-
Original Article04-09-1998
Condyloma Acuminatum in Children and Adolescents
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):377-380
Abstract
Original ArticleCondyloma Acuminatum in Children and Adolescents
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):377-380
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000700002
Views132See moreParpose: to analyze the epidemiologic factors, clinical manifestations and forms of treatment of infection with papiloma virus. Method: all cases of condyloma acuminatum in children and adolescents assisted in the period from 1990 to 1995 in the Service of Children and Adolescent Gynecology were revised. We present the following data: age, diagnosis, clinical manifestations, sites of the lesions, transmission modes and treatment. Results: the average age of the 18 studied cases, was 6 years and 11 months (ranging from 2 to 15 years). The most common clinical manifestation was the presence of warts (61.1%). The lesions were located in the vulvoperineal area in 44.4% of the patients, and perianal and vulvar lesions were observed respectively in 27.8% and 22,2% of the cases. It was not possible to confirm the occurrence of sexual abuse or of condyloma lesions in the parents in 66.7% of the cases. Probable sexual abuse (not confirmed) was reported in 2 cases. The basic therapy was chemical cauterization. Conclusions: sexual abuse in children and adolescents with condyloma acuminatum should be investigated in spite of the existence of other transmission ways including auto- or heteroinoculation. The presentation forms at young age differ from those in adults, and thus an appropriate therapy for this is necessary for this population.
-
Original Article04-09-1998
Clinicopathologic Analysis of Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia: review of 46 Cases
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):371-376
Abstract
Original ArticleClinicopathologic Analysis of Vulvar Intraepithelial Neoplasia: review of 46 Cases
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(7):371-376
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000700001
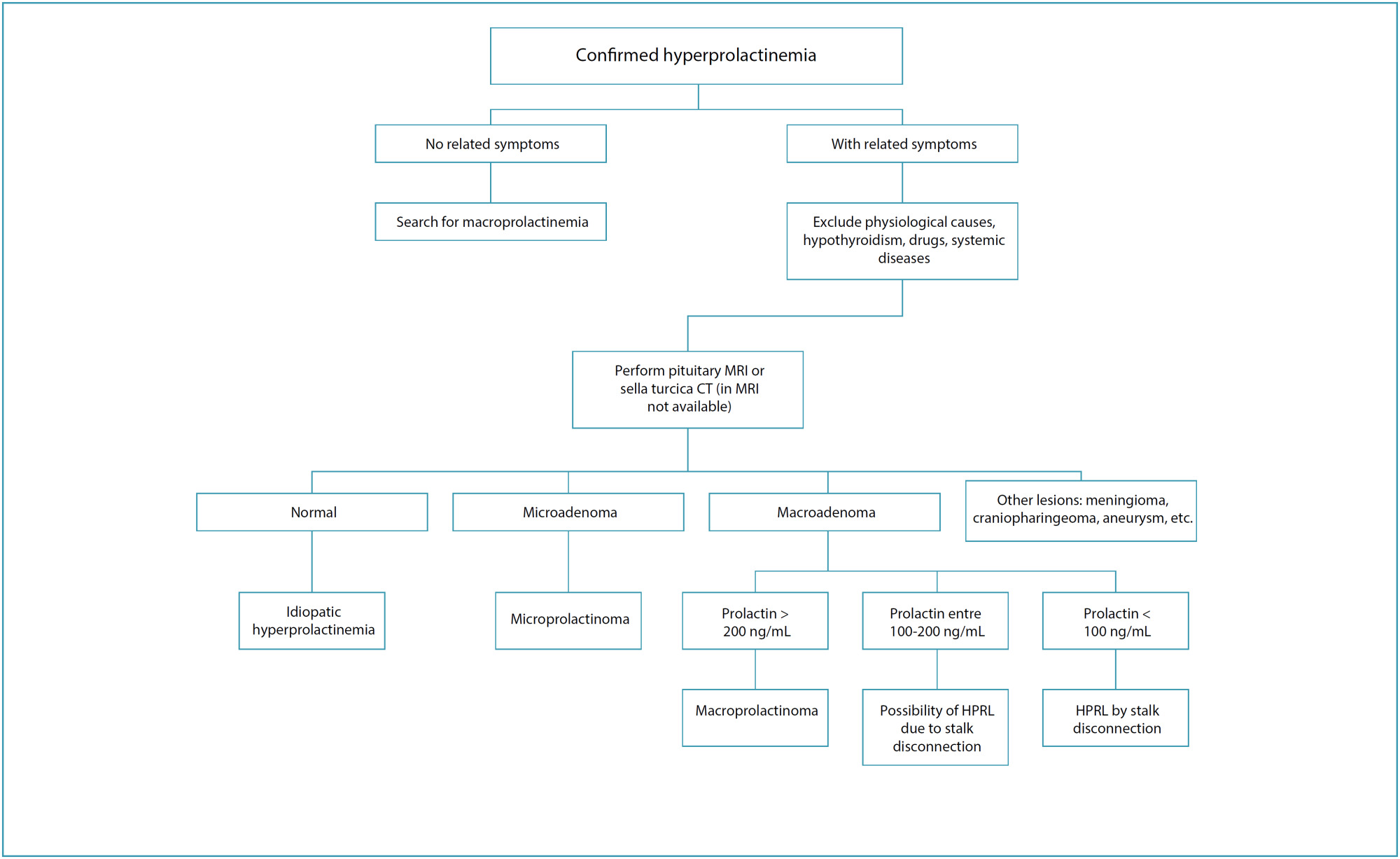
Views151See moreThe purpose of the present study was to evaluate some epidemiological, clinical and pathological characteristics of the different grades of vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN), and its relation with the presence of human papillomavirus (HPV). The charts of 46 women with VIN, examined from 1986 through 1997, were reviewed. For statistical analysis the chi² with yates correction when appropriate, and Fisher’s exact tests were used. Regarding the grade of VIN, six women presented VIN 1, six others had VIN 2 and the remaining 34 presented VIN 3. All women presented similar characteristics such as age, menstrual status and age at first sexual intercourse. Women with more than one lifetime sexual partner had a tendency to show more VIN 3 (p = 0.090). Cigarette smoking was significantly associated with the severity of the vulvar lesion (p = 0.031). HPV was significantly more frequent in women younger than 35 years of age (p = 0.005) and in women with multiple lesions (p = 0.089). Although the number of lesions were not related to the severity of VIN (p = 0.703), lesions with extensions greater than 2 cm were significantly associated with VIN 3 (p = 0.009). The treatment of choice for VIN 3 was surgery, including local resection and simple vulvectomy. Eight women relapsed, and only one had VIN 2. We concluded that among women with VIN, cigarette smoking and more than one lifetime sexual partner were associated with high-grade lesions. HPV was more frequent among patients younger than 35 years of age presenting multiple lesions. Women with VIN 3 presented lesions bigger than 2 cm and a high relapse rate, despite the type of treatment applied.
-
Original Article04-05-1998
Estimation of Fetal Weight: Comparison Between a Clinical Method and Ultrasonography
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(10):551-555
Abstract
Original ArticleEstimation of Fetal Weight: Comparison Between a Clinical Method and Ultrasonography
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(10):551-555
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998001000002
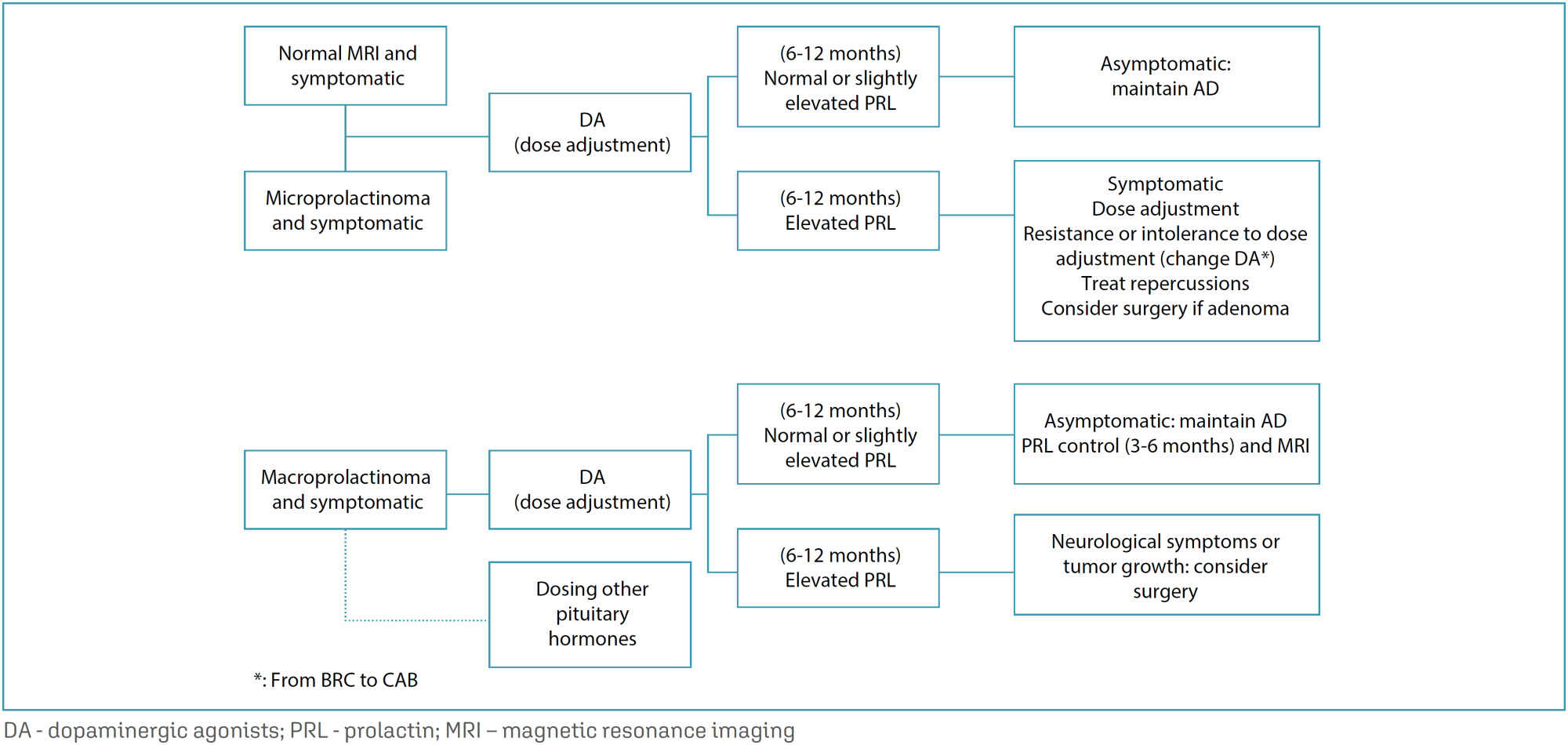
Views110See morePurpose: to assess the validity of fetal weight estimation by a method based on uterine height — Johnson’s rule. Methods: one hundred and one pregnant women and their newborn children were studied. The fetal weight was estimated using an adaptation of Johnson’s rule, which consists of the clinical application of a mathematical model to calculate the fetal weight based on the uterine height and the height of fetal presentation. The estimated weight was obtained on the day of delivery and was compared to the weight observed after birth. This, in turn, was the control of the analysis of validity of the method used. On the same date, a detailed obstetrical ultrasonography (US) was conducted which included the fetal weight, calculated by the use of Sheppard’s tables. This weight, estimated by US, was compared to the birth weight. Results: the results have proven that the clinical estimate used in this study has a similar value to that of the US calculation of birth weight. The accuracy of the clinical method, with variations of 5%, 10% and 15% between estimated and observed weights, was 55.3%, 73% and 86.7%, respectively. Those of the US were 60.7%, 75.4% and 91.1%, respectively. When comparing both sets of figures, values were not different from a statistical standpoint. Conclusion: the clinical evaluation has shown to be accurate, similarly to the US, when calculating the birth weight.
-
04-05-1998
Indice de líquido amniótico em gestantes diabéticas e a qualidade do controle glicêmico na gestação
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(8):485-485
Abstract
Indice de líquido amniótico em gestantes diabéticas e a qualidade do controle glicêmico na gestação
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(8):485-485
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000800011
Views65Indice de Líquido Amniótico em Gestantes Diabéticas e a Qualidade do Controle Glicêmico na Gestação.[…]See more -
04-05-1998
Avaliação do grau nuclear da célula maligna da mama como parâmetro de atividade proliferativa tumoral: comparação com a expressão do antígeno nuclear de proliferação celular (PCNA/ciclina)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(8):485-485
Abstract
Avaliação do grau nuclear da célula maligna da mama como parâmetro de atividade proliferativa tumoral: comparação com a expressão do antígeno nuclear de proliferação celular (PCNA/ciclina)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(8):485-485
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000800010
Views73Avaliação do Grau Nuclear da Célula Maligna da Mama como Parâmetro de Atividade Proliferativa Tumoral: Comparação com a Expressão do Antígeno Nuclear de Proliferação Celular (PCNA/ciclina).[…]See more -
Case Report04-05-1998
Prenatal diagnosis of arthrogryposis multiplex congenita: a case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(8):481-484
Abstract
Case ReportPrenatal diagnosis of arthrogryposis multiplex congenita: a case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(8):481-484
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000800009
Views91See moreArthrogryposis multiplex congenita is characterized by multiple joint contractures present at birth. Prenatal diagnosis is difficult. There are few reports in the literature. Fetal akinesia, abnormal limb position, intrauterine growth retardation, and polyhydramnios are the main findings of the ultrasonographic diagnosis. The authors describe a case of arthrogryposis multiplex congenita ultrasonographically diagnosed in the third gestational trimester. The main findings were absence of fetal movements, polyhydramnios, symmetrical and non-symmetrical fetal growth retardation with marked decrease of abdominal and thoracic circumference, low-set ears, micrognathia, continuous flexure contracture of limbs, internal rotation of the femur, and clubfoot on the right.
-
Original Article04-05-1998
Second-degree family history as a risk factor for breast cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(8):469-473
Abstract
Original ArticleSecond-degree family history as a risk factor for breast cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(8):469-473
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000800007
Views138See morePurpose: to evaluate the association between second-degree family history of breast cancer and the risk to develop the disease. Methods: case-control study of incident cases. Sixty-six incident breast cancer cases and 198 controls were selected among women who were submitted to mammography in a private clinic between January 1994 and July 1997. Cases and controls were paired regarding age, age at menarche, at first live birth, at menopause, parity, oral contraceptives and use of hormonal replacement therapy. Results: there was no significant difference between cases and controls regarding all risk factors evaluated, besides second-degree family history. Patients with breast cancer were more likely to have second-degree relatives with breast cancer when compared to controls (OR=2.77; 95% CI, 1.03-7.38; p=0.039). Conclusions: malignant neoplasm of the breast is significantly associated with a second-degree family history of this disease.
Search
Search in:
Tag Cloud
Pregnancy (252)Breast neoplasms (104)Pregnancy complications (104)Risk factors (103)Menopause (88)Ultrasonography (83)Cesarean section (78)Prenatal care (71)Endometriosis (70)Obesity (61)Infertility (57)Quality of life (55)prenatal diagnosis (51)Women's health (48)Maternal mortality (46)Postpartum period (46)Pregnant women (45)Breast (44)Prevalence (43)Uterine cervical neoplasms (43)