- Recent Articles
- Most Citedi
- Most Visitedi
- Future Articles
-
Original Article04-11-1998
Prenatal diagnosis of fetal lung maturity in high-risk pregnancies
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(6):315-321
Views80

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticlePrenatal diagnosis of fetal lung maturity in high-risk pregnancies
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(6):315-321
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000600004
Views80See moreThe objective was to evaluate the accuracy of the foam stability test, lecithin/sphingomyelin (LS) ratio, presence of phosphatidylglycerol (PG) and lung profile (L/S ratio > 1.7 and PG present simultaneously) in 121 consecutive high-risk gestations at the São Paulo Hospital from January 1990 to January 1995. Delivery occurred within 3 days of fetal lung maturation testing. This is a prospective study in which the sensitivity, specificity, positive (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) of all the tests were determined. Neonatal respiratory outcome and amniocentesis results were stratified by gestational age for comparison. The distribution of the studied population according to maternal pathology was diabetes mellitus (48), hypertensive disorders (41), Rh isoimmunization (14) and miscellaneous (18). Respiratory distress (RD) was present in 33 infants (27.2%), mainly in the diabetic group. There was no false negative using lung profile (all patients) and foam stability tests among hypertensive pregnancies (specificity 100%), but there were about 20% to 50% false positives in the other tests. Overall, all four tests had a low PPV: 23% for foam test, 51% for L/S ratio, 63% for PG, 61% for lung profile, and high NPV: 92% for foam test, 88% for L/S ratio, 89% for PG and 100% for lung profile. All tests had less accuracy in the diabetic pregnant women. This study shows that the presence of PG and L/S ratio > 1.7 in the amniotic fluid of high-risk pregnancies confirms maturity with a very low risk to develop RD and that the foam stability test was useful as a first-line test to predict the absence of surfactant-deficient respiratory distress syndrome, particularly in hypertensive pregnant women.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article04-11-1998
The effects of nomegestrol acetate subdermal implant on carbohydrate metabolism, serum lipoproteins and on hepatic function
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(6):309-313
Views108

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleThe effects of nomegestrol acetate subdermal implant on carbohydrate metabolism, serum lipoproteins and on hepatic function
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(6):309-313
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000600003
Views108Objective: to evaluate variations in body weight, arterial blood pressure, fasting glucose, HbA1C, insulin, total cholesterol, HDL-C, LDL-C, triglycerides, Sgot, SGPT, GGT and bilirubin in women bearing a single subdermal Silastic implant containing 55 mg (+ 10%) of nomegestrol acetate during two years. Methods: eighteen healthy volunteers of reproductive age who desired to use anticonceptive drugs and who did not present contraindications to hormonal contraception participated in the study. All women were investigated before starting treatment and were followed-up for two years. At the end of the first year the capsules were inserted. Results: body weight increased from 54.9 + 1.5 kg at admission to 55.3 + 2.0 kg at 12 months of use (p<0.05) and from 56.0 + 2.7 kg at 24 months of use. There was a slight increase in arterial blood pressure, both systolic and diastolic, at month 12 (p<0.01). At month 24, the arterial blood pressure was not significantly different from the values at admission. All values were within the normal range. Insulin, HbA1C, LDL-C and GGT remained unchanged during the use of the implant. A significant decrease in total cholesterol (p<0.05) was observed in the third month and of HDL-C (p<0.01) in the sixth month. All lipoprotein alterations were inconsistent and values were within the normal range. Significant increases in fast glucose (p<0.05 and p<0.01) were observed in the third and sixth months, respectively. Significant SGOT decreases (p<0.05, p<0.01 and p<0.05) were observed in months 6, 18 and 24, respectively, and of SGPT (p<0.05) in month 18. Significant bilirubin increase (p<0.05) was observed only in the third month of implant use. All these variations remained within the normal range. Conclusions: these results show that, within the normal range, fasting glucose variations do not correlate with alterations in insulin levels. The slight serum lipoprotein, SGTO, SGPT and insulin alterations were transient. No clinical effects could be observed regarding lipoproteins, carbohydrate metabolism, insulin levels and liver function among the users during the two years.
Key-words ContraceptionCorbohydrate metabolismInjectable contraceptive drugsLiver functionProgesteroneSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article04-11-1998
Mammographic density variation in users and nonusers of hormonal replacement therapy
- Cesar Cabello dos Santos,
- Aarão Mendes Pinto-Neto,
- Lúcia Helena Simões Costa-Paiva,
- Henrique Benedito Brenelli
Abstract
Original ArticleMammographic density variation in users and nonusers of hormonal replacement therapy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(6):303-308
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000600002
- Cesar Cabello dos Santos,
- Aarão Mendes Pinto-Neto,
- Lúcia Helena Simões Costa-Paiva,
- Henrique Benedito Brenelli
Views87See moreObjective: to compare mammographic density changes, case by case, according to image digitization in three consecutive evaluations of users or nonusers of hormonal replacement therapy (HRT). Methods: 59 postmenopausal women were evaluated, 43 being users of cyclic or continuous estro-progestin hormonal replacement therapy, and 16 nonusers. The criteria of inclusion were: amenorrhea for at least 12 months, a normal mammographic examination at the beginning of the HRT (users) or the clinical follow-up without HRT (nonusers), at two incidences (mediolateral and craniocaudal). The following variables were used for the evaluation of mammary density: initial change – the difference between the first mammography after HRT performed in 12 ± 3 months and the mammography performed before HRT-and final change – the difference between the second mammography after HRT performed in 24 ± 3 months and the mammography performed before HRT. Wilcoxon and c² tests were used in order to evaluate the differences in mammographic density changes. Results: more than half (56.3%) of the women, HRT users with initial increase in mammographic density remained with the increase after the final evaluation. This finding was not significant (p=0.617). In the same group, the initial nonincrease was significantly associated with the final nonincrease (p=0.017). Among the nonusers, all breasts that were not totally fat at the initial evaluation presented a mammographic density decrease at the final evaluation. Conclusions: the majority of HRT users presenting mammographic density increase at the first evaluation, after approximately one year of use, remained with the increase at a second evaluation. After some time, the nonusers tended to present a significant mammographic density decrease (p=0.003).


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
04-11-1998
A FEBRASGO e as ações voltadas para a promoção da saúde
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(6):301-301
Abstract


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
04-10-1998
Avaliação longitudinal de aspectos imunológicos e virológicos durante a gravidez e puerpério em mulheres portadoras do vírus da imunodeficiência humana tipo 1 (HIV-1)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):170-170
Abstract
Avaliação longitudinal de aspectos imunológicos e virológicos durante a gravidez e puerpério em mulheres portadoras do vírus da imunodeficiência humana tipo 1 (HIV-1)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):170-170
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000300011
Views89Avaliação Longitudinal de Aspectos Imunológicos e Virológicos Durante a Gravidez e Puerpério em Mulheres Portadoras do Vírus da Imunodeficiência Humana Tipo 1 (HIV-1)[…]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
04-10-1998
A dopplervelocimetria com mapeamento em cores dos ramos intramiometriais da artéria uterina de mulheres na pós-menopausa, com e sem carcinoma de endométrio
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):169-170
Abstract
A dopplervelocimetria com mapeamento em cores dos ramos intramiometriais da artéria uterina de mulheres na pós-menopausa, com e sem carcinoma de endométrio
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):169-170
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000300010
Views72A Dopplervelocimetria com Mapeamento em Cores dos Ramos Intramiometriais da Artéria Uterina de Mulheres na Pós-Menopausa, com e sem Carcinoma de Endométrio[…]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
04-10-1998
Avaliação da esteroidogênese das supra-renais em mulheres normais por meio dos testes de ACTH simples de depósito
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):169-169
Abstract
Avaliação da esteroidogênese das supra-renais em mulheres normais por meio dos testes de ACTH simples de depósito
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):169-169
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000300009
Views71Avaliação da Esteroidogênese das Supra-Renais em Mulheres Normais por Meio dos Testes de ACTH Simples de Depósito[…]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Case Report04-10-1998
Recurrent HELLP syndrome: report on two cases
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):165-167
Views73

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Case ReportRecurrent HELLP syndrome: report on two cases
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):165-167
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000300008
Views73See moreHELLP syndrome is a severe complication of preeclampsia that increases maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality. Two cases of recurrent HELLP syndrome are described, maternal death occurring in one of the cases. This study is a warning about the increased risk of HELLP syndrome in the next pregnancy.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
-
Original Article11-28-2005
Cardiofemoral index for the evaluation of fetal anemia in isoimmunized pregnancies
- Antônio Carlos Vieira Cabral,
- Thales Bittencourt de Barcelos,
- Isabela Gomes Melo Apocalipse,
- Henrique Vitor Leite,
- Zilma Silveira Nogueira Reis
Views130

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleCardiofemoral index for the evaluation of fetal anemia in isoimmunized pregnancies
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(8):450-455
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000800003
- Antônio Carlos Vieira Cabral,
- Thales Bittencourt de Barcelos,
- Isabela Gomes Melo Apocalipse,
- Henrique Vitor Leite,
- Zilma Silveira Nogueira Reis
Views130See morePURPOSE: to test a new, noninvasive method for the diagnosis of fetal anemia in red blood cell isoimmunized pregnancies. METHODS: the index obtained by the ratio between the ultrasonographic measurement of the biventricular outer dimension (BVOD) and femur length (both in centimeters) was correlated with fetal hemoglobin values in a cross-sectional study. Fifty-nine fetuses of isoimmunized pregnancies selected for invasive treatment and submitted to 130 cordocenteses for the diagnosis and treatment of anemia were included in the study. The cardiofemoral index was obtained immediately before the cordocentesis and the fetal hemoglobin index was obtained from fetal blood samples. Linear regression was carried out to assess the correlation between the index and fetal hemoglobin; ROC curve was applied to determine the most accurate cutoff for the diagnosis of the fetal hemoglobin concentration below 10g/dl. RESULTS: BVOD measurement varied from 1.6 to 4.7 cm (average 2.5±1.3cm), and length of the femur, from 3.0 to 6.9 cm (average 4.3±0.9 cm). The cardiofemoral index varied from 0.4 to 1.0 (average 0.6±0.1). A significant inverse correlation between the cardiofemoral index and fetal hemoglobin (R²=0.37 and p<0.0001) was observed. The cutoff of 0.60 was the best to predict a level of fetal hemoglobin below or equal to 10.0g/dl: 80.85% sensitivity, 83.13% specificity, 73.8% positive predictive value, and 88.46% negative predictive value, in the diagnosis of fetuses anemia. CONCLUSION: the cardiofemoral index allows for good accuracy in the prediction of fetal hemoglobin concentration below 10g/dl in red blood cell isoimmunized pregnancies. It may thus be applied as a noninvasive method to the diagnosis of this pathology.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article01-30-2005
Fetal macrosomia risk factors in pregnancies complicated by diabetes or daily hyperglycemia
- Luciane Teresa Rodrigues Lima Kerche,
- Joelcio Francisco Abbade,
- Roberto Antonio Araújo Costa,
- Marilza Vieira Cunha Rudge,
- Iracema de Mattos Paranhos Calderon
Views110

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleFetal macrosomia risk factors in pregnancies complicated by diabetes or daily hyperglycemia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(10):580-587
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001000003
- Luciane Teresa Rodrigues Lima Kerche,
- Joelcio Francisco Abbade,
- Roberto Antonio Araújo Costa,
- Marilza Vieira Cunha Rudge,
- Iracema de Mattos Paranhos Calderon
Views110See morePURPOSE: to identify risk factors for fetal macrosomia in pregnant women with diabetes or daily hyperglycemia. METHODS: retrospective study, control-case, including 803 pairs of mothers and newborns belonging to this specific population, divided into two groups – macrosomic (cases, n=242) and non-macrosomic (controls, n=561). Variables regarding age, parity, weight and body mass index (BMI), weight gain (WG), diabetes history, high blood pressure and tabagism, diabetes type and classification, and glycemic control indicators in the third trimester were compared. The means were evaluated by the F test and the categorized variables were submitted to univariate analysis using the chi² test. The significative results were included in the multiple regression model for the identification of macrosomia independent risk considering OR, 95% CI and p value. The statistical significance limit of 5% was established for all analyses. RESULTS: there was a significative association between macrosomia and WG >16 kg, BMI >25 kg/m², personal, obstetric and macrosomic history, classification in the Rudge groups (IB and IIA + IIB), glycemic mean (GM) >120 mg/dL and postprandial glycemic mean >130 mg/dL in the third trimester. In the multiple regression analysis, WG >16 kg (OR=1,79; 95% CI: 1,23-1.60), BMI >25 kg/m² (OR=1.83; 95% CI: 1.27-2.64), personal history of diabetes (OR=1.56; 95% CI: 1.05-2.31) and of macrosomia (OR=2.37; 95% CI: 1.60-3.50) and GM >120 mg/dL in the third trimester (OR=1.78; 95% CI: 1.13-2.80) confirmed to be independent risk factors for macrosomia in these pregnancies. CONCLUSION: WG >16 kg, BMI >25 kg/m², GM >120 mg/dL in the third trimester and personal history of macrosomia and diabetes were identified as risk factors for fetal macrosomia in pregnant women with diabetes or daily hyperglycemia.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article01-12-2008
Tibolone’s effect on retinal and ophthalmic arteries flowmetry
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(11):537-543
Views118

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleTibolone’s effect on retinal and ophthalmic arteries flowmetry
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(11):537-543
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008001100002
Views118PURPOSE: to evaluate the effect of tibolone use on dopplervelocimetric parameters of ophthalmic and retinal arteries. METHODS: clinical, prospective, longitudinal, randomized, placebo-controlled, triple-blind study, in which among 100 menopausal women, 50 have used 2.5 mg of the active principle tibolone (Tib Group) and 50, placebo as a means to form the control-group (Plac Group). In the Tib Group, 44 of the 50 women returned after 84 days to finish the exams, and in the Plac Group, 47. The ophthalmic and retinal arteries were studied to determine the resistance index (RI), the pulsatility index (PI) and the systole/diastole ratio (S/D). Assessments have been done before and 84 days after medication. The t-Student test has been used for the comparison of means between the groups in independent samples, as well as for within-group comparisons in dependent samples. RESULTS: in both groups, the women’s characteristics were similar in age, menopause duration, body mass index, arterial blood pressure, deliveries and cardiac rate. The Tib Group presented the following values in the ophthalmic artery: RI(pre)=0.71±0.05, RI(post)0.72±0.08 (p=0.43); PI(pre)=1.29±0.22, PI(post)=1.30±0.25 (p=0.4) and S/D(pre)=3.49±0.77, SD(post)=3.65±0.94 (p=0.32). In the retinal artery, the following values have been found: RI(pre)=0.67±0.09, RI(post)=0.69±0.10 (p=0.7); PI(pre)=1.20±0.29, PI(post)=1.22±0.3 (p=0.2) and SD(pre)=3.29±0.95, SD(post)=3.30±1.07 (p=0.3). Also, the tibolone and control groups did not show any significant difference in regard to the above indexes in the end of the study. CONCLUSIONS: the 2.5 mg dose of tibolone had no effect on the Doppler velocimetry indexes of the ophthalmic and retinal arteries.
Key-words Laser-doppler flowmetryNorpregnanesOphthalmic arteryPlacebosRandomized controlled trialsRetinal arteryUltrasonographySee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article07-02-2010
Myomectomy in the second trimester of pregnancy: case report
- Guilherme Karam Corrêa Leite,
- Henri Augusto Korkes,
- Arildo de Toledo Viana,
- Alexandre Pitorri,
- Grecy Kenj, [ … ],
- Nelson Sass
Views109

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleMyomectomy in the second trimester of pregnancy: case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(4):198-201
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000400008
- Guilherme Karam Corrêa Leite,
- Henri Augusto Korkes,
- Arildo de Toledo Viana,
- Alexandre Pitorri,
- Grecy Kenj,
- Nelson Sass
Views109See moreUterine leiomyomas are characterized as a benign disease and are observed in 2 to 3% of all normal pregnancies. Out of these, about 10% may present complications during pregnancy. We present a case of a pregnant patient sought emergency obstetric care at the 17th week, complaining of severe pain, presenting with painful abdominal palpation and sudden positive decompression. Ultrasonography revealed a myoma nodule measuring 9.1 x 7.7 cm; the patient was hospitalized and medicated, being also submitted to laparotomy and myomectomy due to worsening of her condition. Prenatal care revealed no further abnormalities, with resolution of gestation at 39 weeks. The newborn weighed 3,315 g, with Apgar scores of 9 and 10. In such cases, clinical treatment should always be attempted and surgery should be considered only in selected cases, mainly in the impossibility of conservative treatment or when the patient’s clinical features require immediate intervention. In this case, myomectomy was effective against maternal-fetal obstetric complications.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article01-06-2011
Assessment of fetal well-being in pregnancies complicated by maternal moderate to severe thrombocytopenia
- Roseli Mieko Yamamoto Nomura,
- Ana Maria Kondo Igai,
- Verbênia Nunes Costa,
- Seizo Miyadahira,
- Marcelo Zugaib
Views117

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleAssessment of fetal well-being in pregnancies complicated by maternal moderate to severe thrombocytopenia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(10):280-285
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011001000002
- Roseli Mieko Yamamoto Nomura,
- Ana Maria Kondo Igai,
- Verbênia Nunes Costa,
- Seizo Miyadahira,
- Marcelo Zugaib
Views117See morePURPOSE: To analyze the results of assessment of fetal well-being in pregnancies complicated by moderate or severe maternal thrombocytopenia. METHODS: Data from April 2001 to July 2011 of 96 women with a diagnosis of thrombocytopenia in pregnancy were retrospectively analyzed. We analyzed the following tests performed during the antepartum period for fetal assessment: cardiotocography, fetal biophysical profile, amniotic fluid index and umbilical artery Doppler velocimetry. RESULTS: A total of 96 pregnancies with the following diagnoses were analyzed: gestational thrombocytopenia (n=37, 38.5%) hypersplenism (n=32, 33.3%), immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP, n=14, 14.6%), secondary immune thrombocytopenia (n=6, 6.3%), bone marrow aplasia (n=3, 3.1%), and others (n=4, 4.1%). Cardiotocography showed normal results in 94% of cases, a fetal biophysical profile with an index of 8 or 10 in 96.9% and an amniotic fluid index >5.0 cm in 89.6%. Doppler umbilical artery velocimetry showed normal results in 96.9% of cases. In the analysis of the major groups of thrombocytopenia, the diagnosis of oligohydramnios was found to be significantly more frequent in the group with ITP (28.6%) compared to the other groups (gestational thrombocytopenia: 5.4% and hypersplenism: 9.4%, p=0.04). CONCLUSIONS: This study indicates that in pregnancies complicated by moderate or severe maternal thrombocytopenia, even though the fetal well-being remains preserved in most cases, fetal surveillance is important in pregnant women with ITP, with emphasis on amniotic fluid volume evaluation due to its association with oligohydramnios.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article01-10-2013
Quality of clinical studies published in the RBGO over one decade (1999-2009): methodological and ethical aspects and statistical procedures
- Joceline Cássia Ferezini de Sá,
- Gabriela Marini,
- Rafael Bottaro Gelaleti,
- João Batista da Silva,
- George Dantas de Azevedo, [ … ],
- Marilza Vieira Cunha Rudge
Abstract
Original ArticleQuality of clinical studies published in the RBGO over one decade (1999-2009): methodological and ethical aspects and statistical procedures
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(11):477-482
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013001100001
- Joceline Cássia Ferezini de Sá,
- Gabriela Marini,
- Rafael Bottaro Gelaleti,
- João Batista da Silva,
- George Dantas de Azevedo,
- Marilza Vieira Cunha Rudge
Views121PURPOSE: To evaluate the methodological and statistical design evolution of the publications in the Brazilian Journal of Gynecology and Obstetrics (RBGO) from resolution 196/96. METHODS: A review of 133 articles published in 1999 (65) and 2009 (68) was performed by two independent reviewers with training in clinical epidemiology and methodology of scientific research. We included all original clinical articles, case and series reports and excluded editorials, letters to the editor, systematic reviews, experimental studies, opinion articles, besides abstracts of theses and dissertations. Characteristics related to the methodological quality of the studies were analyzed in each article using a checklist that evaluated two criteria: methodological aspects and statistical procedures. We used descriptive statistics and the χ2 test for comparison of the two years. RESULTS: There was a difference between 1999 and 2009 regarding the study and statistical design, with more accuracy in the procedures and the use of more robust tests between 1999 and 2009. CONCLUSIONS: In RBGO, we observed an evolution in the methods of published articles and a more in-depth use of the statistical analyses, with more sophisticated tests such as regression and multilevel analyses, which are essential techniques for the knowledge and planning of health interventions, leading to fewer interpretation errors.
Key-words Clinical trials as topicEthics Committees, researchEthics, researchGynecologyHelsinki DeclarationObstetricsPeriodicals as topicScientific misconductStatisticsSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Case Report12-01-2015
Renal vein thrombosis in the puerperium: case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(12):593-597
Abstract
Case ReportRenal vein thrombosis in the puerperium: case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2015;37(12):593-597
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320150005455
Views109Abstract
Pregnancy and puerperium are periods of blood hypercoagulability and, therefore, of risk for thromboembolic events. Renal vein thrombosis is a serious and infrequent condition of difficult diagnosis. This study reported a case of renal vein thrombosis in the puerperium, and described the clinical case, risk factors, diagnostic methods, and treatment instituted.
Key-words Case reportsPostpartum periodPregnancy complications, hematologicThrombophiliaVenous thrombosisSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article06-27-2024
Prevalence of karyotype alterations in couples with recurrent pregnancy loss in a tertiary center in Brazil
- Elaine Cristina Fontes de Oliveira
 ,
, - Ines Katerina Damasceno Cavallo Cruzeiro
 ,
, - Cezar Antônio Abreu de Souza
 ,
, - Fernando Marcos Reis

Views176

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticlePrevalence of karyotype alterations in couples with recurrent pregnancy loss in a tertiary center in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo51
- Elaine Cristina Fontes de Oliveira
 ,
, - Ines Katerina Damasceno Cavallo Cruzeiro
 ,
, - Cezar Antônio Abreu de Souza
 ,
, - Fernando Marcos Reis

Views176Abstract
Objective
To assess the prevalence and type of chromosomal abnormalities in Brazilian couples with recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL) and compare the clinical characteristics of couples with and without chromosome abnormalities.
Methods
We assessed the medical records of 127 couples with a history of two or more miscarriages, referred to a tertiary academic hospital in Belo Horizonte, Brazil, from January 2014 to May 2023. Karyotype was generated from peripheral blood lymphocyte cultures, and cytogenetic analysis was performed according to standard protocols by heat-denatured Giemsa (RHG) banding.
Results
Abnormal karyotypes were detected in 10 couples (7.8%). The prevalence of chromosomal abnormalities was higher among females (6.3%) compared to males (2.0%), but this difference was not statistically significant (p=0.192). The mean number of miscarriages was. 3.3 ± 1.1 in couples with chromosome abnormalities and 3.1 ± 1.5 in couples without chromosome abnormalities (p=0.681). Numerical chromosomal anomalies (6 cases) were more frequent than structural anomalies. Four women presented low-grade Turner mosaicism. No differences were found between couples with and without karyotype alterations, except for maternal age, which was higher in the group with chromosome alterations.
Conclusion
The prevalence of parental chromosomal alterations in our study was higher than in most series described in the literature and was associated with increased maternal age. These findings suggest that karyotyping should be part of the investigation for Brazilian couples with RPL, as identifying the genetic etiology may have implications for subsequent pregnancies.
Key-words Abortion, habitualAbortion, spontaneousChromosome aberrationsKaryotypeTranslocation, geneticSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Elaine Cristina Fontes de Oliveira
-
Review Article06-01-2018
Breastfeeding and the Benefits of Lactation for Women’s Health
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):354-359
Views476

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleBreastfeeding and the Benefits of Lactation for Women’s Health
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):354-359
Views476See moreAbstract
The offer of the maternal breast to the baby is an unquestionable right of mothers and their children, and all efforts should bemade to promote, follow and maintain exclusive breastfeeding for up to 6months and supplement it until the child completes 2 years of age. Many publications are available in the literature about the qualities of breast milk, its benefits and health repercussions, stimulating the practice of breastfeeding and supporting campaigns for its implementation. However, although it is widely known that breastfeeding is an important step in the reproductive process of women and its practice offers benefits to both mother and child, most of the available information highlights the benefits of breast milk for children, while mention of the effects of breastfeeding on the health of the mother is usually neglected. Thus, the objective of the present study is to highlight the multiple benefits of breastfeeding for the physical and emotional health of the nursing mother. The authors consulted articles published in the databases PubMed, Virtual Health Library andWeb of Science using the keywords breastfeeding, breast milk, lactation and maternal health.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article09-01-2017
Preeclampsia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(9):496-512
Views495

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticlePreeclampsia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(9):496-512
Views495Abstract
The authors review hypertensive disease during pregnancy with an academic and practical view, and using the best evidence available. This disease, which is the most important clinical disease in Brazilian pregnant women, may have its incidence reduced with prevention through the use of calcium and aspirin in pregnant women at risk. Previously, it was a disease that presented with hypertension with proteinuria, but it has now been classified with new clinical parameters besides proteinuria. Morbidity and mortality should be reduced in a continental country such as Brazil using protocols for the early treatment of complications by calculating severe outcomes in preeclampsia. The early treatment of acute hypertension, use of magnesium sulfate and early hospitalization in cases of preeclampsia are concepts to pursue the reduction of our pregnant women’s mortality.
Key-words HELLP syndromeHigh risk pregnancyPreeclampsiapregnancy arterial hypertensionPregnancy complicationsSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 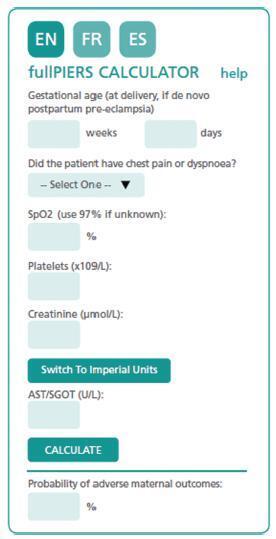
-
Review Article09-25-2020
Primary Dysmenorrhea: Assessment and Treatment
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(8):501-507
Views480

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticlePrimary Dysmenorrhea: Assessment and Treatment
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(8):501-507
Views480See moreAbstract
Primary dysmenorrhea is defined asmenstrual pain in the absence of pelvic disease. It is characterized by overproduction of prostaglandins by the endometrium, causing uterine hypercontractility that results in uterine muscle ischemia, hypoxia, and, subsequently, pain. It is the most common gynecological illness in women in their reproductive years and one of the most frequent causes of pelvic pain; however, it is underdiagnosed, undertreated, and even undervalued by women themselves, who accept it as part of themenstrual cycle. It hasmajor implications for quality of life, such as limitation of daily activities and psychological stress, being one of themain causes of school and work absenteeism. Its diagnosis is essentially clinical, based on the clinical history and normal physical examination. It is important to exclude secondary causes of dysmenorrhea. The treatment may have different approaches (pharmacological, nonpharmacological and surgical), but the first line of treatment is the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and, in cases of women who want contraception, the use of hormonal contraceptives. Alternative treatments, such as topical heat, lifestyle modification, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, dietary supplements, acupuncture, and acupressure, may be an option in cases of conventional treatments’ contraindication. Surgical treatment is only indicated in rare cases of women with severe dysmenorrhea refractory to treatment.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article09-01-2018
Multiple Pregnancy: Epidemiology and Association with Maternal and Perinatal Morbidity
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):554-562
Views374

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleMultiple Pregnancy: Epidemiology and Association with Maternal and Perinatal Morbidity
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):554-562
Views374See moreAbstract
Twin pregnancy accounts for 2 to 4% of total births, with a prevalence ranging from 0.9 to 2.4% in Brazil. It is associated with worse maternal and perinatal outcomes. Many conditions, such as severe maternal morbidity (SMM) (potentially life-threatening conditions and maternal near-miss) and neonatal near-miss (NNM) still have not been properly investigated in the literature. The difficulty in determining the conditions associated with twin pregnancy probably lies in its relatively low occurrence and the need for larger population studies. The use of the whole population and of databases from large multicenter studies, therefore, may provide unprecedented results. Since it is a rare condition, it ismore easily evaluated using vital statistics from birth e-registries. Therefore, we have performed a literature review to identify the characteristics of twin pregnancy in Brazil and worldwide. Twin pregnancy has consistently been associated with SMM, maternal near-miss (MNM) and perinatal morbidity, with still worse results for the second twin, possibly due to some characteristics of the delivery, including safety and availability of appropriate obstetric care to women at a high risk of perinatal complications.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 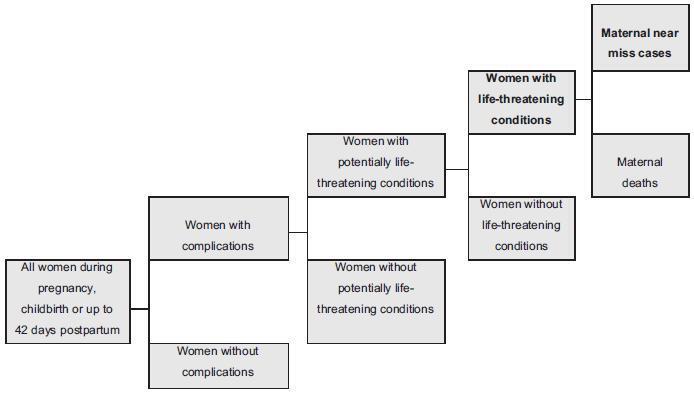
-
Review Article05-01-2018
Uterine Artery Doppler in Screening for Preeclampsia and Fetal Growth Restriction
- Marianna Amaral Pedroso,
- Kirsten Rebecca Palmer,
- Ryan James Hodges,
- Fabricio da Silva Costa,
- Daniel Lorber Rolnik
Views333

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleUterine Artery Doppler in Screening for Preeclampsia and Fetal Growth Restriction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(5):287-293
- Marianna Amaral Pedroso,
- Kirsten Rebecca Palmer,
- Ryan James Hodges,
- Fabricio da Silva Costa,
- Daniel Lorber Rolnik
Views333See moreAbstract
Objective
To perform a comprehensive review of the current evidence on the role of uterine artery Doppler, isolated or in combination with other markers, in screening for preeclampsia (PE) and fetal growth restriction (FGR) in the general population. The review included recently published large cohort studies and randomized trials.
Methods
A search of the literature was conducted usingMedline, PubMed, MeSH and ScienceDirect. Combinations of the search terms “preeclampsia,” “screening,” “prediction,” “Doppler,” “Doppler velocimetry,” “fetal growth restriction,” “small for gestational age” and “uterine artery” were used. Articles in English (excluding reviews) reporting the use of uterine artery Doppler in screening for PE and FGR were included.
Results
Thirty articles were included. As a single predictor, uterine artery Doppler detects less than 50% of the cases of PE and no more than 40% of the pregnancies affected by FGR. Logistic regression-based models that allow calculation of individual risk based on the combination of multiple markers, in turn, is able to detect ~ 75% of the cases of preterm PE and 55% of the pregnancies resulting in small for gestational age infants.
Conclusion
The use of uterine artery Doppler as a single predictive test for PE and FGR has poor accuracy. However, its combined use in predictive models is promising, being more accurate in detecting preterm PE than FGR.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article02-01-2016
Conservative Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- Rafael Mendes Moroni,
- Pedro Sergio Magnani,
- Jorge Milhem Haddad,
- Rodrigo de Aquino Castro,
- Luiz Gustavo Oliveira Brito
Views304

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleConservative Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(2):97-111
- Rafael Mendes Moroni,
- Pedro Sergio Magnani,
- Jorge Milhem Haddad,
- Rodrigo de Aquino Castro,
- Luiz Gustavo Oliveira Brito
Views304See moreWe performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials that studied the conservative management of stress urinary incontinence (SUI). There were 1058 results after the initial searches, from which 37 studies were eligible according to previously determined inclusion criteria. For the primary outcomes, pelvic floor muscle training (PFMT) was more efficacious than no treatment in improving incontinence-specific quality of life (QoL) scales (SMD = [1]1.24SDs; CI 95% = [1]1.77 to [1]0.71SDs). However, its effect on pad tests was imprecise. Combining biofeedback with PFMT had an uncertain effect on QoL (MD = [1]4.4 points; CI 95% = [1]16.69 to 7.89 points), but better results on the pad test, although with elevated heterogeneity (MD = 0.9g; 95%CI = 0.71 to 1,10g); group PFMT was not less efficacious than individual treatment, and home PFMT was not consistently worse than supervised PFMT. Both intravaginal and superficial electrical stimulation (IES and SES) were better than no treatment for QoL and pad test. Vaginal cones had mixed results. The association of IES with PFMT may improve the efficacy of the latter for QoL and pad test, but the results of individual studies were not consistent. Thus, there is evidence of the use of PFMT on the treatment of SUI, with and without biofeedback.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 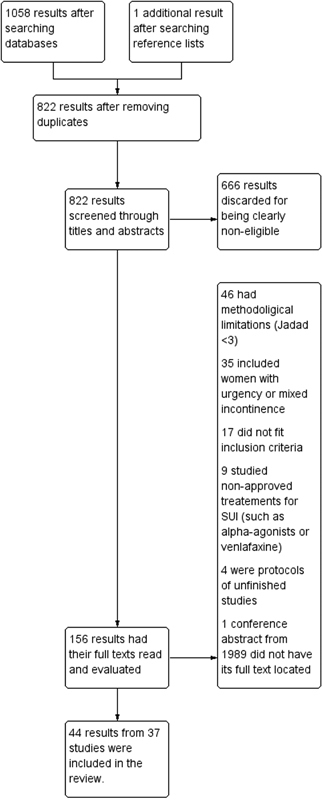
-
Review Article09-16-2019
Do Women have Adequate Knowledge about Pelvic Floor Dysfunctions? A Systematic Review
- Júlia Ferreira Fante,
- Thais Daniel Silva,
- Elaine Cristine Lemes Mateus-Vasconcelos,
- Cristine Homsi Jorge Ferreira,
- Luiz Gustavo Oliveira Brito

Views299

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleDo Women have Adequate Knowledge about Pelvic Floor Dysfunctions? A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(8):508-519
- Júlia Ferreira Fante,
- Thais Daniel Silva,
- Elaine Cristine Lemes Mateus-Vasconcelos,
- Cristine Homsi Jorge Ferreira,
- Luiz Gustavo Oliveira Brito

Views299See moreAbstract
Objective
We sought to investigate whether women present adequate knowledge of the main pelvic floor disorders (PFDs) (urinary incontinence – UI, fecal incontinence – FI, and pelvic organ prolapse – POP).
Data
sources A systematic review was performed in the MEDLINE, PEDro, CENTRAL, and Cochrane databases for publications from inception to April 2018. Selection of studies A total of 3,125 studies were reviewed. Meta-analysis was not possible due to the heterogeneity of primary outcomes and the diversity of instruments for measuring knowledge. The quality of the articles included in the analysis was evaluated with the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) adapted for cross-sectional studies.
Data collection
Two authors performed data extraction into a standardized spreadsheet.
Data synthesis
Nineteen studies were included, comprising 11,512 women. About the methodological quality (NOS), most of the studies (n= 11) presented a total score of 6 out of 10. Validated questionnaires and designed pilot-tested forms were the most frequently used ways of assessing knowledge. Some studies were stratified by race, age, or group minorities. The most used questionnaire was the prolapse and incontinence knowledge questionnaire (PIKQ) (n= 5). Knowledge and/or awareness regarding PFD was low to moderate among the studies. Urinary incontinence was the most prevalent PFD investigated, and the most important risk factors associated with the lack of knowledge of the pelvic floor were: African-American ethnicity (n= 3), low educational level (n= 4), low access to information (n= 5) and socioeconomic status (n= 3).
Conclusion
Most women have a gap in the knowledge of pelvic floor muscle dysfunctions, do not understand their treatment options, and are not able to identify risk factors for these disorders.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article08-26-2020
Covid-19 and Pregnancy: An Overview
- Pedro Castro
 ,
, - Ana Paula Matos
 ,
, - Heron Werner
 ,
, - Flávia Paiva Lopes
 ,
, - Gabriele Tonni
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Edward Araujo Júnior

Views210

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleCovid-19 and Pregnancy: An Overview
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(7):420-426
- Pedro Castro
 ,
, - Ana Paula Matos
 ,
, - Heron Werner
 ,
, - Flávia Paiva Lopes
 ,
, - Gabriele Tonni
 ,
, - Edward Araujo Júnior

Views210See moreAbstract
Since the World Health Organization (WHO) declared coronavirus infection (COVID-19) a Public Health Emergency of International Concern in January 2020, there have been many concerns about pregnant women and the possible effects of this emergency with catastrophic outcomes inmany countries. Information on COVID-19 and pregnancy are scarce and spread throughout a fewcase series, with no more than 50 cases in total. The present review provides a brief analysis of COVID-19, pregnancy in the COVID-19 era, and the effects of COVID-19 on pregnancy.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Pedro Castro
Search
Search in:
Tag Cloud
Pregnancy (252)Breast neoplasms (104)Pregnancy complications (104)Risk factors (103)Menopause (88)Ultrasonography (83)Cesarean section (78)Prenatal care (71)Endometriosis (70)Obesity (61)Infertility (57)Quality of life (55)prenatal diagnosis (51)Women's health (48)Postpartum period (46)Maternal mortality (45)Pregnant women (45)Breast (44)Prevalence (43)Uterine cervical neoplasms (43)
