-
Original Article
The top hat procedure does not impact the management of women treated by LEEP in cervical cancer screening
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo44
06-03-2024
Summary
Original ArticleThe top hat procedure does not impact the management of women treated by LEEP in cervical cancer screening
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo44
06-03-2024Views138Abstract
Objective:
To describe Top-hat results and their association with margin status and disease relapse in a referral facility in Brazil.
Methods:
A retrospective study of 440 women submitted to LEEP to treat HSIL, in which 80 cases were complemented immediately by the top hat procedure (Top-hat Group - TH). TH Group was compared to women not submitted to Top-hat (NTH). The sample by convenience included all women that underwent LEEP from January 2017 to July 2020. The main outcome was the histological result. Other variables were margins, age, transformation zone (TZ), depth, and relapse. The analysis used the Chi-square test and logistic regression.
Results:
The TH Group was predominantly 40 and older (NTH 23.1% vs. TH 65.0%, p<0.001). No difference was found in having CIN2/CIN3 as the final diagnosis (NTH 17.0% vs. TH 21.3%, p=0.362), or in the prevalence of relapse (NTH 12.0% vs. TH 9.0%, p=0.482). Of the 80 patients submitted to top hat, the histological result was CIN2/CIN3 in eight. A negative top hat result was related to a negative endocervical margin of 83.3%. A CIN2/CIN3 Top-hat result was related to CIN2/CIN3 margin in 62.5% (p=0.009). The chance of obtaining a top hat negative result was 22.4 times higher (2.4-211.0) when the endocervical margin was negative and 14.5 times higher (1.5-140.7) when the ectocervical margin was negative.
Conclusion:
The top hat procedure did not alter the final diagnosis of LEEP. No impact on relapse was observed. The procedure should be avoided in women of reproductive age.
Key-words Cervical intraepithelial neoplasiaCervix uteriColposcopyConizationElectrosurgeryGynecologic surgical proceduresUterine cervical neoplasmsSee more -
Original Article
When is There no Benefit in Performing a Biopsy in the Suspicion of Intraepithelial Lesions of the Cervix?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(3):272-279
06-27-2022
Summary
Original ArticleWhen is There no Benefit in Performing a Biopsy in the Suspicion of Intraepithelial Lesions of the Cervix?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(3):272-279
06-27-2022Views95See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate whether colposcopy-directed biopsy is necessary to increase the accuracy of diagnosing cervical intraepithelial lesions in relation to colposcopy.
Methods
We performed a retrospective, observational study by analyzing medical records obtained fromHospital de Clínicas do Paraná fromFebruary 2008 to February 2018. Patients with results of Pap tests, colposcopy, colposcopy-directed biopsy, and surgical procedures (high-frequency surgery or cold conization) were included. Data such as quadrants involved during colposcopy and age differences were also analyzed.
Results
A total of 299 women were included. Colposcopy was found to have an accuracy rate of 76.25% (95% confidence interval [CI], 71.4-81.1). Among the highest-grade lesions, the accuracy rate was 80.5% (95% CI, 75.7-85.3). The accuracy rates for biopsy were 79.6% (95% CI, 75-84.2) and 84.6% (95% CI, 80-89.1) for the highest-grade lesions. High-grade lesions were accurately confirmed in 76.9% and 85% of patients with 1 and 2 or more affected quadrants, respectively. For women younger than 40 years, the accuracy rates were 77.6% and 80.8% for colposcopy and biopsy, respectively. For women 40 years or older, the accuracy rates were 72.5% and 76.3% for colposcopy and biopsy, respectively.
Conclusion
There is no difference between the accuracy of colposcopy and that of biopsy in diagnosing cervical intraepithelial lesions in relation with the result of conization. The patients who received the greatest benefit when biopsy was not performed were those with high-grade lesions at colposcopy, a lesion involving 2 or more quadrants, and those younger than 40 years.
-
Original Article
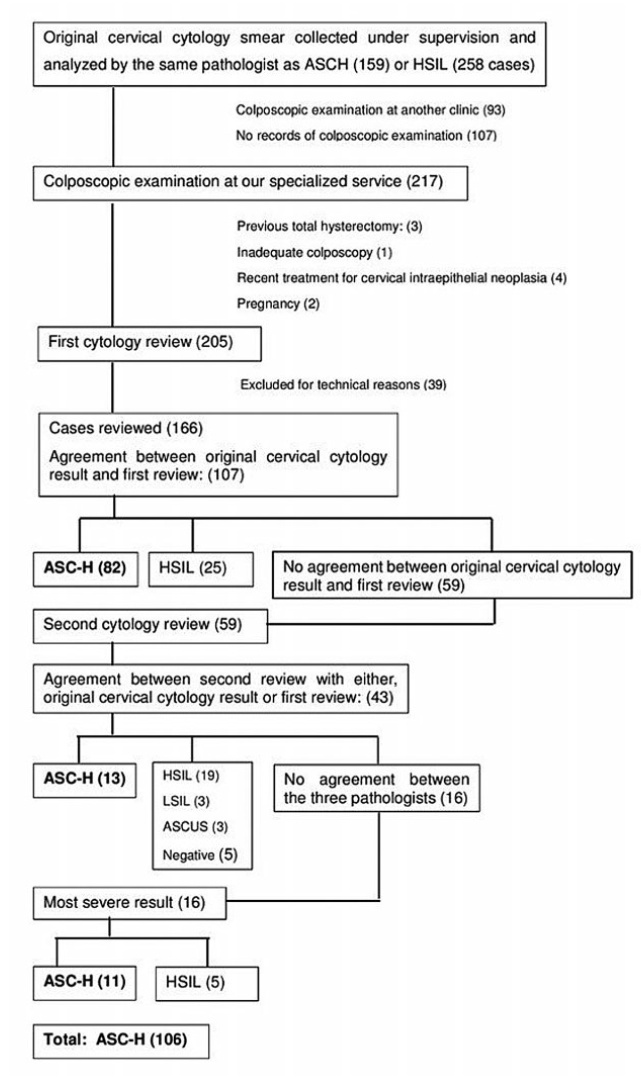
Colposcopic Findings and Diagnosis in Low-Income Brazilian Women with ASC-H pap Smear Results
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):178-186
04-08-2022
Summary
Original ArticleColposcopic Findings and Diagnosis in Low-Income Brazilian Women with ASC-H pap Smear Results
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):178-186
04-08-2022Views128See moreAbstract
Objective
To determine the accuracy of colposcopy findings in diagnosing cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) in women with an atypical squamous cells, cannot exclude high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (ASC-H) pap smear result and analyze whether the prevalence of HSIL and cancer correlates with sociodemographic risk factors and specific colposcopic findings.
Methods
Colposcopic findings and sociodemographic risk factors were analyzed as possible predictors of a CIN 2 or worse diagnosis in women with an ASC-H pap smear result.
Results
Accuracy of the colposcopic impression was 92%, sensitivity was 91.6%, and specificity was 93.1%, with a positive predictive value of 96.4% and negative predictive value of 84.3%. Diagnosis of CIN 2 or worse was more frequent in patients with a previous history of cervical dysplasia and pre-menopausal patients. Identification of major colposcopic findings, dense acetowhite epithelium, coarse mosaicism, and punctuation correlated significantly with CIN 2 or worse.
Conclusion
Colposcopy performed by an experienced examiner can accurately differentiate patients with CIN 1 or less from patients with CIN 2 or worse. Diagnosis of CIN 2 or worse was more frequent in patients with a previous history of cervical dysplasia and pre-menopausal patients. The degree of acetowhite changes was the best colposcopic feature to predict CIN2 or worse.
-
Original Article
Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia: Analyzing the Disease Present Exclusively in the Endocervical Canal
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(4):385-390
03-11-2022
Summary
Original ArticleCervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia: Analyzing the Disease Present Exclusively in the Endocervical Canal
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(4):385-390
03-11-2022Views152See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the role of cervical cytology (Pap smear) in the diagnosis of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia 2 or greater (CIN2+), presented exclusively in the endocervical canal, the clinical-epidemiological characteristics of this lesion, the necessary length of canal to be removed to treat, and the rate of invasive lesion hidden in the endocervical canal.
Methods
Cross-sectional study, by database analysis, of patients with abnormal cytology (high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion [HSIL]), without visible colposcopy lesion, submitted to loop electrosurgical procedure (LEEP) to evaluate the association of cytology results with the histological product of the conization, to identify the epidemiological characteristics of endocervical lesion and clinical evolution, using a pvalue< 0.05 and 95% CI.
Results
In 444 cases, the Pap smear sensitivity for CIN2+ diagnosis was 75% (95% CI: 69.8-79.7), specificity was 40% (95% CI: 30.2-49.5), and the prevalence rate of histological lesion was 73% (95% CI: 70.1-78.7). There was a higher prevalence of CIN2+ in women over 42 years old and invasive cancer in those over 56 years old (p<0.001), and it was necessary to remove 2.6 cm in length of the canal to reduce the chance of recurrence (p<0.006). The rate of invasive cancer was 2.7%.
Conclusion
Cytology was related to a high prevalence to histological lesion (73%) in the diagnosis of CIN2+ in the endocervical disease; older patients presented a higher relationship with histological lesions in the canal disease, and it was necessary to remove an average of 2.6 cm in length of the endocervical canal to avoid the persistence and progression of CIN. The rate of occult neoplasia in the endocervical canal was 2.7%.
-
Original Article
Pathways of IFN-alpha Activation in Patients with Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia (CIN)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(9):682-689
11-29-2021
Summary
Original ArticlePathways of IFN-alpha Activation in Patients with Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia (CIN)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(9):682-689
11-29-2021Views171See moreAbstract
Objective
The aim of the present study was to compare the local and systemic expression of the factors linked to the interferon alpha (IFN-α) activation pathway in different degrees of cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) and cervical cancer.
Methods
A total of 128 patients with CIN I, CIN II, CIN III and cervical cancer was evaluated. The real-time polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) technique was used to evaluate the gene expression of IFNR1, IFNR2, IFN-α, oligoadenylate synthase (2’5′OAS), cytokine signal suppressor 1 (SOCS) 1, SOCS3, signal transducer and transcription activator 1 (STAT1), and IRF9 from 128 biopsies. A total of 46 out of 128 samples were evaluated by flow cytometry for IFNAR1, IFNAR2, STAT1, IRF7 and IFN-α in peripheral blood cells.
Results
Patients with CIN II and III (63 samples) had a low local expression of IFNR1, but not IFNR2. Patients with some degree of injury showed high expression of SOCS1 and SOCS3. Systemically, patients with CIN II and III (20 samples) had a significant increase in IFNR1, IFNR2, STAT1, IRF7, and IFN-α in helper, cytotoxic T lymphocytes, and in monocytes.
Conclusion
Patients with high-grade lesions have increased systemic expression of IFN-α and its activation pathways in helper and cytotoxic T lymphocytes, as well as in monocytes due to an exacerbation of the immune response in these patients. This phenomenon is not accompanied by resolution of the lesion due to a defect in the IFN-α activation pathway that revealed by low local IFNAR1 expression and high local expression of SOCS1 and SOCS3.
-
Original Articles
Sexually Transmitted Infections Detected by Multiplex Real Time PCR in Asymptomatic Women and Association with Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):540-546
09-01-2018
Summary
Original ArticlesSexually Transmitted Infections Detected by Multiplex Real Time PCR in Asymptomatic Women and Association with Cervical Intraepithelial Neoplasia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):540-546
09-01-2018Views177Abstract
Objective
To determine the frequency of sexually transmitted infections (STIs) in asymptomatic women and the association of STIs with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN).
Methods
A cross-sectional studywas performed, enrollingwomen examined in a general gynecology clinic and in a colposcopy referral center fromOctober 2014 to October 2015. The colposcopy groupconsisted of 71women, and the general gynecologygroupconsisted of 55 women. Cervical samples were collected for cervical cytology and a multiplex realtime polymerase chain reaction (PCR) was developed to detect human papillomavirus (HPV) and the STIs caused by the following microorganisms: Chlamydia trachomatis, Mycoplasma hominis, Mycoplasma genitalium, Ureaplasma urealyticum, and Neisseria gonorrhoeae. A multivariate analysis was performed by logistic regression, considering the significance level of 0.05.
Results
The general frequency of STIs was: 46.8% (HPV); 27.8% (C. trachomatis); 28.6% (M. genitalium); 0.8% (M. hominis); 4.8% (U. urealyticum); and 4.8% (N. gonorrhoeae). The significant risk factors for CIN were: HPV infection (odds ratio [OR] = 2.53; p = 0.024); C. trachomatis (OR = 3.04; p = 0.009); M. genitalium (OR = 2.37; p = 0.04); and HPV and C. trachomatis coinfection (OR = 3.11; p = 0.023). After the multivariate analysis, a significant associationwas found betweenHPVand CIN(OR = 2.48; 95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 1.04-5.92; p = 0.04); and between C. trachomatis and CIN (OR = 2.69; 95%CI: 1.11-6.53; p = 0.028).
Conclusion
The frequency of STIs was high in asymptomatic patients. Infections by HPV and C. trachomatis were independently associated with the presence of CIN. The high frequency of STIs in asymptomatic women suggests the need for routine screening of these infections.
Key-words Cervical intraepithelial neoplasiaChlamydiaPapillomavirus infectionsPolymerase chain reactionSexually transmitted diseasesSee more -
Original Article
Performance of Conventional Cytology and Colposcopy for the Diagnosis of Cervical Squamous and Glandular Neoplasias
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(7):410-416
07-01-2018
Summary
Original ArticlePerformance of Conventional Cytology and Colposcopy for the Diagnosis of Cervical Squamous and Glandular Neoplasias
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(7):410-416
07-01-2018Views123Abstract
Objective
To estimate the cytological and colposcopic performances for the diagnosis of cervical neoplasias.
Methods
Cross-sectional retrospective study with data from patients’ charts. The participants underwent colposcopy, guided biopsies, and excision when needed. The cytological and colposcopic categorization followed the Bethesda System and the international colposcopic terminologies. The cytology and colposcopy performances were evaluated by sensitivity (SE), specificity (SP), positive predictive value (PPV), and negative predictive value (NPV) analyses with 95% confidence interval (95% CI).
Results
From 1,571 participants, a total of 1,154 (73.4%) were diagnosed with cervical squamous intraepithelial neoplasia grade 2 or worse (CIN 2+), 114 (7.2%) with adenocarcinoma in situ or worse (AIS+), 615 (39.2%) presented atypical squamous cells, cannot exclude high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion or worse (ASC-H+) cytology, and 934 (59.4%) presented major or suspicious for invasion colposcopic abnormalities. The SE, SP, PPV, and NPV of ASC-H+ for diagnoses of CIN 2+ and AIS+ were, respectively: 44% (95% CI: 41-47) and 72% (95% CI: 67-76), 79% (95% CI: 77-81) and 79% (95% CI: 75-83), 88% (95% CI: 87-90) and 55% (95% CI: 50-60), and 28% (95% CI: 26-31) and 88% (95% CI: 85-91). The SE, SP, PPV, and NPV of major or suspicious for invasion colposcopic abnormalities for diagnoses of CIN 2+ and AIS+were, respectively: 62% (95% CI: 60-65) and 86% (95% CI: 83-89), 59% (95% CI: 57-62) and 59% (95% CI: 55-64), 85% (95% CI: 83-87) and 44% (95% CI: 40-49), and 29% (95% CI: 27-32) and 92% (95% CI: 89-94).
Conclusion
The SE analyses results of ASC-H+ and major or suspicious for invasion colposcopic abnormalities were higher for diagnoses of glandular neoplasias. These results confirm the role of cytology in identifying women at risk who will have their final diagnoses settled by colposcopy and histology.
Key-words adenocarcinoma in situCervical intraepithelial neoplasiaColposcopyPapanicolaou testSensitivity and specificitysquamous intraepithelial lesions of the cervixUterine cervical neoplasmsSee more
-
Review Article
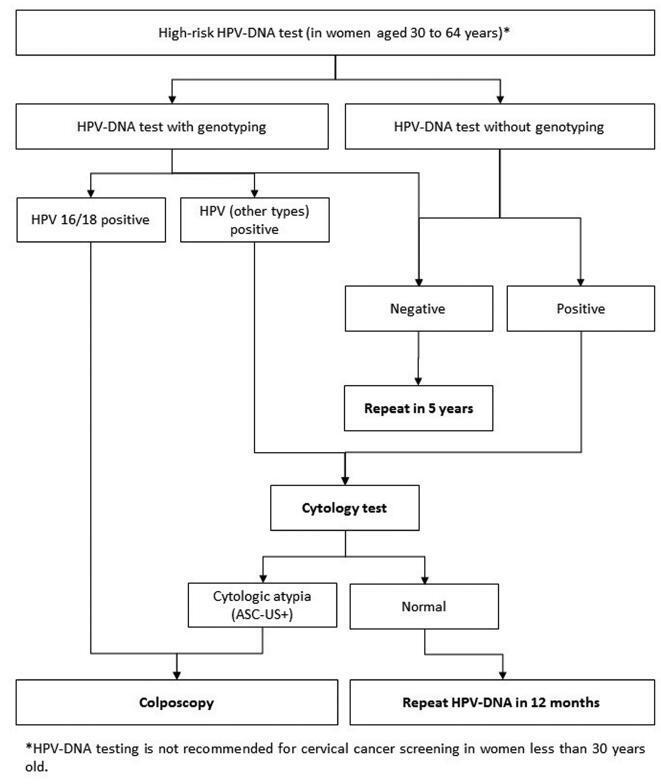
Guidelines for HPV-DNA Testing for Cervical Cancer Screening in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):360-368
06-01-2018
Summary
Review ArticleGuidelines for HPV-DNA Testing for Cervical Cancer Screening in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):360-368
06-01-2018Views246See moreAbstract
Evidence-based clinical guidelines ensure best practice protocols are available in health care. There is a widespread use of human papillomavirus deoxyribonucleic acid (HPVDNA) tests in Brazil, regardless of the lack of official guidelines. On behalf of the Brazilian Association for the Lower Genital Tract Pathology and Colposcopy (ABPTGIC, in the Portuguese acronym), a team of reviewers searched for published evidence and developed a set of recommendations for the use of HPV-DNA tests in cervical cancer screening in Brazil. The product of this process was debated and consensus was sought by the participants. One concern of the authors was the inclusion of these tests in the assessment of women with cytologic atypia and women treated for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN). Testing for HPV is recommended in an organized screening scenario to identify women with precursor lesions or asymptomatic cervical cancer older than 30 years of age, and it can be performed every 5 years. It also has value after the cytology showing atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASC-US) or low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (LSILs) as a triage test for colposcopy, in the investigation of other cytological alterations when no abnormal findings are observed at colposcopy, seeking to exclude disease, or, further, after treatment of high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, to rule out residual disease.