-
Original Article
A new screening of preterm birth in gestation with short cervix after pessary plus progesterone
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo39i
09-06-2024
Summary
Original ArticleA new screening of preterm birth in gestation with short cervix after pessary plus progesterone
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo39i
09-06-2024Views137See moreAbstract
Objective
This study aims to create a new screening for preterm birth < 34 weeks after gestation with a cervical length (CL) ≤ 30 mm, based on clinical, demographic, and sonographic characteristics.
Methods
This is a post hoc analysis of a randomized clinical trial (RCT), which included pregnancies, in middle-gestation, screened with transvaginal ultrasound. After observing inclusion criteria, the patient was invited to compare pessary plus progesterone (PP) versus progesterone only (P) (1:1). The objective was to determine which variables were associated with severe preterm birth using logistic regression (LR). The area under the curve (AUC), sensitivity, specificity, and positive predictive value (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV) were calculated for both groups after applying LR, with a false positive rate (FPR) set at 10%.
Results
The RCT included 936 patients, 475 in PP and 461 in P. The LR selected: ethnics white, absence of previous curettage, previous preterm birth, singleton gestation, precocious identification of short cervix, CL < 14.7 mm, CL in curve > 21.0 mm. The AUC (CI95%), sensitivity, specificity, PPV, and PNV, with 10% of FPR, were respectively 0.978 (0.961-0.995), 83.4%, 98.1%, 83.4% and 98.1% for PP < 34 weeks; and 0.765 (0.665-0.864), 38.7%, 92.1%, 26.1% and 95.4%, for P < 28 weeks.
Conclusion
Logistic regression can be effective to screen preterm birth < 34 weeks in patients in the PP Group and all pregnancies with CL ≤ 30 mm.
-
Original Article
Maintaining accuracy and expanding access: evaluating the efficacy of the Botucatu Abbreviated Breast MRI Protocol
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo55
07-26-2024
Summary
Original ArticleMaintaining accuracy and expanding access: evaluating the efficacy of the Botucatu Abbreviated Breast MRI Protocol
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo55
07-26-2024Views112See moreAbstract
Objective
Our study evaluated the effectiveness of the Botucatu Abbreviated Protocol in breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) within Brazil’s public healthcare system, focusing on its impact on patient access to MRI exams.
Methods
This retrospective study involved 197 breast MRI exams of female patients over 18 years with histological breast carcinoma diagnosis, conducted at Hospital das Clínicas de Botucatu - UNESP between 2014 and 2018. Two experienced examiners prospectively and blindly analyzed the exams using an Integrated Picture Archiving and Communication System (PACS). They first evaluated the Botucatu Abbreviated Protocol, created from sequences of the complete protocol (PC), and after an average interval of 30 days, they reassessed the same 197 exams with the complete protocol. Dynamic and morphological characteristics of lesions were assessed according to BI-RADS 5th edition criteria. The study also analyzed the average number of monthly exams before and after the implementation of Botucatu Abbreviated Protocol.
Results
The Botucatu Abbreviated Protocol showed high sensitivity (99% and 96%) and specificity (90.9% and 96%). There was a significant increase in the average monthly MRI exams from 6.62 to 23.8 post-implementation.
Conclusion
The Botucatu Abbreviated Protocol proved effective in maintaining diagnostic accuracy and improving accessibility to breast MRI exams, particularly in the public healthcare setting.
-
Original Article
Screening and prevention of preterm birth: how is it done in clinical practice?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo32
04-09-2024
Summary
Original ArticleScreening and prevention of preterm birth: how is it done in clinical practice?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo32
04-09-2024Views448Abstract
Objective:
To ascertain how screening for preterm birth is performed among obstetricians working in public and private practice in a middle-income country.
Methods:
Cross-sectional study of 265 obstetrician-gynecologists employed at public and private facilities. An online questionnaire was administered, with items designed to collect data on prematurity screening and prevention practices.
Results:
The mean age of respondents was 44.5 years; 78.5% were female, and 97.7% had completed a medical residency program. Universal screening (i.e., by ultrasound measurement of cervical length) was carried out by only 11.3% of respondents in public practice; 43% request transvaginal ultrasound if the manual exam is abnormal, and 74.6% request it in pregnant women with risk factors for preterm birth. Conversely, 60.7% of respondents in private practice performed universal screening. This difference in screening practices between public and private practice was highly significant (p < 0.001). Nearly all respondents (90.6%) reported prescribing vaginal progesterone for short cervix.
Conclusion:
In the setting of this study, universal ultrasound screening to prevent preterm birth was used by just over half of doctors in private practice. In public facilities, screening was even less common. Use of vaginal progesterone in cervical shortening was highly prevalent. There is an unmet need for formal protocols for screening and prevention of preterm birth in middle-income settings.
Key-words attitudes, practiceCervical length measurementgynecologistshealth knowledgeInfant, prematureobstetriciansPreterm birthPreventionScreeningsurveys and questionnairesSee more -
Review Article
Breast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS®): a success history and particularities of its use in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo6
03-14-2024
Summary
Review ArticleBreast Imaging Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS®): a success history and particularities of its use in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo6
03-14-2024Views259See moreAbstract
BI-RADS® is a standardization system for breast imaging reports and results created by the American College of Radiology to initially address the lack of uniformity in mammography reporting. The system consists of a lexicon of descriptors, a reporting structure with final categories and recommended management, and a structure for data collection and auditing. It is accepted worldwide by all specialties involved in the care of breast diseases. Its implementation is related to the Mammography Quality Standards Act initiative in the United States (1992) and breast cancer screening. After its initial creation in 1993, four additional editions were published in 1995, 1998, 2003 and 2013. It is adopted in several countries around the world and has been translated into 6 languages. Successful breast cancer screening programs in high-income countries can be attributed in part to the widespread use of BI-RADS®. This success led to the development of similar classification systems for other organs (e.g., lung, liver, thyroid, ovaries, colon). In 1998, the structured report model was adopted in Brazil. This article highlights the pioneering and successful role of BI-RADS®, created by ACR 30 years ago, on the eve of publishing its sixth edition, which has evolved into a comprehensive quality assurance tool for multiple imaging modalities. And, especially, it contextualizes the importance of recognizing how we are using BI-RADS® in Brazil, from its implementation to the present day, with a focus on breast cancer screening.
-
Original Article
Underestimated Cervical Cancer among Women over 65 Years Old: Is It Time to Revise the Screening Target Age Group?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(12):790-795
01-11-2023
Summary
Original ArticleUnderestimated Cervical Cancer among Women over 65 Years Old: Is It Time to Revise the Screening Target Age Group?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(12):790-795
01-11-2023Views185See moreAbstract
Objective
To compare cytological and histological results from women > 64 years old who followed the Brazilian national cervical cancer screening guidelines with those who did not.
Methods
The present observational retrospective study analyzed 207 abnormal cervical smear results from women > 64 years old in a mid-sized city in Brazil over 14 years. All results were reported according to the Bethesda System. The women were divided into those who followed the screening guidelines and those who did not.
Results
Atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance and low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion cytology results were found in 128 (62.2%) cases. Of these, 112 (87.5%) had repeated cytology with positive results. The other 79 (38.1%) with abnormal results should have been referred to colposcopy and biopsy. Out of 41 (51.9%) biopsied women, 23 (29.1%) had a confirmed diagnosis of neoplasia or precursor lesion. In contrast, among the 78 (37.7%) biopsied patients, 40 (51.3%) followed the guideline recommendations, with 9 (22.5%) positive biopsies. Of the 38 (48.7%) women who did not follow the guidelines, there were 24 (63.1%) positive results. Women who did not follow the guidelines demonstrated higher chances of cancer and precursor lesions (odds ratio [OR]: 5.904; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 2.188–15.932; p = 0.0002).
Conclusion
Women > 64 years old who did not follow the national screening protocol showed significant differences in the frequency of abnormal results and severity of diagnosis compared with those who followed the protocol.
-
Original Article
Cytology-based Screening for Anal Intraepithelial Neoplasia in Immunocompetent Brazilian Women with a History of High-Grade Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia or Cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(7):678-685
08-29-2022
Summary
Original ArticleCytology-based Screening for Anal Intraepithelial Neoplasia in Immunocompetent Brazilian Women with a History of High-Grade Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia or Cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(7):678-685
08-29-2022Views104See moreAbstract
Objective
To determine the prevalence and possible variables associated with anal intraepithelial neoplasia and anal cancer in immunocompetent women with high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia.
Methods
A cross-sectional study involving immunocompetent women with a histological diagnosis of high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical cancer, conducted between January 2016 and September 2020. All women underwent anal cytology and answered a questionnaire on characterization and potential risk factors. Women with altered cytology were submitted to anoscopy and biopsy.
Results
A total of 69 women were included in the study. Of these, 7 (10.1%) had abnormal anal cytology results: (high-grade lesion, atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance, and atypical squamous cells, cannot exclude high-grade lesions: 28,5% each; low grade lesion: 14,3%). Of the anoscopies, 3 (42.8%) showed alterations. Of the 2 (28,5% of all abnormal cytology results) biopsies performed, only 1 showed low-grade anal intraepithelial neoplasia. The average number of pregnancies, vaginal deliveries, and abortions was associated with abnormal anal cytology. However, the highest mean regarding the cesarean sections was associated with normal cytology.
Conclusion
The prevalence of anal intraepithelial neoplasia was compatible with data from recent studies, especially those conducted in Brazil. Opportunistic screening for anal intraepithelial neoplasia in this high-risk population should be considered. Anal cytology is suitable for this purpose, due to its low cost and feasibility in public health services.
-
Original Article
Behavior of the Genetic Markers at Screening during the First Trimester of Pregnancy in Euploid Fetuses
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(7):646-653
06-01-2022
Summary
Original ArticleBehavior of the Genetic Markers at Screening during the First Trimester of Pregnancy in Euploid Fetuses
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(7):646-653
06-01-2022Views194See moreAbstract
Objective
This study aims to describe the behavior of chromosomopathy screenings in euploid fetuses.
Methods
This is a prospective descriptive study with 566 patients at 11 to 14 weeks of gestation. The associations between ultrasound scans and serological variables were studied. For the quantitative variables we used the Spearman test; for the qualitative with quantitative variables the of Mann-Whitney U-test; and for qualitative variables, the X2 test was applied. Significance was set at p ≤ 0.05.
Results
We have found that gestational age has correlation with ductus venosus, nuchal translucency, free fraction of β subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin, pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A and placental growth factor; there is also a correlation between history of miscarriages and nasal bone. Furthermore, we correlated body mass index with nuchal translucency, free fraction of β subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin, and pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A. Maternal age was associated with free fraction of β subunit of human chorionic gonadotropin and pregnancy-associated plasma protein-A.
Conclusion
Our study demonstrates for the first time the behavior of the biochemical and ultrasonographic markers of chromosomopathy screenings during the first trimester in euploid fetuses in Colombia. Our information is consistent with international reference values. Moreover, we have shown the correlation of different variables with maternal characteristics to determine the variables that could help with development of a screening process during the first trimester with high detection rates.
-
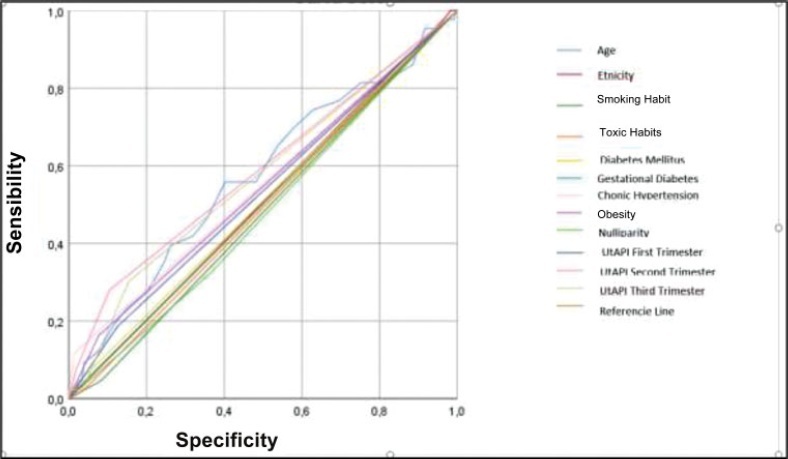
Original Article
Uterine Artery Pulsatility Index as a Pre-eclampsia Predictor in the 3 Trimesters in Women with Singleton Pregnancies
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(12):904-910
01-24-2021
Summary
Original ArticleUterine Artery Pulsatility Index as a Pre-eclampsia Predictor in the 3 Trimesters in Women with Singleton Pregnancies
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(12):904-910
01-24-2021Views164See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the mean uterine artery pulsatility index (UtAPI) in each trimester of pregnancy as a predictor of early or late pre-eclampsia (PE) in Colombian pregnant women.
Methods
The UtAPI was measured in singleton pregnancies in each trimester. Uterine artery pulsatility index as predictor of PE was evaluated by odds ratio (OR), receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves, and Kaplan-Meier diagram.
Results
Analysis in the 1st and 3rd trimester showed that abnormal UtAPI was associated with early PE (OR: 5.99: 95% confidence interval [CI]: 1.64–21.13; and OR: 10.32; 95%CI: 2.75–42.49, respectively). Sensitivity and specificity were 71.4 and 79.6%, respectively, for developing PE (area under the curve [AUC]: 0.922). The Kaplan-Meier curve showed that a UtAPI of 0.76 (95%CI: 0.58–1.0) in the 1st trimester was associated with early PE, and a UtAPI of 0.73 (95%CI: 0.55–0.97) in the 3rd trimester was associated with late PE.
Conclusion
Uterine arteries proved to be a useful predictor tool in the 1st and 3rd trimesters for early PE and in the 3rd trimester for late PE in a pregnant population with high prevalence of PE.