Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(8):480-488
To present the update of the recommendations of the Brazilian College of Radiology and Diagnostic Imaging, the Brazilian Society of Mastology and the Brazilian Federation of Associations of Gynecology and Obstetrics for breast cancer screening in Brazil.
Scientific evidence published in Medline, EMBASE, Cochrane Library, EBSCO, CINAHL and Lilacs databases between January 2012 and July 2022 was searched. Recommendations were based on this evidence by consensus of the expert committee of the three entities.
Annual mammography screening is recommended for women at usual risk aged 40–74 years. Above 75 years, it should be reserved for those with a life expectancy greater than seven years. Women at higher than usual risk, including those with dense breasts, with a personal history of atypical lobular hyperplasia, classic lobular carcinoma in situ, atypical ductal hyperplasia, treatment for breast cancer or chest irradiation before age 30, or even, carriers of a genetic mutation or with a strong family history, benefit from complementary screening, and should be considered individually. Tomosynthesis is a form of mammography and should be considered in screening whenever accessible and available.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(8):489-498
To perform a systematic review and meta-analysis of studies on maternal, fetal, and neonatal outcomes of women with singleton pregnancies, after spontaneous conception, and with the diagnosis of amniotic sludge before 37 weeks of gestational age.
We conducted a search on the PubMed, Cochrane, Bireme, and Theses databases until June 2022.
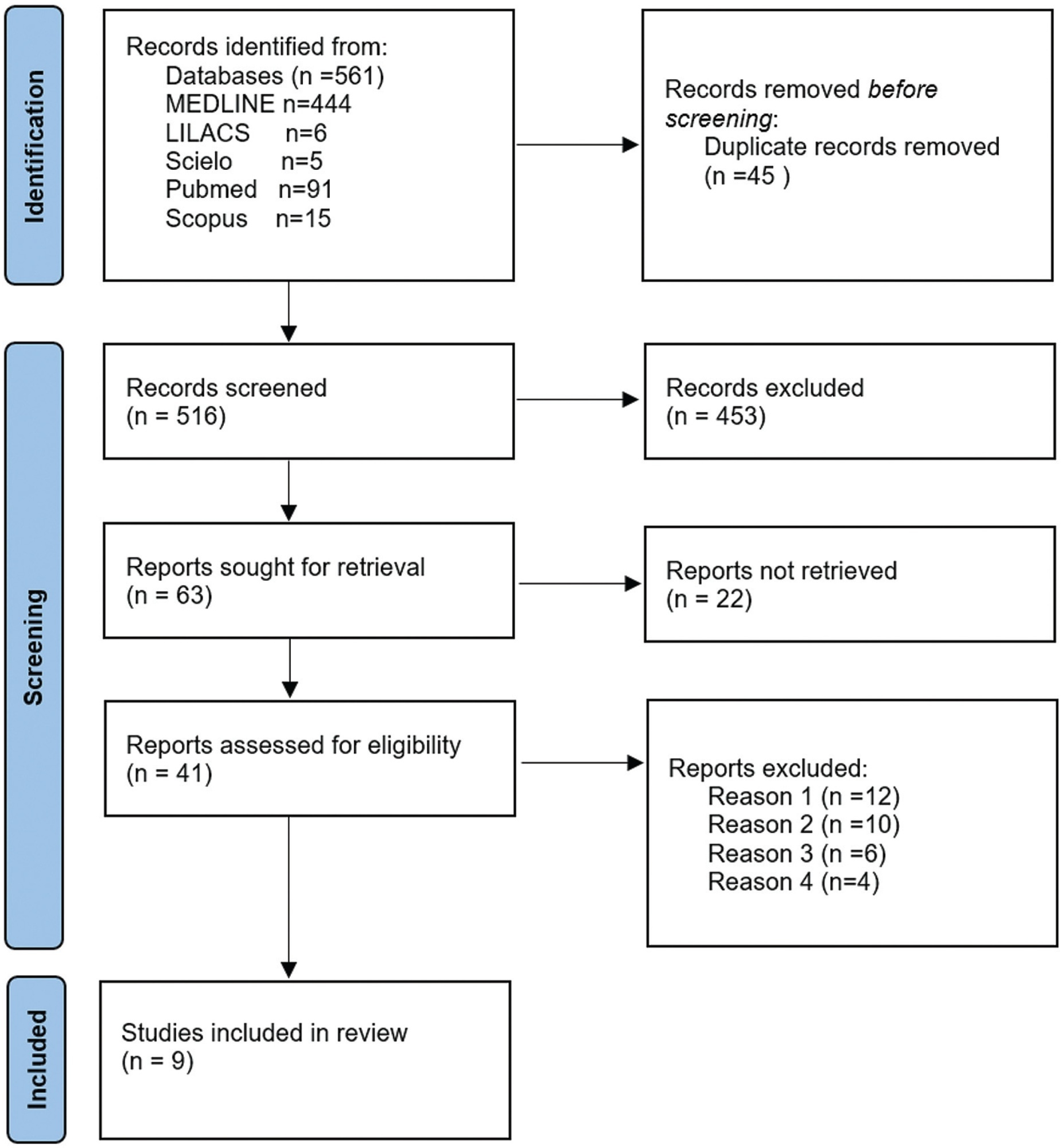
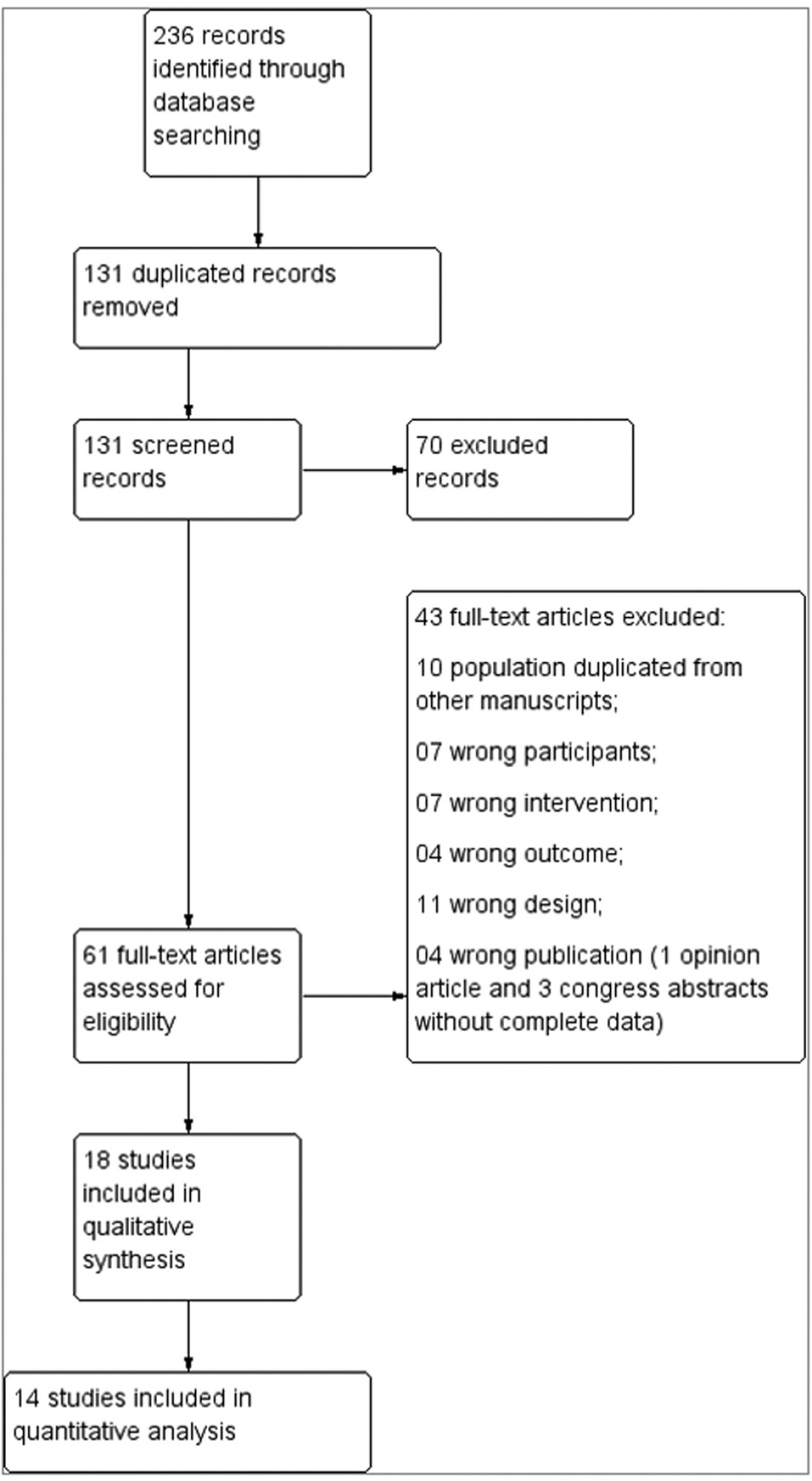
Using the keywords intra-amniotic sludge or fluid sludge or echogenic particles, we found 263 articles, 132 of which were duplicates, and 70 were discarded because they did not meet the inclusion criteria.
The articles retrieved were analyzed by 2 reviewers; 61 were selected for full-text analysis, 18 were included for a qualitative analysis, and 14, for a quantitative analysis.
Among the maternal outcomes analyzed, there was an increased risk of preterm labor (95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 1.45–2.03), premature rupture of ovular membranes (95%CI: 1.99–3.79), and clinical (95%CI: 1.41–6.19) and histological chorioamnionitis (95%CI: 1.75–3.12). Regarding the fetal outcomes, there was a significant increase in the risk of morbidity (95%CI: 1.80–3.17), mortality (95%CI: 1.14–18.57), admission to the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU; 95%CI: 1.17–1.95), and neonatal sepsis (95%CI: 2.29–7.55).
The results of the present study indicate that the presence of amniotic sludge is a risk marker for preterm delivery. Despite the heterogeneity of the studies analyzed, even in patients with other risk factors for prematurity, such as short cervix and previous preterm delivery, the presence of amniotic sludge increases the risk of premature labor. Moreover, antibiotic therapy seems to be a treatment for amniotic sludge, and it may prolong pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(7):371-376
To compare cesarean section (CS) rates according to the Robson Ten Group Classification System (RTGCS) and its indications in pregnant women admitted for childbirth during the first wave of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic with those of the previous year.
We conducted a cross-sectional study to compare women admitted for childbirth from April to October 2019 (before the pandemic) and from March to September 2020 (during the pandemic). The CSs and their indications were classified on admission according to the RTGCS, and we also collected data on the route of delivery (vaginal or CS). Both periods were compared using the Chi-squared (χ2) test or the Fisher exact test.
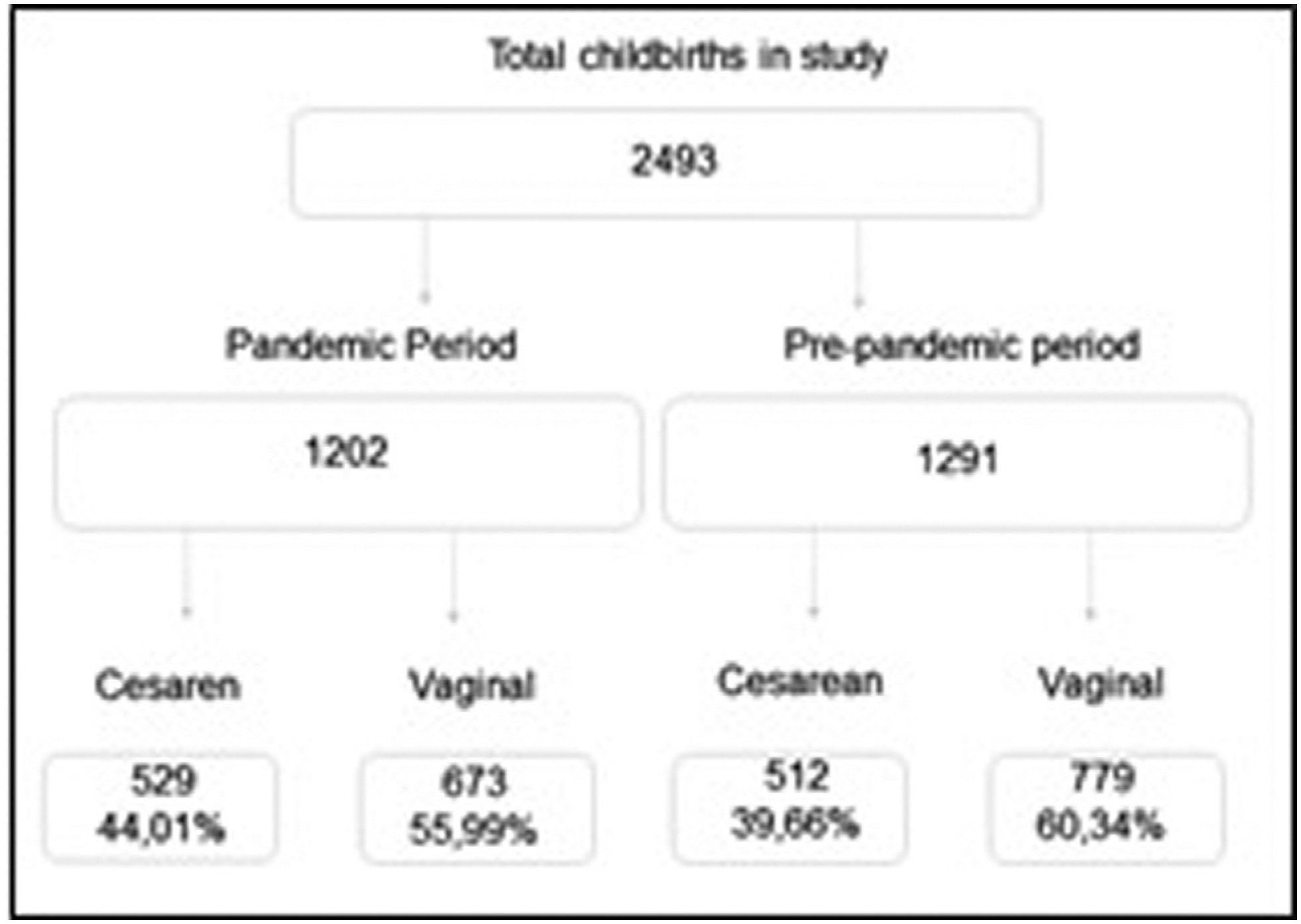
In total, 2,493 women were included, 1,291 in the prepandemic and 1,202 in the pandemic period. There was a a significant increase in the CS rate (from 39.66% to 44.01%; p = 0.028), mostly due to maternal request (from 9.58% to 25.38%; p < 0.01). Overall, groups 5 and 2 contributed the most to the CS rates. The rates decreased among group 1 and increased among group 2 during the pandemic, with no changes in group 10.
There was an apparent change in the RTGSC comparing both periods, with a significant increase in CS rates, mainly by maternal request, most likely because of changes during the pandemic and uncertainties and fear concerning COVID-19.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(7):377-383
To analyze the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on the residency of gynecology and obstetrics in São Paulo.
Cross-sectional study developed by representatives of residents of the Association of Gynecology and Obstetrics of the State of São Paulo (SOGESP, in the Portuguese acronym). Data were collected from questionnaires applied to gynecology and obstetrics residents registered on the SOGESP website in February 2022. The interviewees answered about the repercussions of the pandemic on medical residency and whether they had technical and psychological support during the period.
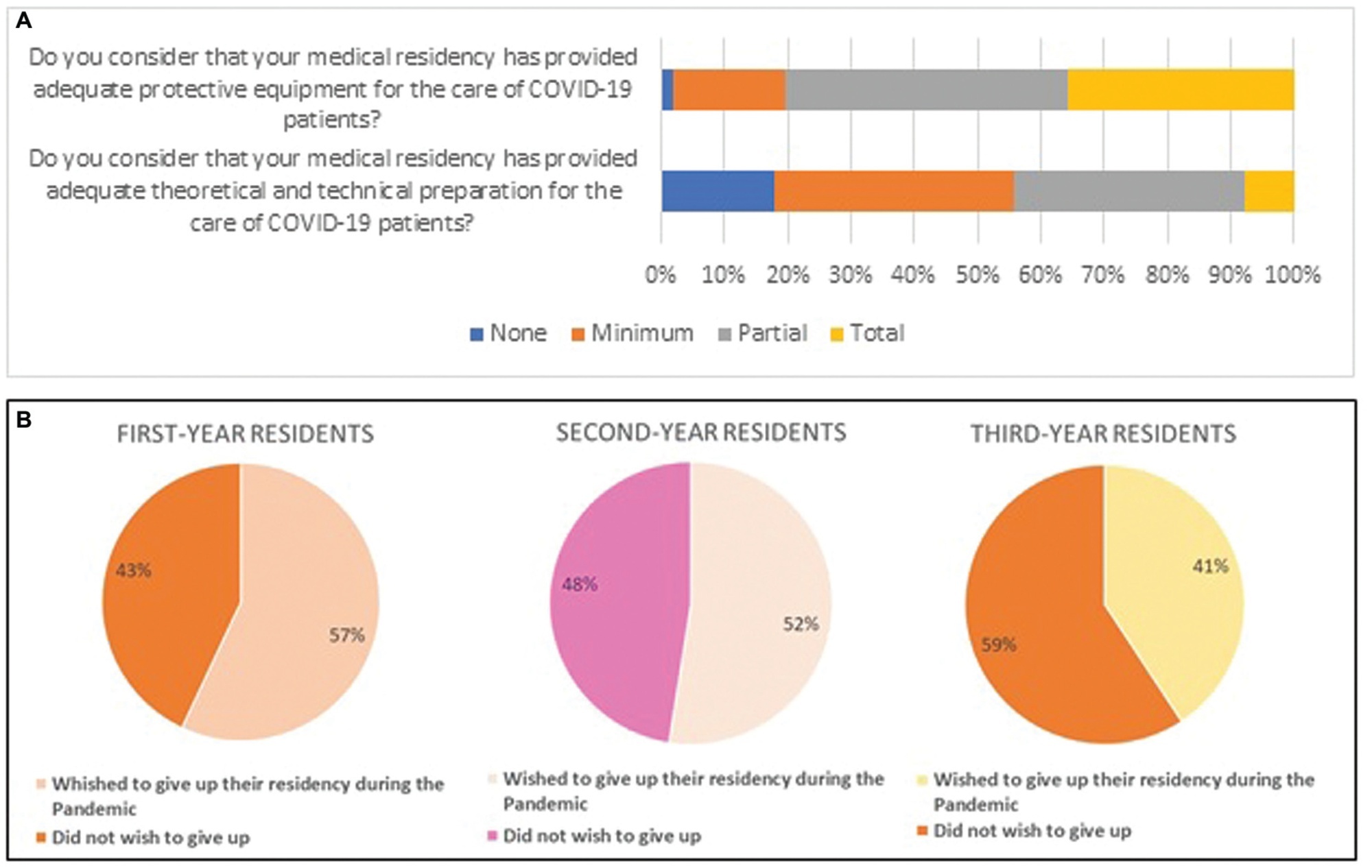
A total of 247 questionnaires were collected from residents of gynecology and obstetrics. The residents had an age of 28.3 ± 3 years old, and most of them were female (88.4%). The displacement to COVID care was reported by 62.34% of the students, but only 35.6% reported completely adequate personal protective equipment and only 7.7% reported complete theoretical and technical instruction to support these patients. Almost all of the interviewees stated that the gynecology sector was the most affected. The majority of the interviewees considered that the second-year residents had the greatest loss, and more than half of the residents in the 1st and 2nd year said they wished to give up their residency during the pandemic. More than 80% of the residents reported online theoretical classes and/or presentation of articles, reinforcing the fact that virtual activities gained a greater space within the medical residency.
The pandemic impacted the residency in greater proportion in outpatient clinics and gynecological surgeries, also interfering with the physician's desire to continue with the program.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(7):384-392
To assess the potential relationship of clinical status upon admission and distance traveled from geographical health district in women with gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD).
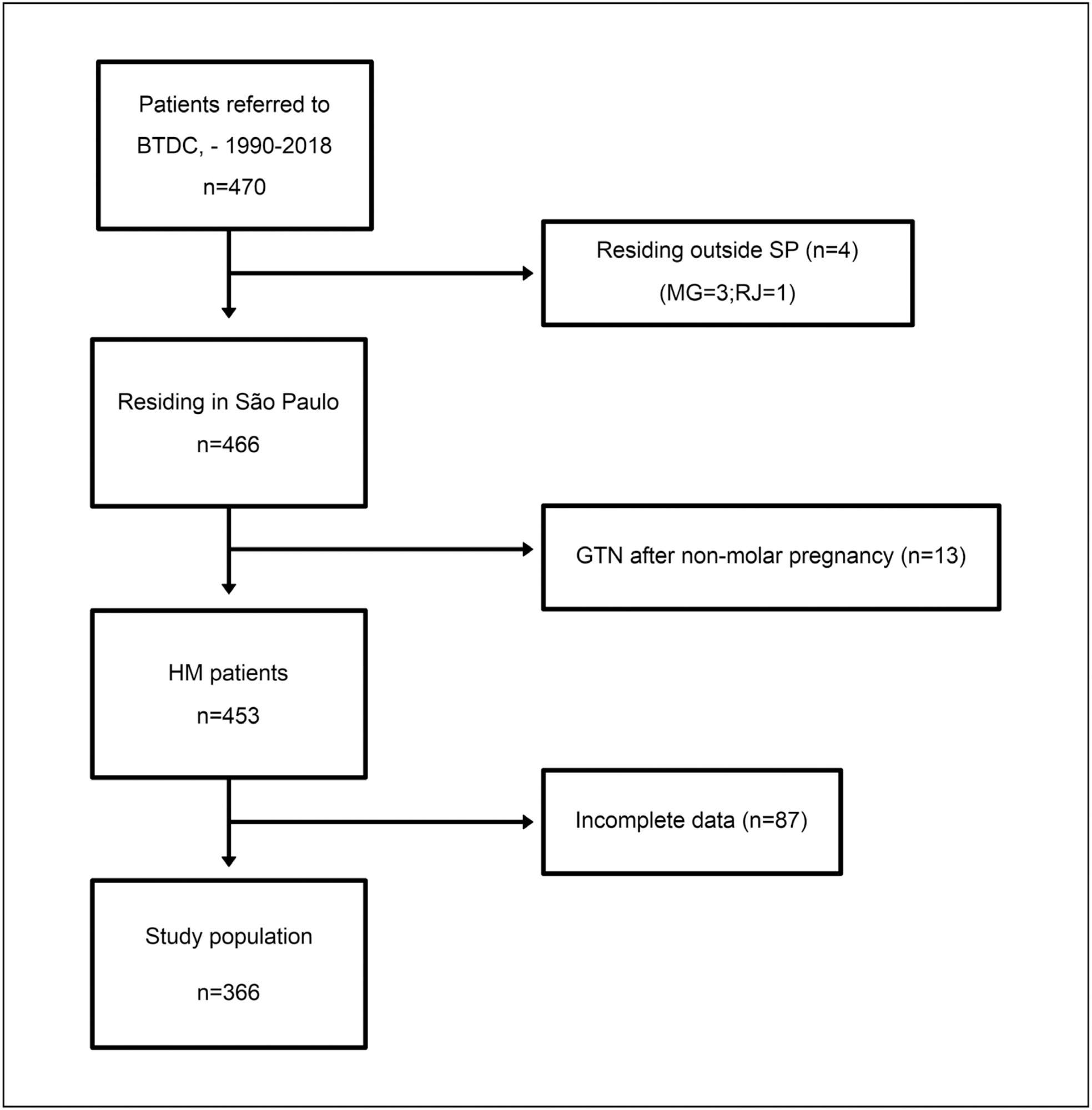
This is a cross-sectional study including women with GTD from the 17 health districts from the São Paulo state (I–XVII), Brazil, referred to the Botucatu Trophoblastic Disease Center (specialized center, district VI), between 1990 and 2018. At admission, hydatidiform mole was assessed according to the risk score system of Berkowitz et al. Gestational trophoblastic neoplasia was evaluated using the International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics / World Health Organization (FIGO/WHO) staging/risk score. Data on demographics, clinical status and distance traveled were collected. Multiple regression analyses were performed.
This study included 366 women (335 hydatidiform mole, 31 gestational trophoblastic neoplasia). The clinical status at admission and distance traveled significantly differed between the specialized center district and other districts. Patients referred from health districts IX (β = 2.38 [0.87–3.88], p = 0.002) and XVI (β = 0.78 [0.02–1.55], p = 0.045) had higher hydatidiform mole scores than those from the specialized center district. Gestational trophoblastic neoplasia patients from district XVI showed a 3.32 increase in FIGO risk scores compared with those from the specialized center area (β = 3.32, 95% CI = 0.78–5.87, p = 0.010). Distance traveled by patients from districts IX (200km) and XVI (203.5km) was significantly longer than that traveled by patients from the specialized center district (76km).
Patients from health districts outside the specialized center area had higher risk scores for both hydatidiform mole and gestational trophoblastic neoplasia at admission. Long distances (>80 km) seemed to adversely influence gestational trophoblastic disease clinical status at admission, indicating barriers to accessing specialized centers.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(7):393-400
Endometriosis causes a decrease in oocyte quality. However, this mechanism is not fully understood. The present study aimed to analyze the effect of endometriosis on cumulus cell adenosine triphosphate ATP level, the number of mitochondria, and the oocyte maturity level.
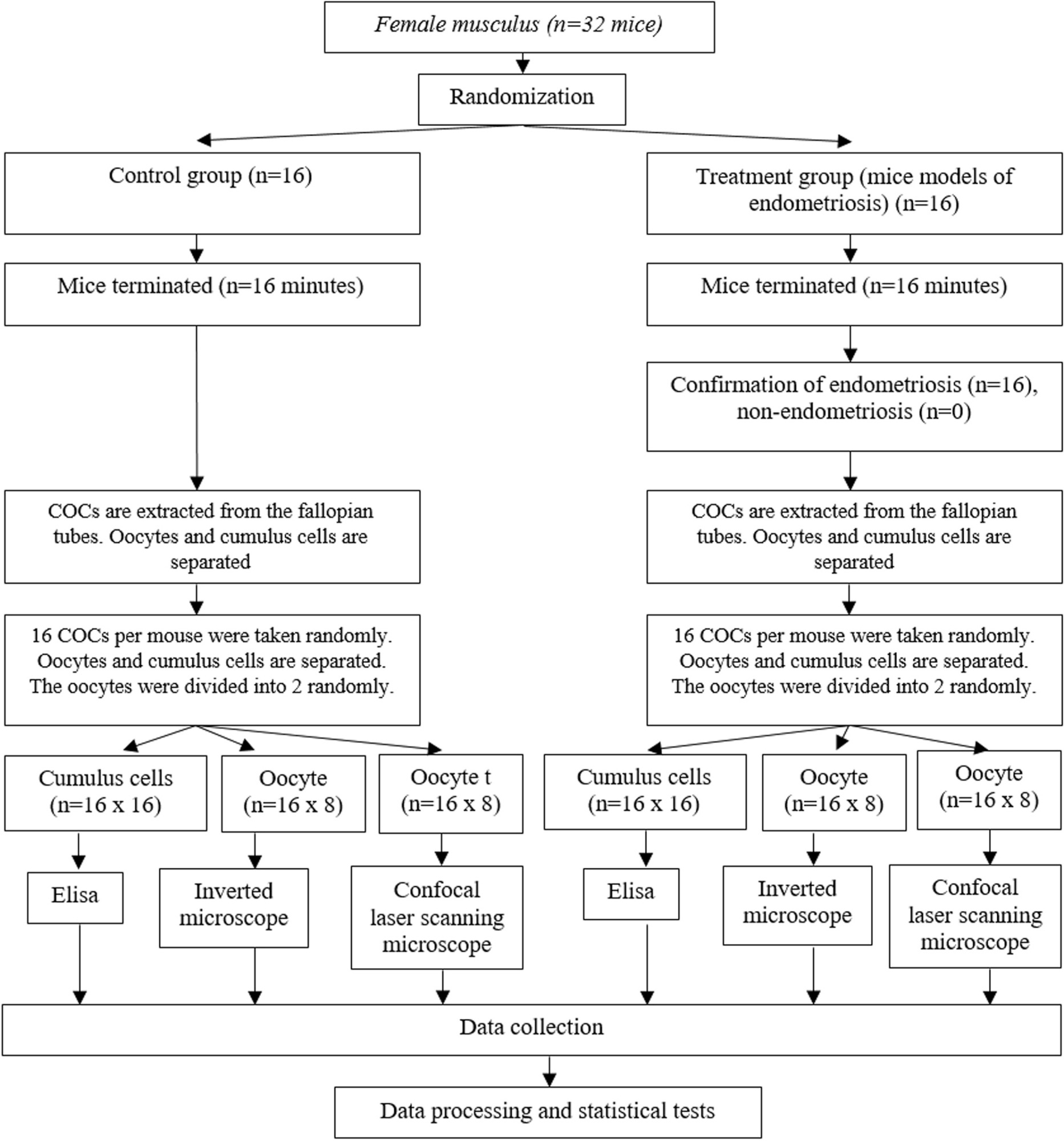
A true experimental study with a post-test only control group design on experimental animals. Thirty-two mice were divided into control and endometriosis groups. Cumulus oocyte complex (COC) was obtained from all groups. Adenosine triphosphate level on cumulus cells was examined using the Elisa technique, the number of mitochondria was evaluated with a confocal laser scanning microscope and the oocyte maturity level was evaluated with an inverted microscope.
The ATP level of cumulus cells and the number of mitochondria in the endometriosis group increased significantly (p < 0.05; p < 0.05) while the oocyte maturity level was significantly lower (p < 0.05). There was a significant relationship between ATP level of cumulus cells and the number of mitochondrial oocyte (p < 0.01). There was no significant relationship between cumulus cell ATP level and the number of mitochondrial oocytes with oocyte maturity level (p > 0.01; p > 0.01). The ROC curve showed that the number of mitochondrial oocytes (AUC = 0.672) tended to be more accurate than cumulus cell ATP level (AUC = 0.656) in determining the oocyte maturity level.
In endometriosis model mice, the ATP level of cumulus cells and the number of mitochondrial oocytes increased while the oocyte maturity level decreased. There was a correlation between the increase in ATP level of cumulus cells and an increase in the number of mitochondrial oocytes.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(7):401-408
To analyze the outcomes of a cohort of patients with high-risk histologies of endometrial cancer (EC) treated at Instituto Nacional de Câncer (National Cancer Institute, INCA, in Portuguese), in Brazil.
We reviewed the medical records of patients with high-risk histologies of EC in any stage registered at INCA between 2010 and 2016 to perform a clinical and demographic descriptive analysis and to evaluate the outcomes in terms of recurrence and survival.
From 2010 to 2016, 2,145 EC patients were registered and treated at INCA, and 466 had high-grade histologies that met the inclusion criteria. The mean age of the patients was 65 years, 44.6% were Caucasian, and 90% had a performance status of 0 or 1. The most common histology was high-grade endometrioid (31.1%), followed by serous carcinoma (25.3%), mixed (20.0%), carcinosarcoma (13.5%), and clear cell carcinoma (9.4%). Considering the 2018 Fédération Internationale de Gynécologie et d'Obstétrique (International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics, FIGO, in French) staging system, 44.8%, 12.4%, 29.8%, and 12.9% of the patient were in stages I, II, III or IV respectively. Age (> 60 years), more than 50% of myoinvasion, higher stage, poor performance status, serous and carcinosarcoma histologies, and adjuvant treatment were independent factors associated with recurrence-free survival (RFS) and overall survival (OS) in the multivariate analysis.
The current findings reinforced the international data showing poor outcomes of these tumors, especially for serous and carcinosarcomas and tumors with advanced stages, with shorter survival and high recurrence rates in distant sites, independently of the FIGO stage. Adjuvant therapy was associated with better survival.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(7):409-414
In this integrative review, we aimed to describe the records of time devoted by physicians to breast ultrasound in a review of articles in the literature, in order to observe whether the automation of the method enabled a reduction in these values. We selected articles from the Latin American and Caribbean Literature in Health Sciences (LILACS) and MEDLINE databases, through Virtual Health Library (BVS), SciELO (Scientific Electronic Library Online), PubMed, and Scopus. We obtained 561 articles, and, after excluding duplicates and screening procedures, 9 were selected, whose main information related to the guiding question of the research was synthesized and analyzed. It was concluded that the automation of breast ultrasound represents a possible strategy for optimization of the medical time dedicated to the method, but this needs to be better evaluated in comparative studies between both methods (traditional and automated), with methodology directed to the specific investigation of this potentiality.