About
The Brazilian Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics (RBGO), a scientific publication of the Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics Societies (FEBRASGO), is aimed at gynecologists, obstetricians and professionals in related fields, with the aim of publishing research results on relevant topics in the field of Gynecology, Obstetrics and related areas.
- Recent Articles
- Most Citedi
- Most Visitedi
- Future Articles
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT05-16-2025
Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-FPS4
Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTMayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-FPS4
Views119See moreKey points
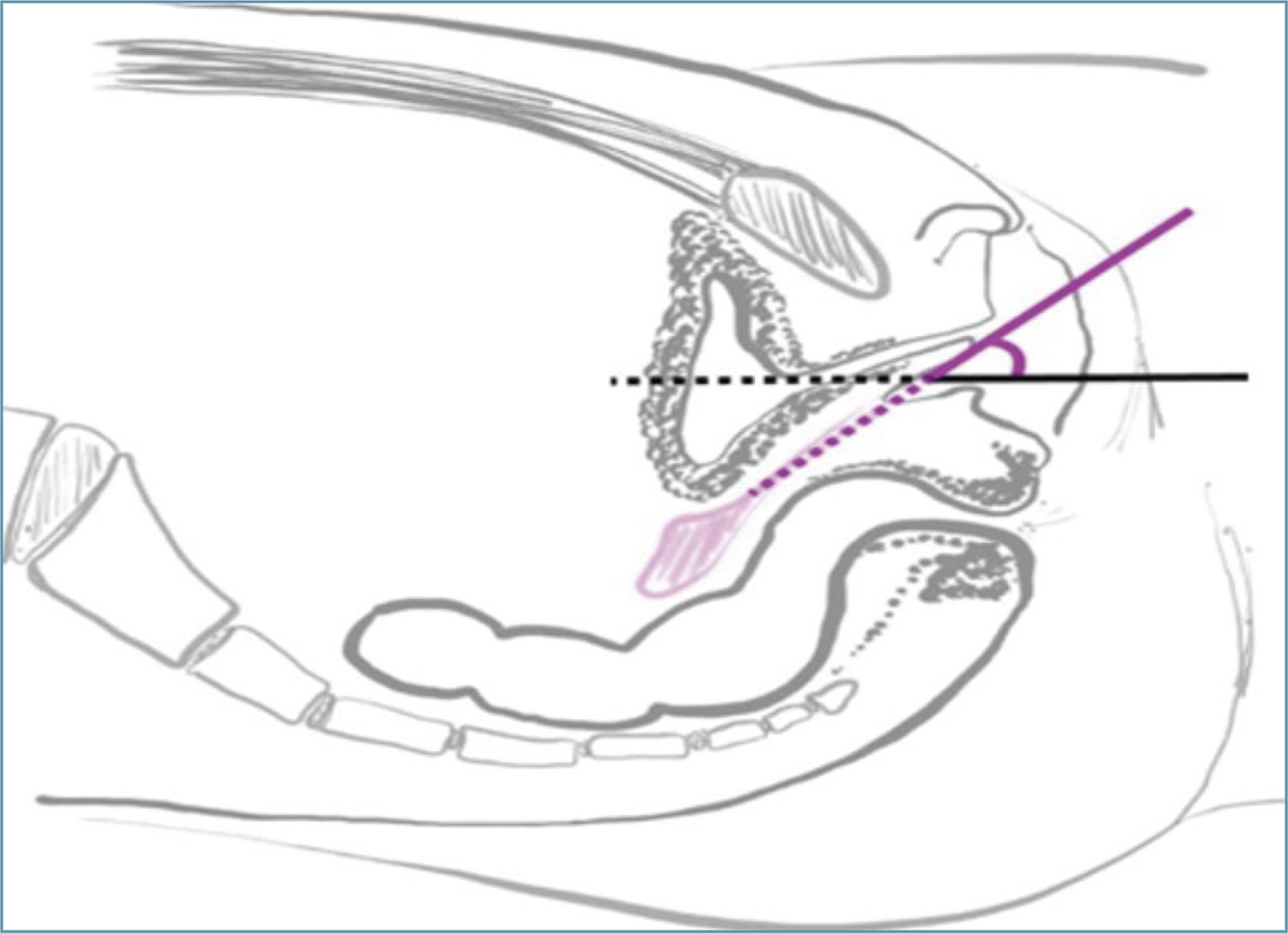
•Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome (MRKH) is the leading cause of vaginal agenesis.
•It is characterized by primary amenorrhea with typical adrenarche and telarche and may be associated with congenital urological and skeletal conditions that should be investigated.
•Differential diagnoses include: vaginal obstructions (imperforate hymen, distal vaginal atresia, transverse vaginal septum), uterine obstructions (cervical atresia), and differences in sexual development (gonadal dysgenesis, complete androgen insensitivity and congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to CYP17 deficiency).
•Laboratory tests (testosterone, follicle-stimulating hormone [FSH] and karyotype) and radiological tests (pelvic ultrasound and MRI) are necessary.
•Vaginal dilation is the first line of treatment with high success rates.
Views119

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTMayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-FPS4
Views119See moreKey points
•Mayer-Rokitansky-Kuster-Hauser syndrome (MRKH) is the leading cause of vaginal agenesis.
•It is characterized by primary amenorrhea with typical adrenarche and telarche and may be associated with congenital urological and skeletal conditions that should be investigated.
•Differential diagnoses include: vaginal obstructions (imperforate hymen, distal vaginal atresia, transverse vaginal septum), uterine obstructions (cervical atresia), and differences in sexual development (gonadal dysgenesis, complete androgen insensitivity and congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to CYP17 deficiency).
•Laboratory tests (testosterone, follicle-stimulating hormone [FSH] and karyotype) and radiological tests (pelvic ultrasound and MRI) are necessary.
•Vaginal dilation is the first line of treatment with high success rates.
-
Original Article04-30-2025
Hysterectomy rates per resident in final year of training in teaching hospitals: an ecologic study
- Luiza Nestori Chiozzotto
 ,
, - Nino José Wilson Moterani Júnior
 ,
, - Laura Bresciani Bento Gonçalves Moterani
 ,
, - Vinicius César Moterani
 ,
, - Francisco José Candido dos Reis

Abstract
Original ArticleHysterectomy rates per resident in final year of training in teaching hospitals: an ecologic study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo24
- Luiza Nestori Chiozzotto
 ,
, - Nino José Wilson Moterani Júnior
 ,
, - Laura Bresciani Bento Gonçalves Moterani
 ,
, - Vinicius César Moterani
 ,
, - Francisco José Candido dos Reis

Views150Abstract
Objective:
Analyze the hysterectomy rates per resident in graduation year in teaching hospitals in the state of São Paulo (Brazil).
Methods:
We selected teaching hospitals in the state of São Paulo and gathered information from two public databases to estimate the hysterectomy rates per resident in their final year of training between 2009 and 2019.
Results:
Between 2009 and 2019, there was a 37.5% increase in the number of residents in their final year of training, a 4.31% increase in the number of hysterectomies, and a drop in the hysterectomy rates per resident of 24.1%. The reduction of the rate of hysterectomy per resident was more pronounced for vaginal route (46.4%) followed by abdominal route (23.3%). The ratio of laparoscopic hysterectomy per resident increased 264% during the period, however, this route was used in only 7% of the surgeries in 2019.
Conclusions:
The hysterectomy rates per resident in their final year of training showed a notable reduction. This trend, particularly pronounced in vaginal and abdominal routes, signals a shift towards minimally invasive techniques.
Key-words Clinical competenceEducation, medicalHospitals, teachingHysterectomylearning curveMedical staff, hospitalPhysiciansStudents, medicalSurgical procedures, operativeSee moreViews150

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleHysterectomy rates per resident in final year of training in teaching hospitals: an ecologic study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo24
- Luiza Nestori Chiozzotto
 ,
, - Nino José Wilson Moterani Júnior
 ,
, - Laura Bresciani Bento Gonçalves Moterani
 ,
, - Vinicius César Moterani
 ,
, - Francisco José Candido dos Reis

Views150Abstract
Objective:
Analyze the hysterectomy rates per resident in graduation year in teaching hospitals in the state of São Paulo (Brazil).
Methods:
We selected teaching hospitals in the state of São Paulo and gathered information from two public databases to estimate the hysterectomy rates per resident in their final year of training between 2009 and 2019.
Results:
Between 2009 and 2019, there was a 37.5% increase in the number of residents in their final year of training, a 4.31% increase in the number of hysterectomies, and a drop in the hysterectomy rates per resident of 24.1%. The reduction of the rate of hysterectomy per resident was more pronounced for vaginal route (46.4%) followed by abdominal route (23.3%). The ratio of laparoscopic hysterectomy per resident increased 264% during the period, however, this route was used in only 7% of the surgeries in 2019.
Conclusions:
The hysterectomy rates per resident in their final year of training showed a notable reduction. This trend, particularly pronounced in vaginal and abdominal routes, signals a shift towards minimally invasive techniques.
Key-words Clinical competenceEducation, medicalHospitals, teachingHysterectomylearning curveMedical staff, hospitalPhysiciansStudents, medicalSurgical procedures, operativeSee more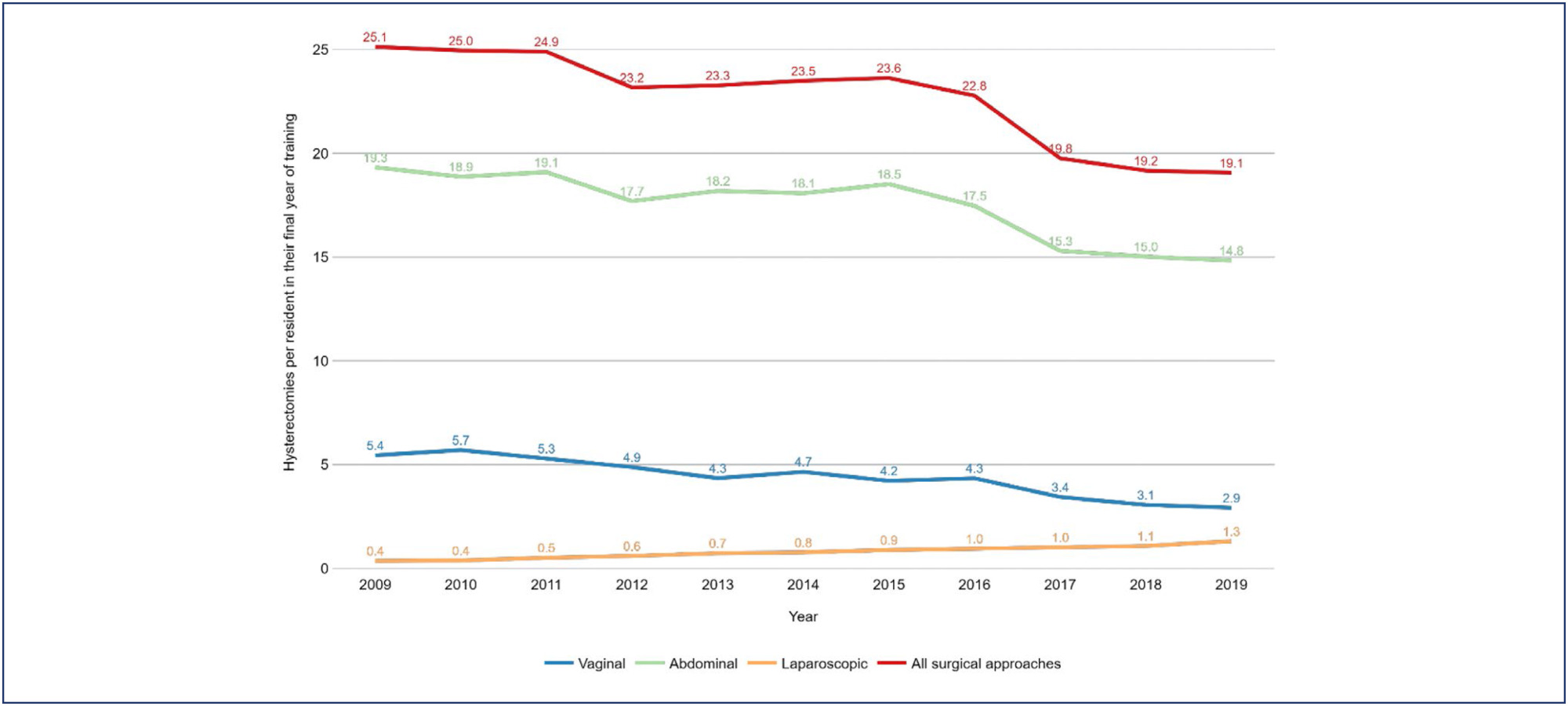
- Luiza Nestori Chiozzotto
-
Original Article04-30-2025
Prevalence of antiphospholipid syndrome among women with recurrent pregnancy loss: a cohort study
- Elaine Cristina Fontes de Oliveira
 ,
, - Daniel Dias Ribeiro
 ,
, - Janaína Campos Senra
 ,
, - Fernando Marcos dos Reis

Abstract
Original ArticlePrevalence of antiphospholipid syndrome among women with recurrent pregnancy loss: a cohort study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo23
- Elaine Cristina Fontes de Oliveira
 ,
, - Daniel Dias Ribeiro
 ,
, - Janaína Campos Senra
 ,
, - Fernando Marcos dos Reis

Views146Abstract
Objective:
This study aimed to evaluate the prevalence of antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) among women experiencing recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL).
Methods:
A cross-sectional was conducted, reviewing the medical records of 134 women with a history of two or more miscarriages, treated between January 2014 and May 2024 at a tertiary university center in Belo Horizonte, Brazil. APS screening was performed by assessing anticardiolipin (IgG and IgM), lupus anticoagulant, and anti-β2-glycoprotein-1 (IgG and IgM) antibodies, based on Sapporo criteria. All tests were performed during non-pregnant periods and at least 12 weeks after the last miscarriage.
Results:
The study included 134 women with a mean age of 33.8 ± 5.7 years. The number of prior miscarriages ranged from 2 to 11 per couple. Among the patients who presented the lupus anticoagulant, only two (1.49%) tested positive in two samples, as per revised Sapporo criteria. Considering IgG and IgM anticardiolipin antibodies, four patients (2.98%) tested positive in two samples according to old Sapporo criteria, with one patient having a positive IgG test in two samples, two having positive IgM in two samples and a single patient having both positive tests. None of the 56 patients tested positive for anti-β2-glycoprotein-1 antibodies in two samples.
Conclusion:
The prevalence of antiphospholipid antibodies, in line with revised Sapporo criteria, is low among Brazilian women with recurrent pregnancy loss, consistent with recent studies in literature. Ensuring the appropriateness of diagnostic criteria is crucial to avoid unnecessary treatment with platelet anticoagulants and heparin in this population.
Key-words Abortion, habitualAbortion, spontaneousAntibodiesAnticardiolipinAntiphospholipid syndromePrevalenceThrombophiliaSee moreViews146

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticlePrevalence of antiphospholipid syndrome among women with recurrent pregnancy loss: a cohort study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo23
- Elaine Cristina Fontes de Oliveira
 ,
, - Daniel Dias Ribeiro
 ,
, - Janaína Campos Senra
 ,
, - Fernando Marcos dos Reis

Views146Abstract
Objective:
This study aimed to evaluate the prevalence of antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) among women experiencing recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL).
Methods:
A cross-sectional was conducted, reviewing the medical records of 134 women with a history of two or more miscarriages, treated between January 2014 and May 2024 at a tertiary university center in Belo Horizonte, Brazil. APS screening was performed by assessing anticardiolipin (IgG and IgM), lupus anticoagulant, and anti-β2-glycoprotein-1 (IgG and IgM) antibodies, based on Sapporo criteria. All tests were performed during non-pregnant periods and at least 12 weeks after the last miscarriage.
Results:
The study included 134 women with a mean age of 33.8 ± 5.7 years. The number of prior miscarriages ranged from 2 to 11 per couple. Among the patients who presented the lupus anticoagulant, only two (1.49%) tested positive in two samples, as per revised Sapporo criteria. Considering IgG and IgM anticardiolipin antibodies, four patients (2.98%) tested positive in two samples according to old Sapporo criteria, with one patient having a positive IgG test in two samples, two having positive IgM in two samples and a single patient having both positive tests. None of the 56 patients tested positive for anti-β2-glycoprotein-1 antibodies in two samples.
Conclusion:
The prevalence of antiphospholipid antibodies, in line with revised Sapporo criteria, is low among Brazilian women with recurrent pregnancy loss, consistent with recent studies in literature. Ensuring the appropriateness of diagnostic criteria is crucial to avoid unnecessary treatment with platelet anticoagulants and heparin in this population.
Key-words Abortion, habitualAbortion, spontaneousAntibodiesAnticardiolipinAntiphospholipid syndromePrevalenceThrombophiliaSee more - Elaine Cristina Fontes de Oliveira
-
Original Article04-30-2025
An assessment of total antioxidant and oxidant parameters and their correlation with embryo quality in in-vitro fertilization patients
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo22
Abstract
Original ArticleAn assessment of total antioxidant and oxidant parameters and their correlation with embryo quality in in-vitro fertilization patients
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo22
Views141Abstract
Objective:
In vitro, fertilization is the primary treatment method for infertility. Follicular fluid analysis is an approach used to optimize the results of assisted reproductive techniques. Oxidative stress represents the imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species and their detoxification. Total Antioxidant and Oxidant Status, and Oxidative Stress Index levels are the main oxidative stress markers. This study investigated the effects of oxidative stress markers on infertility etiology, embryo quality, and success of In vitro fertilization.
Methods:
Before enrolling in the ICSI-ET cycle, participants had their FSH and LH levels assessed on the second day of the cycle. The ovarian degrees of the participants were evaluated by transvaginal ultrasonography. Participants underwent controlled ovarian stimulation using the GnRH antagonist protocol. TV-USG and serial E2 measurements were performed at appropriate intervals to follow follicular development. Follicle sizes, quantity, and endometrial thickness were recorded. Total Antioxidant and Oxidant Status, and Oxidative analyses were conducted using Rel Assay Diagnostics Assay Kits.
Results:
The average number of total oocytes in the participants was 10.25±6.66, and the average of mature M2 stage oocytes was 6.71±3.72. The average number of fertilized oocytes was 4.65±2.81. Fertilization rates were calculated as approximately 54.75±25.58%. A statistically significant positive correlation was found between embryo quality and serum Total Antioxidant Status levels (p=0.004). Similarly, a significant positive correlation was observed between embryo quality and follicular Total Antioxidant Status values (r = 0.42, p = 0.01).
Conclusion:
This study concluded that oxidative stress markers affect certain stages of the IVF treatment process.
Key-words AntioxidantsFertilization in vitroFollicular fluidInfertilityOocytesOxidantsOxidative stressSee moreViews141

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleAn assessment of total antioxidant and oxidant parameters and their correlation with embryo quality in in-vitro fertilization patients
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo22
Views141Abstract
Objective:
In vitro, fertilization is the primary treatment method for infertility. Follicular fluid analysis is an approach used to optimize the results of assisted reproductive techniques. Oxidative stress represents the imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species and their detoxification. Total Antioxidant and Oxidant Status, and Oxidative Stress Index levels are the main oxidative stress markers. This study investigated the effects of oxidative stress markers on infertility etiology, embryo quality, and success of In vitro fertilization.
Methods:
Before enrolling in the ICSI-ET cycle, participants had their FSH and LH levels assessed on the second day of the cycle. The ovarian degrees of the participants were evaluated by transvaginal ultrasonography. Participants underwent controlled ovarian stimulation using the GnRH antagonist protocol. TV-USG and serial E2 measurements were performed at appropriate intervals to follow follicular development. Follicle sizes, quantity, and endometrial thickness were recorded. Total Antioxidant and Oxidant Status, and Oxidative analyses were conducted using Rel Assay Diagnostics Assay Kits.
Results:
The average number of total oocytes in the participants was 10.25±6.66, and the average of mature M2 stage oocytes was 6.71±3.72. The average number of fertilized oocytes was 4.65±2.81. Fertilization rates were calculated as approximately 54.75±25.58%. A statistically significant positive correlation was found between embryo quality and serum Total Antioxidant Status levels (p=0.004). Similarly, a significant positive correlation was observed between embryo quality and follicular Total Antioxidant Status values (r = 0.42, p = 0.01).
Conclusion:
This study concluded that oxidative stress markers affect certain stages of the IVF treatment process.
Key-words AntioxidantsFertilization in vitroFollicular fluidInfertilityOocytesOxidantsOxidative stressSee more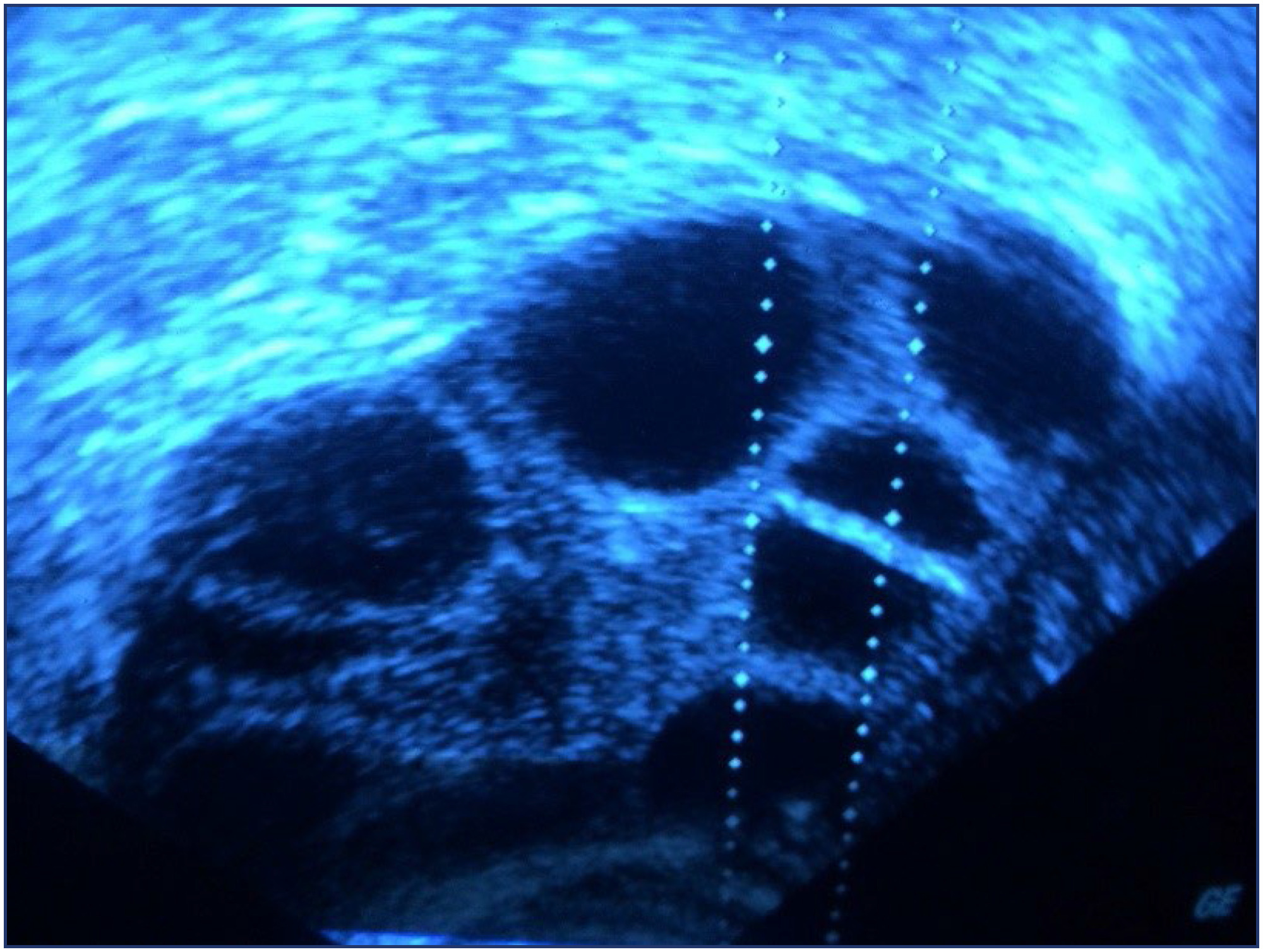
-
Review Article04-30-2025
Letrozole and clomiphene versus letrozole alone for ovulation induction in women with PCOS: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- Karine Eskandar
 ,
, - Juliana Almeida Oliveira
 ,
, - Sandro Augusto Ribeiro
 ,
, - Matheus Pedrotti Chavez
 ,
, - Ana Isabela de Araujo Zotti
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Andrea Mora de Marco Novellino

Abstract
Review ArticleLetrozole and clomiphene versus letrozole alone for ovulation induction in women with PCOS: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo21
- Karine Eskandar
 ,
, - Juliana Almeida Oliveira
 ,
, - Sandro Augusto Ribeiro
 ,
, - Matheus Pedrotti Chavez
 ,
, - Ana Isabela de Araujo Zotti
 ,
, - Yasmin Jardim Meirelles Dias
 ,
, - Andrea Mora de Marco Novellino

Views159Abstract
Objective:
We aimed to compare the efficacy and safety of letrozole and clomiphene versus letrozole alone for ovulation induction in patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS).
Data Sources:
We systematically searched EMBASE, PubMed, and Cochrane databases on October 31, 2024.
Study selection:
We included studies of women with PCOS treated with a combination of clomiphene and letrozole or letrozole alone to induce ovulation that reported any of the outcomes of interest, namely rate of mature follicles and ovulation, ovulation, pregnancy, miscarriages, endometrial thickness, and number of mature follicles.
Data collection:
We pooled odds ratios (OR) and mean difference (MD) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) using a random effects model using R statistical software, version 4.2.1. Heterogeneity was assessed with I statistics, and a random effects model was used.
Data Synthesis:
Four RCTs and two observational studies comprising 592 patients were included. Combined therapy was associated with a higher rate of a mature follicle (OR 2.74; 95% CI 1.72-4.37; p< 0.001; I=0%) and ovulation (OR 2.55; 95% CI 1.57-4.12; p< 0.001; I=35.9%). The number of mature follicles, number of pregnancies, thickness of endometrial lining, and the incidence of adverse events, including headache, abdominal bloating, fatigue, back pain, breast discomfort, and night sweats, were similar between groups.
Conclusion:
In women with anovulatory infertility secondary to PCOS, letrozole and clomiphene citrate combined therapy was associated with improved mature follicle and ovulation rates, with a similar safety profile compared to letrozole alone. However, no significant impact was observed on pregnancy rates.
Key-words ClomipheneInfertility, femaleLetrozoleOvulationOvulation InductionPolycystic ovary syndromeSee moreViews159

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleLetrozole and clomiphene versus letrozole alone for ovulation induction in women with PCOS: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo21
- Karine Eskandar
 ,
, - Juliana Almeida Oliveira
 ,
, - Sandro Augusto Ribeiro
 ,
, - Matheus Pedrotti Chavez
 ,
, - Ana Isabela de Araujo Zotti
 ,
, - Yasmin Jardim Meirelles Dias
 ,
, - Andrea Mora de Marco Novellino

Views159Abstract
Objective:
We aimed to compare the efficacy and safety of letrozole and clomiphene versus letrozole alone for ovulation induction in patients with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS).
Data Sources:
We systematically searched EMBASE, PubMed, and Cochrane databases on October 31, 2024.
Study selection:
We included studies of women with PCOS treated with a combination of clomiphene and letrozole or letrozole alone to induce ovulation that reported any of the outcomes of interest, namely rate of mature follicles and ovulation, ovulation, pregnancy, miscarriages, endometrial thickness, and number of mature follicles.
Data collection:
We pooled odds ratios (OR) and mean difference (MD) with 95% confidence intervals (CI) using a random effects model using R statistical software, version 4.2.1. Heterogeneity was assessed with I statistics, and a random effects model was used.
Data Synthesis:
Four RCTs and two observational studies comprising 592 patients were included. Combined therapy was associated with a higher rate of a mature follicle (OR 2.74; 95% CI 1.72-4.37; p< 0.001; I=0%) and ovulation (OR 2.55; 95% CI 1.57-4.12; p< 0.001; I=35.9%). The number of mature follicles, number of pregnancies, thickness of endometrial lining, and the incidence of adverse events, including headache, abdominal bloating, fatigue, back pain, breast discomfort, and night sweats, were similar between groups.
Conclusion:
In women with anovulatory infertility secondary to PCOS, letrozole and clomiphene citrate combined therapy was associated with improved mature follicle and ovulation rates, with a similar safety profile compared to letrozole alone. However, no significant impact was observed on pregnancy rates.
Key-words ClomipheneInfertility, femaleLetrozoleOvulationOvulation InductionPolycystic ovary syndromeSee more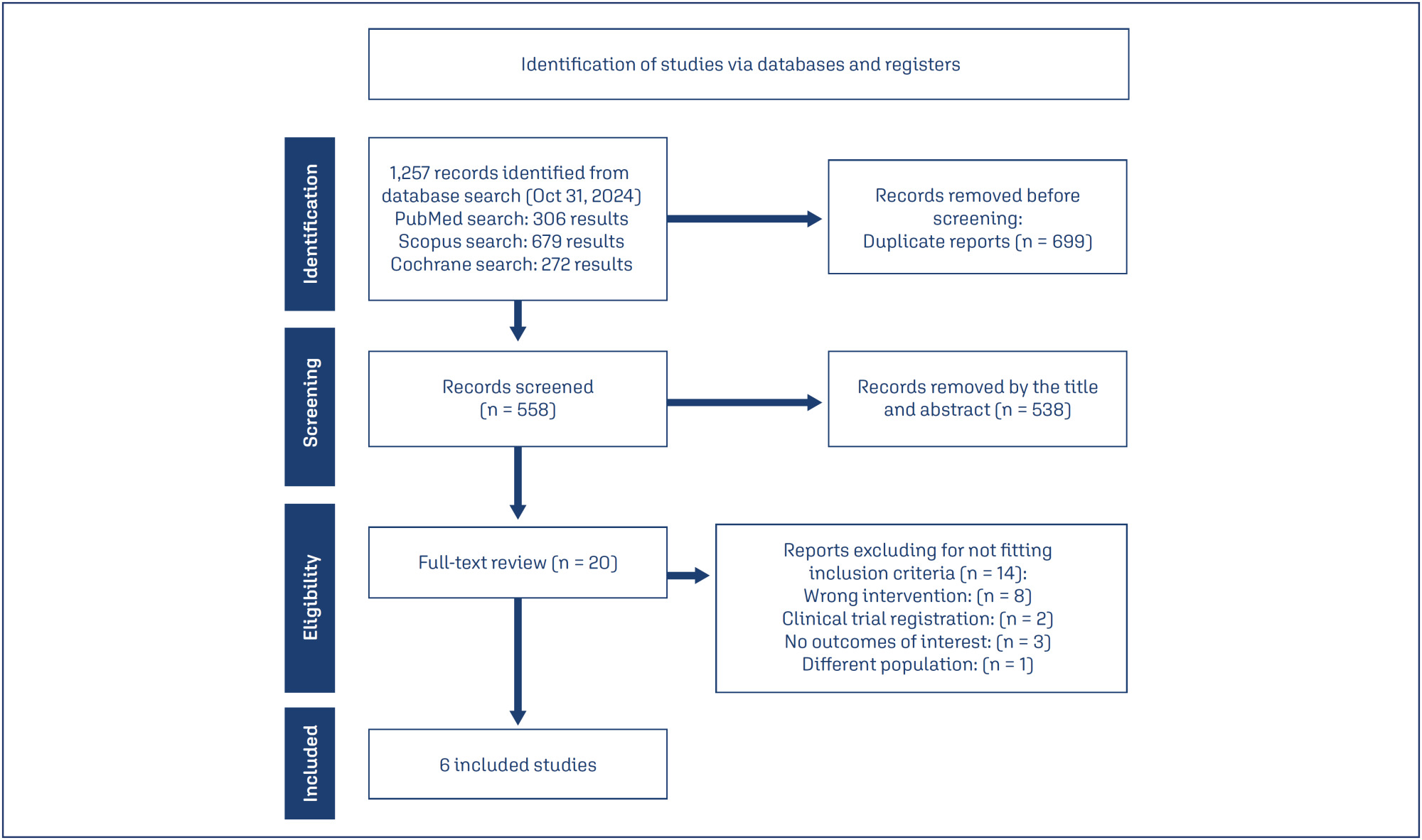
- Karine Eskandar
-
Original Article04-30-2025
Incidence of small-for-gestational-age newborns in pregnant women with COVID-19
- Gustavo dos Santos Raupp
 ,
, - Renato Teixeira Souza
 ,
, - Maria Laura Costa
 ,
, - Jose Guilherme Cecatti
 ,
, - Annerose Barros
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Janete Vettorazzi

Abstract
Original ArticleIncidence of small-for-gestational-age newborns in pregnant women with COVID-19
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo20
- Gustavo dos Santos Raupp
 ,
, - Renato Teixeira Souza
 ,
, - Maria Laura Costa
 ,
, - Jose Guilherme Cecatti
 ,
, - Annerose Barros
 ,
, - Ellen Machado Arlindo
 ,
, - Edson Vieira Cunha Filho
 ,
, - Janete Vettorazzi

Views130Abstract
Objective:
This study aimed to assess the incidence of small for gestational age (SGA) newborns in pregnant women infected with COVID-19 and examine the associated neonatal outcomes.
Methods:
This study involved a secondary analysis of the REBRACO Network, a prospective cohort study conducted in 15 maternity hospitals in Brazil before the introduction of COVID-19 vaccination (February 2020 to February 2021). Demographic data of pregnant women tested for COVID-19 were analyzed, and fetal outcomes were compared between women with positive and negative COVID-19 results who had SGA fetuses.
Results:
A total of 729 symptomatic pregnant women with COVID-19 were included in the study. However, there were 248 participants with missing information regarding childbirth or loss of follow-up, and 107 participants without confirmatory tests for COVID-19. Among the remaining participants, 198 had confirmed COVID-19 and 176 tested negative. The incidence of SGA among women with COVID-19 was 22.4%, whereas the incidence among women who tested negative for COVID-19 was 14.8%. SGA newborns born to COVID-19 positive pregnant women were 1.6 times more likely to experience adverse outcomes (such as prematurity, stillbirth, neonatal death, and admission to a neonatal ICU) compared to non-SGA newborns [OR = 1.655 (1.145 – 2.394); P=0.017]. In SGA newborns of pregnant women with confirmed COVID-19 infection, mechanical ventilation use was found to be associated with the infection [OR = 0.692 (0.562 – 0.853); P=0.002].
Conclusion:
The higher incidence of SGA newborns and its stronger association with prematurity in pregnant women with confirmed COVID-19 infection suggest that COVID-19 infection is a significant factor contributing to neonatal morbidity and mortality.
Key-words coronavirus infectionsCOVID-19Infant, newbornInfant, small for gestational agematernal healthPregnancy complicationsSee moreViews130

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleIncidence of small-for-gestational-age newborns in pregnant women with COVID-19
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo20
- Gustavo dos Santos Raupp
 ,
, - Renato Teixeira Souza
 ,
, - Maria Laura Costa
 ,
, - Jose Guilherme Cecatti
 ,
, - Annerose Barros
 ,
, - Ellen Machado Arlindo
 ,
, - Edson Vieira Cunha Filho
 ,
, - Janete Vettorazzi

Views130Abstract
Objective:
This study aimed to assess the incidence of small for gestational age (SGA) newborns in pregnant women infected with COVID-19 and examine the associated neonatal outcomes.
Methods:
This study involved a secondary analysis of the REBRACO Network, a prospective cohort study conducted in 15 maternity hospitals in Brazil before the introduction of COVID-19 vaccination (February 2020 to February 2021). Demographic data of pregnant women tested for COVID-19 were analyzed, and fetal outcomes were compared between women with positive and negative COVID-19 results who had SGA fetuses.
Results:
A total of 729 symptomatic pregnant women with COVID-19 were included in the study. However, there were 248 participants with missing information regarding childbirth or loss of follow-up, and 107 participants without confirmatory tests for COVID-19. Among the remaining participants, 198 had confirmed COVID-19 and 176 tested negative. The incidence of SGA among women with COVID-19 was 22.4%, whereas the incidence among women who tested negative for COVID-19 was 14.8%. SGA newborns born to COVID-19 positive pregnant women were 1.6 times more likely to experience adverse outcomes (such as prematurity, stillbirth, neonatal death, and admission to a neonatal ICU) compared to non-SGA newborns [OR = 1.655 (1.145 – 2.394); P=0.017]. In SGA newborns of pregnant women with confirmed COVID-19 infection, mechanical ventilation use was found to be associated with the infection [OR = 0.692 (0.562 – 0.853); P=0.002].
Conclusion:
The higher incidence of SGA newborns and its stronger association with prematurity in pregnant women with confirmed COVID-19 infection suggest that COVID-19 infection is a significant factor contributing to neonatal morbidity and mortality.
Key-words coronavirus infectionsCOVID-19Infant, newbornInfant, small for gestational agematernal healthPregnancy complicationsSee more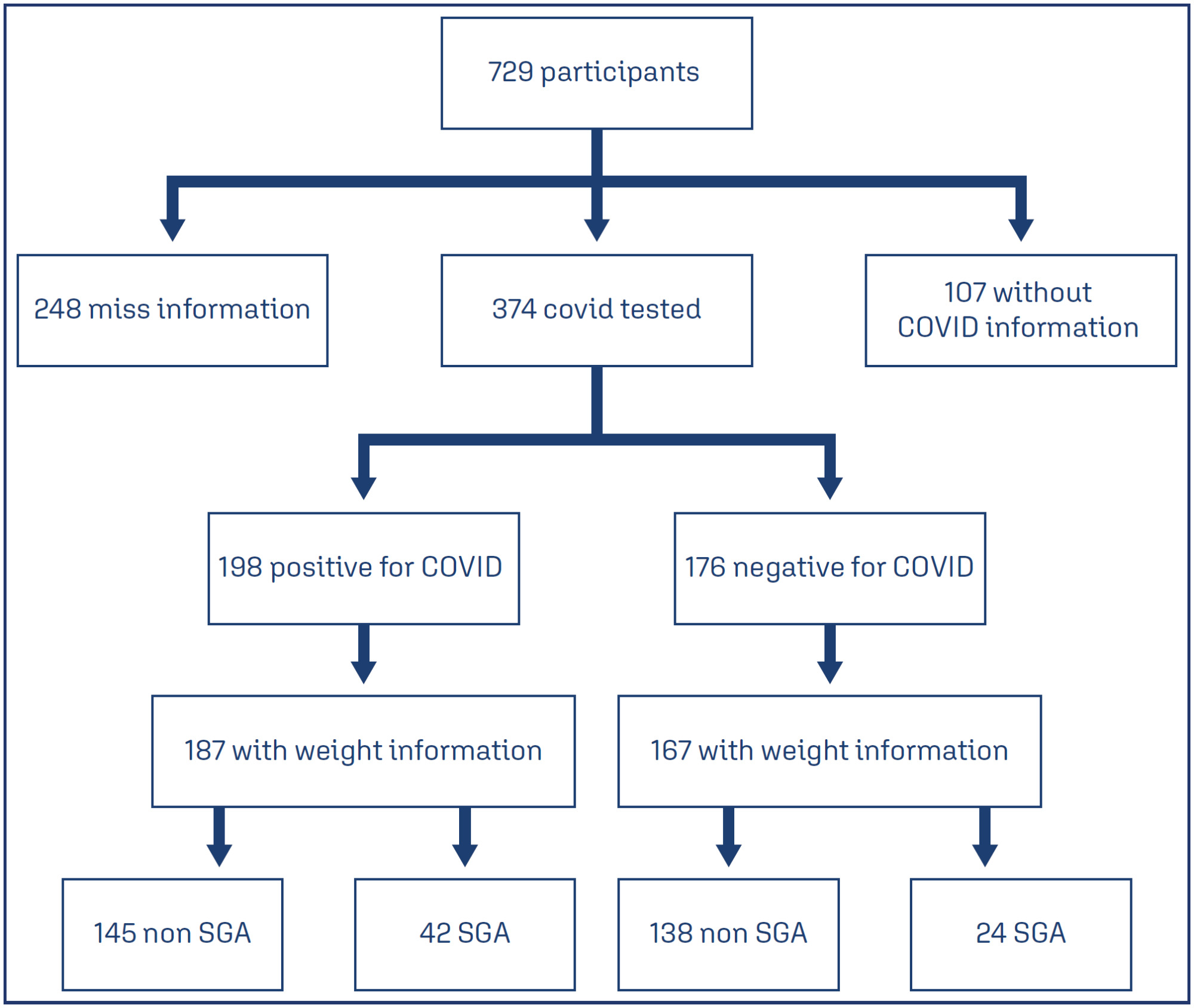
- Gustavo dos Santos Raupp
-
Review Article04-30-2025
Efficacy of tranexamic acid application in gynecology and obstetrics procedures: a umbrella review of systematic reviews of randomized trials
- Nicole Cristina Lottermann
 ,
, - Nathalia Luiza Andreazza
 ,
, - Matheus de Araújo Moura Cavalcante
 ,
, - Laura Andrade Fernandez
 ,
, - Carla Vitola Gonçalvez
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Linjie Zhang

Abstract
Review ArticleEfficacy of tranexamic acid application in gynecology and obstetrics procedures: a umbrella review of systematic reviews of randomized trials
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo18
- Nicole Cristina Lottermann
 ,
, - Nathalia Luiza Andreazza
 ,
, - Matheus de Araújo Moura Cavalcante
 ,
, - Laura Andrade Fernandez
 ,
, - Carla Vitola Gonçalvez
 ,
, - Linjie Zhang

Views135Abstract
Objective:
This umbrella review aimed to synthesize evidence from systematic reviews of clinical trials on the efficacy of tranexamic acid in gynecology and obstetrics procedures.
Methods:
We searched Medline, Embase, SciELO and Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews on March 11, 2024, using the term “tranexamic acid”. Four reviewers independently select studies and extract data. We assessed the quality of systematic review and the quality of evidence, using AMSTAR 2 and GRADE tools, respectively.
Results:
Of 651 systematic reviews identified, 16 reviews with 96663 patients were included. The surgical procedures were cesarean section, myomectomy, hysterectomy, and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia surgery. All reviews showed a statistically significant and clinically relevant reduction in intraoperative and post-procedure blood loss, associated with intravenous or topical use of tranexamic acid. Tranexamic acid resulted in a significant reduction in the need for blood transfusions and a less pronounced drop in postoperative hematocrit and hemoglobin levels in cesarean section. Several reviews addressed the same question, but the number of included trials varied substantially, which might indicate flaws in search and selection of studies of these reviews. The quality of systematic reviews was low or critically low, and the quality of evidence was moderate.
Conclusions:
This umbrella review shows that tranexamic acid can reduce blood loss and hemorrhage in gynecology and obstetrics procedures. High quality systematic reviews are still needed.
Key-words Blood transfusionCesarean sectionEfficacyGynecologic surgical procedureshematocritHemorrhageHysterectomyObstetric surgical proceduresTranexamic acidUterine cervical dysplasiauterine myomectomySee moreViews135

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleEfficacy of tranexamic acid application in gynecology and obstetrics procedures: a umbrella review of systematic reviews of randomized trials
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo18
- Nicole Cristina Lottermann
 ,
, - Nathalia Luiza Andreazza
 ,
, - Matheus de Araújo Moura Cavalcante
 ,
, - Laura Andrade Fernandez
 ,
, - Carla Vitola Gonçalvez
 ,
, - Linjie Zhang

Views135Abstract
Objective:
This umbrella review aimed to synthesize evidence from systematic reviews of clinical trials on the efficacy of tranexamic acid in gynecology and obstetrics procedures.
Methods:
We searched Medline, Embase, SciELO and Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews on March 11, 2024, using the term “tranexamic acid”. Four reviewers independently select studies and extract data. We assessed the quality of systematic review and the quality of evidence, using AMSTAR 2 and GRADE tools, respectively.
Results:
Of 651 systematic reviews identified, 16 reviews with 96663 patients were included. The surgical procedures were cesarean section, myomectomy, hysterectomy, and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia surgery. All reviews showed a statistically significant and clinically relevant reduction in intraoperative and post-procedure blood loss, associated with intravenous or topical use of tranexamic acid. Tranexamic acid resulted in a significant reduction in the need for blood transfusions and a less pronounced drop in postoperative hematocrit and hemoglobin levels in cesarean section. Several reviews addressed the same question, but the number of included trials varied substantially, which might indicate flaws in search and selection of studies of these reviews. The quality of systematic reviews was low or critically low, and the quality of evidence was moderate.
Conclusions:
This umbrella review shows that tranexamic acid can reduce blood loss and hemorrhage in gynecology and obstetrics procedures. High quality systematic reviews are still needed.
Key-words Blood transfusionCesarean sectionEfficacyGynecologic surgical procedureshematocritHemorrhageHysterectomyObstetric surgical proceduresTranexamic acidUterine cervical dysplasiauterine myomectomySee more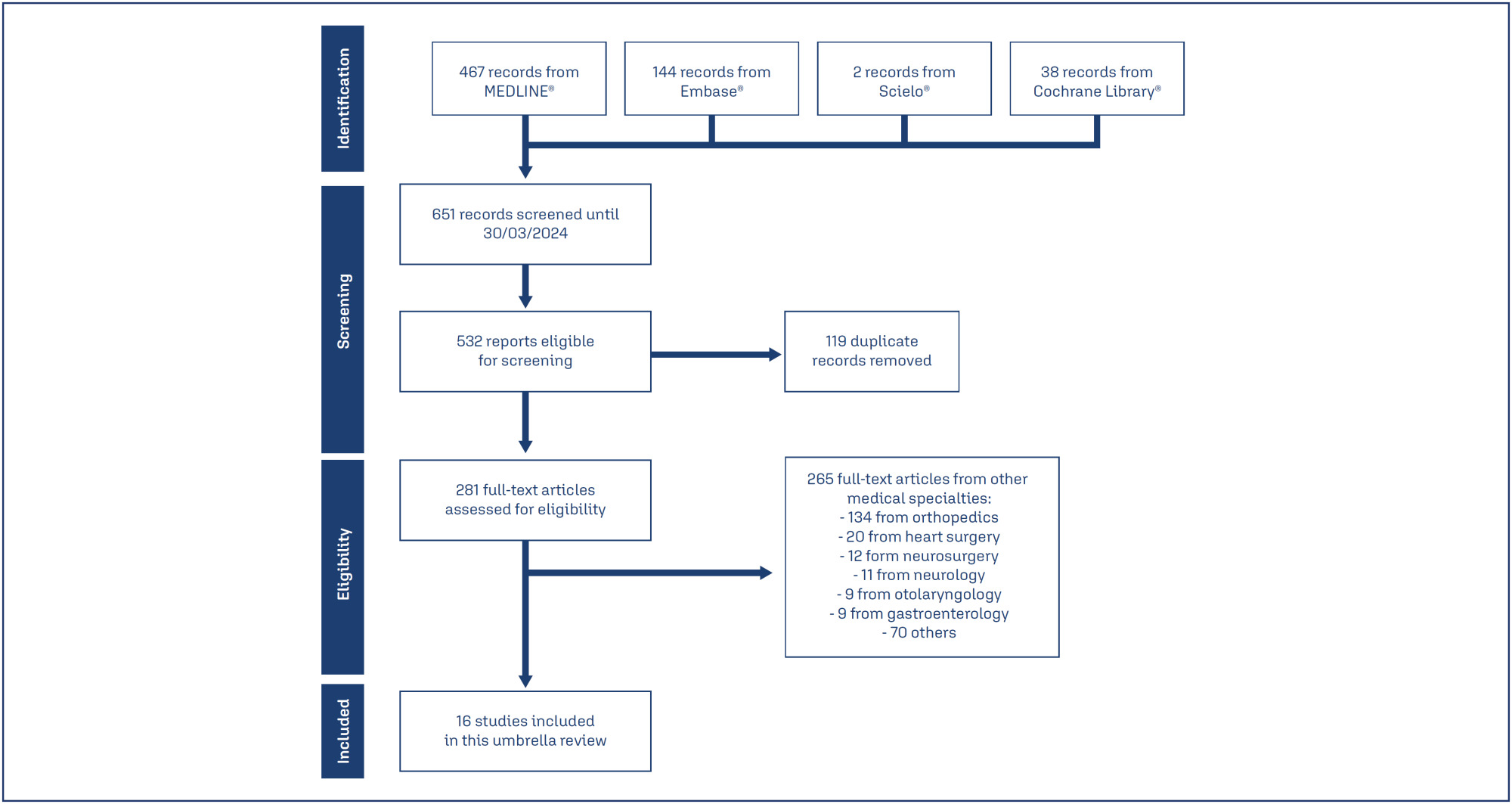
- Nicole Cristina Lottermann
-
Original Article04-30-2025
Assessıng the predıctıve accuracy of blood-based bıomarkers ın neonatal outcomes for pregestatıonal dıabetes mellıtus
- Ayse Cigdem Bayrak
 ,
, - Erdem Fadiloglu
 ,
, - Haticegul Tuncer
 ,
, - Edip Alptug Kir
 ,
, - Umutcan Kayikci
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Ozgur Deren

Abstract
Original ArticleAssessıng the predıctıve accuracy of blood-based bıomarkers ın neonatal outcomes for pregestatıonal dıabetes mellıtus
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo17
- Ayse Cigdem Bayrak
 ,
, - Erdem Fadiloglu
 ,
, - Haticegul Tuncer
 ,
, - Edip Alptug Kir
 ,
, - Umutcan Kayikci
 ,
, - Ozgur Deren

Views114Abstract
Objective:
This retrospective study aimed to investigate blood-based immune-inflammatory biomarkers (IIBs) in predicting neonatal outcomes in pregnancies with pregestational diabetes mellitus (PGDM).PIV[(neutrophil×platelet×monocyte)/lymphocyte)], SII (neutrophil×platelet/lymphocyte), and NLR neutrophil/lymphocyte) values were evaluated in all three trimesters, and their correlation with neonatal outcomes was examined.
Methods:
We included 82 cases of PGDM pregnancies delivered after 32 weeks. Maternal age, gravidity, parity, types of diabetes, and route of delivery were noted. For neonatal outcomes, we recorded gestational age at birth, birth weight percentile, existence of fetal growth restriction, LGA, neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) requirement, Apgar Score <7 at 1, 5, or 10 minutes, need for positive pressure ventilation (PPV), need for mechanical ventilation, hypoglycaemia, hyperbilirubinemia and the need for phototherapy. PIV, SII and NLR values were calculated in each trimester and their association with adverse neonatal outcomes was analyzed.
Results:
We could not detect any consistent and significant correlation between SII and PIV values and adverse neonatal outcomes for each trimester. There was a correlation between 3rd trimester NLR and adverse neonatal outcomes, including APGAR <7, the requirement for PPV and mechanical ventilation (p=0.056, 0.013 and 0.060, respectively).
Conclusion:
While SII and PIV values did not consistently correlate with adverse neonatal outcomes throughout each trimester in PGDM pregnancies, 3rd-trimester NLR showed a notable association with the requirement for PPV with statistical significance and with Apgar Score <7 and the requirement for mechanical ventilation without statistical significance. NLR in the third trimester may hold potential as a predictive marker for specific adverse neonatal outcomes in PGDM pregnancies, warranting further investigation.
Key-words biomarkersDiabetes mellitusGestational ageHypoglycemiaInfant, newbornIntensive care units, neonatalLymphocytesMaternal ageMonocytesNeuthrophilsPregancyPregnancy in diabetesRespiration, artificialSee moreViews114

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleAssessıng the predıctıve accuracy of blood-based bıomarkers ın neonatal outcomes for pregestatıonal dıabetes mellıtus
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo17
- Ayse Cigdem Bayrak
 ,
, - Erdem Fadiloglu
 ,
, - Haticegul Tuncer
 ,
, - Edip Alptug Kir
 ,
, - Umutcan Kayikci
 ,
, - Ozgur Deren

Views114Abstract
Objective:
This retrospective study aimed to investigate blood-based immune-inflammatory biomarkers (IIBs) in predicting neonatal outcomes in pregnancies with pregestational diabetes mellitus (PGDM).PIV[(neutrophil×platelet×monocyte)/lymphocyte)], SII (neutrophil×platelet/lymphocyte), and NLR neutrophil/lymphocyte) values were evaluated in all three trimesters, and their correlation with neonatal outcomes was examined.
Methods:
We included 82 cases of PGDM pregnancies delivered after 32 weeks. Maternal age, gravidity, parity, types of diabetes, and route of delivery were noted. For neonatal outcomes, we recorded gestational age at birth, birth weight percentile, existence of fetal growth restriction, LGA, neonatal intensive care unit (NICU) requirement, Apgar Score <7 at 1, 5, or 10 minutes, need for positive pressure ventilation (PPV), need for mechanical ventilation, hypoglycaemia, hyperbilirubinemia and the need for phototherapy. PIV, SII and NLR values were calculated in each trimester and their association with adverse neonatal outcomes was analyzed.
Results:
We could not detect any consistent and significant correlation between SII and PIV values and adverse neonatal outcomes for each trimester. There was a correlation between 3rd trimester NLR and adverse neonatal outcomes, including APGAR <7, the requirement for PPV and mechanical ventilation (p=0.056, 0.013 and 0.060, respectively).
Conclusion:
While SII and PIV values did not consistently correlate with adverse neonatal outcomes throughout each trimester in PGDM pregnancies, 3rd-trimester NLR showed a notable association with the requirement for PPV with statistical significance and with Apgar Score <7 and the requirement for mechanical ventilation without statistical significance. NLR in the third trimester may hold potential as a predictive marker for specific adverse neonatal outcomes in PGDM pregnancies, warranting further investigation.
Key-words biomarkersDiabetes mellitusGestational ageHypoglycemiaInfant, newbornIntensive care units, neonatalLymphocytesMaternal ageMonocytesNeuthrophilsPregancyPregnancy in diabetesRespiration, artificialSee more - Ayse Cigdem Bayrak
-
Original Article11-28-2005
Cardiofemoral index for the evaluation of fetal anemia in isoimmunized pregnancies
- Antônio Carlos Vieira Cabral,
- Thales Bittencourt de Barcelos,
- Isabela Gomes Melo Apocalipse,
- Henrique Vitor Leite,
- Zilma Silveira Nogueira Reis
Abstract
Original ArticleCardiofemoral index for the evaluation of fetal anemia in isoimmunized pregnancies
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(8):450-455
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000800003
- Antônio Carlos Vieira Cabral,
- Thales Bittencourt de Barcelos,
- Isabela Gomes Melo Apocalipse,
- Henrique Vitor Leite,
- Zilma Silveira Nogueira Reis
Views130See morePURPOSE: to test a new, noninvasive method for the diagnosis of fetal anemia in red blood cell isoimmunized pregnancies. METHODS: the index obtained by the ratio between the ultrasonographic measurement of the biventricular outer dimension (BVOD) and femur length (both in centimeters) was correlated with fetal hemoglobin values in a cross-sectional study. Fifty-nine fetuses of isoimmunized pregnancies selected for invasive treatment and submitted to 130 cordocenteses for the diagnosis and treatment of anemia were included in the study. The cardiofemoral index was obtained immediately before the cordocentesis and the fetal hemoglobin index was obtained from fetal blood samples. Linear regression was carried out to assess the correlation between the index and fetal hemoglobin; ROC curve was applied to determine the most accurate cutoff for the diagnosis of the fetal hemoglobin concentration below 10g/dl. RESULTS: BVOD measurement varied from 1.6 to 4.7 cm (average 2.5±1.3cm), and length of the femur, from 3.0 to 6.9 cm (average 4.3±0.9 cm). The cardiofemoral index varied from 0.4 to 1.0 (average 0.6±0.1). A significant inverse correlation between the cardiofemoral index and fetal hemoglobin (R²=0.37 and p<0.0001) was observed. The cutoff of 0.60 was the best to predict a level of fetal hemoglobin below or equal to 10.0g/dl: 80.85% sensitivity, 83.13% specificity, 73.8% positive predictive value, and 88.46% negative predictive value, in the diagnosis of fetuses anemia. CONCLUSION: the cardiofemoral index allows for good accuracy in the prediction of fetal hemoglobin concentration below 10g/dl in red blood cell isoimmunized pregnancies. It may thus be applied as a noninvasive method to the diagnosis of this pathology.
Views130

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleCardiofemoral index for the evaluation of fetal anemia in isoimmunized pregnancies
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(8):450-455
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000800003
- Antônio Carlos Vieira Cabral,
- Thales Bittencourt de Barcelos,
- Isabela Gomes Melo Apocalipse,
- Henrique Vitor Leite,
- Zilma Silveira Nogueira Reis
Views130See morePURPOSE: to test a new, noninvasive method for the diagnosis of fetal anemia in red blood cell isoimmunized pregnancies. METHODS: the index obtained by the ratio between the ultrasonographic measurement of the biventricular outer dimension (BVOD) and femur length (both in centimeters) was correlated with fetal hemoglobin values in a cross-sectional study. Fifty-nine fetuses of isoimmunized pregnancies selected for invasive treatment and submitted to 130 cordocenteses for the diagnosis and treatment of anemia were included in the study. The cardiofemoral index was obtained immediately before the cordocentesis and the fetal hemoglobin index was obtained from fetal blood samples. Linear regression was carried out to assess the correlation between the index and fetal hemoglobin; ROC curve was applied to determine the most accurate cutoff for the diagnosis of the fetal hemoglobin concentration below 10g/dl. RESULTS: BVOD measurement varied from 1.6 to 4.7 cm (average 2.5±1.3cm), and length of the femur, from 3.0 to 6.9 cm (average 4.3±0.9 cm). The cardiofemoral index varied from 0.4 to 1.0 (average 0.6±0.1). A significant inverse correlation between the cardiofemoral index and fetal hemoglobin (R²=0.37 and p<0.0001) was observed. The cutoff of 0.60 was the best to predict a level of fetal hemoglobin below or equal to 10.0g/dl: 80.85% sensitivity, 83.13% specificity, 73.8% positive predictive value, and 88.46% negative predictive value, in the diagnosis of fetuses anemia. CONCLUSION: the cardiofemoral index allows for good accuracy in the prediction of fetal hemoglobin concentration below 10g/dl in red blood cell isoimmunized pregnancies. It may thus be applied as a noninvasive method to the diagnosis of this pathology.
-
Original Article01-30-2005
Fetal macrosomia risk factors in pregnancies complicated by diabetes or daily hyperglycemia
- Luciane Teresa Rodrigues Lima Kerche,
- Joelcio Francisco Abbade,
- Roberto Antonio Araújo Costa,
- Marilza Vieira Cunha Rudge,
- Iracema de Mattos Paranhos Calderon
Abstract
Original ArticleFetal macrosomia risk factors in pregnancies complicated by diabetes or daily hyperglycemia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(10):580-587
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001000003
- Luciane Teresa Rodrigues Lima Kerche,
- Joelcio Francisco Abbade,
- Roberto Antonio Araújo Costa,
- Marilza Vieira Cunha Rudge,
- Iracema de Mattos Paranhos Calderon
Views110See morePURPOSE: to identify risk factors for fetal macrosomia in pregnant women with diabetes or daily hyperglycemia. METHODS: retrospective study, control-case, including 803 pairs of mothers and newborns belonging to this specific population, divided into two groups – macrosomic (cases, n=242) and non-macrosomic (controls, n=561). Variables regarding age, parity, weight and body mass index (BMI), weight gain (WG), diabetes history, high blood pressure and tabagism, diabetes type and classification, and glycemic control indicators in the third trimester were compared. The means were evaluated by the F test and the categorized variables were submitted to univariate analysis using the chi² test. The significative results were included in the multiple regression model for the identification of macrosomia independent risk considering OR, 95% CI and p value. The statistical significance limit of 5% was established for all analyses. RESULTS: there was a significative association between macrosomia and WG >16 kg, BMI >25 kg/m², personal, obstetric and macrosomic history, classification in the Rudge groups (IB and IIA + IIB), glycemic mean (GM) >120 mg/dL and postprandial glycemic mean >130 mg/dL in the third trimester. In the multiple regression analysis, WG >16 kg (OR=1,79; 95% CI: 1,23-1.60), BMI >25 kg/m² (OR=1.83; 95% CI: 1.27-2.64), personal history of diabetes (OR=1.56; 95% CI: 1.05-2.31) and of macrosomia (OR=2.37; 95% CI: 1.60-3.50) and GM >120 mg/dL in the third trimester (OR=1.78; 95% CI: 1.13-2.80) confirmed to be independent risk factors for macrosomia in these pregnancies. CONCLUSION: WG >16 kg, BMI >25 kg/m², GM >120 mg/dL in the third trimester and personal history of macrosomia and diabetes were identified as risk factors for fetal macrosomia in pregnant women with diabetes or daily hyperglycemia.
Views110

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleFetal macrosomia risk factors in pregnancies complicated by diabetes or daily hyperglycemia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(10):580-587
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001000003
- Luciane Teresa Rodrigues Lima Kerche,
- Joelcio Francisco Abbade,
- Roberto Antonio Araújo Costa,
- Marilza Vieira Cunha Rudge,
- Iracema de Mattos Paranhos Calderon
Views110See morePURPOSE: to identify risk factors for fetal macrosomia in pregnant women with diabetes or daily hyperglycemia. METHODS: retrospective study, control-case, including 803 pairs of mothers and newborns belonging to this specific population, divided into two groups – macrosomic (cases, n=242) and non-macrosomic (controls, n=561). Variables regarding age, parity, weight and body mass index (BMI), weight gain (WG), diabetes history, high blood pressure and tabagism, diabetes type and classification, and glycemic control indicators in the third trimester were compared. The means were evaluated by the F test and the categorized variables were submitted to univariate analysis using the chi² test. The significative results were included in the multiple regression model for the identification of macrosomia independent risk considering OR, 95% CI and p value. The statistical significance limit of 5% was established for all analyses. RESULTS: there was a significative association between macrosomia and WG >16 kg, BMI >25 kg/m², personal, obstetric and macrosomic history, classification in the Rudge groups (IB and IIA + IIB), glycemic mean (GM) >120 mg/dL and postprandial glycemic mean >130 mg/dL in the third trimester. In the multiple regression analysis, WG >16 kg (OR=1,79; 95% CI: 1,23-1.60), BMI >25 kg/m² (OR=1.83; 95% CI: 1.27-2.64), personal history of diabetes (OR=1.56; 95% CI: 1.05-2.31) and of macrosomia (OR=2.37; 95% CI: 1.60-3.50) and GM >120 mg/dL in the third trimester (OR=1.78; 95% CI: 1.13-2.80) confirmed to be independent risk factors for macrosomia in these pregnancies. CONCLUSION: WG >16 kg, BMI >25 kg/m², GM >120 mg/dL in the third trimester and personal history of macrosomia and diabetes were identified as risk factors for fetal macrosomia in pregnant women with diabetes or daily hyperglycemia.
-
Original Article01-12-2008
Tibolone’s effect on retinal and ophthalmic arteries flowmetry
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(11):537-543
Abstract
Original ArticleTibolone’s effect on retinal and ophthalmic arteries flowmetry
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(11):537-543
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001100002
Views118PURPOSE: to evaluate the effect of tibolone use on dopplervelocimetric parameters of ophthalmic and retinal arteries. METHODS: clinical, prospective, longitudinal, randomized, placebo-controlled, triple-blind study, in which among 100 menopausal women, 50 have used 2.5 mg of the active principle tibolone (Tib Group) and 50, placebo as a means to form the control-group (Plac Group). In the Tib Group, 44 of the 50 women returned after 84 days to finish the exams, and in the Plac Group, 47. The ophthalmic and retinal arteries were studied to determine the resistance index (RI), the pulsatility index (PI) and the systole/diastole ratio (S/D). Assessments have been done before and 84 days after medication. The t-Student test has been used for the comparison of means between the groups in independent samples, as well as for within-group comparisons in dependent samples. RESULTS: in both groups, the women’s characteristics were similar in age, menopause duration, body mass index, arterial blood pressure, deliveries and cardiac rate. The Tib Group presented the following values in the ophthalmic artery: RI(pre)=0.71±0.05, RI(post)0.72±0.08 (p=0.43); PI(pre)=1.29±0.22, PI(post)=1.30±0.25 (p=0.4) and S/D(pre)=3.49±0.77, SD(post)=3.65±0.94 (p=0.32). In the retinal artery, the following values have been found: RI(pre)=0.67±0.09, RI(post)=0.69±0.10 (p=0.7); PI(pre)=1.20±0.29, PI(post)=1.22±0.3 (p=0.2) and SD(pre)=3.29±0.95, SD(post)=3.30±1.07 (p=0.3). Also, the tibolone and control groups did not show any significant difference in regard to the above indexes in the end of the study. CONCLUSIONS: the 2.5 mg dose of tibolone had no effect on the Doppler velocimetry indexes of the ophthalmic and retinal arteries.
Key-words Laser-doppler flowmetryNorpregnanesOphthalmic arteryPlacebosRandomized controlled trialsRetinal arteryUltrasonographySee moreViews118

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleTibolone’s effect on retinal and ophthalmic arteries flowmetry
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(11):537-543
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001100002
Views118PURPOSE: to evaluate the effect of tibolone use on dopplervelocimetric parameters of ophthalmic and retinal arteries. METHODS: clinical, prospective, longitudinal, randomized, placebo-controlled, triple-blind study, in which among 100 menopausal women, 50 have used 2.5 mg of the active principle tibolone (Tib Group) and 50, placebo as a means to form the control-group (Plac Group). In the Tib Group, 44 of the 50 women returned after 84 days to finish the exams, and in the Plac Group, 47. The ophthalmic and retinal arteries were studied to determine the resistance index (RI), the pulsatility index (PI) and the systole/diastole ratio (S/D). Assessments have been done before and 84 days after medication. The t-Student test has been used for the comparison of means between the groups in independent samples, as well as for within-group comparisons in dependent samples. RESULTS: in both groups, the women’s characteristics were similar in age, menopause duration, body mass index, arterial blood pressure, deliveries and cardiac rate. The Tib Group presented the following values in the ophthalmic artery: RI(pre)=0.71±0.05, RI(post)0.72±0.08 (p=0.43); PI(pre)=1.29±0.22, PI(post)=1.30±0.25 (p=0.4) and S/D(pre)=3.49±0.77, SD(post)=3.65±0.94 (p=0.32). In the retinal artery, the following values have been found: RI(pre)=0.67±0.09, RI(post)=0.69±0.10 (p=0.7); PI(pre)=1.20±0.29, PI(post)=1.22±0.3 (p=0.2) and SD(pre)=3.29±0.95, SD(post)=3.30±1.07 (p=0.3). Also, the tibolone and control groups did not show any significant difference in regard to the above indexes in the end of the study. CONCLUSIONS: the 2.5 mg dose of tibolone had no effect on the Doppler velocimetry indexes of the ophthalmic and retinal arteries.
Key-words Laser-doppler flowmetryNorpregnanesOphthalmic arteryPlacebosRandomized controlled trialsRetinal arteryUltrasonographySee more -
Original Article07-02-2010
Myomectomy in the second trimester of pregnancy: case report
- Guilherme Karam Corrêa Leite,
- Henri Augusto Korkes,
- Arildo de Toledo Viana,
- Alexandre Pitorri,
- Grecy Kenj, [ … ],
- Nelson Sass
Abstract
Original ArticleMyomectomy in the second trimester of pregnancy: case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(4):198-201
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000400008
- Guilherme Karam Corrêa Leite,
- Henri Augusto Korkes,
- Arildo de Toledo Viana,
- Alexandre Pitorri,
- Grecy Kenj,
- Nelson Sass
Views109See moreUterine leiomyomas are characterized as a benign disease and are observed in 2 to 3% of all normal pregnancies. Out of these, about 10% may present complications during pregnancy. We present a case of a pregnant patient sought emergency obstetric care at the 17th week, complaining of severe pain, presenting with painful abdominal palpation and sudden positive decompression. Ultrasonography revealed a myoma nodule measuring 9.1 x 7.7 cm; the patient was hospitalized and medicated, being also submitted to laparotomy and myomectomy due to worsening of her condition. Prenatal care revealed no further abnormalities, with resolution of gestation at 39 weeks. The newborn weighed 3,315 g, with Apgar scores of 9 and 10. In such cases, clinical treatment should always be attempted and surgery should be considered only in selected cases, mainly in the impossibility of conservative treatment or when the patient’s clinical features require immediate intervention. In this case, myomectomy was effective against maternal-fetal obstetric complications.
Views109

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleMyomectomy in the second trimester of pregnancy: case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(4):198-201
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000400008
- Guilherme Karam Corrêa Leite,
- Henri Augusto Korkes,
- Arildo de Toledo Viana,
- Alexandre Pitorri,
- Grecy Kenj,
- Nelson Sass
Views109See moreUterine leiomyomas are characterized as a benign disease and are observed in 2 to 3% of all normal pregnancies. Out of these, about 10% may present complications during pregnancy. We present a case of a pregnant patient sought emergency obstetric care at the 17th week, complaining of severe pain, presenting with painful abdominal palpation and sudden positive decompression. Ultrasonography revealed a myoma nodule measuring 9.1 x 7.7 cm; the patient was hospitalized and medicated, being also submitted to laparotomy and myomectomy due to worsening of her condition. Prenatal care revealed no further abnormalities, with resolution of gestation at 39 weeks. The newborn weighed 3,315 g, with Apgar scores of 9 and 10. In such cases, clinical treatment should always be attempted and surgery should be considered only in selected cases, mainly in the impossibility of conservative treatment or when the patient’s clinical features require immediate intervention. In this case, myomectomy was effective against maternal-fetal obstetric complications.
-
Original Article01-06-2011
Assessment of fetal well-being in pregnancies complicated by maternal moderate to severe thrombocytopenia
- Roseli Mieko Yamamoto Nomura,
- Ana Maria Kondo Igai,
- Verbênia Nunes Costa,
- Seizo Miyadahira,
- Marcelo Zugaib
Abstract
Original ArticleAssessment of fetal well-being in pregnancies complicated by maternal moderate to severe thrombocytopenia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(10):280-285
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011001000002
- Roseli Mieko Yamamoto Nomura,
- Ana Maria Kondo Igai,
- Verbênia Nunes Costa,
- Seizo Miyadahira,
- Marcelo Zugaib
Views117See morePURPOSE: To analyze the results of assessment of fetal well-being in pregnancies complicated by moderate or severe maternal thrombocytopenia. METHODS: Data from April 2001 to July 2011 of 96 women with a diagnosis of thrombocytopenia in pregnancy were retrospectively analyzed. We analyzed the following tests performed during the antepartum period for fetal assessment: cardiotocography, fetal biophysical profile, amniotic fluid index and umbilical artery Doppler velocimetry. RESULTS: A total of 96 pregnancies with the following diagnoses were analyzed: gestational thrombocytopenia (n=37, 38.5%) hypersplenism (n=32, 33.3%), immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP, n=14, 14.6%), secondary immune thrombocytopenia (n=6, 6.3%), bone marrow aplasia (n=3, 3.1%), and others (n=4, 4.1%). Cardiotocography showed normal results in 94% of cases, a fetal biophysical profile with an index of 8 or 10 in 96.9% and an amniotic fluid index >5.0 cm in 89.6%. Doppler umbilical artery velocimetry showed normal results in 96.9% of cases. In the analysis of the major groups of thrombocytopenia, the diagnosis of oligohydramnios was found to be significantly more frequent in the group with ITP (28.6%) compared to the other groups (gestational thrombocytopenia: 5.4% and hypersplenism: 9.4%, p=0.04). CONCLUSIONS: This study indicates that in pregnancies complicated by moderate or severe maternal thrombocytopenia, even though the fetal well-being remains preserved in most cases, fetal surveillance is important in pregnant women with ITP, with emphasis on amniotic fluid volume evaluation due to its association with oligohydramnios.
Views117

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleAssessment of fetal well-being in pregnancies complicated by maternal moderate to severe thrombocytopenia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(10):280-285
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011001000002
- Roseli Mieko Yamamoto Nomura,
- Ana Maria Kondo Igai,
- Verbênia Nunes Costa,
- Seizo Miyadahira,
- Marcelo Zugaib
Views117See morePURPOSE: To analyze the results of assessment of fetal well-being in pregnancies complicated by moderate or severe maternal thrombocytopenia. METHODS: Data from April 2001 to July 2011 of 96 women with a diagnosis of thrombocytopenia in pregnancy were retrospectively analyzed. We analyzed the following tests performed during the antepartum period for fetal assessment: cardiotocography, fetal biophysical profile, amniotic fluid index and umbilical artery Doppler velocimetry. RESULTS: A total of 96 pregnancies with the following diagnoses were analyzed: gestational thrombocytopenia (n=37, 38.5%) hypersplenism (n=32, 33.3%), immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP, n=14, 14.6%), secondary immune thrombocytopenia (n=6, 6.3%), bone marrow aplasia (n=3, 3.1%), and others (n=4, 4.1%). Cardiotocography showed normal results in 94% of cases, a fetal biophysical profile with an index of 8 or 10 in 96.9% and an amniotic fluid index >5.0 cm in 89.6%. Doppler umbilical artery velocimetry showed normal results in 96.9% of cases. In the analysis of the major groups of thrombocytopenia, the diagnosis of oligohydramnios was found to be significantly more frequent in the group with ITP (28.6%) compared to the other groups (gestational thrombocytopenia: 5.4% and hypersplenism: 9.4%, p=0.04). CONCLUSIONS: This study indicates that in pregnancies complicated by moderate or severe maternal thrombocytopenia, even though the fetal well-being remains preserved in most cases, fetal surveillance is important in pregnant women with ITP, with emphasis on amniotic fluid volume evaluation due to its association with oligohydramnios.
-
Original Article01-10-2013
Quality of clinical studies published in the RBGO over one decade (1999-2009): methodological and ethical aspects and statistical procedures
- Joceline Cássia Ferezini de Sá,
- Gabriela Marini,
- Rafael Bottaro Gelaleti,
- João Batista da Silva,
- George Dantas de Azevedo, [ … ],
- Marilza Vieira Cunha Rudge
Abstract
Original ArticleQuality of clinical studies published in the RBGO over one decade (1999-2009): methodological and ethical aspects and statistical procedures
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(11):477-482
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013001100001
- Joceline Cássia Ferezini de Sá,
- Gabriela Marini,
- Rafael Bottaro Gelaleti,
- João Batista da Silva,
- George Dantas de Azevedo,
- Marilza Vieira Cunha Rudge
Views121PURPOSE: To evaluate the methodological and statistical design evolution of the publications in the Brazilian Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics (RBGO) from resolution 196/96. METHODS: A review of 133 articles published in 1999 (65) and 2009 (68) was performed by two independent reviewers with training in clinical epidemiology and methodology of scientific research. We included all original clinical articles, case and series reports and excluded editorials, letters to the editor, systematic reviews, experimental studies, opinion articles, besides abstracts of theses and dissertations. Characteristics related to the methodological quality of the studies were analyzed in each article using a checklist that evaluated two criteria: methodological aspects and statistical procedures. We used descriptive statistics and the χ2 test for comparison of the two years. RESULTS: There was a difference between 1999 and 2009 regarding the study and statistical design, with more accuracy in the procedures and the use of more robust tests between 1999 and 2009. CONCLUSIONS: In RBGO, we observed an evolution in the methods of published articles and a more in-depth use of the statistical analyses, with more sophisticated tests such as regression and multilevel analyses, which are essential techniques for the knowledge and planning of health interventions, leading to fewer interpretation errors.
Key-words Clinical trials as topicEthics Committees, researchEthics, researchGynecologyHelsinki DeclarationObstetricsPeriodicals as topicScientific misconductStatisticsSee moreViews121

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleQuality of clinical studies published in the RBGO over one decade (1999-2009): methodological and ethical aspects and statistical procedures
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(11):477-482
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013001100001
- Joceline Cássia Ferezini de Sá,
- Gabriela Marini,
- Rafael Bottaro Gelaleti,
- João Batista da Silva,
- George Dantas de Azevedo,
- Marilza Vieira Cunha Rudge
Views121PURPOSE: To evaluate the methodological and statistical design evolution of the publications in the Brazilian Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics (RBGO) from resolution 196/96. METHODS: A review of 133 articles published in 1999 (65) and 2009 (68) was performed by two independent reviewers with training in clinical epidemiology and methodology of scientific research. We included all original clinical articles, case and series reports and excluded editorials, letters to the editor, systematic reviews, experimental studies, opinion articles, besides abstracts of theses and dissertations. Characteristics related to the methodological quality of the studies were analyzed in each article using a checklist that evaluated two criteria: methodological aspects and statistical procedures. We used descriptive statistics and the χ2 test for comparison of the two years. RESULTS: There was a difference between 1999 and 2009 regarding the study and statistical design, with more accuracy in the procedures and the use of more robust tests between 1999 and 2009. CONCLUSIONS: In RBGO, we observed an evolution in the methods of published articles and a more in-depth use of the statistical analyses, with more sophisticated tests such as regression and multilevel analyses, which are essential techniques for the knowledge and planning of health interventions, leading to fewer interpretation errors.
Key-words Clinical trials as topicEthics Committees, researchEthics, researchGynecologyHelsinki DeclarationObstetricsPeriodicals as topicScientific misconductStatisticsSee more -
Case Report12-01-2015
Renal vein thrombosis in the puerperium: case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(12):593-597
Abstract
Case ReportRenal vein thrombosis in the puerperium: case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(12):593-597
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320150005455
Views109Abstract
Pregnancy and puerperium are periods of blood hypercoagulability and, therefore, of risk for thromboembolic events. Renal vein thrombosis is a serious and infrequent condition of difficult diagnosis. This study reported a case of renal vein thrombosis in the puerperium, and described the clinical case, risk factors, diagnostic methods, and treatment instituted.
Key-words Case reportsPostpartum periodPregnancy complications, hematologicThrombophiliaVenous thrombosisSee moreViews109

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Case ReportRenal vein thrombosis in the puerperium: case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(12):593-597
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320150005455
Views109Abstract
Pregnancy and puerperium are periods of blood hypercoagulability and, therefore, of risk for thromboembolic events. Renal vein thrombosis is a serious and infrequent condition of difficult diagnosis. This study reported a case of renal vein thrombosis in the puerperium, and described the clinical case, risk factors, diagnostic methods, and treatment instituted.
Key-words Case reportsPostpartum periodPregnancy complications, hematologicThrombophiliaVenous thrombosisSee more -
Original Article06-27-2024
Prevalence of karyotype alterations in couples with recurrent pregnancy loss in a tertiary center in Brazil
- Elaine Cristina Fontes de Oliveira
 ,
, - Ines Katerina Damasceno Cavallo Cruzeiro
 ,
, - Cezar Antônio Abreu de Souza
 ,
, - Fernando Marcos Reis

Abstract
Original ArticlePrevalence of karyotype alterations in couples with recurrent pregnancy loss in a tertiary center in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo51
- Elaine Cristina Fontes de Oliveira
 ,
, - Ines Katerina Damasceno Cavallo Cruzeiro
 ,
, - Cezar Antônio Abreu de Souza
 ,
, - Fernando Marcos Reis

Views176Abstract
Objective
To assess the prevalence and type of chromosomal abnormalities in Brazilian couples with recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL) and compare the clinical characteristics of couples with and without chromosome abnormalities.
Methods
We assessed the medical records of 127 couples with a history of two or more miscarriages, referred to a tertiary academic hospital in Belo Horizonte, Brazil, from January 2014 to May 2023. Karyotype was generated from peripheral blood lymphocyte cultures, and cytogenetic analysis was performed according to standard protocols by heat-denatured Giemsa (RHG) banding.
Results
Abnormal karyotypes were detected in 10 couples (7.8%). The prevalence of chromosomal abnormalities was higher among females (6.3%) compared to males (2.0%), but this difference was not statistically significant (p=0.192). The mean number of miscarriages was. 3.3 ± 1.1 in couples with chromosome abnormalities and 3.1 ± 1.5 in couples without chromosome abnormalities (p=0.681). Numerical chromosomal anomalies (6 cases) were more frequent than structural anomalies. Four women presented low-grade Turner mosaicism. No differences were found between couples with and without karyotype alterations, except for maternal age, which was higher in the group with chromosome alterations.
Conclusion
The prevalence of parental chromosomal alterations in our study was higher than in most series described in the literature and was associated with increased maternal age. These findings suggest that karyotyping should be part of the investigation for Brazilian couples with RPL, as identifying the genetic etiology may have implications for subsequent pregnancies.
Key-words Abortion, habitualAbortion, spontaneousChromosome aberrationsKaryotypeTranslocation, geneticSee moreViews176

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticlePrevalence of karyotype alterations in couples with recurrent pregnancy loss in a tertiary center in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo51
- Elaine Cristina Fontes de Oliveira
 ,
, - Ines Katerina Damasceno Cavallo Cruzeiro
 ,
, - Cezar Antônio Abreu de Souza
 ,
, - Fernando Marcos Reis

Views176Abstract
Objective
To assess the prevalence and type of chromosomal abnormalities in Brazilian couples with recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL) and compare the clinical characteristics of couples with and without chromosome abnormalities.
Methods
We assessed the medical records of 127 couples with a history of two or more miscarriages, referred to a tertiary academic hospital in Belo Horizonte, Brazil, from January 2014 to May 2023. Karyotype was generated from peripheral blood lymphocyte cultures, and cytogenetic analysis was performed according to standard protocols by heat-denatured Giemsa (RHG) banding.
Results
Abnormal karyotypes were detected in 10 couples (7.8%). The prevalence of chromosomal abnormalities was higher among females (6.3%) compared to males (2.0%), but this difference was not statistically significant (p=0.192). The mean number of miscarriages was. 3.3 ± 1.1 in couples with chromosome abnormalities and 3.1 ± 1.5 in couples without chromosome abnormalities (p=0.681). Numerical chromosomal anomalies (6 cases) were more frequent than structural anomalies. Four women presented low-grade Turner mosaicism. No differences were found between couples with and without karyotype alterations, except for maternal age, which was higher in the group with chromosome alterations.
Conclusion
The prevalence of parental chromosomal alterations in our study was higher than in most series described in the literature and was associated with increased maternal age. These findings suggest that karyotyping should be part of the investigation for Brazilian couples with RPL, as identifying the genetic etiology may have implications for subsequent pregnancies.
Key-words Abortion, habitualAbortion, spontaneousChromosome aberrationsKaryotypeTranslocation, geneticSee more - Elaine Cristina Fontes de Oliveira
-
Review Article06-01-2018
Breastfeeding and the Benefits of Lactation for Women’s Health
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):354-359
Abstract
Review ArticleBreastfeeding and the Benefits of Lactation for Women’s Health
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):354-359
Views475See moreAbstract
The offer of the maternal breast to the baby is an unquestionable right of mothers and their children, and all efforts should bemade to promote, follow and maintain exclusive breastfeeding for up to 6months and supplement it until the child completes 2 years of age. Many publications are available in the literature about the qualities of breast milk, its benefits and health repercussions, stimulating the practice of breastfeeding and supporting campaigns for its implementation. However, although it is widely known that breastfeeding is an important step in the reproductive process of women and its practice offers benefits to both mother and child, most of the available information highlights the benefits of breast milk for children, while mention of the effects of breastfeeding on the health of the mother is usually neglected. Thus, the objective of the present study is to highlight the multiple benefits of breastfeeding for the physical and emotional health of the nursing mother. The authors consulted articles published in the databases PubMed, Virtual Health Library andWeb of Science using the keywords breastfeeding, breast milk, lactation and maternal health.
Views475

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleBreastfeeding and the Benefits of Lactation for Women’s Health
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):354-359
Views475See moreAbstract
The offer of the maternal breast to the baby is an unquestionable right of mothers and their children, and all efforts should bemade to promote, follow and maintain exclusive breastfeeding for up to 6months and supplement it until the child completes 2 years of age. Many publications are available in the literature about the qualities of breast milk, its benefits and health repercussions, stimulating the practice of breastfeeding and supporting campaigns for its implementation. However, although it is widely known that breastfeeding is an important step in the reproductive process of women and its practice offers benefits to both mother and child, most of the available information highlights the benefits of breast milk for children, while mention of the effects of breastfeeding on the health of the mother is usually neglected. Thus, the objective of the present study is to highlight the multiple benefits of breastfeeding for the physical and emotional health of the nursing mother. The authors consulted articles published in the databases PubMed, Virtual Health Library andWeb of Science using the keywords breastfeeding, breast milk, lactation and maternal health.
-
Review Article09-01-2017
Preeclampsia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(9):496-512
Abstract
Review ArticlePreeclampsia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(9):496-512
Views495Abstract
The authors review hypertensive disease during pregnancy with an academic and practical view, and using the best evidence available. This disease, which is the most important clinical disease in Brazilian pregnant women, may have its incidence reduced with prevention through the use of calcium and aspirin in pregnant women at risk. Previously, it was a disease that presented with hypertension with proteinuria, but it has now been classified with new clinical parameters besides proteinuria. Morbidity and mortality should be reduced in a continental country such as Brazil using protocols for the early treatment of complications by calculating severe outcomes in preeclampsia. The early treatment of acute hypertension, use of magnesium sulfate and early hospitalization in cases of preeclampsia are concepts to pursue the reduction of our pregnant women’s mortality.
Key-words HELLP syndromeHigh risk pregnancyPreeclampsiapregnancy arterial hypertensionPregnancy complicationsSee moreViews495

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticlePreeclampsia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(9):496-512
Views495Abstract
The authors review hypertensive disease during pregnancy with an academic and practical view, and using the best evidence available. This disease, which is the most important clinical disease in Brazilian pregnant women, may have its incidence reduced with prevention through the use of calcium and aspirin in pregnant women at risk. Previously, it was a disease that presented with hypertension with proteinuria, but it has now been classified with new clinical parameters besides proteinuria. Morbidity and mortality should be reduced in a continental country such as Brazil using protocols for the early treatment of complications by calculating severe outcomes in preeclampsia. The early treatment of acute hypertension, use of magnesium sulfate and early hospitalization in cases of preeclampsia are concepts to pursue the reduction of our pregnant women’s mortality.
Key-words HELLP syndromeHigh risk pregnancyPreeclampsiapregnancy arterial hypertensionPregnancy complicationsSee more
-
Review Article09-25-2020
Primary Dysmenorrhea: Assessment and Treatment
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(8):501-507
Abstract
Review ArticlePrimary Dysmenorrhea: Assessment and Treatment
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(8):501-507
Views480See moreAbstract
Primary dysmenorrhea is defined asmenstrual pain in the absence of pelvic disease. It is characterized by overproduction of prostaglandins by the endometrium, causing uterine hypercontractility that results in uterine muscle ischemia, hypoxia, and, subsequently, pain. It is the most common gynecological illness in women in their reproductive years and one of the most frequent causes of pelvic pain; however, it is underdiagnosed, undertreated, and even undervalued by women themselves, who accept it as part of themenstrual cycle. It hasmajor implications for quality of life, such as limitation of daily activities and psychological stress, being one of themain causes of school and work absenteeism. Its diagnosis is essentially clinical, based on the clinical history and normal physical examination. It is important to exclude secondary causes of dysmenorrhea. The treatment may have different approaches (pharmacological, nonpharmacological and surgical), but the first line of treatment is the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and, in cases of women who want contraception, the use of hormonal contraceptives. Alternative treatments, such as topical heat, lifestyle modification, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, dietary supplements, acupuncture, and acupressure, may be an option in cases of conventional treatments’ contraindication. Surgical treatment is only indicated in rare cases of women with severe dysmenorrhea refractory to treatment.
Views480

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticlePrimary Dysmenorrhea: Assessment and Treatment
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(8):501-507
Views480See moreAbstract
Primary dysmenorrhea is defined asmenstrual pain in the absence of pelvic disease. It is characterized by overproduction of prostaglandins by the endometrium, causing uterine hypercontractility that results in uterine muscle ischemia, hypoxia, and, subsequently, pain. It is the most common gynecological illness in women in their reproductive years and one of the most frequent causes of pelvic pain; however, it is underdiagnosed, undertreated, and even undervalued by women themselves, who accept it as part of themenstrual cycle. It hasmajor implications for quality of life, such as limitation of daily activities and psychological stress, being one of themain causes of school and work absenteeism. Its diagnosis is essentially clinical, based on the clinical history and normal physical examination. It is important to exclude secondary causes of dysmenorrhea. The treatment may have different approaches (pharmacological, nonpharmacological and surgical), but the first line of treatment is the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and, in cases of women who want contraception, the use of hormonal contraceptives. Alternative treatments, such as topical heat, lifestyle modification, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, dietary supplements, acupuncture, and acupressure, may be an option in cases of conventional treatments’ contraindication. Surgical treatment is only indicated in rare cases of women with severe dysmenorrhea refractory to treatment.
-
Review Article09-01-2018
Multiple Pregnancy: Epidemiology and Association with Maternal and Perinatal Morbidity
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):554-562
Abstract
Review ArticleMultiple Pregnancy: Epidemiology and Association with Maternal and Perinatal Morbidity
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):554-562
Views374See moreAbstract
Twin pregnancy accounts for 2 to 4% of total births, with a prevalence ranging from 0.9 to 2.4% in Brazil. It is associated with worse maternal and perinatal outcomes. Many conditions, such as severe maternal morbidity (SMM) (potentially life-threatening conditions and maternal near-miss) and neonatal near-miss (NNM) still have not been properly investigated in the literature. The difficulty in determining the conditions associated with twin pregnancy probably lies in its relatively low occurrence and the need for larger population studies. The use of the whole population and of databases from large multicenter studies, therefore, may provide unprecedented results. Since it is a rare condition, it ismore easily evaluated using vital statistics from birth e-registries. Therefore, we have performed a literature review to identify the characteristics of twin pregnancy in Brazil and worldwide. Twin pregnancy has consistently been associated with SMM, maternal near-miss (MNM) and perinatal morbidity, with still worse results for the second twin, possibly due to some characteristics of the delivery, including safety and availability of appropriate obstetric care to women at a high risk of perinatal complications.
Views374

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleMultiple Pregnancy: Epidemiology and Association with Maternal and Perinatal Morbidity
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):554-562
Views374See moreAbstract
Twin pregnancy accounts for 2 to 4% of total births, with a prevalence ranging from 0.9 to 2.4% in Brazil. It is associated with worse maternal and perinatal outcomes. Many conditions, such as severe maternal morbidity (SMM) (potentially life-threatening conditions and maternal near-miss) and neonatal near-miss (NNM) still have not been properly investigated in the literature. The difficulty in determining the conditions associated with twin pregnancy probably lies in its relatively low occurrence and the need for larger population studies. The use of the whole population and of databases from large multicenter studies, therefore, may provide unprecedented results. Since it is a rare condition, it ismore easily evaluated using vital statistics from birth e-registries. Therefore, we have performed a literature review to identify the characteristics of twin pregnancy in Brazil and worldwide. Twin pregnancy has consistently been associated with SMM, maternal near-miss (MNM) and perinatal morbidity, with still worse results for the second twin, possibly due to some characteristics of the delivery, including safety and availability of appropriate obstetric care to women at a high risk of perinatal complications.
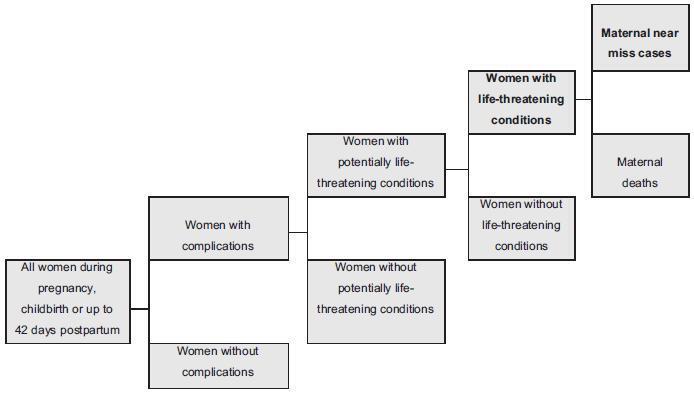
-
Review Article05-01-2018
Uterine Artery Doppler in Screening for Preeclampsia and Fetal Growth Restriction
- Marianna Amaral Pedroso,
- Kirsten Rebecca Palmer,
- Ryan James Hodges,
- Fabricio da Silva Costa,
- Daniel Lorber Rolnik
Abstract
Review ArticleUterine Artery Doppler in Screening for Preeclampsia and Fetal Growth Restriction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(5):287-293
- Marianna Amaral Pedroso,
- Kirsten Rebecca Palmer,
- Ryan James Hodges,
- Fabricio da Silva Costa,
- Daniel Lorber Rolnik
Views333See moreAbstract
Objective
To perform a comprehensive review of the current evidence on the role of uterine artery Doppler, isolated or in combination with other markers, in screening for preeclampsia (PE) and fetal growth restriction (FGR) in the general population. The review included recently published large cohort studies and randomized trials.
Methods
A search of the literature was conducted usingMedline, PubMed, MeSH and ScienceDirect. Combinations of the search terms “preeclampsia,” “screening,” “prediction,” “Doppler,” “Doppler velocimetry,” “fetal growth restriction,” “small for gestational age” and “uterine artery” were used. Articles in English (excluding reviews) reporting the use of uterine artery Doppler in screening for PE and FGR were included.
Results
Thirty articles were included. As a single predictor, uterine artery Doppler detects less than 50% of the cases of PE and no more than 40% of the pregnancies affected by FGR. Logistic regression-based models that allow calculation of individual risk based on the combination of multiple markers, in turn, is able to detect ~ 75% of the cases of preterm PE and 55% of the pregnancies resulting in small for gestational age infants.
Conclusion
The use of uterine artery Doppler as a single predictive test for PE and FGR has poor accuracy. However, its combined use in predictive models is promising, being more accurate in detecting preterm PE than FGR.
Views333

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleUterine Artery Doppler in Screening for Preeclampsia and Fetal Growth Restriction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(5):287-293
- Marianna Amaral Pedroso,
- Kirsten Rebecca Palmer,
- Ryan James Hodges,
- Fabricio da Silva Costa,
- Daniel Lorber Rolnik
Views333See moreAbstract
Objective
To perform a comprehensive review of the current evidence on the role of uterine artery Doppler, isolated or in combination with other markers, in screening for preeclampsia (PE) and fetal growth restriction (FGR) in the general population. The review included recently published large cohort studies and randomized trials.
Methods
A search of the literature was conducted usingMedline, PubMed, MeSH and ScienceDirect. Combinations of the search terms “preeclampsia,” “screening,” “prediction,” “Doppler,” “Doppler velocimetry,” “fetal growth restriction,” “small for gestational age” and “uterine artery” were used. Articles in English (excluding reviews) reporting the use of uterine artery Doppler in screening for PE and FGR were included.
Results
Thirty articles were included. As a single predictor, uterine artery Doppler detects less than 50% of the cases of PE and no more than 40% of the pregnancies affected by FGR. Logistic regression-based models that allow calculation of individual risk based on the combination of multiple markers, in turn, is able to detect ~ 75% of the cases of preterm PE and 55% of the pregnancies resulting in small for gestational age infants.
Conclusion
The use of uterine artery Doppler as a single predictive test for PE and FGR has poor accuracy. However, its combined use in predictive models is promising, being more accurate in detecting preterm PE than FGR.
-
Review Article02-01-2016
Conservative Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- Rafael Mendes Moroni,
- Pedro Sergio Magnani,
- Jorge Milhem Haddad,
- Rodrigo de Aquino Castro,
- Luiz Gustavo Oliveira Brito
Abstract
Review ArticleConservative Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(2):97-111
- Rafael Mendes Moroni,
- Pedro Sergio Magnani,
- Jorge Milhem Haddad,
- Rodrigo de Aquino Castro,
- Luiz Gustavo Oliveira Brito
Views304See moreWe performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials that studied the conservative management of stress urinary incontinence (SUI). There were 1058 results after the initial searches, from which 37 studies were eligible according to previously determined inclusion criteria. For the primary outcomes, pelvic floor muscle training (PFMT) was more efficacious than no treatment in improving incontinence-specific quality of life (QoL) scales (SMD = [1]1.24SDs; CI 95% = [1]1.77 to [1]0.71SDs). However, its effect on pad tests was imprecise. Combining biofeedback with PFMT had an uncertain effect on QoL (MD = [1]4.4 points; CI 95% = [1]16.69 to 7.89 points), but better results on the pad test, although with elevated heterogeneity (MD = 0.9g; 95%CI = 0.71 to 1,10g); group PFMT was not less efficacious than individual treatment, and home PFMT was not consistently worse than supervised PFMT. Both intravaginal and superficial electrical stimulation (IES and SES) were better than no treatment for QoL and pad test. Vaginal cones had mixed results. The association of IES with PFMT may improve the efficacy of the latter for QoL and pad test, but the results of individual studies were not consistent. Thus, there is evidence of the use of PFMT on the treatment of SUI, with and without biofeedback.
Views304

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleConservative Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(2):97-111
- Rafael Mendes Moroni,
- Pedro Sergio Magnani,
- Jorge Milhem Haddad,
- Rodrigo de Aquino Castro,
- Luiz Gustavo Oliveira Brito
Views304See moreWe performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials that studied the conservative management of stress urinary incontinence (SUI). There were 1058 results after the initial searches, from which 37 studies were eligible according to previously determined inclusion criteria. For the primary outcomes, pelvic floor muscle training (PFMT) was more efficacious than no treatment in improving incontinence-specific quality of life (QoL) scales (SMD = [1]1.24SDs; CI 95% = [1]1.77 to [1]0.71SDs). However, its effect on pad tests was imprecise. Combining biofeedback with PFMT had an uncertain effect on QoL (MD = [1]4.4 points; CI 95% = [1]16.69 to 7.89 points), but better results on the pad test, although with elevated heterogeneity (MD = 0.9g; 95%CI = 0.71 to 1,10g); group PFMT was not less efficacious than individual treatment, and home PFMT was not consistently worse than supervised PFMT. Both intravaginal and superficial electrical stimulation (IES and SES) were better than no treatment for QoL and pad test. Vaginal cones had mixed results. The association of IES with PFMT may improve the efficacy of the latter for QoL and pad test, but the results of individual studies were not consistent. Thus, there is evidence of the use of PFMT on the treatment of SUI, with and without biofeedback.
-
Review Article09-16-2019
Do Women have Adequate Knowledge about Pelvic Floor Dysfunctions? A Systematic Review
- Júlia Ferreira Fante,
- Thais Daniel Silva,
- Elaine Cristine Lemes Mateus-Vasconcelos,
- Cristine Homsi Jorge Ferreira,
- Luiz Gustavo Oliveira Brito

Abstract
Review ArticleDo Women have Adequate Knowledge about Pelvic Floor Dysfunctions? A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(8):508-519
- Júlia Ferreira Fante,
- Thais Daniel Silva,
- Elaine Cristine Lemes Mateus-Vasconcelos,
- Cristine Homsi Jorge Ferreira,
- Luiz Gustavo Oliveira Brito

Views299See moreAbstract
Objective
We sought to investigate whether women present adequate knowledge of the main pelvic floor disorders (PFDs) (urinary incontinence – UI, fecal incontinence – FI, and pelvic organ prolapse – POP).
Data
sources A systematic review was performed in the MEDLINE, PEDro, CENTRAL, and Cochrane databases for publications from inception to April 2018. Selection of studies A total of 3,125 studies were reviewed. Meta-analysis was not possible due to the heterogeneity of primary outcomes and the diversity of instruments for measuring knowledge. The quality of the articles included in the analysis was evaluated with the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) adapted for cross-sectional studies.
Data collection
Two authors performed data extraction into a standardized spreadsheet.
Data synthesis
Nineteen studies were included, comprising 11,512 women. About the methodological quality (NOS), most of the studies (n= 11) presented a total score of 6 out of 10. Validated questionnaires and designed pilot-tested forms were the most frequently used ways of assessing knowledge. Some studies were stratified by race, age, or group minorities. The most used questionnaire was the prolapse and incontinence knowledge questionnaire (PIKQ) (n= 5). Knowledge and/or awareness regarding PFD was low to moderate among the studies. Urinary incontinence was the most prevalent PFD investigated, and the most important risk factors associated with the lack of knowledge of the pelvic floor were: African-American ethnicity (n= 3), low educational level (n= 4), low access to information (n= 5) and socioeconomic status (n= 3).
Conclusion
Most women have a gap in the knowledge of pelvic floor muscle dysfunctions, do not understand their treatment options, and are not able to identify risk factors for these disorders.
Views299

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleDo Women have Adequate Knowledge about Pelvic Floor Dysfunctions? A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(8):508-519
- Júlia Ferreira Fante,
- Thais Daniel Silva,
- Elaine Cristine Lemes Mateus-Vasconcelos,
- Cristine Homsi Jorge Ferreira,
- Luiz Gustavo Oliveira Brito

Views299See moreAbstract
Objective
We sought to investigate whether women present adequate knowledge of the main pelvic floor disorders (PFDs) (urinary incontinence – UI, fecal incontinence – FI, and pelvic organ prolapse – POP).
Data
sources A systematic review was performed in the MEDLINE, PEDro, CENTRAL, and Cochrane databases for publications from inception to April 2018. Selection of studies A total of 3,125 studies were reviewed. Meta-analysis was not possible due to the heterogeneity of primary outcomes and the diversity of instruments for measuring knowledge. The quality of the articles included in the analysis was evaluated with the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) adapted for cross-sectional studies.
Data collection
Two authors performed data extraction into a standardized spreadsheet.
Data synthesis
Nineteen studies were included, comprising 11,512 women. About the methodological quality (NOS), most of the studies (n= 11) presented a total score of 6 out of 10. Validated questionnaires and designed pilot-tested forms were the most frequently used ways of assessing knowledge. Some studies were stratified by race, age, or group minorities. The most used questionnaire was the prolapse and incontinence knowledge questionnaire (PIKQ) (n= 5). Knowledge and/or awareness regarding PFD was low to moderate among the studies. Urinary incontinence was the most prevalent PFD investigated, and the most important risk factors associated with the lack of knowledge of the pelvic floor were: African-American ethnicity (n= 3), low educational level (n= 4), low access to information (n= 5) and socioeconomic status (n= 3).
Conclusion
Most women have a gap in the knowledge of pelvic floor muscle dysfunctions, do not understand their treatment options, and are not able to identify risk factors for these disorders.
-
Review Article08-26-2020
Covid-19 and Pregnancy: An Overview
- Pedro Castro
 ,
, - Ana Paula Matos
 ,
, - Heron Werner
 ,
, - Flávia Paiva Lopes
 ,
, - Gabriele Tonni
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Edward Araujo Júnior

Abstract
Review ArticleCovid-19 and Pregnancy: An Overview
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(7):420-426
- Pedro Castro
 ,
, - Ana Paula Matos
 ,
, - Heron Werner
 ,
, - Flávia Paiva Lopes
 ,
, - Gabriele Tonni
 ,
, - Edward Araujo Júnior

Views210See moreAbstract
Since the World Health Organization (WHO) declared coronavirus infection (COVID-19) a Public Health Emergency of International Concern in January 2020, there have been many concerns about pregnant women and the possible effects of this emergency with catastrophic outcomes inmany countries. Information on COVID-19 and pregnancy are scarce and spread throughout a fewcase series, with no more than 50 cases in total. The present review provides a brief analysis of COVID-19, pregnancy in the COVID-19 era, and the effects of COVID-19 on pregnancy.
Views210

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleCovid-19 and Pregnancy: An Overview
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(7):420-426
- Pedro Castro
 ,
, - Ana Paula Matos
 ,
, - Heron Werner
 ,
, - Flávia Paiva Lopes
 ,
, - Gabriele Tonni
 ,
, - Edward Araujo Júnior

Views210See moreAbstract
Since the World Health Organization (WHO) declared coronavirus infection (COVID-19) a Public Health Emergency of International Concern in January 2020, there have been many concerns about pregnant women and the possible effects of this emergency with catastrophic outcomes inmany countries. Information on COVID-19 and pregnancy are scarce and spread throughout a fewcase series, with no more than 50 cases in total. The present review provides a brief analysis of COVID-19, pregnancy in the COVID-19 era, and the effects of COVID-19 on pregnancy.
- Pedro Castro
Search
Search in:
Tag Cloud
Pregnancy (252)Breast neoplasms (104)Pregnancy complications (104)Risk factors (103)Menopause (88)Ultrasonography (83)Cesarean section (78)Prenatal care (71)Endometriosis (70)Obesity (61)Infertility (57)Quality of life (55)prenatal diagnosis (51)Women's health (48)Postpartum period (46)Maternal mortality (45)Pregnant women (45)Breast (44)Prevalence (43)Uterine cervical neoplasms (43)
Featured Articles
- FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT03-18-2025
Use of synthetic slings in the treatment of female stress urinary incontinence: Number 2 – 2025
- Marair Gracio Ferreira Sartori
 ,
, - Marilene Vale de Castro Monteiro
 ,
, - Cássia Raquel Teatin Juliato
 ,
, - Luiz Gustavo Oliveira Brito
 ,
, - Sergio Brasileiro Martins
 ,
, - José Miguel de Deus
 ,
, - Ana Selma Bertelli Picoloto
 ,
, - Jorge Milhem Haddad
 ,
, - Andreisa Paiva Monteiro Bilhar
 ,
, - Leticia Maria de Oliveira
 ,
, - Rafael Mendes Moroni
 ,
, - Lucas Schreiner
 ,
, - Aljerry Dias do Rego
 ,
, - Daniela Siqueira Prado
 ,
, - Emerson de Oliveira

Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTUse of synthetic slings in the treatment of female stress urinary incontinence: Number 2 – 2025
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-FPS2
- Marair Gracio Ferreira Sartori
 ,
, - Marilene Vale de Castro Monteiro
 ,
, - Cássia Raquel Teatin Juliato
 ,
, - Luiz Gustavo Oliveira Brito
 ,
, - Sergio Brasileiro Martins
 ,
, - José Miguel de Deus
 ,
, - Ana Selma Bertelli Picoloto
 ,
, - Jorge Milhem Haddad
 ,
, - Andreisa Paiva Monteiro Bilhar
 ,
, - Leticia Maria de Oliveira
 ,
, - Rafael Mendes Moroni
 ,
, - Lucas Schreiner
 ,
, - Aljerry Dias do Rego
 ,
, - Daniela Siqueira Prado
 ,
, - Emerson de Oliveira

Views219

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTUse of synthetic slings in the treatment of female stress urinary incontinence: Number 2 – 2025
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-FPS2
- Marair Gracio Ferreira Sartori
 ,
, - Marilene Vale de Castro Monteiro
 ,
, - Cássia Raquel Teatin Juliato
 ,
, - Luiz Gustavo Oliveira Brito
 ,
, - Sergio Brasileiro Martins
 ,
, - José Miguel de Deus
 ,
, - Ana Selma Bertelli Picoloto
 ,
, - Jorge Milhem Haddad
 ,
, - Andreisa Paiva Monteiro Bilhar
 ,
, - Leticia Maria de Oliveira
 ,
, - Rafael Mendes Moroni
 ,
, - Lucas Schreiner
 ,
, - Aljerry Dias do Rego
 ,
, - Daniela Siqueira Prado
 ,
, - Emerson de Oliveira



This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Marair Gracio Ferreira Sartori
- Original Article03-18-2025
The experience of pregnancy in the COVID-19 pandemic
- Mariana Corniani Lopes
 ,
, - Cheryl Tatano Beck
 ,
, - Zelina Hilária de Souza Rosa
 ,
, - Erika de Sá Vieira Abuchaim

Abstract
Original ArticleThe experience of pregnancy in the COVID-19 pandemic
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo8
- Mariana Corniani Lopes
 ,
, - Cheryl Tatano Beck
 ,
, - Zelina Hilária de Souza Rosa
 ,
, - Erika de Sá Vieira Abuchaim

Views239See moreAbstract
Objective:
To describe women’s experience of pregnancy during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods:
A qualitative study conducted in a private maternity hospital, from May, 2020 to November, 2021, with women aged ≥ 18 years, gestational age ≥ 36 weeks at birth and ≥ 24 hours post-partum. Data collected through semi-structured interviews, recorded, transcribed, and analyzed adopting Krippendorff’s Content Analysis as theoretical-methodological framework.
Results:
Four main themes emerged: Fear, Taking care and celebrating pregnancy: adjusting to the new reality, Harms of Isolation, and Benefits of Isolation. The fear of contamination and its impact on the health of mother and child resulted in the adoption of severe social isolation, including from those considered sources of support by the expecting mother. Overwhelmed, some of the participants reported loneliness and psychic suffering. The opportunity to focus on the pregnancy, the preparations for the arrival of the child, and the family made isolation a beneficial and positive period for other women.
Conclusion:
The experience of pregnancy in the Pandemic was an event outside of the ordinary and common. The expecting mother faced her worst fears on a daily basis and attended prenatal care, in order to ensure her child would be born healthy. The celebration of the baby’s life, amid so many deaths, had to be adjusted to the virtual environment. It was a tense, solitary, and ambiguous period, which demanded a lot from the mental health of some participants, but to others, brought advantages that would not have been possible in different times.
Views239

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleThe experience of pregnancy in the COVID-19 pandemic
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo8
- Mariana Corniani Lopes
 ,
, - Cheryl Tatano Beck
 ,
, - Zelina Hilária de Souza Rosa
 ,
, - Erika de Sá Vieira Abuchaim

Views239See moreAbstract
Objective:
To describe women’s experience of pregnancy during the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods:
A qualitative study conducted in a private maternity hospital, from May, 2020 to November, 2021, with women aged ≥ 18 years, gestational age ≥ 36 weeks at birth and ≥ 24 hours post-partum. Data collected through semi-structured interviews, recorded, transcribed, and analyzed adopting Krippendorff’s Content Analysis as theoretical-methodological framework.
Results:
Four main themes emerged: Fear, Taking care and celebrating pregnancy: adjusting to the new reality, Harms of Isolation, and Benefits of Isolation. The fear of contamination and its impact on the health of mother and child resulted in the adoption of severe social isolation, including from those considered sources of support by the expecting mother. Overwhelmed, some of the participants reported loneliness and psychic suffering. The opportunity to focus on the pregnancy, the preparations for the arrival of the child, and the family made isolation a beneficial and positive period for other women.
Conclusion:
The experience of pregnancy in the Pandemic was an event outside of the ordinary and common. The expecting mother faced her worst fears on a daily basis and attended prenatal care, in order to ensure her child would be born healthy. The celebration of the baby’s life, amid so many deaths, had to be adjusted to the virtual environment. It was a tense, solitary, and ambiguous period, which demanded a lot from the mental health of some participants, but to others, brought advantages that would not have been possible in different times.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 
- Mariana Corniani Lopes
- Original Article02-13-2025
Anemia levels in the preconception period and the first trimester of pregnancy: a national, multicentric and cross-sectional study
- Aytaj Jafarzade
 ,
, - Veli Mi̇hmanli
 ,
, - And Yavuz
 ,
, - Murat Akbaş
 ,
, - Gürcan Türkyilmaz
 ,
, - Esra Nur Özkan
 ,
, - Murat İbrahim Toplu
 ,
, - Yücel Kaya
 ,
, - Damla Yasemin Yenli̇k Kaya
 ,
, - Mustafa Yildiz
 ,
, - Ali Emre Ati̇k
 ,
, - Elif İlgazi̇ Kiliç
 ,
, - Burcu Özata
 ,
, - Sehtap Nazlı Kiliç Çeti̇n
 ,
, - Berk Bulut
 ,
, - Halide Gül Okuducu Aydin
 ,
, - Lale Aslanova
 ,
, - Çağdaş Nurettin Emekli̇oğlu
 ,
, - Melike Eren
 ,
, - Elif Uçar
 ,
, - Kaan Eray Uzun
 ,
, - Osman Ufuk Eki̇z
 ,
, - Muhittin Tamer Mungan

Abstract
Original ArticleAnemia levels in the preconception period and the first trimester of pregnancy: a national, multicentric and cross-sectional study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:-e-rbgo1001
DOI 10.61622/rbgo/2025rbgo10001
- Aytaj Jafarzade
 ,
, - Veli Mi̇hmanli
 ,
, - And Yavuz
 ,
, - Murat Akbaş
 ,
, - Gürcan Türkyilmaz
 ,
, - Esra Nur Özkan
 ,
, - Murat İbrahim Toplu
 ,
, - Yücel Kaya
 ,
, - Damla Yasemin Yenli̇k Kaya
 ,
, - Mustafa Yildiz
 ,
, - Ali Emre Ati̇k
 ,
, - Elif İlgazi̇ Kiliç
 ,
, - Burcu Özata
 ,
, - Sehtap Nazlı Kiliç Çeti̇n
 ,
, - Berk Bulut
 ,
, - Halide Gül Okuducu Aydin
 ,
, - Lale Aslanova
 ,
, - Çağdaş Nurettin Emekli̇oğlu
 ,
, - Melike Eren
 ,
, - Elif Uçar
 ,
, - Kaan Eray Uzun
 ,
, - Osman Ufuk Eki̇z
 ,
, - Muhittin Tamer Mungan

Views333Abstract
Objective
The study aimed to determine the level of anemia in pregnant women in the first trimester and in the preconception period by conducting nationwide research.
Methods
The study was designed as retrospective, cross-sectional, and multicenter research. A total of 17 centers from 13 provinces were included in the study. The study was conducted with the participation of two groups of patients who applied to the obstetrics polyclinic between 1 January 2023 and 1 July 2023, who were in the first trimester of pregnancy and who were in the preconception period planning pregnancy.
Results
In total 4,265 women were included in the study. Of these women, 3,884 (91%) were in the first trimester of their pregnancy and 381 (9%) were in the preconception period. Anemia was detected in 24.1% (n=1030) of the patients. Of these patients, 20.6% (n=877) were pregnant women in the first trimester and 3.6% (n=153) were in the preconception period. A statistically significant and positive relationship was found between anemia and meat consumption frequency, educational status, and socioeconomic status of the patients (p=0.000, p=0.000, p=0.000). In addition, a statistically significant and negative correlation was determined between anemia and the number of pregnancies and the parity number (p=0.001, p=0.000) in both groups.
Conclusion
Anemia is a public health problem. Anemia has been determined to be an important problem both in the preconception period and early periods of pregnancy. It is necessary to revise the programs and interventions to reduce the prevalence of anemia and redesign them in line with current conditions.
Key-words Anemia, iron-deficiencypreconception carePregnancy complications, hematologicPregnancy trimester, firstSee moreViews333

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleAnemia levels in the preconception period and the first trimester of pregnancy: a national, multicentric and cross-sectional study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:-e-rbgo1001
DOI 10.61622/rbgo/2025rbgo10001
- Aytaj Jafarzade
 ,
, - Veli Mi̇hmanli
 ,
, - And Yavuz
 ,
, - Murat Akbaş
 ,
, - Gürcan Türkyilmaz
 ,
, - Esra Nur Özkan
 ,
, - Murat İbrahim Toplu
 ,
, - Yücel Kaya
 ,
, - Damla Yasemin Yenli̇k Kaya
 ,
, - Mustafa Yildiz
 ,
, - Ali Emre Ati̇k
 ,
, - Elif İlgazi̇ Kiliç
 ,
, - Burcu Özata
 ,
, - Sehtap Nazlı Kiliç Çeti̇n
 ,
, - Berk Bulut
 ,
, - Halide Gül Okuducu Aydin
 ,
, - Lale Aslanova
 ,
, - Çağdaş Nurettin Emekli̇oğlu
 ,
, - Melike Eren
 ,
, - Elif Uçar
 ,
, - Kaan Eray Uzun
 ,
, - Osman Ufuk Eki̇z
 ,
, - Muhittin Tamer Mungan

Views333Abstract
Objective
The study aimed to determine the level of anemia in pregnant women in the first trimester and in the preconception period by conducting nationwide research.
Methods
The study was designed as retrospective, cross-sectional, and multicenter research. A total of 17 centers from 13 provinces were included in the study. The study was conducted with the participation of two groups of patients who applied to the obstetrics polyclinic between 1 January 2023 and 1 July 2023, who were in the first trimester of pregnancy and who were in the preconception period planning pregnancy.
Results
In total 4,265 women were included in the study. Of these women, 3,884 (91%) were in the first trimester of their pregnancy and 381 (9%) were in the preconception period. Anemia was detected in 24.1% (n=1030) of the patients. Of these patients, 20.6% (n=877) were pregnant women in the first trimester and 3.6% (n=153) were in the preconception period. A statistically significant and positive relationship was found between anemia and meat consumption frequency, educational status, and socioeconomic status of the patients (p=0.000, p=0.000, p=0.000). In addition, a statistically significant and negative correlation was determined between anemia and the number of pregnancies and the parity number (p=0.001, p=0.000) in both groups.
Conclusion
Anemia is a public health problem. Anemia has been determined to be an important problem both in the preconception period and early periods of pregnancy. It is necessary to revise the programs and interventions to reduce the prevalence of anemia and redesign them in line with current conditions.
Key-words Anemia, iron-deficiencypreconception carePregnancy complications, hematologicPregnancy trimester, firstSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 
- Aytaj Jafarzade
Objectives and Vision
The Brazilian Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics (RBGO) aims to publish basic and clinical research in gynecology, obstetrics and other related specialties and to be a reference to support and promote the professional education of residents, researchers and university professors. As a VISION, RBGO aims to become an internationally recognized reference among the main global journals in Gynecology and Obstetrics.