-
Original Article07-27-2021
Prenatal Diagnosis of Aberrant Right Subclavian Artery: Association with Genetic Abnormalities
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(6):452-456
Abstract
Original ArticlePrenatal Diagnosis of Aberrant Right Subclavian Artery: Association with Genetic Abnormalities
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(6):452-456
Views165See moreAbstract
Objective
The objective of the present study was to determine the frequency of malformations and chromosomal abnormalities in a population of fetuses with an aberrant right subclavian artery (ARSA).
Methods
This is a 6-year retrospective study of fetuses with a prenatal diagnosis of ARSA conducted during the period between September 2013 and June 2019 at a fetal medicine unit. Data were collected from ultrasound, fetal echocardiograms, genetic studies, and neonatal records.
Results
An ARSA was diagnosed in 22 fetuses. An ARSA was an isolated finding in 18 out of 22 cases (82%). Associated abnormal sonographic findings were found in 4 cases. All cases underwent invasive testing. In 1 of the cases, a chromosomal abnormality was detected (mos 45,X [13]/46,X,e(X) (p22.1q22.1)). No cases of congenital heart disease were found in any of these fetuses. There were two cases in which the postnatal evaluation revealed amalformation: one case of hypospadias and 1 case of cleft palate.
Conclusion
The presence of an isolated ARSA is benign and is not associated with chromosomal abnormalities. The finding of ARSA, however, warrants a detailed fetal ultrasound in order to exclude major fetal abnormalities and other soft markers.
PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 3
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 66
- Abstract Views: 16
- Captures
- Readers: 14
-
Original Article05-24-2021
Comparison of Automated Breast Ultrasound and Hand-Held Breast Ultrasound in the Screening of Dense Breasts
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):190-199
Abstract
Original ArticleComparison of Automated Breast Ultrasound and Hand-Held Breast Ultrasound in the Screening of Dense Breasts
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):190-199
Views240See moreAbstract
Objective
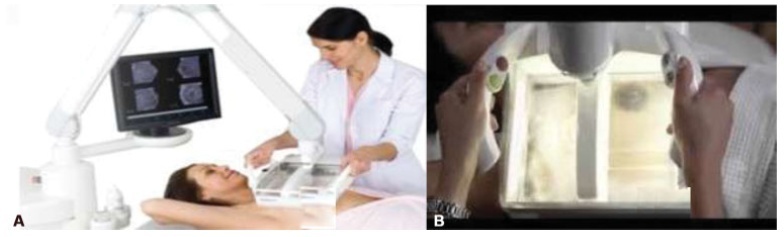
To compare hand-held breast ultrasound (HHBUS) and automated breast ultrasound (ABUS) as screening tool for cancer.
Methods
A cross-sectional study in patients with mammographically dense breasts was conducted, and both HHBUS and ABUS were performed. Hand-held breast ultrasound was acquired by radiologists and ABUS by mammography technicians and analyzed by breast radiologists. We evaluated the Breast Imaging Reporting and
Data System
(BI-RADS) classification of the exam and of the lesion, as well as the amount of time required to perform and read each exam. The statistical analysis employed was measures of central tendency and dispersion, frequencies, Student t test, and a univariate logistic regression, through the odds ratio and its respective 95% confidence interval, and with p<0.05 considered of statistical significance.
Results
Atotal of 440 patientswere evaluated. Regarding lesions,HHBUS detected 15 (7.7%) BI-RADS 2, 175 (89.3%) BI-RADS 3, and 6 (3%) BI-RADS 4, with 3 being confirmed by biopsy as invasive ductal carcinomas (IDCs), and 3 false-positives. Automated breast ultrasound identified 12 (12.9%) BI-RADS 2, 75 (80.7%) BI-RADS 3, and 6 (6.4%) BI-RADS 4, including 3 lesions detected by HHBUS and confirmed as IDCs, in addition to 1 invasive lobular carcinoma and 2 high-risk lesions not detected by HHBUS. The amount of time required for the radiologist to read the ABUS was statistically inferior compared with the time required to read the HHBUS (p<0.001). The overall concordance was 80.9%. A total of 219 lesions were detected, from those 70 lesions by both methods, 126 only by HHBUS (84.9% not suspicious by ABUS) and 23 only by ABUS.
Conclusion
Compared with HHBUS, ABUS allowed adequate sonographic study in supplemental screening for breast cancer in heterogeneously dense and extremely dense breasts.
PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 7
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 174
- Abstract Views: 21
- Captures
- Readers: 30
-
Clinical Consensus Recommendation03-08-2021
Pre-eclampsia: Universal Screening or Universal Prevention for Low andMiddle-Income Settings?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(1):61-65
Abstract
Clinical Consensus RecommendationPre-eclampsia: Universal Screening or Universal Prevention for Low andMiddle-Income Settings?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(1):61-65
Views281See moreAbstract
Pre-eclampsia (PE) is a severe disorder that affects up to 8% of all pregnancies and represents an important cause of maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality. The screening of the disease is a subject of studies, but the complexity and uncertainties regarding its etiology make this objective a difficult task. In addition, the costs related to screening protocols, the heterogeneity of the most affected populations and the lack of highly effective prevention methods reduce the potential of current available algorithms for screening. Thus, the National Specialized Commission of Hypertension in Pregnancy of the Brazilian Association of Gynecology and Obstetrics Federation (Febrasgo, in the Portuguese acronym) (NSC Hypertension in Pregnancy of the Febrasgo) considers that there are no screening algorithms to be implemented in the country to date and advocates that Aspirin and calcium should be widely used.
-
Original Article07-17-2020
High-risk Human Papillomavirus Testing for Triage of Women with Previous Cytological Abnormalities from the Vale do Ribeira Region
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(6):340-348
Abstract
Original ArticleHigh-risk Human Papillomavirus Testing for Triage of Women with Previous Cytological Abnormalities from the Vale do Ribeira Region
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(6):340-348
Views157See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the performance of the hybrid capture 2 (HC2) high-risk papillomavirus (hrHPV) assay and cytological test in women with previous abnormalities, to detect cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2 or worse (≥ CIN 2).
Methods
A cytological test and HC2 (Qiagen, Gaithersburg, Maryland, EUA) for hrHPV were conducted in 359 liquid-based (Sure Path, Becton Dickinson, TriPath Imaging, Burlington, NC, USA) samples collected from women from the Vale do Ribeira Region, during July 2013 and September 2015 with previous cytology classified as atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASC-US), low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LSIL), atypical squamous cells, cannot exclude high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (ASC-H), and atypical glandular cells (AGC). The histopathological examination was conducted in 179 women. The performance evaluations were calculated using the “exact” Clopper-Pearson 95% confidence interval (CI) test by MEDCALC (Medcalc Software Ltd, Ostend, Belgium).
Results
The ≥ CIN 2 frequency was 11.7% (21/179). The HC2 for hrHPV and repeat cytology to detect ≥ CIN 2 obtained, respectively, a sensitivity of 90.5% (95% CI = 69.6-98.8) and 90.5%, (95%CI = 69.6-98.8), a specificity of 65.8% (95% CI = 57.9-73.2) and 43.7% (95%CI = 35.8-51.8), a positive predictive value of 26.0% (95% CI = 21.4-31.3) and 17.6%, (95%CI = 14.9-20.6), and a negative predictive value of 98.1% (95%CI = 93.3-99.5) and 97.2% (95% CI = 90.1-99.2).
Conclusion
Hybrid capture 2 for hrHPV improves the performance of the detection of ≥ CIN 2, without compromising sensitivity, and provides a greater safety margin to return to the triennial screening of women undergoing follow-up due to previous abnormalities, without underlying ≥ CIN 2.
-
Review Article06-01-2018
Guidelines for HPV-DNA Testing for Cervical Cancer Screening in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):360-368
Abstract
Review ArticleGuidelines for HPV-DNA Testing for Cervical Cancer Screening in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):360-368
Views308See moreAbstract
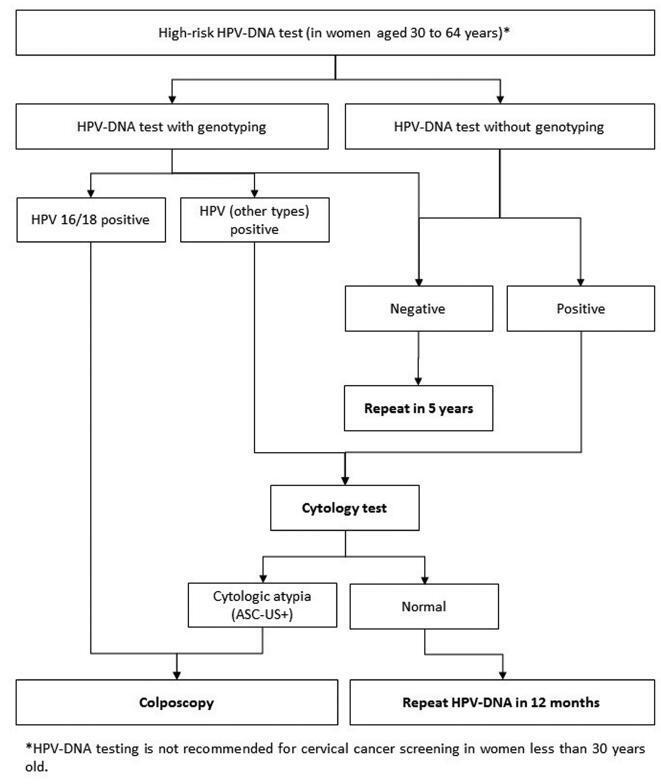
Evidence-based clinical guidelines ensure best practice protocols are available in health care. There is a widespread use of human papillomavirus deoxyribonucleic acid (HPVDNA) tests in Brazil, regardless of the lack of official guidelines. On behalf of the Brazilian Association for the Lower Genital Tract Pathology and Colposcopy (ABPTGIC, in the Portuguese acronym), a team of reviewers searched for published evidence and developed a set of recommendations for the use of HPV-DNA tests in cervical cancer screening in Brazil. The product of this process was debated and consensus was sought by the participants. One concern of the authors was the inclusion of these tests in the assessment of women with cytologic atypia and women treated for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN). Testing for HPV is recommended in an organized screening scenario to identify women with precursor lesions or asymptomatic cervical cancer older than 30 years of age, and it can be performed every 5 years. It also has value after the cytology showing atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASC-US) or low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (LSILs) as a triage test for colposcopy, in the investigation of other cytological alterations when no abnormal findings are observed at colposcopy, seeking to exclude disease, or, further, after treatment of high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, to rule out residual disease.
PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 27
- Policy Citations: 1
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 3338
- Abstract Views: 1756
- Captures
- Readers: 104
-
Review Article05-01-2018
Uterine Artery Doppler in Screening for Preeclampsia and Fetal Growth Restriction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(5):287-293
Abstract
Review ArticleUterine Artery Doppler in Screening for Preeclampsia and Fetal Growth Restriction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(5):287-293
Views307See moreAbstract
Objective
To perform a comprehensive review of the current evidence on the role of uterine artery Doppler, isolated or in combination with other markers, in screening for preeclampsia (PE) and fetal growth restriction (FGR) in the general population. The review included recently published large cohort studies and randomized trials.
Methods
A search of the literature was conducted usingMedline, PubMed, MeSH and ScienceDirect. Combinations of the search terms “preeclampsia,” “screening,” “prediction,” “Doppler,” “Doppler velocimetry,” “fetal growth restriction,” “small for gestational age” and “uterine artery” were used. Articles in English (excluding reviews) reporting the use of uterine artery Doppler in screening for PE and FGR were included.
Results
Thirty articles were included. As a single predictor, uterine artery Doppler detects less than 50% of the cases of PE and no more than 40% of the pregnancies affected by FGR. Logistic regression-based models that allow calculation of individual risk based on the combination of multiple markers, in turn, is able to detect ~ 75% of the cases of preterm PE and 55% of the pregnancies resulting in small for gestational age infants.
Conclusion
The use of uterine artery Doppler as a single predictive test for PE and FGR has poor accuracy. However, its combined use in predictive models is promising, being more accurate in detecting preterm PE than FGR.
-
Original Article07-01-2017
Psychometric Properties of Brief Screening Tests for Alcohol Use Disorders during Pregnancy in Argentina
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(7):322-329
Abstract
Original ArticlePsychometric Properties of Brief Screening Tests for Alcohol Use Disorders during Pregnancy in Argentina
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(7):322-329
Views140See moreAbstract
Background
Considering the physical, mental and behavioral problems related to fetal alcohol exposure, prenatal clinical guides suggest a brief evaluation of alcohol consumption during pregnancy to detect alcohol intake and to adjust interventions, if required. Even if any alcohol use should be considered risky during pregnancy, identifying women with alcohol use disorders is important because they could need a more specific intervention than simple advice to abstain. Most screening tests have been developed and validated in male populations and focused on the long-term consequences of heavy alcohol use, so they might be inappropriate to assess consumption in pregnant women.
Objective
To analyze the internal reliability and validity of the alcohol screening instruments Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT), Alcohol Use Disorders IdentificationTest- Consumption (AUDIT-C), Tolerance, Worried, Eye-Opener, Amnesia and Cut-Down (TWEAK), Rapid Alcohol Problems Screen - Quantity Frequency (RAPSQF) and Tolerance, Annoyed, Cut-Down and Eye-Opener (T-ACE) to identify alcohol use disorders in pregnant women.
Methods
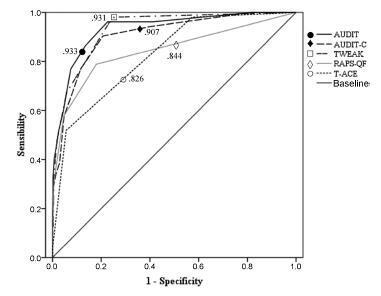
A total of 641 puerperal women were personally interviewed during the 48 hours after delivery. The receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curves and the sensitivity and specificity of each instrument using different cut-off points were analyzed.
Results
All instruments showed areas under the ROC curves above 0.80. Larger areas were found for the TWEAK and the AUDIT. The TWEAK, the T-ACE and the AUDIT-C showed higher sensitivity, while the AUDIT and the RAPS-QF showed higher specificity. Reliability (internal consistency) was low for all instruments, improving when optimal cut-off points were used, especially for the AUDIT, the AUDIT-C and the RAPS-QF.
Conclusions
In other cultural contexts, studies have concluded that T-ACE and TWEAK are the best instruments to assess pregnant women. In contrast, our results evidenced the low reliability of those instruments and a better performance of the AUDIT in this population.
-
Original Article05-02-1998
Frequency of performance and accuracy of breast self-examination in the detection of breast lumps in women who underwent mammographic examination
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(1):37-43
Abstract
Original ArticleFrequency of performance and accuracy of breast self-examination in the detection of breast lumps in women who underwent mammographic examination
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(1):37-43
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000100007
Views114See moreWe conducted a prospective cross-sectional study to evaluate the accuracy of the breast self-examination (BSE) in the detection of palpable breast lumps and the relation to its frequency of performance. Two thousand six hundred and seventy two women who have had a mammogram in a private clinic in Vale dos Sinos-RS between January 1994 and July 1997 were asked about BSE performance frequency. They were divided in two groups: group I (monthly), group II (almost never). The women who referred performing BSE on a occasional basis were excluded from the main analysis. The woman was asked wheter she or her physician had palpated something in her breasts. The patient's BSE findings were compared with those of her physician (based on the patients' report). The sensitivity of the BSE was higher in group I compared to group II (57.4% versus 33.3%; rho<0.05). We concluded that there is an association between frequency of performance and sensitivity of BSE to detect breast lumps.



