-
Review Article
Effects of Hydrosalpinx on Endometrial Implantation Failures: Evaluating Salpingectomy in Women Undergoing in vitro fertilization
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(4):304-310
02-18-2021
Summary
Review ArticleEffects of Hydrosalpinx on Endometrial Implantation Failures: Evaluating Salpingectomy in Women Undergoing in vitro fertilization
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(4):304-310
02-18-2021Views196See moreAbstract
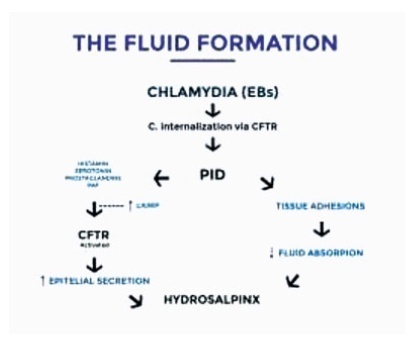
Hydrosalpinx is a disease characterized by the obstruction of the salpinx, with progressive accumulation in the shape of a fluid-filled sac at the distal part of the tuba uterina, and closed to the ovary. Women with hydrosalpinges have lower implantation and pregnancy rates due to a combination of mechanical and chemical factors thought to disrupt the endometrial environment. Evidence suggests that the presence of hydrosalpinx reduces the rate of pregnancy with assisted reproductive technology. The main aim of the present is review to make an overview of the possible effects of hydrosalpinx on in vitro fertilization (IVF).We conducted a literature search on the PubMed, Ovid MEDLINE, and Google Scholar data bases regarding hydrosalpinx and IVF outcomes. Hydrosalpinx probably has a direct toxic effect on sperm motility and on the embryos. In addition, the increasing liquid inside the salpinges could alter the mechanisms of endometrial receptivity. The window of endometrial receptivity is essential in the implantation of blastocysts, and it triggers multiple reactions arising from the endometrium as well as the blastocysts. Hydrosalpinx could influence the expression of homeobox A10 (HOXA10) gene, which plays an essential role in directing embryonic development and implantation. Salpingectomy restores the endometrial expression of HOXA10; therefore, it may be one mechanism by which tubal
-
Review Article
Reproductive Outcomes in Cases of Subclinical Hypothyroidism and Thyroid Autoimmunity: A Narrative Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(12):829-833
01-11-2020
Summary
Review ArticleReproductive Outcomes in Cases of Subclinical Hypothyroidism and Thyroid Autoimmunity: A Narrative Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(12):829-833
01-11-2020Views179Abstract
Thyroid diseases are relatively common in women in the reproductive period. It is currently understood that clinically-evident thyroid disorders may impair ovulation and, consequently, fertility. However, to date it has not been proven that high serum levels of thyroid-stimulating hormone and/or positivity for antithyroid antibodies are associated to a reduction in fertility, mainly in the absence of altered thyroxine levels. The present comprehensive review aims to present current data on the association between subclinical hypothyroidism and/or thyroid autoimmunity and reproductive outcomes.
Key-words autoimmunityfemale infertilityHypothyroidismthyroid diseasesthyroid function teststhyroid hormonesSee more -
Review Article
Update on Thrombocytopenia in Pregnancy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(12):834-840
01-11-2020
Summary
Review ArticleUpdate on Thrombocytopenia in Pregnancy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(12):834-840
01-11-2020Views214See moreAbstract
Thrombocytopenia, defined as platelet count < 150,000mm3, is frequently diagnosed by obstetricians since this parameter is included in routine surveillance during pregnancy, with an incidence of between 7 and 12%. Therefore, decisions regarding subsequent examination and management are primordial. While most of the cases are due to physiological changes, as gestational thrombocytopenia, other causes can be related to severe conditions that can lead to fetal or maternal death. Differentiating these conditions might be challenging: they can be pregnancy-specific (pre-eclampsia/ HELLP syndrome [hemolysis, elevated liver enzymes, low platelets]), or not (immune thrombocytopenia purpura, thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura or hemolytic uremic syndrome). Understanding the mechanisms and recognition of symptoms and signs is essential to decide an adequate line of investigation. The severity of thrombocytopenia, its etiology and gestational age dictates different treatment regimens.
-
Review Article
Cytotoxic Activity of Antineoplastic Agents on Fertility: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(11):759-768
12-21-2020
Summary
Review ArticleCytotoxic Activity of Antineoplastic Agents on Fertility: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(11):759-768
12-21-2020Views135See moreAbstract
Objective:
To analyze the long-term effects of antineoplastic treatments on patient fertility.
Selection of Studies:
The studies were selected through the New PubMed, Scielo and Lilacs databases along with references used for the creation of the present work. For the selection of studies, articles published between the periods from January 1, 2015 to April 6, 2020 in the English, Portuguese and Spanish languages were used. As inclusion criteria: cohort studies and studies conducted in vitro. As exclusion criteria: review articles, reported cases, studies that do not address thematic reproduction, studies that do not address the cancer theme, articles that used animals, articles that address the preservation of fertility and articles in duplicate in the bases.
Data Collection:
The collected data included: age of the patient at the beginning of treatment, type of neoplasm, type of antineoplastic treatment, chemotherapy used, radiotherapy dosage, radiotherapy site, effect of antineoplastic agents on fertility and number of patients in the study.
Data Synthesis:
Thirty studies were evaluated, antineoplastic chemotherapy agents and radiotherapy modulate serum hormone levels, reduces germ cell quantities and correlated with an increase in sterility rates. The effects mentioned occur in patients in the prepubertal and postpubertal age.
Conclusion:
Antineoplastic treatments have cytotoxic effects on the germ cells leading to hormonal modulation, and pubertal status does not interfere with the cytotoxic action of therapies.
-
Review Article
Use of GnRH Analogues in the Reduction of Submucous Fibroid for Surgical Hysteroscopy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(10):649-658
12-21-2020
Summary
Review ArticleUse of GnRH Analogues in the Reduction of Submucous Fibroid for Surgical Hysteroscopy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(10):649-658
12-21-2020Views225See moreAbstract
Objective
Gonadotropin-releasing hormone analogues (GnRH-a) have been used preoperatively before hysteroscopic myomectomy to decrease the size and vascularization of the myomas, but evidence to support this practice is weak. Our objective was to analyze the use of GnRH-a in the reduction of submucous fibroid as a facilitator for surgical hysteroscopy from published clinical trials.
Data sources
Studies from electronic databases (Pubmed, Scielo, EMBASE, Scopus, PROSPERO), published between 1980 and December 2018. The keywords used were fibroid, GnRH analogue, submucous, histeroscopy, histeroscopic resection and their correspondents in Portuguese.
Study selection
The inclusion criteria were controlled trials that evaluated the GnRH-a treatment before hysteroscopic resection of submucous myomas. Four clinical trials were included in the meta-analysis.
Data collection
Two review authors extracted the data without modification of the original data, using the agreed form. We resolved discrepancies through discussion or, if required, we consulted a third person.
Data synthesis
The present meta-analysis included a total of 213 women and showed no statistically significant differences in the use of GnRH-a compared with the control group for complete resection of submucous myoma (relative risk [RR]: 0.94; 95%; confidence interval [CI]: 0.80-1.11); operative time (mean difference [MD]: - 3.81; 95%;CI : - 3.81-2.13); fluid absorption (MD: - 65.90; 95%;CI: - 9.75-2.13); or complications (RR 0.92; 95%;CI: 0.18-4.82).
Conclusion
The present review did not support the routine preoperative use of GnRH-a prior to hysteroscopic myomectomy. However, it is not possible to determine its inferiority when compared with the other methods due to the heterogeneity of existing studies and the small sample size.
-
Review Article
Clinical Procedures for the Prevention of Preeclampsia in Pregnant Women: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(10):659-668
12-21-2020
Summary
Review ArticleClinical Procedures for the Prevention of Preeclampsia in Pregnant Women: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(10):659-668
12-21-2020Views248See moreAbstract
Objective
To identify the most effective procedures recommended for the prevention of preeclampsia.
Data Sources
A systematic review was performed in the following databases: Pubmed/MEDLINE, CINAHL, Web of Science, Cochrane and LILACS via the Virtual Health Library (VHL). A manual search was also performed to find additional references. The risk of bias, the quality of the evidence, and the classification of the strength of the recommendations were evaluated using the Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluations (GRADE) approach.
Selection of Studies
In the initial search in the databases, the total number of articles retrieved was 351, and 2 were retrieved through the manual search; after duplicate articles were removed, 333 citations remained. After a thorough review of the titles and abstracts, 315 references were excluded. Accordingly, 18 articles were maintained for selection of the complete text (phase 2). This process led to the exclusion of 6 studies. In total, 12 articles were selected for data extraction and qualitative synthesis.
Data Collection
The articles selected for the study were analyzed, and we inserted the synthesis of the evidence in the online software GRADEpro Guideline Development Tool (GDT) (McMaster University and Evidence Prime Inc. All right reserved. McMaster University, Hamilton, Ontário, Canada); thus, it was possible to develop a table of evidence, with the quality of the evidence and the classification of the strength of the recommendations.
Data Synthesis
In total, seven studies recommended the individual use of aspirin, or aspirin combined with calcium, heparin or dipyridamole. The use of calcium alone or in combination with phytonutrients was also highlighted. All of the studies were with women at a high risk of developing preeclampsia.
Conclusion
According to the studies evaluated, the administration of aspirin is still the best procedure to be used in the clinical practice to prevent preeclampsia.
-
Review Article
Do Thyroid Diseases during Pregnancy and Lactation Affect the Nutritional Composition of Human Milk?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(11):752-758
12-21-2020
Summary
Review ArticleDo Thyroid Diseases during Pregnancy and Lactation Affect the Nutritional Composition of Human Milk?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(11):752-758
12-21-2020Views144See moreAbstract
Objective:
To identify whether the effects of thyroid disease during pregnancy and lactation affect the nutritional composition of human milk.
Methods:
Systematic review of the scientific literature using the Medical Literature Analysis and Retrieval System Online/MedLine databases to evaluate the association of thyroid diseases during pregnancy and lactation with the nutritional composition of human milk. There was no delimitation by period or by language, and the searches were completed in March 2019. The following descriptors were applied: human milk AND thyroid AND composition, using the preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA) protocol for data search, selection, and extraction. The flowchart proposed for bibliographic search resulted in 12 articles and, of these, four were selected.
Results:
The articles elected for this review were published between 1976 and 2018. Two studies found significant differences in the nutritional composition of mothers' milk with hypothyroidism or overweight compared with the milk of those without hypothyroidism. Studies have shown that the presence of the disease led to changes in the nutritional composition of human milk, especially a higher concentration of human milk fat.
Conclusion:
It is extremely important that these women have continuous nutritional follow-up to minimize the impact of these morbidities on the nutritional composition of human milk.
-
Review Article
SARS-CoV-2 and Pregnancy: A Review of the Facts
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(9):562-568
10-23-2020
Summary
Review ArticleSARS-CoV-2 and Pregnancy: A Review of the Facts
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(9):562-568
10-23-2020Views214See moreAbstract
Objective
The present comprehensive review aims to show the full extent of what is known to date and provide a more thorough view on the effects of SARS-CoV2 in pregnancy.
Methods
Between March 29 and May, 2020, the words COVID-19, SARS-CoV2, COVID- 19 and pregnancy, SARS-CoV2 and pregnancy, and SARS and pregnancy were searched in the PubMed and Google Scholar databases; the guidelines from well-known societies and institutions (Royal College of Obstetricians and Gynaecologists [RCOG], American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists [ACOG], International Society of Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology [ISUOG], Centers for Disease Control and Prevention [CDC], International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics [FIGO]) were also included.
Conclusion
The COVID-19 outbreak resulted in a pandemic with > 3.3 million cases and 230 thousand deaths until May 2nd. It is caused by the SARS-CoV2 virus and may lead to severe pulmonary infection and multi-organ failure. Past experiences show that unique characteristics in pregnancy make pregnant women more susceptible to complications from viral infections. Yet, this has not been reported with this new virus. There are risk factors that seem to increase morbidity in pregnancy, such as obesity (body mass index [BMI] > 35), asthma and cardiovascular disease. Current reports describe an increased rate of pretermbirth and C-section. Vertical transmission


