-
Review Article03-18-2025
Efficacy of vitamin C supplementation during pregnancy in the prevention of preterm birth: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo1
Abstract
Review ArticleEfficacy of vitamin C supplementation during pregnancy in the prevention of preterm birth: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo1
Views156Abstract
Objective:
Preterm birth is a leading global cause of neonatal mortality and morbidity, with oxidative stress playing a role in its pathogenesis. Vitamin C, a powerful antioxidant, may help reduce this risk. This study assessed the effectiveness of vitamin C supplementation, both alone and with vitamin E, in preventing preterm birth compared to a placebo.
Data source:
Databases were systematically searched in PubMed, Cochrane and Embase in December 2023 and updated in May 2024.
Study Selection:
Included RCTs evaluated vitamin C’s effect on preterm birth and related neonatal outcomes.
Data collect:
Statistical analyses used a random-effects model for pooled risk ratios (RR) and 95% confidence intervals (CI). Heterogeneity was assessed with the I² statistic.
Data synthesis:
Seventeen RCTs (21,567 patients) were analyzed. Vitamin C supplementation showed no significant difference compared to placebo for preterm birth (RR 1.04; 95% CI 0.96, 1.14). No significant differences were observed for neonatal death (RR 0.77; 95% CI 0.55, 1.08), NICU admission (RR 1.03; 95% CI 0.95, 1.13), preterm PROM (RR 1.04; 95% CI 0.63, 1.71), or birth weight (MD 52.41; 95% CI −19.65, 124.47). A slight decrease in gestational age was observed (MD 0.26; 95% CI −0.02, 0.55).
Conclusion:
Vitamin C supplementation alone or in combination with vitamin E does not significantly prevent preterm birth or improve related neonatal outcomes.
Key-words Ascorbic acidFetal membranes, premature ruptureGestational ageIntensive care units, neonatalPregnancyPremature birthVitamin C supplementationVitamin ESee more
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT03-18-2025
Use of synthetic slings in the treatment of female stress urinary incontinence: Number 2 – 2025
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-FPS2
Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTUse of synthetic slings in the treatment of female stress urinary incontinence: Number 2 – 2025
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-FPS2
-
Original Article02-13-2025
Anemia levels in the preconception period and the first trimester of pregnancy: a national, multicentric and cross-sectional study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:-e-rbgo1001
Abstract
Original ArticleAnemia levels in the preconception period and the first trimester of pregnancy: a national, multicentric and cross-sectional study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:-e-rbgo1001
DOI 10.61622/rbgo/2025rbgo10001
Views320Abstract
Objective
The study aimed to determine the level of anemia in pregnant women in the first trimester and in the preconception period by conducting nationwide research.
Methods
The study was designed as retrospective, cross-sectional, and multicenter research. A total of 17 centers from 13 provinces were included in the study. The study was conducted with the participation of two groups of patients who applied to the obstetrics polyclinic between 1 January 2023 and 1 July 2023, who were in the first trimester of pregnancy and who were in the preconception period planning pregnancy.
Results
In total 4,265 women were included in the study. Of these women, 3,884 (91%) were in the first trimester of their pregnancy and 381 (9%) were in the preconception period. Anemia was detected in 24.1% (n=1030) of the patients. Of these patients, 20.6% (n=877) were pregnant women in the first trimester and 3.6% (n=153) were in the preconception period. A statistically significant and positive relationship was found between anemia and meat consumption frequency, educational status, and socioeconomic status of the patients (p=0.000, p=0.000, p=0.000). In addition, a statistically significant and negative correlation was determined between anemia and the number of pregnancies and the parity number (p=0.001, p=0.000) in both groups.
Conclusion
Anemia is a public health problem. Anemia has been determined to be an important problem both in the preconception period and early periods of pregnancy. It is necessary to revise the programs and interventions to reduce the prevalence of anemia and redesign them in line with current conditions.
Key-words Anemia, iron-deficiencypreconception carePregnancy complications, hematologicPregnancy trimester, firstSee more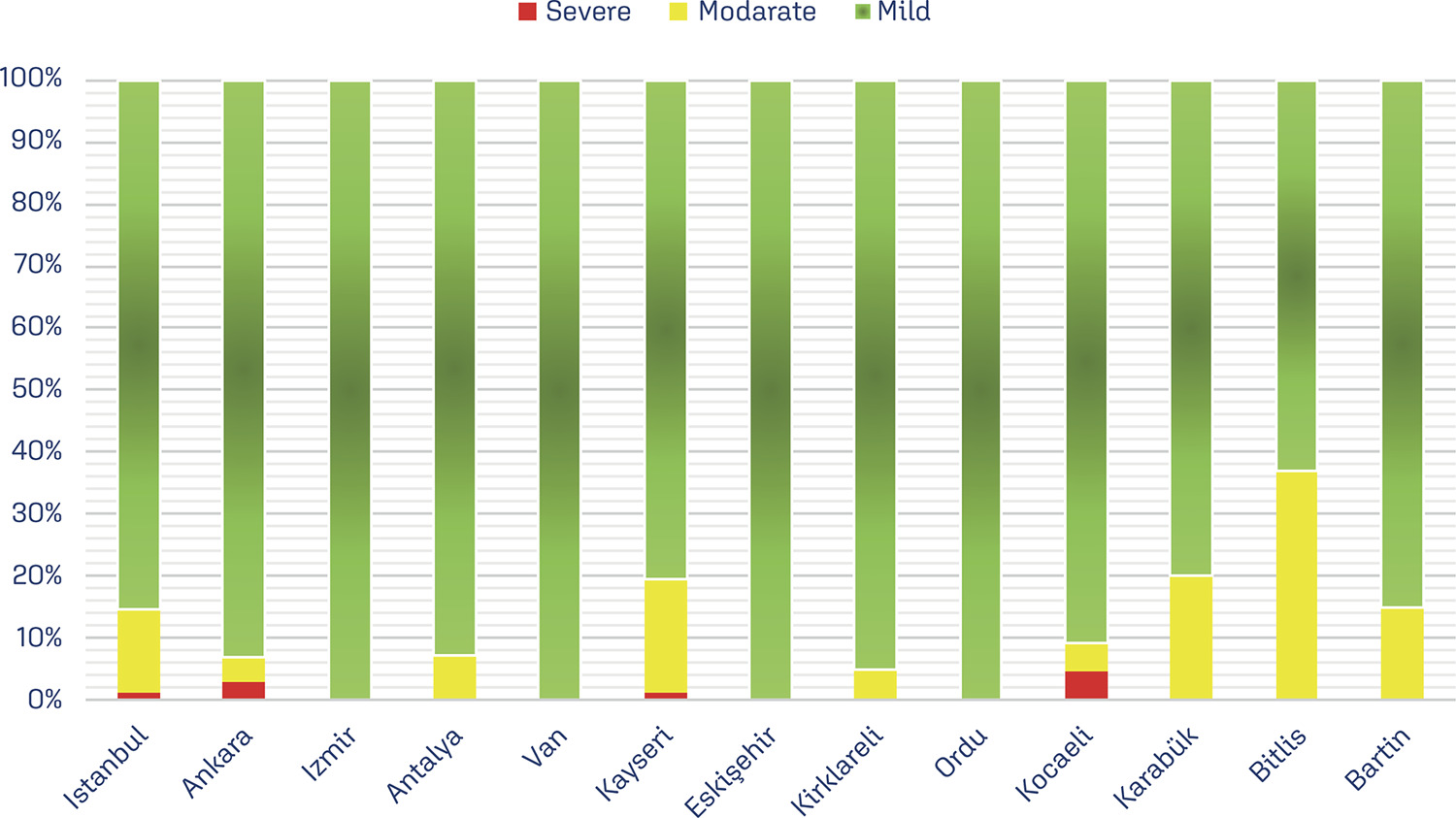
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT02-06-2025
Menopause in gynecologic cancer survivors: evidence for decision-making
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-FPS1
Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTMenopause in gynecologic cancer survivors: evidence for decision-making
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-FPS1
Views271See moreKey points
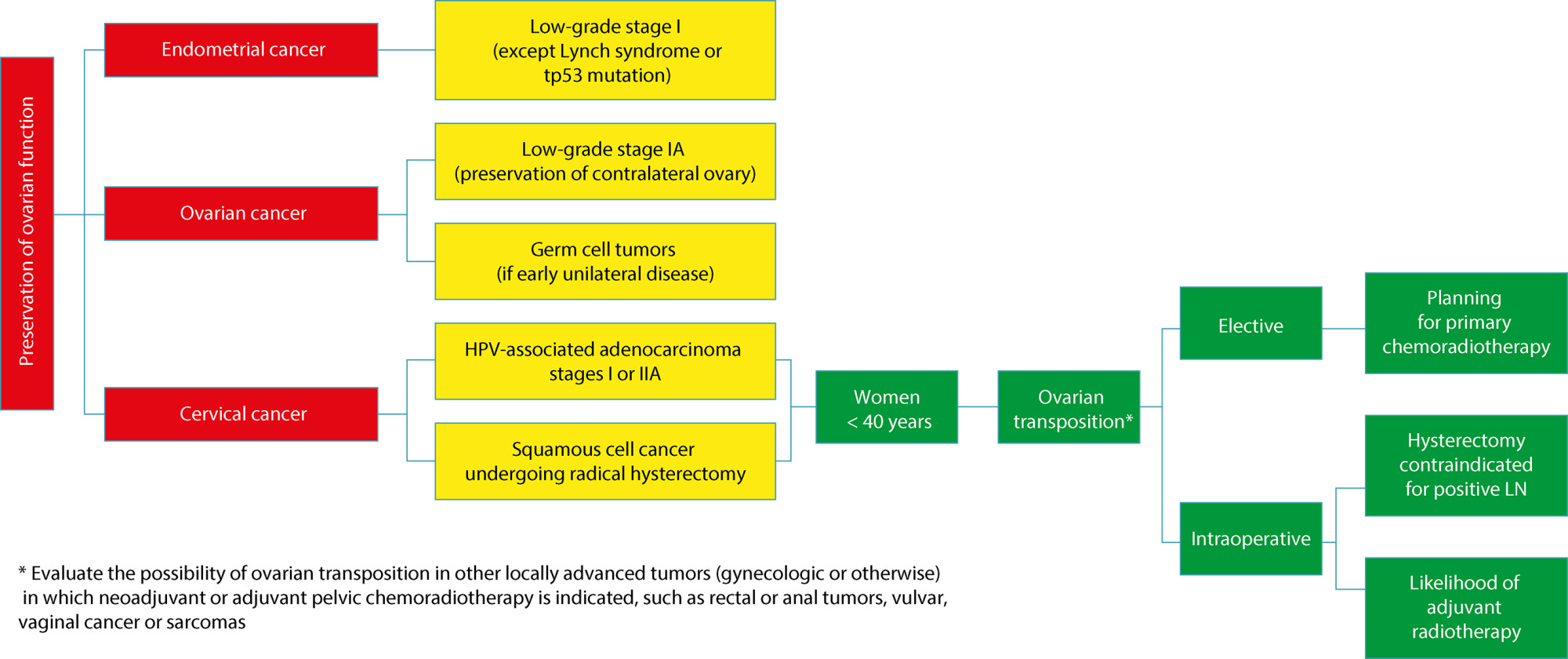
• Although advances in the treatment of gynecological cancer have improved survival rates, they may also increase the effects of induced menopause, especially in young women.
• Cancer treatments such as oophorectomy, gonadotoxic chemotherapy, and pelvic radiotherapy can induce menopause.
• Gonadotoxic chemotherapy, especially alkylating-containing regimens, often damages ovarian function and may result in permanent menopause.
• Pelvic radiotherapy usually results in permanent loss of ovarian function unless ovarian transposition is performed.
• Diagnosing menopause after cancer is challenging, and common diagnostic criteria such as 12 months or more of amenorrhea and elevated follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) levels are not entirely reliable, since ovarian function may return years after treatment.
• A multidisciplinary approach to post-cancer menopause is essential and should include an appropriate line of care, since hormone replacement therapy after treatment of gynecologic malignancy is controversial.
-
Original Article01-23-2025
A comparison of the efficacy of the effect of online versus face-to-face group counseling based on positive-approach on sexual intimacy of women after benign abdominal hysterectomy: a clinical trial
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo102
Abstract
Original ArticleA comparison of the efficacy of the effect of online versus face-to-face group counseling based on positive-approach on sexual intimacy of women after benign abdominal hysterectomy: a clinical trial
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo102
Views265See moreAbstract
Objective
The study investigates the influence of positive-approach counseling through both online and face-to-face group therapy on the sexual intimacy of women after benign complete abdominal hysterectomy, addressing challenges such as the loss of femininity and other psychosexual complications that disrupt the couple’s relationship post-surgery.
Methods
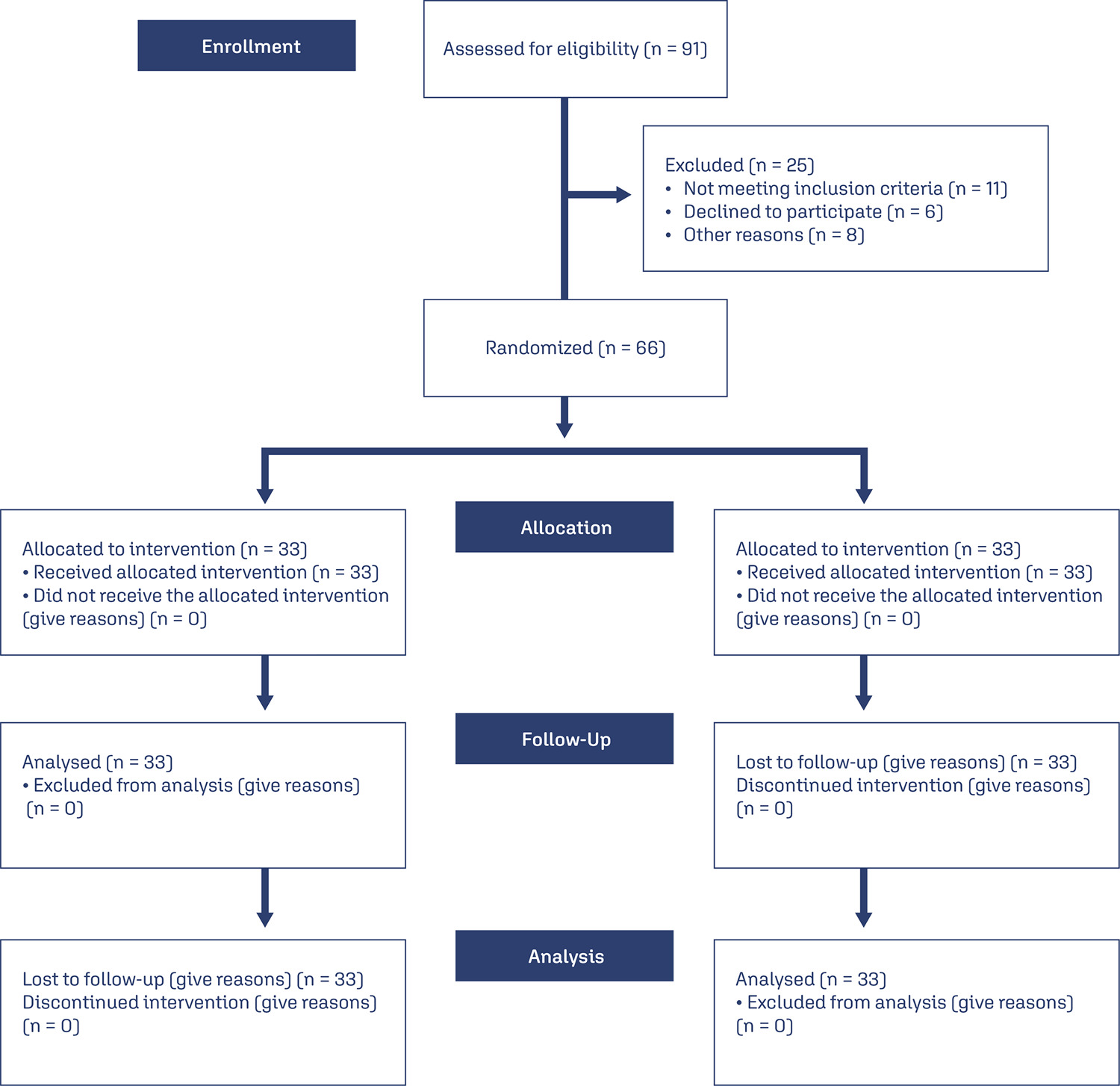
This is a parallel clinical trial, conducted in 2023 in Yazd, Iran; with sixty-six participants post- benign complete abdominal hysterectomy were randomly assigned to online and face-to-face counseling groups. Each group had eight 90-minute sessions, and data were collected using demographic and intimacy scale (IS) questionnaires at baseline, eighth week, and twelfth week follow-up. Statistical analysis used SPSS version 23 (P < 0.05).
Results
In the Online Group, the mean sexual intimacy score significantly increased from 72.42 ± 9.05 to 87.06 ± 7.98 at eight weeks and 90.30 ± 8.23 at twelve weeks (P < 0.001). In the Face-to-Face Group, the mean score increased from 70.21 ± 6.75 to 81.24 ± 5.55 at eight weeks and 85.03 ± 5.40 at twelve weeks (P < 0.001). Online counseling proved more effective than face-to-face counseling in enhancing sexual intimacy (P = 0.043).
Conclusion
Online and face-to-face counseling based on the positive approach improved sexual intimacy in women with a history of benign hysterectomy. Moreover, it seems that online counseling was more effective, so it is recommended that this method be employed in follow-up sessions after hysterectomy. Iranian Registry of Clinical Trials – IRCT20230209057373N1
-
Original Article01-23-2025
Therapeutic resources used by physiotherapists for the relief of labor pain: a cross-sectional study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo99
Abstract
Original ArticleTherapeutic resources used by physiotherapists for the relief of labor pain: a cross-sectional study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo99
Views289Abstract
Objective
The aim of the study was to identify non-pharmacological therapeutic resources used by physiotherapists for pain relief during labor and childbirth.
Methods
This is a cross-sectional study conducted from January to March 2021, followed the STROBE guidelines. It included Brazilian physiotherapists with a minimum of two years in obstetric care experience. Data were collected using a 33-item online questionnaire, which covered sociodemographic details and the utilization of non-pharmacological resources. Descriptive analysis was used to determine participant characteristics. Associations between sociodemographic variables, specialist titles, participation in scientific events, and methods for pain relief methods during childbirth were assessed using chi-square or Fisher’s exact tests. Data were analyzed using SPSS version 23.0, with a significance level set at 5% (p < 0.05).
Results
A total of 114 Brazilian physiotherapists participated in this study. Participants chose to utilize non-pharmacological therapies and resources that are within the scope of physiotherapists’ practice for labor pain. Kinesiotherapy with the use of devices was the most employed technique for pain relief during the birthing process.
Conclusion
The study highlights the prevalent use of non-pharmacological therapeutic resources, particularly kinesiotherapy with devices, among Brazilian physiotherapists for labor pain relief.
Key-words childbirthlabor painLabor, obstetricNon-pharmacological resourcespain managementParturiationPhysical therapistsPregnancysurveys and questionnairesSee more -
Original Article01-23-2025
Maternal erythrocytosis as a risk factor for small for gestational age at term in high altitude
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo98
Abstract
Original ArticleMaternal erythrocytosis as a risk factor for small for gestational age at term in high altitude
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo98
Views278Abstract
Objective
To determine if maternal erythrocytosis is a risk factor for small-for-gestational age at term at 3,400-m altitude in pregnant women without intercurrent disease.
Methods
Analytical study of retrospective cohorts at Cusco, a city at 3,400-m altitude. Our participants were 224 and 483 pregnant women with and without exposure to maternal erythrocytosis, respectively. A logistic regression with the goodness of fit to the proposed model was also performed with the Hosmer and Lemeshow test, evaluating the small-for-gestational-age results with or without exposure to hemoglobin >14.5 g/dl.
Results
The incidence of small-for-gestational-age was 6.9% for this entire cohort. The maternal erythrocytosis during gestation without any maternal morbidity at 3,400-m altitude has an ORa=0.691 (p=0.271) for small-for-gestational-age at term. Inadequate prenatal control has an ORa=2.115 (p=0.016) for small-for-gestational-age compared to adequate prenatal control.
Conclusion
Maternal erythrocytosis in pregnant women without any morbidity is not a risk factor for small-for-gestational-age at 3,400 m-altitude.
Key-words AltitudeFetal growth retardationGestational agehemoglobinHypoxiaMorbidityNeonatal mortalityPolycythemiaPregnancyPregnant womenRisk factorssmall for gestational ageSee more -
Original Article01-23-2025
Comparison of serum ischemia modified albumin levels between preeclamptic and healthy pregnant women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo97
Abstract
Original ArticleComparison of serum ischemia modified albumin levels between preeclamptic and healthy pregnant women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo97
Views339See moreAbstract
Objective
Our aims to compare level of serum ischemia modified albümin(IMA) between healthy and preeclamptic pregnancies and to evaluate the relationship of IMA with preeclampsia, preeclampsia severity and perinatal outcomes.
Methods
Our study is a prospective case-control study. A total of 134 pregnant women (66 preeclamptic and 68 healthy pregnant) between 18-45 years of age and between 24- 41 gestational weeks participated. Serum IMA levels were measured by the Albumin Cobalt Binding (ACB) test.
Results
The mean IMA values were found to be significantly higher in the preeclampsia group compared to the control group (p<0,001). Patients were divided into 3 groups; severe preeclampsia(n=29), non-severe preeclampsia(n=37) and healthy pregnant(n=68). Statistically significant difference was not found between severe preeclampsia and non-severe preeclampsia (p=0.505). The performance of IMA values in predicting the development of preeclampsia among all participants was evaluated with Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) analysis. According to the ROC analysis, the best cut-off value at which the maximum area under the curve (AUC) was obtained was found when IMA>0.98(AUC: 0.690 95% Confidence Interval (CI): 0.600-0.781 p<0.001). When IMA threshold value of >0.98 was taken to predict preeclampsia; the sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) were calculated as 65.15%, 64.71%, 64.18%, and 65.67%, respectively.
Conclusion
IMA level may be a useful new marker in recognizing and predicting preeclampsia. However, despite the power of recognizing the disease, serum IMA levels do not give an idea about the severity of the disease. More comprehensive studies are needed in order to use IMA levels in the diagnosis of preeclampsia.
Search
Search in:
Tag Cloud
Pregnancy (252)Breast neoplasms (104)Pregnancy complications (104)Risk factors (103)Menopause (88)Ultrasonography (83)Cesarean section (78)Prenatal care (71)Endometriosis (70)Obesity (61)Infertility (57)Quality of life (55)prenatal diagnosis (51)Women's health (48)Postpartum period (46)Maternal mortality (45)Pregnant women (45)Breast (44)Prevalence (43)Uterine cervical neoplasms (43)