-
Case Report11-01-2018
Fetal Noncompaction Cardiomyopathy and Histologic Diagnosis of Spongy Myocardium: Case Report and Review of the Literature
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(11):722-725
Abstract
Case ReportFetal Noncompaction Cardiomyopathy and Histologic Diagnosis of Spongy Myocardium: Case Report and Review of the Literature
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(11):722-725
Views152Abstract
Noncompaction cardiomyopathy (NCCM) and left ventricular noncompaction (LVNC), in their isolated form, are rare cardiomyopathies. They are characterized by a thickened myocardium due to the presence of deep trabeculae recesses, and to thick trabeculae. This condition is associated with a variable clinical phenotype including heart failure, thromboembolism, and sudden death. We report a case of LVNC at 26 weeks and 4 days of gestation revised on the basis of what is currently reported in the literature. A review of the literature was performed to better describe this rare condition. Left ventricular noncompaction is a rare fetal condition and it should be suspected in case of cardiomyopathy.
Key-words left ventricular noncompaction cardiomyopathynoncompaction cardiomyopathyspongy myocardiumSee more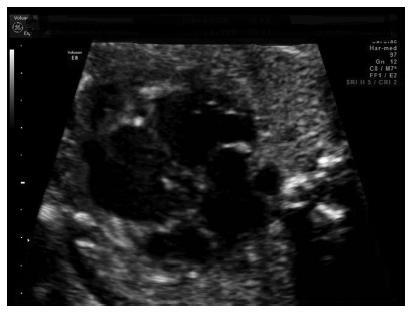
-
Case Report11-01-2018
Oophoropexy to the Round Ligament after Recurrent Adnexal Torsion
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(11):726-730
Abstract
Case ReportOophoropexy to the Round Ligament after Recurrent Adnexal Torsion
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(11):726-730
Views168See moreAbstract
Recurrent adnexal torsion is a rare gynecological emergency. We report a case of recurrent ipsilateral adnexal torsion in a woman with polycystic ovaries, previously submitted to a laparoscopic plication of the utero-ovarian ligament. Due to the recurrence after the plication of the utero-ovarian ligament, the authors performed a laparoscopic oophoropexy to the round ligament, which is an underreported procedure. The patient was asymptomatic for 1 year, after which she had a new recurrence and needed a unilateral laparoscopic adnexectomy. Since then, she regained the quality of life without any gynecological symptoms.
Oophoropexy to the round ligament may be considered when other techniques fail or, perhaps, as a first option in selected cases of adnexal torsion, as it may allow the prevention of recurrence without increasing morbidity while preserving the adnexa.
-
Case Report10-01-2018
Vulvar Lipoma: A Case Report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(10):647-649
Abstract
Case ReportVulvar Lipoma: A Case Report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(10):647-649
Views161See moreAbstract
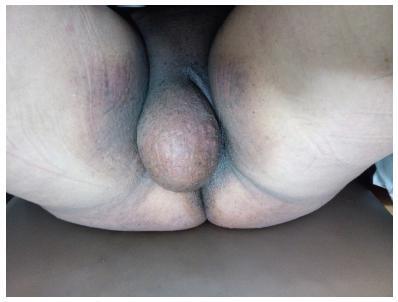
The present study is a case report of vulvar lipoma. The vulva is a rare site for the development of lipomas, and the aim of the study is to determine if the current imaging modalities can diagnose lipomas correctly. A 43-year-old patient presented with a painless, slowly progressive, oval, mobile and non-tender right vulvar mass compressing the vagina and totally covering the introitus. Both the ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) exams suggested the diagnosis of lipoma. Surgical excision was performed, and the histopathological examination of the mass confirmed a lipoma.
-
Case Report10-01-2018
Management of Transverse Vaginal Septum by Vaginoscopic Resection: Hymen Conservative Technique
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(10):642-646
Abstract
Case ReportManagement of Transverse Vaginal Septum by Vaginoscopic Resection: Hymen Conservative Technique
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(10):642-646
Views158See moreAbstract
Transverse vaginal septum is a rare female genital tract anomaly, and little is described about its surgical treatment. We report the case of a patient who wished to preserve hymenal integrity due to social and cultural beliefs. We performed a vaginoscopic resection of the septum under laparoscopic view, followed by the introduction of a Foley catheter in the vagina, thus preserving the hymen. After 12 months of follow-up, no septal closure was present, and the menstrual flow was effective. Vaginoscopic hysteroscopy is an effectivemethod of vaginal septum resection, even in cases in which hymenal integrity must be preserved due to social and cultural beliefs.
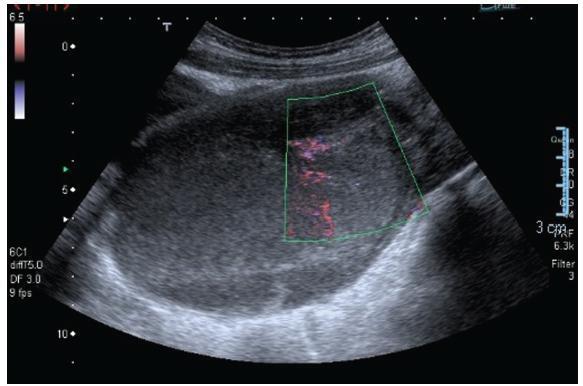
-
Case Report09-01-2018
Vesicouterine Fistula (Youssef Syndrome): Case Report and Literature Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):563-569
Abstract
Case ReportVesicouterine Fistula (Youssef Syndrome): Case Report and Literature Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):563-569
Views175See moreAbstract
Objective
To describe a case of vesicouterine fistula and to review the literature related to this condition.
Methods
For the review, we accessed the MEDLINE, BIREME and LILACS databases; the references of the searched articles were also reviewed.
Results
A 38-year-old woman, in the 1st day after her 3rd cesarean, presented heavy hematuria, which was considered secondary to a difficult dissection of the bladder. A total of 6 months after delivery, she failed to resume her regular menstrual cycles and presented cyclic menouria and amenorrhea. At this time, she had two episodes of urethral obstruction by blood clots. She remained without a correct diagnosis until about two years postdelivery, when a vesicouterine fistula was confirmed through cystoscopy. A surgical correction through open abdominal route, coupled with hysterectomy, was performed. After the surgery, the symptoms disappeared. The review showed a tendency of change in the relative frequency of the different types of genitourinary fistulae. Vesicovaginal fistulae, usually caused by inadequate care during labor, are becoming less frequent than those secondary tomedical procedures, such as vesicouterine fistulae. The most common cause of this latter kind of fistula is cesarean section, especially repeated cesarean sections. The diagnosis is confirmed through one or more imaging exams, or through cystoscopy. The most common treatment is surgical, and the routes are: open abdominal, laparoscopic, vaginal or robotic. There are some reports of success with the conservative treatment.
Conclusion
Vesicouterine fistulae are becoming more common because of the increase in the performance of cesarean sections, and the condition must be considered a possible complication thereof.
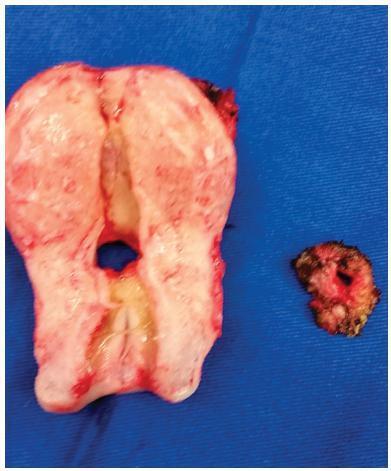
-
Case Report09-01-2018
Diagnosis of Atelosteogenesis Type I suggested by Fetal Ultrasonography and Atypical Paternal Phenotype with Mosaicism
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):570-575
Abstract
Case ReportDiagnosis of Atelosteogenesis Type I suggested by Fetal Ultrasonography and Atypical Paternal Phenotype with Mosaicism
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):570-575
Views217Abstract
Atelosteogenesis type I (AOI) is an autosomal dominant skeletal dysplasia caused by mutations in the filamin B (FLNB) gene with classic and well-recognizable clinical findings. However, parents affected with a mild phenotype, probably with somatic mosaicism, can generate offspring with a much more severe phenotype of AOI. In the present report, we describe a female newborn with classic AOI leading to early neonatal death, whose diagnostic was based on prenatal radiological findings and on the physical examination of the father. Since her father had limb deformities and corporal asymmetry, suggesting somatic mosaicism, his biological samples were analyzed through a gene panel for skeletal dysplasias. A missense mutation not previously described in the literature was detected in the FLNB gene, affecting ~ 20% of the evaluated cells and, therefore, confirming the diagnosis ofmosaic AOI in the father. The molecular analysis of the father was crucial to suggest the diagnosis of AOI in the newborn, since she died early and there were no biological samples available.
Key-words atelosteogenesisexome-target sequencingFetal ultrasonographyFLNBskeletal dysplasiasomatic mosaicismSee more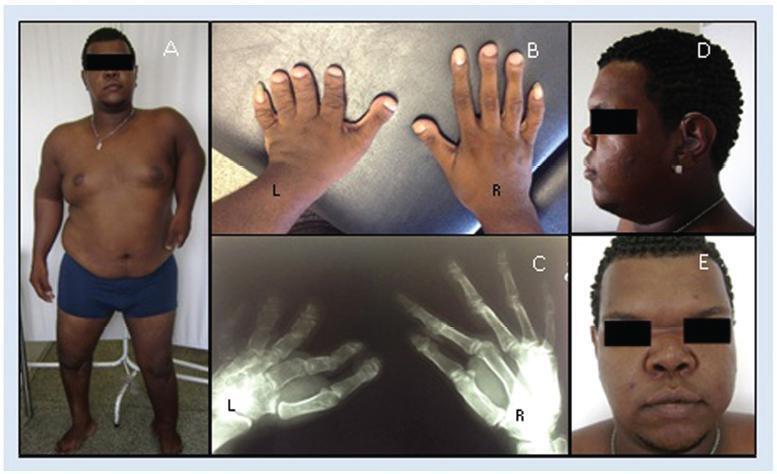
-
Case Report08-01-2018
Fine-needle Aspiration Cytology to Identify a Rare Mimicker of Breast Cancer: Plasma Cell Mastitis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(8):491-493
Abstract
Case ReportFine-needle Aspiration Cytology to Identify a Rare Mimicker of Breast Cancer: Plasma Cell Mastitis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(8):491-493
Views157See moreAbstract
There are rare benign diseases that can mimic malignant breast neoplasms in the clinical exam and in mammography. We evaluated the contribution of an accessible procedure to most clinicians, the fine-needle aspiration cytology, to identify a rare mimicker of malignant breast neoplasms. A type 2 diabetic 85-year-old female presented with a 6-month history of a left breast lump. The physical exam and mammography were compatible with breast cancer. Nevertheless, after fine-needle aspiration cytology, the diagnosis was plasma cellmastitis. Once this rare diagnosis was established, the tumor was extirpated, and the final histologic diagnosis corroborated chronic plasma cellmastitis. The patient’s postoperative evolution was uneventful, and no other treatment was needed. Fine-needle aspiration cytology could be a valuable tool to identify rare mimickers of malignant breast neoplasms.
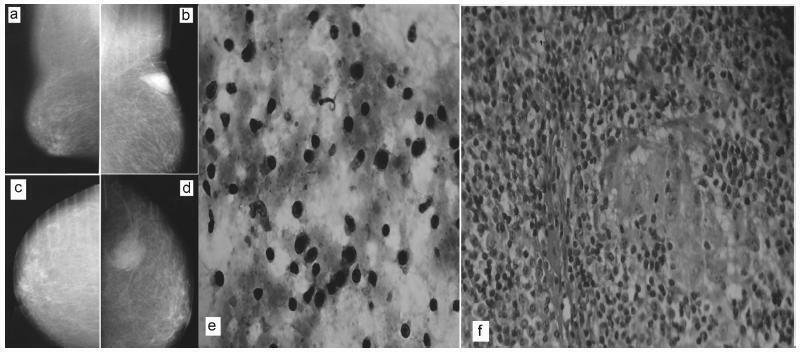
-
Case Report08-01-2018
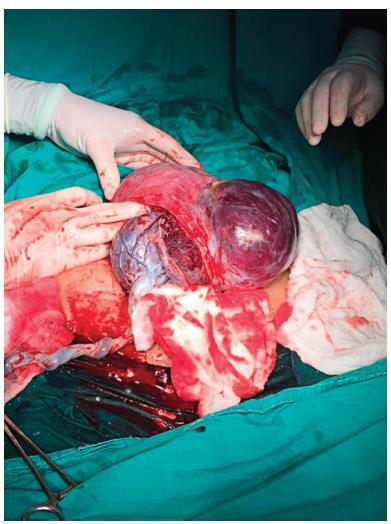
Conservative Surgical Treatment of a Case of Placenta Accreta
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(8):494-496
Abstract
Case ReportConservative Surgical Treatment of a Case of Placenta Accreta
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(8):494-496
Views194See moreAbstract
Placenta accreta syndromes are associated with increased maternal mortality and morbidity. Cesarean hysterectomy is usually performed in cases of placenta accreta syndrome. Fertility sparing methods can be applied. In the present study, we report a successful segmental uterine resection method for placenta accreta in the anterior uterine wall in a cesarean section case. A 39-year-old woman underwent an elective cesarean section at 38 + 2 weeks. A placental tissue with an area of 10 cm was observed extending fromthe anterior uterine wall to the serosa, 2 cm above the uterine incision line. The placental tissue was removed with the help of monopolar electrocautery. The uterine incision was continuously sutured. The patient was discharged on the second postoperative day. The placental pathology was reported as placenta accreta. The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) generally recommends cesarean section hysterectomy in cases of placenta accreta because removal of placenta associated with significant hemorrhage. Conservative and fertility sparing methods include placenta left in situ, cervical inversion technique and triple-P procedure. There are several studies reporting that segmental uterine resection is performed with and without balloon placement or artery ligation. Segmental uterine resection may be an alternative to cesarean hysterectomy to preserve fertility or to protect the uterus in cases of placenta accreta when there is no placenta previa. received