-
Review Article01-24-2021
The Effect of Aromatherapy Alone or in Combination with Massage on Dysmenorrhea: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(12):968-979
Abstract
Review ArticleThe Effect of Aromatherapy Alone or in Combination with Massage on Dysmenorrhea: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(12):968-979
Views290See moreAbstract
Objective
The aim of the present systematic review meta-analysis is to assess the effect of olfactory stimulation on reducing dysmenorrhea.
Methods
Systematic search was conducted in several databases, such as PubMed, Web of Science, Cochrane, and Scopus, to identify relevant research up to October 26, 2019. The identified studies were evaluated based on a modified Jadad scale. The intervention involves aromatherapy alone or in combination with essential oils. There was no restriction for the control group such as a placebo group or other common treatments. The Comprehensive Meta-Analysis Version 2 (Bio stat, Englewood, NJ, USA) was used for meta-analysis. Cochran’s Q and I2 tests were utilized.
Results
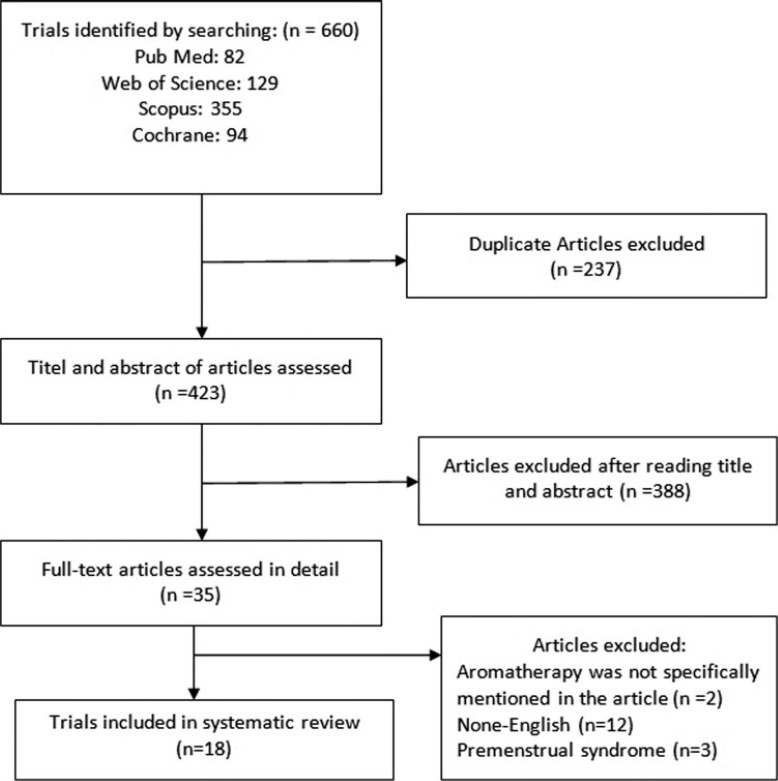
The findings of our meta-analysis, which contained 13 trials (15 data), showed that dysmenorrhea decreased significantly in the group receiving aromatherapy with herbal compared with the control group (standardized mean difference [SMD] =-0.795; 95% confidence interval [CI]: -0.922 to- 0.667; 17 trials O < 0.001); heterogeneity; I2 = 19.47%; p = 0.236). In addition, four studies with insufficient data were not included in our meta-analysis. The results of all studies suggested that aromatherapy with herbal medicine group compared with control group is effective.
Conclusion
Aromatherapy with herbal medicine decreased dysmenorrhea. This treatment was particularly effective when aroma oil was combined with massage or when a mixture of aroma oil was used for the treatment of dysmenorrhea.
-
Review Article01-12-2021
Dyspnea and COVID-19: A Review of Confounding Diagnoses during the Postpartum Period
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(11):862-869
Abstract
Review ArticleDyspnea and COVID-19: A Review of Confounding Diagnoses during the Postpartum Period
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(11):862-869
Views193See moreAbstract
The puerperium is a complex period that begins with placental delivery and lasts for 6 weeks, during which readaptation of the female organism and redistribution of blood volume occur. This period is conducive to the occurrence of thromboembolic events. In the context of the SARS-CoV-2 pandemic, the virus responsible for COVID-19, the attention of the scientific community and health professionals has been focused on obtaining insights on different aspects of this disease, including etiology, transmission, diagnosis, and treatment. Regarding the pregnancy-postpartum cycle, it is opportune to review the clinical conditions that can occur during this period and to investigate dyspnea as a postpartum symptom in order to avoid its immediate association with COVID-19 without further investigation, which can lead to overlooking the diagnosis of other important and occasionally fatal conditions.
-
Review Article01-12-2021
Can Prenatal and Postnatal Cell Phone Exposure Increase Adverse Maternal, Infant and Child Outcomes?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(11):870-877
Abstract
Review ArticleCan Prenatal and Postnatal Cell Phone Exposure Increase Adverse Maternal, Infant and Child Outcomes?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(11):870-877
Views185See moreAbstract
Objective
To determine the association between maternal mobile phone use and adverse outcomes in infants, children, and mothers.
Method
In March 202, we conducted a search on the MEDLINE, Embase, and Scopus databases. Data extraction and an assessment of the quality of the studies were performed by two authors. The quality of the studies was assessed using the checklist of the Newcastle-Ottawa scale.
Results
Studies assessing behavioral problems in infants aged 6 to 18 months reported null findings. However, an increased risk of emotional and behavioral disorders was observed in children aged between 7 and 11 years whose mothers had been exposed to cell phones. The findings regarding the association between maternal cell phone exposure and adverse outcomes in children aged 3 to 5 are controversial. A study found a significant association between the call time (p=0.002) or the history of mobile phone use (in months) and speech disorders in the children (p=0.003). However, another study found that maternal cell phone use during pregnancy was not significantly associated with child psychomotor and mental developments. Inconclusive results were observed about the adverse outcomes in fetuses, such as fetal growth restriction or t scores for birth weight in cell phone users as opposed to non-users. On the contrary, the children ofmothers who were cell phone users had a lower risk of scoring low on motor skills. Similar results were observed regarding the adverse outcomes of cell phone use in infants, such as fetal growth restriction or low birth weight, and the risk of preeclampsia was lower among subjects with medium and high cell phone exposure, as opposed to those with low exposure.
Conclusion
Studies on behavioral problems have reported different postnatal results, such as null findings among infants and a positive association in children.
-
Review Article12-17-2021
Association of the Maternal Folic Acid Supplementation with the Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(10):775-781
Abstract
Review ArticleAssociation of the Maternal Folic Acid Supplementation with the Autism Spectrum Disorder: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(10):775-781
Views289See moreAbstract
Objective
To analyze the scientific production regarding maternal folic acid (FA) supplementation and its relationship with autistic spectrum disorder (ASD).
Data Sources
We performed unrestricted electronic searches in the BIREME virtual bank, Virtual Health Library (VHL) and Medical Literature Analysis and Retrieval System Online (MEDLINE/PubMed) databases.
Selection of Studies
For sample selection, articles that met the proposed objectives were included, published in English, Spanish and Portuguese, the use of Health Sciences Descriptors (DeCS): autistic OR autism AND autism spectrum disorder AND folic acid, AND, with the use of the Medical Subject Headings (MeSH): autistic OR autism AND autistic spectrum disorder AND folic acid.
Data Collection
Data extraction was performed by the reviewers with a preestablished data collection formulary.
Data Synthesis
The Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis Protocols (PRISMA-P) was used based on a checklist with 27 items and a 4-step flowchart.
Results
A total of 384 articles was found by the search strategies, of which 17 were eligible following the pre-established criteria. The main findings of the present review point to maternal FA supplementation in the pre-conception period and beginning of pregnancy as a protective effect in relation to ASD, which should be indicated in this period as prevention to the problem.
Conclusion
According to the research analyzed, more studies are necessary to know its effects on pregnancy, since the consumption of excessive FA may not be innocuous.
-
Review Article12-17-2021
Oral Iron Supplementation in Pregnancy: Current Recommendations and Evidence-Based Medicine Suplementação oral de ferro na gravidez: recomendações atuais e medicina baseada na evidência
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(10):782-788
Abstract
Review ArticleOral Iron Supplementation in Pregnancy: Current Recommendations and Evidence-Based Medicine Suplementação oral de ferro na gravidez: recomendações atuais e medicina baseada na evidência
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(10):782-788
Views392See moreAbstract
Objective
To review the evidence about universal iron supplementation in pregnancy to prevent maternal anemia.
Methods
Bibliographic research of randomized and controlled clinical trials, meta-analyses, systematic reviews, and clinical guidelines, published between August 2009 and August 2019, using the MeSH terms: iron; therapeutic use; pregnancy; anemia, prevention and control.
Results
We included six clinical guidelines, three meta-analyses and one randomized controlled clinical trial.
Discussion
Most articles point to the improvement of hematological parameters and reduction of maternal anemia risk, with supplementary iron. However, they do not correlate this improvement in pregnant women without previous anemia with the eventual improvement of clinical parameters.
Conclusion
Universal iron supplementation in pregnancy is controversial, so we attribute a SORT C recommendation strength.
-
Review Article11-15-2021
Expectant Versus Interventionist Care in the Management of Severe Preeclampsia Remote from Term: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(8):627-637
Abstract
Review ArticleExpectant Versus Interventionist Care in the Management of Severe Preeclampsia Remote from Term: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(8):627-637
Views165See moreAbstract
Objective
To compare the effects of expectant versus interventionist care in the management of pregnant women with severe preeclampsia remote from term.
Data sources
An electronic search was conducted in the Medical Literature Analysis and Retrieval System Online (MEDLINE), Excerpta Medica Database (EMBASE), Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), Latin American and Caribbean Health Sciences Literature (LILACS, for its Spanish acronym), World Health Organization’s International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (WHO-ICTRP), and Open- Grey databases. The International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO, for its French acronym), Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists (RCOG), American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG), and Colombian Journal of Obstetrics and Gynecology (CJOG) websites were searched for conference proceedings, without language restrictions, up to March 25, 2020.
Selection of studies
Randomized clinical trials (RCTs), and non-randomized controlled studies (NRSs) were included. The Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) approach was used to evaluate the quality of the evidence.
Data collection
Studies were independently assessed for inclusion criteria, data extraction, and risk of bias. Disagreements were resolved by consensus.
Data synthesis
Four RCTs and six NRS were included. Low-quality evidence from the RCTs showed that expectant care may result in a lower incidence of appearance, pulse, grimace, activity, and respiration (Apgar) scores<7 at 5 minutes (risk ratio [RR]: 0.48; 95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 0.23%to 0.99) and a higher average birth weight (mean difference [MD]: 254.7 g; 95%CI: 98.5 g to 410.9 g). Very low quality evidence from the NRSs suggested that expectant care might decrease the rates of neonatal death (RR: 0.42; 95%CI 0.22 to 0.80), hyalinemembrane disease (RR: 0.59; 95%CI: 0.40 to 0.87), and admission to neonatal care (RR: 0.73; 95%CI: 0.54 to 0.99). Nomaternal or fetal differences were found for other perinatal outcomes.
Conclusion
Compared with interventionist management, expectant care may improve neonatal outcomes without increasing maternal morbidity and mortality.
-
Review Article10-18-2021
Prenatal Ultrasound Diagnosis of Biometric changes in the Brain of Growth Restricted Fetuses. A Systematic Review of Literature
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(7):545-559
Abstract
Review ArticlePrenatal Ultrasound Diagnosis of Biometric changes in the Brain of Growth Restricted Fetuses. A Systematic Review of Literature
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(7):545-559
Views155See moreAbstract
Fetal growth restriction (FGR) occurswhen the fetus does not reach its intrauterine potential for growth and development as a result of compromise in placental function. It is a condition that affects 5 to 10% of pregnancies and is the second most common cause of perinatal morbidity and mortality. Children born with FGR are at risk of impaired neurological and cognitive development and cardiovascular or endocrine diseases in adulthood. The purpose of the present revision is to perform a literature search for evidence on the detection and assessment by ultrasound of brain injury linked to FGR during fetal life. Using a systematic approach and quantitative evaluation as study methodology, we reviewed ultrasound studies of the fetal brain structure of growth-restricted fetuses with objective quality measures. A total of eight studies were identified. High quality studies were identified for measurement of brain volumes; corpus callosum; brain fissure depth measurements, and cavum septi pellucidi width measurement. A low-quality study was available for transverse cerebellar diameter measurement in FGR. Further prospective randomized studies are needed to understand the changes that occur in the brain of fetuseswith restricted growth, as well as their correlation with the changes in cognitive development observed.
PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 2
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 46
- Abstract Views: 11
- Captures
- Readers: 30



