Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(6):319-324
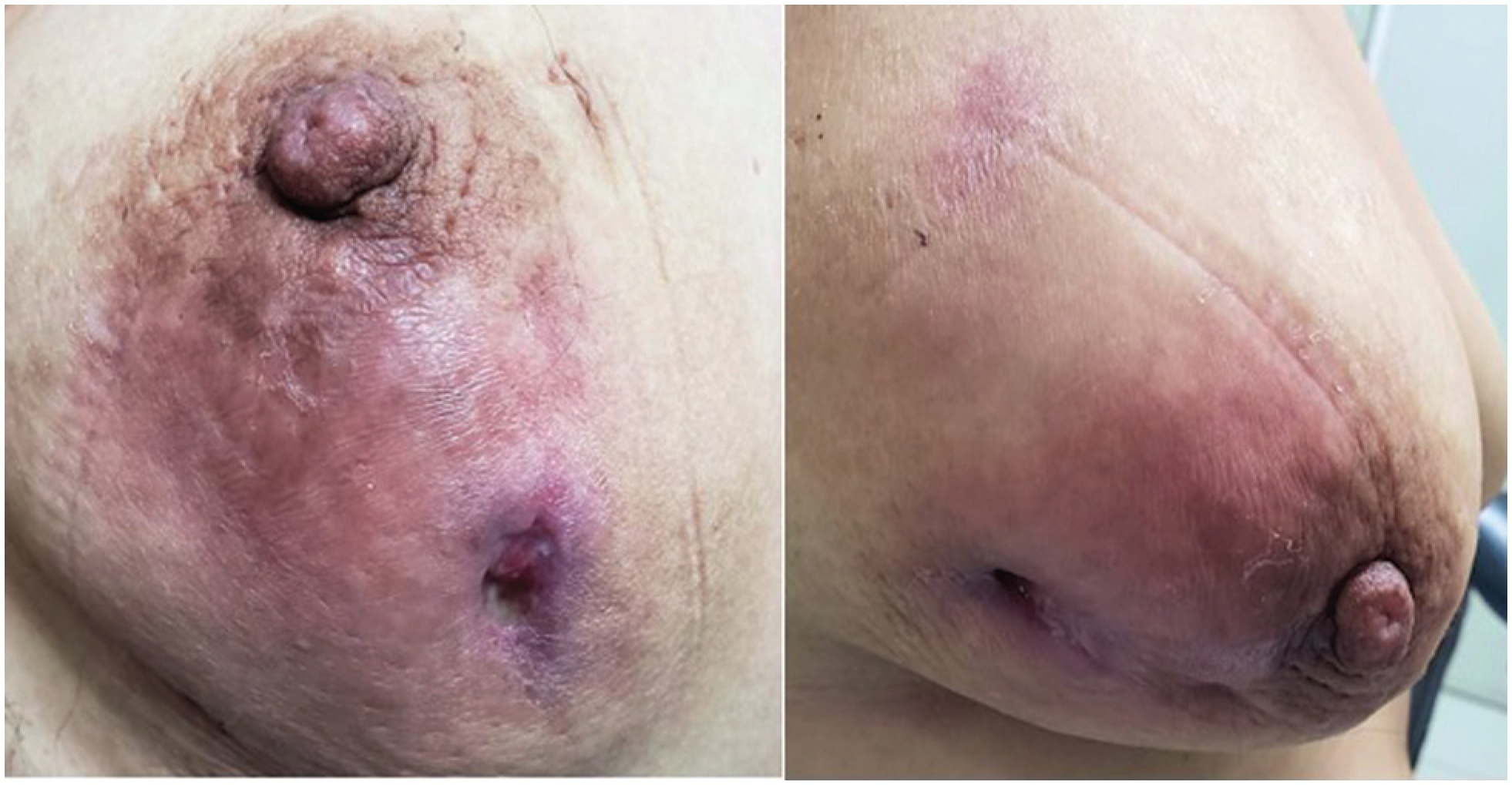
Reporting our experience of the management and treatment of Idiopathic granulomatous mastitis (IGM) in a low-income country by describing patients characteristics and therapy with emphasis on conservative surgical excision and postoperative care as the cornerstone of treatment.
A retrospective cohort of women with histopathological diagnosis of IGM from 2014 to 2018 at Instituto Nacional Materno Perinatal in Lima, Peru. Patients' characteristics, clinical presentation, treatment, management, postoperative care, and follow-up were analyzed.
Thirty-eight patients with histopathological diagnosis of IGM were identified. Their average age was 35.9 years and 23 (60.5%) reported previous use of hormonal contraceptives. Nine (23.7%) patients had chronic mastitis with previous treatment. The time from the onset of symptoms to the first clinic consult was 5.1 months on average. Twenty-one (55.3%) patients had the lesion in the right breast, with a mean size of 6.9 cm. Conservative surgical excision was performed in all patients. Additionally, 86.8% required corticosteroids and 78.9% were treated with antibiotics. Complete remission was obtained at 141 days on average (range 44 to 292 days). Six (15.8%) women reported ipsilateral recurrence and 5 (13.2%), contralateral. The latency time was 25.5 months on average.
The conservative surgical treatment demonstrated and close follow-up made for a high cure rate, but with recurrence similar to that reported in the literature. Use of gloves is an alternative to manage post operative wounds in a low-income country. The most frequent adverse effect was breast surgical scar.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(6):325-332
To determine the efficacy of Uterine Artery Embolization in patients with bleeding acquired uterine arteriovenous malformations (AVMs).
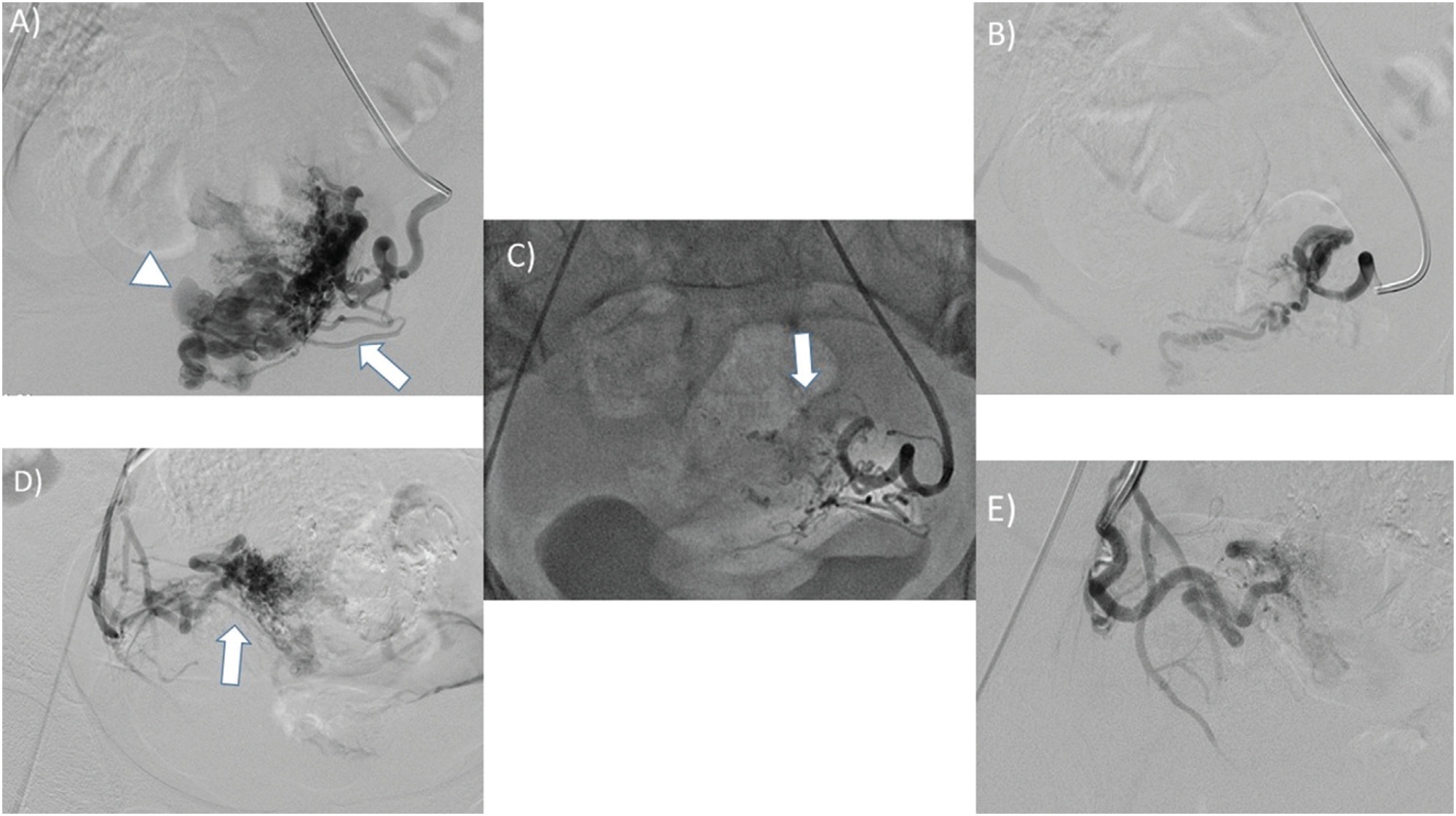
A prospective review of all patients who underwent Uterine Artery Embolization at our institution between July 2015 and April 2022 was performed. 225 patients were diagnosed with a uterine vascular malformation on doppler and corresponding MRI imaging. All patients underwent transcatheter embolization of the uterine arteries. Embolic agents in the 375 procedures included Histoacryl glue only (n = 326), polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) particles and Histoacryl glue (n = 29), PVA particles (n = 5), Gelfoam (n = 5), coils (n = 4), PVA particles and coils (n = 3), Histoacryl glue and Gelfoam (n = 2), and Histoacryl glue and coils (n = 1).
A total of 375 embolization procedures were performed in 225 patients. 90 patients required repeat embolization for recurrence of bleeding. The technical success rate of embolization was 100%. The clinical success rate was 92%: bleeding was controlled in 222 of 225 patients and three patients underwent a hysterectomy. 60 of the 225 patients had uneventful intrauterine pregnancies carried to term. The 210 patients who underwent successful embolization had no recurrence of bleeding at a median follow-up of 53 months (range, 5-122 months) after treatment. 15 patients were eventually lost to follow-up. One minor complication (0.4%) of non-flow-limiting dissection of the internal iliac artery occurred.
Uterine Artery Embolization is a safe, effective, minimally invasive method to treat uterine AVMs with long-term efficacy, which can provide the preservation of fertility.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(2):059-064
To evaluate the seroprevalence of toxoplasmosis among puerperal women cared for at a tertiary university hospital and the level of understanding of these puerperal women about toxoplasmosis, vertical transmission, and its prophylaxis.
For this cross-sectional study, we evaluated 225 patients using presential interviews, prenatal documentation, and electronic medical records. Data were stored using Research Electronic Data Capture (REDCap) software. Prevalence rates were estimated by the presence of reactive IgG antibodies against Toxoplasma gondii. Data analysis was performed using the chi-square test and calculation of the odds ratio (OR). Seroreactivity to T. gondii and exposure variables (age, educational level, and parity) were analyzed using a confidence interval (95%CI) and a significance level of 5% (p < 0.05).
The seropositivity rate for T. gondii was 40%. There was no association between seroprevalence and age. Primiparity was a protective factor against seropositivity and low education was a risk factor.
Knowledge of T. gondii infection and its transmission forms was significantly limited, presenting a risk for acute maternal toxoplasmosis and vertical transmission of this protozoan. Increasing the education level regarding the risk of toxoplasmosis during pregnancy could reduce the rates of infection and vertical transmission of this parasite.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(2):065-073
The study was conducted to determine the quality of life and depression of women with gestational diabetes during pregnancy and the postpartum period.
100 pregnant women with gestational diabetes and 100 healthy pregnant women were included in the present study. Data were obtained from pregnant women in their third trimester who agreed to take part in the study. The data was collected during the third trimester and six to eight weeks after the baby was born. The data were obtained by socio-demographic characteristics form, postpartum data collection form, the MOS 36 Item Short Form Health Survey and Center for Epidemiologic Studies Depression Scale (CESD).
The mean age of pregnant women with gestational diabetes in the study was the same as the average age of healthy pregnant women. The CESD score of pregnant women with gestational diabetes was 26,77 ± 4,85 while the corresponding score was 25,19 ± 4,43 for healthy women. Additionally, the score in the postpartum period was 32.47 ± 5.94 for pregnant women with gestational diabetes and 35.47 ± 8.33 for healthy pregnant women. CESD scores were found to be higher than the cut-off score of 16 in both groups, and the mean scores increased during the postpartum period.
During the postpartum period, the quality of life of pregnant women with gestational diabetes was affected more negatively than healthy pregnant women. Depressive symptoms of women with both gestational diabetes and healthy pregnancy were found to be high in pregnancy and postpartum periods.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(2):074-081
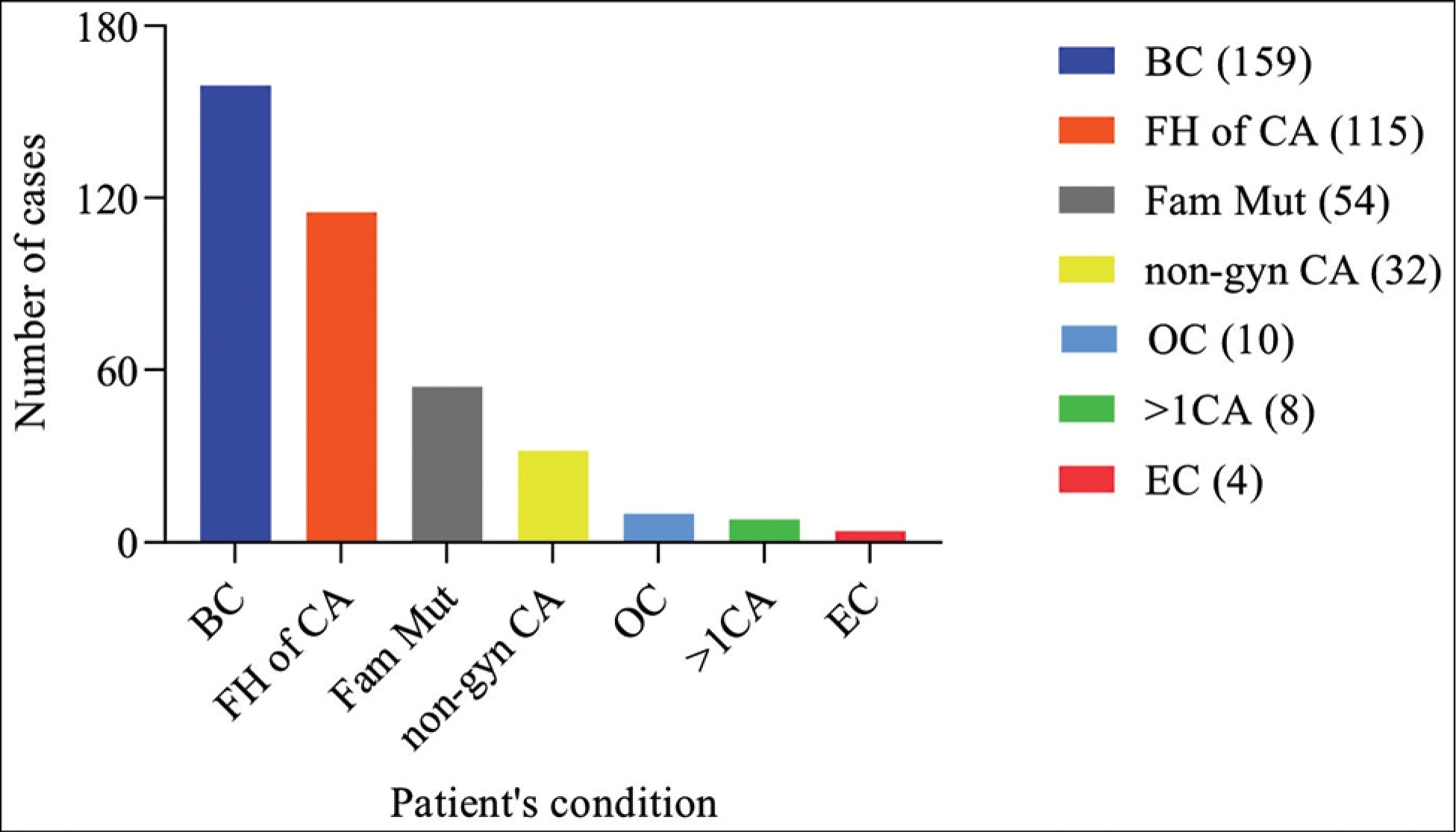
The present study evaluated the profile of germline mutations present in patients who underwent genetic counseling for risk assessment for breast cancer (BC), ovarian cancer (OC), and endometrial cancer (EC) with a possible hereditary pattern.
Medical records of 382 patients who underwent genetic counseling after signing an informed consent form were analyzed. A total of 55.76% of patients (213/382) were symptomatic (personal history of cancer), and 44.24% (169/382) were asymptomatic (absence of the disease). The variables analyzed were age, sex, place of birth, personal or family history of BC, OC, EC, as well as other types of cancer associated with hereditary syndromes. The Human Genome Variation Society (HGVS) nomenclature guidelines were used to name the variants, and their biological significance was determined by comparing 11 databases.
We identified 53 distinct mutations: 29 pathogenic variants, 13 variants of undetermined significance (VUS), and 11 benign. The most frequent mutations were BRCA1 c.470_471delCT, BRCA1 c.4675 + 1G > T, and BRCA2 c.2T> G. Furthermore, 21 variants appear to have been described for the first time in Brazil. In addition to BRCA1/2 mutations, variants in other genes related to hereditary syndromes that predispose to gynecological cancers were found.
This study allowed a deeper understanding of the main mutations identified in families in the state of Minas Gerais and demonstrates the need to assess the family history of non-gynecological cancer for risk assessment of BC, OC, and EC. Moreover, it is an effort that contributes to population studies to evaluate the cancer risk mutation profile in Brazil.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(2):082-088
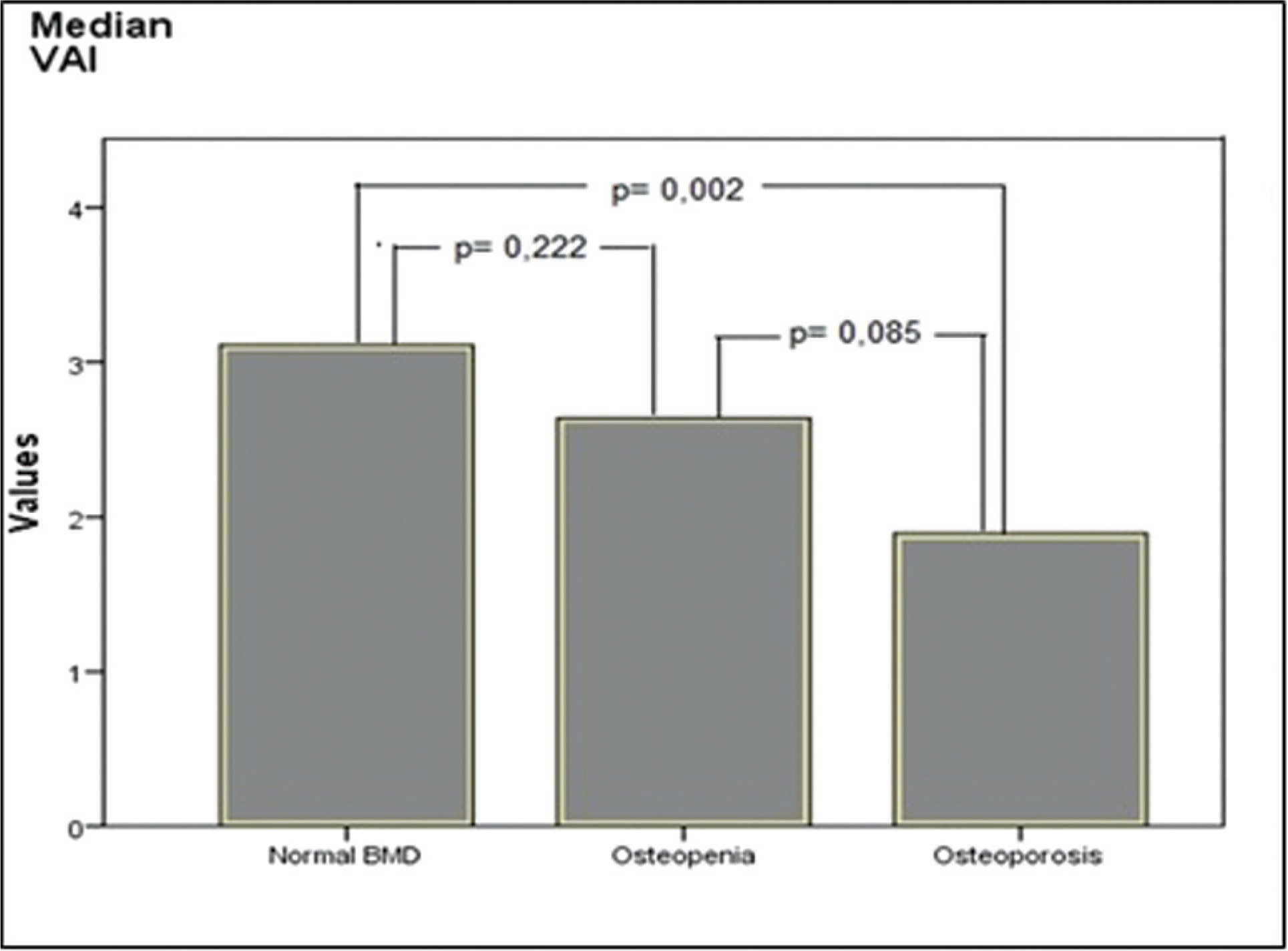
It was aimed to compare visceral adiposity index (VAI) levels in patients with normal bone mineral density (BMD), osteopenia, and osteoporosis.
One hundred twenty postmenopausal women (40 with normal BMD, 40 with osteopenia, and 40 with osteoporosis) between the ages of 50 to 70 years were included in the study. For females, the VAI was calculated using the formula (waist circumference [WC]/[36.58 + (1.89 x body mass index (BMI))]) x (1.52/High-density lipoprotein [HDL]-cholesterol [mmol/L]) x (triglyceride [TG]/0.81 [mmol/L]).
The time of menopause from the beginning was similar in all groups. Waist circumference was found to be higher in those with normal BMD than in the osteopenic and osteoporotic groups (p = 0.018 and p < 0.001, respectively), and it was also higher in the osteopenic group than in the osteoporotic group (p = 0.003). Height and body weight, BMI, blood pressure, insulin, glucose, HDL-cholesterol, and homeostasis model assessment-insulin resistance (HOMA-IR) levels were similar in all groups. Triglyceride levels were found to be higher in the normal BMD group, compared with the osteoporotic group (p = 0.005). The level of VAI was detected as higher in those with normal BMD, compared with the women with osteoporosis (p = 0.002). Additionally, the correlation analysis showed a positive correlation between dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) spine T-scores, WC, VAI, and a negative correlation between DXA spine T-scores and age.
In our study, we found higher VAI levels in those with normal BMD, compared with women with osteoporosis. We consider that further studies with a larger sample size will be beneficial in elucidating the entity.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(2):089-095
We evaluated internal consistency, test-retest reliability, and criterion validity of the Brazilian Portuguese version of the Female Sexual Function Index 6-item Version (FSFI-6) for postpartum women.
Therefore, questionnaires were applied to 100 sexually active women in the postpartum period. The Cronbach α coefficient was used to evaluate the internal consistency. Test-retest reliability was analyzed by Kappa for each item of the questionnaire and by the Wilcoxon parametric test, comparing the total scores of each evaluation. For the assessment of criterion validity, the FSFI was used as the gold standard and the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve was constructed. Statistical analysis was performed using IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, version 21.0 (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). It was found that the internal consistency of the FSFI-6 questionnaire was considerably high (0.839).
The test-retest reliability results were satisfactory. It can also be stated that the FSFI-6 questionnaire presented excellent discriminant validity (area under the curve [AUC] = 0.926). Women may be considered as having sexual dysfunction if the overall FSFI-6 score is < 21, with 85.5% sensitivity, 82.2% specificity, positive likelihood ratio of 4.81 and negative likelihood ratio of 0.18.
We conclude that the Brazilian Portuguese version of FSFI-6 is valid for use in postpartum women.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(3):113-120
To evaluate the impact of the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pandemic on the care of patients with miscarriage and legal termination of pregnancy in a university hospital in Brazil.
A cross-sectional study of women admitted for abortion due to any cause at Hospital da Mulher Prof. Dr. J. A. Pinotti of Universidade Estadual de Campinas (UNICAMP), Brazil, between July 2017 and September 2021. Dependent variables were abortion-related complications and legal interruption of pregnancy. Independent variables were prepandemic period (until February 2020) and pandemic period (from March 2020). The Cochran-Armitage test, Chi-squared test, Mann-Whitney test, and multiple logistic regression were used for statistical analysis.
Five-hundred sixty-one women were included, 376 during the prepandemic period and 185 in the pandemic period. Most patients during pandemic were single, without comorbidities, had unplanned pregnancy, and chose to initiate contraceptive method after hospital discharge. There was no significant tendency toward changes in the number of legal interruptions or complications. Complications were associated to failure of the contraceptive method (odds ratio [OR] 2.44; 95% confidence interval [CI] 1.23–4.84), gestational age (OR 1.126; 95% CI 1.039–1.219), and preparation of the uterine cervix with misoprostol (OR 1.99; 95% CI 1.01–3.96).
There were no significant differences in duration of symptoms, transportation to the hospital, or tendency of reducing the number of legal abortions and increasing complications. The patients’ profile probably reflects the impact of the pandemic on family planning.