Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(5):225-234
To evaluate the performance of Intergrowth-21 st (INT) and Fetal Medicine Foundation (FMF) curves in predicting perinatal and neurodevelopmental outcomes in newborns weighing below the 3rd percentile.
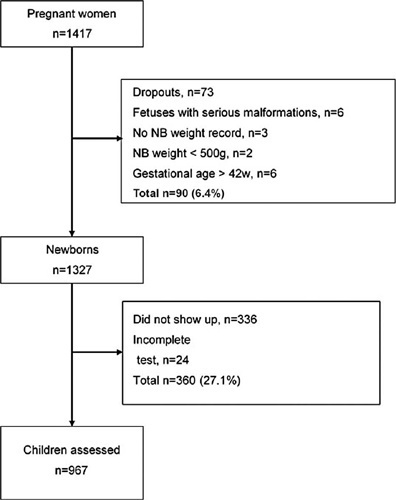
Pregnant women with a single fetus aged less than 20 weeks from a general population in non-hospital health units were included. Their children were evaluated at birth and in the second or third years of life. Newborns (NB) had their weight percentiles calculated for both curves. Sensitivity, specificity, positive (PPV) and negative predictive value (NPV), and area under the ROC curve (ROC-AUC) for perinatal outcomes and neurodevelopmental delay were calculated using birth weight < 3rd percentile as the cutoff.
A total of 967 children were evaluated. Gestational age at birth was 39.3 (± 3.6) weeks and birth weight was 3,215.0 (± 588.0) g. INT and FMF classified 19 (2.4%) and 49 (5.7%) newborns below the 3rd percentile, respectively. The prevalence of preterm birth, tracheal intubation >24 hours in the first three months of life, 5th minute Apgar <7, admission to a neonatal care unit (NICU admission), cesarean section rate, and the neurodevelopmental delay was 9.3%, 3.3%, 1.3%, 5.9%, 38.9%, and 7.3% respectively. In general, the 3rd percentile of both curves showed low sensitivity and PPV and high specificity and NPV. The 3rd percentile of FMF showed superior sensitivity for preterm birth, NICU admission, and cesarean section rate. INT was more specific for all outcomes and presented a higher PPV for the neurodevelopmental delay. However, except for a slight difference in the prediction of preterm birth in favor of INT, the ROC curves showed no differences in the prediction of perinatal and neurodevelopmental outcomes.
Birth weight below the 3rd percentile according to INT or FMF alone was insufficient for a good diagnostic performance of perinatal and neurodevelopmental outcomes. The analyzes performed could not show that one curve is better than the other in our population. INT may have an advantage in resource contingency scenarios as it discriminates fewer NB below the 3rd percentile without increasing adverse outcomes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(5):235-241
To evaluate the accuracy and patient acceptability toward self-sampling using a new device - SelfCervix® - for detecting HPV-DNA.
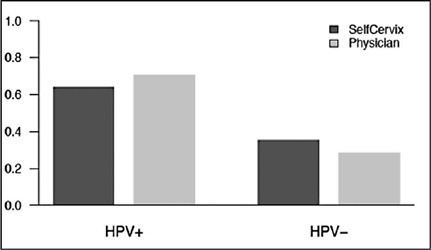
A total of 73 women aged 25–65 who underwent regular cervical cancer screening from March to October 2016 were included. Women performed self-sampling followed by a physician-sampling, and the samples were analyzed for HPV-DNA. After that, patients were surveyed about their acceptability of self-sampling.
HPV-DNA detection rate of self-sampling presented high accuracy and was similar to physician-collection. Sixty-four (87.7%) patients answered the acceptability survey. Most patients (89%) considered the self-sampling comfortable, and 82.5% preferred self-sampling to physician-sampling. The reasons cited were time-saving and convenience. Fifty-one (79.7%) reported that they would recommend self-sampling.
Self-sampling using the new Brazilian device SelfCervix® is not inferior in HPV-DNA detection rate compared with physician-collection, and patients are supportive of the method. Therefore, it might be an option to reach under-screened populations in Brazil.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(5):242-252
Evaluate the effect of combined training on body image (BI), body composition and functional capacity in patients with breast cancer. As also the relationship of BI with body composition and functional capacity.
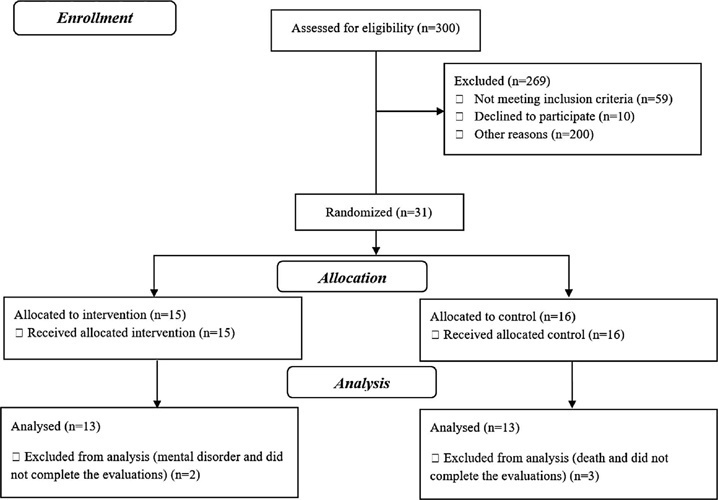
This was a Controlled Clinical Trial study, this study including 26 patients with breast cancer (30 to 59 years). The training group (n = 13) underwent 12 weeks of training, including three 60-min sessions of aerobic exercise and resistance training, and two sessions of flexibility training per week; each flexibility exercise lasted 20s. The Control Group (n = 13) received only the standard hospital treatment. Participants were evaluated at baseline and after 12 weeks. BI (primary outcomes) was assessed using the Body Image After Breast Cancer Questionnaire; Body composition was estimated with the indicators: Body mass index; Weight, Waist hip Ratio; Waist height ratio; Conicity index; Reciprocal ponderal index; Percentage of fat; Circumference of the abdomen and waist; Functional capacity by cardiorespiratory fitness (cycle ergometer) and strength (manual dynamometer). The statistic was performed in the Biostatistics and Stata 14.0 (α = 5%).
The patients in the training group showed a reduction in the limitation dimension (p = 0.036) on BI, However, an increase in waist circumference was observed in both groups. In addition an increase in VO2max (p < 0.001) and strength in the right (p = 0.005) and left arms (p = 0.033).
Combined training demonstrates to be an effective and non-pharmacological strategy to patients with breast cancer, with improvement on BI and functional capacity, changing related variables negatively when there is no physical training.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(5):253-260
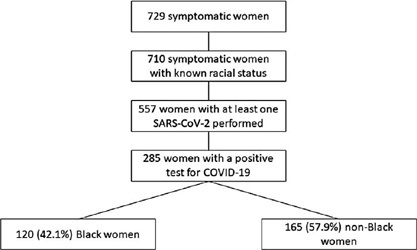
To evaluate the impact of the race (Black versus non-Black) on maternal and perinatal outcomes of pregnant women with COVID-19 in Brazil. Methods This is a subanalysis of REBRACO, a Brazilian multicenter cohort study designed to evaluate the impact of COVID-19 on pregnant women. From February2020 until February 2021, 15 maternity hospitals in Brazil collected data on women with respiratory symptoms. We selected all women with a positive test for COVID-19; then, we divided them into two groups: Black and non-Black women. Finally, we compared, between groups, sociodemographic, maternal, and perinatal outcomes. We obtained the frequency of events in each group and compared them using X2 test; p-values < 0.05 were considered significant. We also estimated the odds ratio (OR) and confidence intervals (CI).
729 symptomatic women were included in the study; of those, 285 were positive for COVID-19, 120 (42.1%) were Black, and 165 (57.9%) were non-Black. Black women had worse education (p = 0.037). The timing of access to the health system was similar between both groups, with 26.3% being included with seven or more days of symptoms. Severe acute respiratory syndrome (OR 2.22 CI 1.17–4.21), intensive care unit admission (OR 2.00 CI 1.07–3.74), and desaturation at admission (OR 3.72 CI 1.41–9.84) were more likely to occur among Black women. Maternal death was higher among Black women (7.8% vs. 2.6%, p = 0.048). Perinatal outcomes were similar between both groups.
Brazilian Black women were more likely to die due to the consequences of COVID-19.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(5):261-265
To determine the existence of SARS-CoV-2 in the peritoneal fluid to assess the risk of exposure through surgical smoke and aerosolization threatening healthcare workers during abdominal surgery.
SARS-CoV-2 is a respiratory virus and possible ways of viral transmission are respiratory droplets, close contact, and fecal-oral route. Surgeries pose risk for healthcare workers due to the close contact with patients. Aerosolized particles may be inhaled via the leaked CO2 during laparoscopic procedures and surgical smoke produced by electrocautery.
All the data of 8 patients, who were tested positive for COVID–19, were collected between August 31, 2020 and April 30, 2021. Recorded clinicopathologic data included age, symptoms, radiological and laboratory findings, antiviral treatment before surgery, type of surgery and existence of the virus in the peritoneal fluid. Nasopharyngeal swab RT-PCR was used for the diagnosis. COVID–19 existence in the peritoneal fluid was determined by RT-PCR test as well.
All 8 COVID–19 positive patients were pregnant, and surgeries were cesarean sections. 1 of the 8 patients was febrile during surgery. Also only 1 patient had pulmonary radiological findings specifically indicating COVID-19 infection. Laboratory findings were as follows: 4 of 8 had lymphopenia and all had elevated D-dimer levels. Peritoneal and amniotic fluid samples of all patients were negative for SARS-CoV-2.
SARS-CoV-2 exposure due to aerosolization or surgical fumes does not seem to be likely, provided the necessary precautions are taken.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(5):266-272
This study analyzes the role of clinical simulation in internal medical residency programs (IMRP) in Obstetrics and Gynecology (OB/GYN), attributed by the supervisors, in the training of residents in the city of São Paulo (SP).
Cross-sectional descriptive, qualitative, and exploratory approach. Semi-structured interviews were performed with ten supervisors of Medical Residency programs in Obstetrics and Gynecology. Interviews were analyzed by means of content analysis under the thematic modality, starting with the core the role of clinical simulation in Obstetrics and Gynecology Medical Residency Programs.
Supervisors view Clinical simulation as: a complementary tool for the teaching and learning process, a possibility of a safe teaching and learning environment, an opportunity to learn from mistakes, a support for professional practice committed to patient safety, a learning scenario for teamwork, a scenario for reflection on the work process in Obstetrics and Gynecology, a scenario for evaluative processes in the medical residency. Still according to supervisors, Clinical Simulation favors decision-making and encourages the resident participation in activities.
Supervisors recognize Clinical Simulation as a powerful pedagogical tool in the learning process of resident doctors in Obstetrics and Gynecology Residency Programs.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(6):303-311
The lack of data on the impact of hyperglycemia and obesity on the prevalence of pregnancy-specific urinary incontinence (PSUI) led us to conduct a cross-sectional study on the prevalence and characteristics of PSUI using validated questionnaires and clinical data.
This cross-sectional study included 539 women with a gestational age of 34 weeks who visited a tertiary university hospital between 2015 and 2018. The main outcome measures were the prevalence of PSUI, the International Consultation on Incontinence Questionnaire Short Form (ICIQ-SF), and the Incontinence Severity Index (ISI) questionnaires. The women were classified into four groups: normoglycemic lean, normoglycemic obese, hyperglycemic lean, and hyperglycemic obese. The differences between groups were tested using descriptive statistics. Associations were estimated using logistic regression analysis and presented as unadjusted and adjusted odds ratios.
Prevalence rates of PSUI were no different between groups. However, significant difference in hyperglycemic groups worse scores for severe and very severe PSUI. When adjusted data for confound factors was compared with normoglycemic lean group, the hyperglycemic obese group had significantly higher odds for severe and very severe forms of UI using ICIQ-SF (aOR 3.157; 95% CI 1.308 to 7.263) and ISI (aOR 20.324; 95% CI 2.265 to 182.329) questionnaires and highest perceived impact of PSUI (aOR 4.449; 95% CI 1.591 to 12.442).
Our data indicate that obesity and hyperglycemia during pregnancy significantly increase the odds of severe forms and perceived impact of PSUI. Therefore, further effective preventive and curative treatments are greatly needed.