Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(4):155-161
To evaluate whether the presence of maternal blood pressure reduces the risks of morbidity, perinatal mortality and morbidity at 24 months of age in very low birth weight infants (VLBWIs) compared with a control group.
A retrospective, observational, case-control study. Total 49 VLBWIs were allocated to the study group, called the maternal arterial hypertension group (AHG), and matched with 44 in the control group (CG). The infants were assessed during hospitalization and at 12 and 24 months corrected age at a specialized clinic. For the assessment of growth, the World Health Organization (WHO) Anthro software (Geneva, 2006) was used, and for the psychomotor assessment, the Denver II test was used.
In relation to the antenatal variables, the infants of the AHG had more centralized circulation assessed by Doppler, received more corticosteroids and magnesium sulfate, and were born by cesarean section more frequently. In terms of the postnatal and in-hospital outcomes, the AHG had a higher gestational age at birth (30.7 versus 29.6 weeks) and a lower frequency of 5-minute Apgar scores of less than 7 (26.5% versus 52.3%). The CG had a higher rate of pulmonary dysplasia (30.2% versus 8.3%). There were no differences in terms of hospital mortality, complications, somatic growth and functional problems at 24 months of corrected age.
The presence of maternal hypertension, especially preeclampsia, was not a protective factor against morbidity, mortality and evolution in VLBWIs aged up to 24 months. Therefore, the clinical practice should be focused on prolonging the pregnancy for as long as possible in these conditions as well.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2005;27(3):155-160
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005000300010
PURPOSE: to evaluate the outcome of fetuses with risk of chromosomal anomalies over 1:300, based on the nuchal translucency measurement, according to the Fetal Medicine Program. METHODS: in the pregnancies with risk of chromosomal anomalies over 1:300, variables like fetal karyotype, spontaneous or induced abortion, prematurity, stillbirth, neonatal death, malformations, and healthy newborn were considered. We used Fisher's exact test to compare differences in proportions between groups. RESULTS: we selected 193 (3.6%) single pregnancies with risk of chromosomal anomalies over 1:300. Only 165 cases fulfilled the inclusion criteria. Of these only 32.1% underwent fetal karyotyping and of which 8.5% had chromosomal anomalies (85.7% had trisomy 21). Regarding pregnancy outcomes, 4.2% were spontaneous miscarriages, 4.2% induced abortions, 4.8% were premature, 1.8% had neonatal death, 1.8% were stillborn, and 4.2% had structural malformation (85.7% congenital heart diseases). Almost 85.0% were healthy newborns. Patients with abnormal karyotyping had more induced abortions (p<0.001) and more structural malformations (p<0.001) than patients with normal karyotyping. None of the genetic diseases or miscarriages was associated with invasive procedures. Sixty-six percent of the pregnancies with prenatal diagnosis of abnormal karyotype were interrupted. CONCLUSION: nuchal translucency is an important screening tool for chromosomal diseases especially for low-risk pregnancies. However, counseling pregnancies with high risk of chromosomal anomalies should consider that, although these fetuses have a worse prognosis, most of the outcomes are favorable.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2003;25(3):155-161
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032003000300003
PURPOSE: the morbidity in HIV-positive patients due to puerperal fever was studied and correlated to the method and duration of labor, the duration of premature rupture of the membranes, CD4+ cell count and the viral load (VL) at peridelivery. METHODS: a total of 207 HIV-positive women with prenatal examinations and deliveries between May 1997 and December 2001 were enrolled. Of these, 32 had natural childbirth and 175 had a cesarean section. Of the total of enrolled patients, 62.8% were submitted to elective cesarean section. The average age of the group was 27.4 years, and 25.6% were nulliparous and 26% were primiparous. At the moment of the delivery the average gestational age was 37.8 weeks. At the end of pregnancy the average of the CD4+ cell count was approximately 481 cells/mm³ and the viral load 49,100 copies/mL. RESULTS: puerperal morbidity occurred in 34 patients, with 33 after cesarean section and one after natural childbirth. The most usual intercurrent post-cesarean infection was that of the surgical wound (13% of the infection cases). Analyzed factors, such as delivery duration, duration of rupture of the membranes, number of CD4+ cells or the viral load at peridelivery, did not interfere in puerperal morbidity. CONCLUSIONS: puerperal morbidity was 16.8% and occurred more frequently after cesarean sections (18.9%) than after vaginal deliveries (3.1%). The other factors did not present a significant effect on puerperal morbidity.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):155-157
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(3):155-163
To evaluate the clinical epidemiological state of women with suspected post partum depression (PPD) in a public maternity hospital in Salvador, state of Bahia, Brazil.
A cross-sectional research was performed with puerperal patients attended at a public maternity hospital in Salvador, Bahia. Data collection was performed from June to September 2017. The Edinburgh Postnatal Depression Scale was used as a screening instrument, and, subsequently, women with positive scores answered a questionnaire to identify their clinical and epidemiological status.
Out of 151 postpartum women from the research, 30 (19.8%) presented suspicion of PPD. There was a prevalence of single mothers 13 (43.3%), women with complete fundamental education 15 (50.0%), women with black skin color 14 (46.7%), and those with a monthly family income of up to one minimum wage 18 (40.0%).
Although PPD is an underdiagnosed disease, a high prevalence of the condition was found in our research. It is, then, considered that these results reinforce its significance as a public health problem, requiring prevention strategies, early diagnosis and effective treatment.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(3):155-159
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000300006
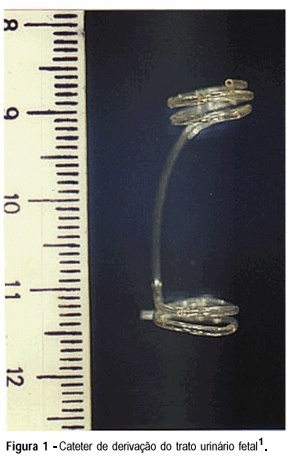
Management of prenatally diagnosed uropathies is controversial, mainly because the prognosis for these fetuses is quite different. However pioneering studies have shown that prenatal drainage of obstructed urinary tract can improve the outcome of selected fetuses. The aim of this study is to describe the experience of the Service with the treatment of fetal obstrutive uropathy with the catheter developed by the Centro de Medicina Fetal do Hospital das Clínicas da UFMG. A total of 25 fetuses with obstructive uropathy received the catheter. Three fetuses required more than one insertion. Ten of 25 (40%) shunted fetuses survived with good postnatal renal and pulmonary function. Complications occurred in 12/25 (48%) cases including: 06/25 (24%) inadequate shunt drainage or migration; 01/25 (04%) urinary ascitis; 01/25 (04%) DPP, 01/25 (04%) premature rupture of membranes, 02/25 (08%) premature labor, 01/25 (04%) scarring and fibrosis of the renal parenchyma. Three of 25 (12%) fetuses died intra-utero and 12 (48%) died during the neonatal period. In conclusion, the drainage of the obstructed urinary tract with this catheter proved to be technically feasible and safe for both mother and fetus, with a survival rate of 40%.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(3):156-162
Venous thromboembolism events are important causes of maternal death during pregnancyandthepostpartumperiodworldwide.Are view of the literature with the objective of evaluating venous thromboembolism events in the puerperium according to the route of delivery was performed through a bibliographic survey in the Medline, LILACS and Scielo databases. We observed that patients submitted to cesarean sections present a significantlyhigher riskofdeveloping venousthromboembolismwhencomparedwiththose who undergo spontaneous vaginal delivery. The pathophysiological bases for this difference were explored and described in this review, as well as the indications of prophylaxis and treatment. Doctors and health professionals must be continuously vigilant regarding this condition, since it is associated with high morbidity and mortality.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2010;32(4):156-162
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032010000400002
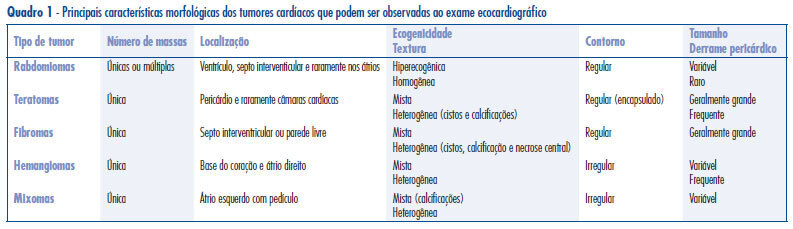
PURPOSE: to analyze the differential diagnosis, follow-up and therapeutic approach in five cases of primary cardiac tumors diagnosed during the prenatal period. METHODS: during the period from January 1997 to December 2008, 7989 pregnant women were submitted to morphological ultrasound due to the presence of risk factors for fetal malformations. Fetuses with hyperechogenic intracardiac masses larger than 1 mm diagnosed by ultrasound evaluation of the fetal heart, were selected for study. The differential diagnosis between the different tumor types was made on the basis of the ultrasound characteristics of the masses. RESULTS: five fetuses with hiperechogenic intracardiac masses were diagnosed, corresponding to a 0.06% prevalence rate. Gestational age ranged from 28 to 36 weeks (mean: 31), and maternal age ranged from 23 to 45 years (mean: 34,2). The most frequent location of the masses was the left ventricle (100%). Echographically, all masses were single or multiple, hyperechogenic, homogeneous and well delimited, compatible with a diagnosis of rhabomyoma. In cases in which the diameters of the masses were less than 20 mm, an expectant conduct was followed and no complications occurred during the prenatal period. One case with a huge tumor presented arrhythmia and cardiac insufficiency during the 35 gestational weeks, and the interruption of pregnancy was indicated. Tuberous sclerosis was associated in four cases (80%) and the diagnosis was confirmed during the postnatal follow-up. CONCLUSIONS: fetal morphological ultrasonography is the main form of early detection of primary cardiac tumors. The fetal cardiac evaluation is of fundamental importance for the differential morphological characterization of cardiac masses and for the evaluation of cardiac function. Rhabdomyomas are the most common type of fetal tumor. An expectant pre and postnatal conduct is followed, with a low risk of complications and with the possibility of spontaneous regression in most cases. Postnatal clinical follow-up is mandatory due to the high frequency of associated tuberous sclerosis.