: to evaluate predictive factors of response to GnRHa treatment in girls with idiopathic central precocious puberty. METHODS: a retrospective cohort study was conducted involving 33 girls diagnosed with idiopathic central precocious puberty and treated with GnRHa. The following independent variables were assessed: age at the beginning of therapy and at the onset of symptoms, time elapsed since the appearance of pubertal characteristics and the beginning of treatment, bone age, bone age advance, duration of GnRHa treatment, actual height and Z-score, predicted height and Z-score and hormone measurements of FSH and LH after GnRH stimulation, which were correlated with gain in height as a dependent variable at treatment discontinuation, calculated by the difference between the predicted height at the end and beginning of treatment. For statistical analysis, Pearson's linear correlation was used, in addition to multiple linear regression analysis. RESULTS: the mean age at the beginning of treatment was 7.8±1.3 years, with a mean bone age of 10.1±1.6 years. Bone age advance was 2.3±1.1 years and was controlled during the treatment period. Gain in predicted height was 2.5±1.3cm. It was positively correlated with time elapsed since the beginning of symptoms and the beginning of treatment and with bone age advance, while negatively correlated with the Z-score of height at the beginning of treatment and predicted height at the beginning of treatment, and the latter was the main factor determining gain from treatment. CONCLUSIONS: girls who had the most significant compromise of predicted adult height, as detected by a larger deviation from the population (Z-score) and the most considerable advance in bone age, received benefit from GnRHa therapy, and they must not be excluded from the group to be treated.
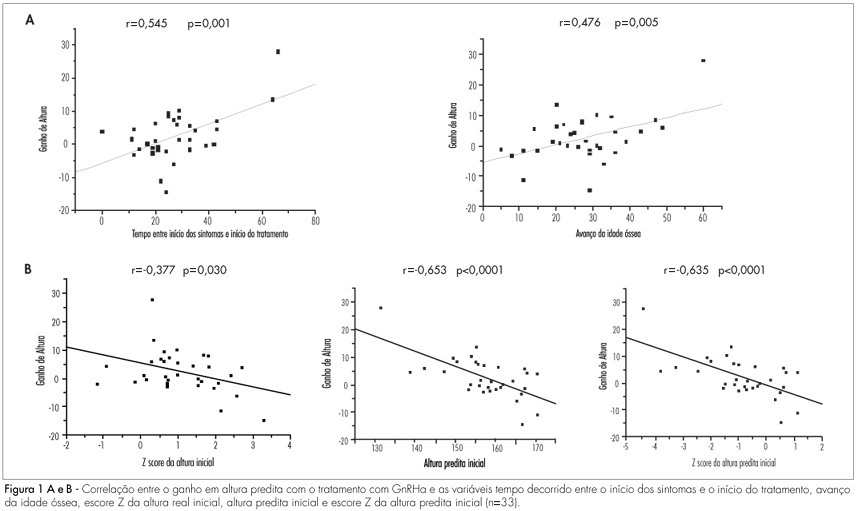
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(12):602-608
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001200003
PURPOSE: to evaluate the agreement between histopathologic diagnoses of breast lesions made by general pathologists and by a specialist in breast pathology. METHODS: a cohort retrospective study comparing histopathologic diagnoses of 329 cases of breast lesions received in consultation for a second opinion was carried out. The material received for consultation included slides (152 cases), paraffin blocks (59 cases) or slides and blocks (118 cases). Cases were reviewed and the original diagnoses and diagnoses from a specialist in breast pathology were compared. The main diagnoses, nuclear grade of ductal carcinoma in situ, and the histopathologic grade of invasive mammary carcinomas were evaluated. The kappa index and percentual concordance were used in the statistical analyses. RESULTS: a moderate agreement was observed between the original histopathologic diagnoses and the second opinion (kappa index=0.48; percentual concordance=59.9%). The diagnosis of malignancy was confirmed in 185/225 cases (82.2%) and diagnosis of benign lesions was confirmed in 89/104 cases (85.6%). The highest agreement was observed in the diagnosis of invasive mammary carcinomas (81%) and the highest disagreement was observed among diagnoses of ductal carcinoma in situ with microinvasion (74%), lobular carcinoma in situ (70%), and atypical epithelial hyperplasias (61%). There was a moderate agreement in the nuclear grade of ductal carcinoma in situ (kappa index=0.52; percentual concordance=68.8%), and good concordance in the histologic grade of invasive carcinomas (kappa index=0.61; percentual concordance=74.3). CONCLUSIONS: the results show higher concordance rate in the diagnosis of invasive carcinomas and lower concordance in the diagnosis of ductal carcinoma in situ with microinvasion and premalignant breast lesions, especially lobular neoplasia in situ, and atypical epithelial hyperplasias.
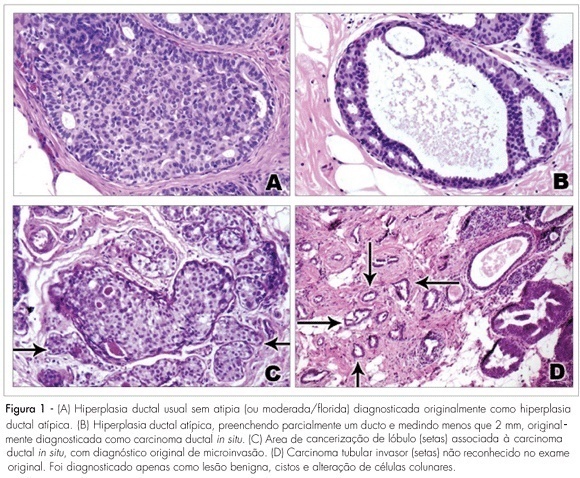
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(7):360-365
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000700007
PURPOSE: to determine the relationship between the morphology of the first spindle pole of human oocytes and rates of fertilization, fragmentation and embryo quality in procedures of Intracytoplasmic Sperm Injection (ICSI). METHODS: retrospective study of 582 consecutive ICSI cycles, from July 2003 to July 2005. The morphology of the first spindle pole (SP) was assessed through the analysis of 3,177 oocytes in metaphase II, immediately before the ICSI procedure, always by the same observer. SP has been classified in the following categories: normal size intact, fragmented or augmented SP. Fertilization rate and fragmentation, and the number and rate of good quality embryos in each one of the three groups studied have been evaluated, 48 hours after ICSI (D2). Embryos with four cells, without fragmentation and with symmetric blastomeres in D2 were considered as of good quality. RESULTS: rates of fertilization, fragmentation and of good quality embryo formation, resulting from oocyte insemination, with augmented SP (20.7, 16.7 and 5% respectively) were significantly lower than the ones from intact and normal size SP (70.8, 62.5 and 19%, respectively) or from fragmented SP oocytes (69.7, 60.5 and 17.1%, respectively). CONCLUSIONS: it has been observed that the presence of augmented first spindle pole is related to worse rates of fertilization, fragmentation and bad quality embryo formation. Nevertheless, fragmentation in the first spindle pole of the oocyte does not seem to affect ICSI results.
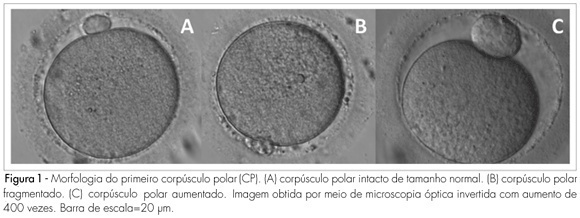
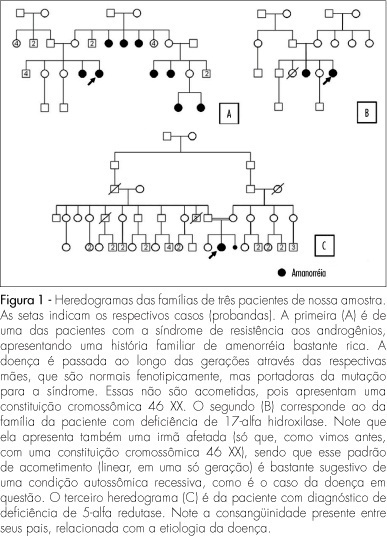
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(11):566-572
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001100007
PURPOSE: to verify the prevalence and clinical characteristics of patients with primary amenorrhea and XY caryotype, evaluated in our Service, aiming at identifying findings which could help their recognition. METHODS: from January 1975 to November 2007, 104 patients with amenorrhea were evaluated. All the cases were analyzed by the caryotype by GTG bands. Among them, 21 (20.2%) presented a XY 46 constitution. Nevertheless, two of them were excluded from the study, because of incomplete data in their patient's chart. Most of the 19 patients who formed the sample had been referred to us by the gynecology clinics (63.2%). Their ages varied from 16 to 41 years old (an average of 22.1). Data were collected about their family and previous history, physical examination and results of complementary exams and the information was taken into consideration to determine the diagnosis. RESULTS: the predominant diagnosis was resistance to androgens syndrome (n=12; 63.2%); five patients (25.3%) presented XY pure gonadal dysgenesis (XY PGD), one (5.3%) 17 alpha-hydroxylase deficiency, and one (5.3%), 5 alpha-reductase deficiency. Clinical findings frequently found in these patients included abnormal development of secondary sexual characters (n=19), uterine agenesia with a blind vagina (n=14), family history of amenorrhea (n=8), and palpable gonads in the inguinal canal (n=5). Two of them presented a history of inguinal hernia. Systemic arterial hypertension was only diagnosed in the patient with 17 alpha-hydroxylase deficiency, and gonadal malignization, in the one with XY PGD. CONCLUSIONS: the rate of patients with XY caryotype (20%) was higher than the one described in the literature (3 to 11%). It is believed that this fact is related to the way patients are usually referred to our service. Some findings from the clinical history and from the physical examination should be evaluated as a routine in individuals with primary amenorrhea. This way, there would be a more precocious detection of XY 46 patients, and a better clinical management of them, as a consequence.