Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(3):203-205
Autoimmune progesterone dermatitis (APD) is a rare autoimmune dermatosis characterized by recurrent cutaneous and mucosal lesions during the luteal phase of the menstrual cycle that disappear some days after the menses.
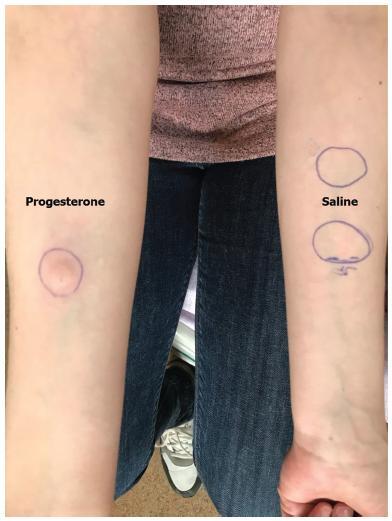
Report A 34-year-old primipara woman with no significant past medical history and no prior exogenous hormone use, who presented with cyclic skin eruptions starting 1 year after the delivery. The lesions occurred 6 days before the menses and disappeared in between 1 and 2 days after the menstruation ceased. The patient was diagnosed after a positive response to an intradermal test with progesterone and was successfully treated with combined oral contraceptives. The skin eruptions have not returned since the initiation of this therapy.
Dermatologists, gynecologists, and obstetricians should be aware of this rare entity. Furthermore, if this condition is suspected, a thorough history taking on the menstrual cycle and results of the intradermal progesterone test are mandatory.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(3):199-202
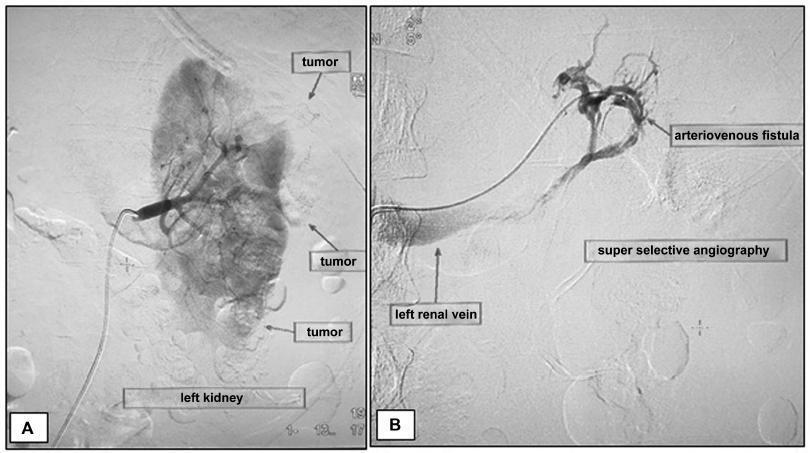
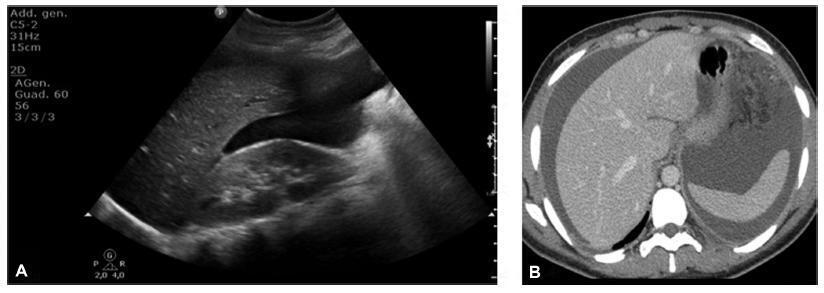
Angiomyolipomas (AMLs) are rare benign tumors derived from mesenchymal tissue and composed of varying degrees of adipose tissue, muscle and blood vessels. Renal AMLs (RAMLs) are the result of a sporadic event, and, in most of cases, the diagnosis is usually incidental, but hemorrhage and shock may be present. During pregnancy, the size of AMLs may increase and they may rupture, probably due to the high expression of hormone receptors, and the increase in maternal circulation and abdominal pressure. The authors present a case of a woman with ruptured RAML submitted to urgent endovascular treatment four days after giving birth by cesarean section.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(2):129-132
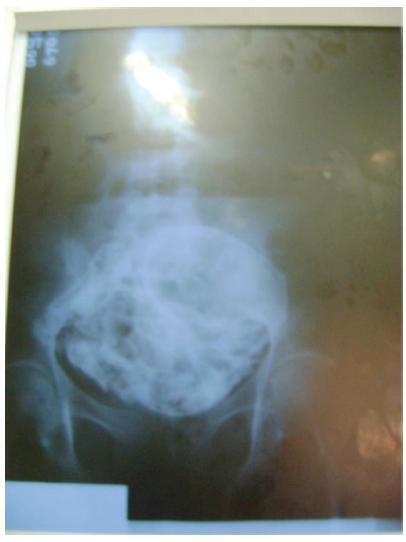
Ectopic pregnancy is the leading cause of pregnancy-related death during the first trimester, and it occurs in 1 to 2% of pregnancies. Over 90% of ectopic pregnancies are located in the fallopian tube. Abdominal pregnancy refers to an ectopic pregnancy that has implanted in the peritoneal cavity, external to the uterine cavity and fallopian tubes. The estimated incidence is 1 per 10,000 births and 1.4%of ectopic pregnancies. Lithopedion is a rare type of ectopic pregnancy, and it occurs when the fetus from an unrecognized abdominal pregnancymay die and calcify. The resulting “stone baby” may not be detected for decades andmay cause a variety of complications. Lithopedion is a very rare event that occurs in 0.0054% of all gestations. About 1.5 to 1.8% of the abdominal babies develop into lithopedion. There are only ~ 330 known cases of lithopedion in the world. We describe a lithopedion that complicated as intestinal obstruction in a 71-year-old woman.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(2):124-128
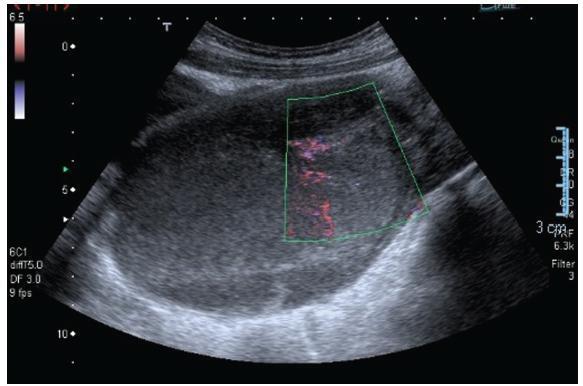
Müllerian adenosarcoma is a very rare gynecological disease, comprising 5% of uterine sarcomas. Extragenital localizations are even rarer.We report a very interesting case of a 27-year-old woman complaining of pelvic pain, with a subsequent diagnosis of extragenital Müllerian adenosarcoma. This is the first case reported in the literature with a complete and wide imaging description. Even if rare, Müllerian adenosarcoma should be hypothesized in case of young female patients presenting with suspicious pelvic mass.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(12):803-807
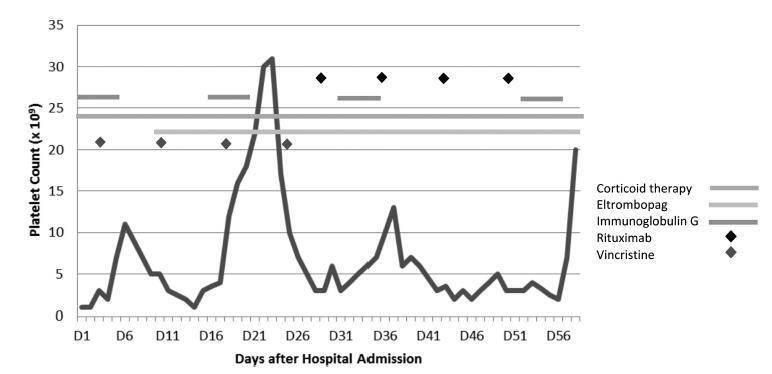
Thrombocytopenia is the most common hemostatic change in pregnancy, but severe thrombocytopenia is rare. One of the causes, immune thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP), is characterized by increased platelet destruction by immunoglobulin G (IgG) antibodies, presenting a high risk of hemorrhage for the patient, but also for the fetus, since antibodiesmay cross the placenta.We present the case of a 23-year-old pregnant woman with a history of Langerhans cell histiocytosis of the mandible submitted to surgery and chemotherapy when she was 10 years old, with diagnosis of ITP since then. At 28 weeks of gestation, she presented with petechiae, epistaxis, and gingival bleeding, with a platelet count of 3 x 109/L and positive IgG antiplatelet antibodies test. At a multidisciplinary discussion, it was decided to delay a cesarean section, due to the absence of fetal distress and to the high risk of morbidity for the patient. Many therapies were attempted without success. The IgG produced a slight and transient increase in the platelet count. On the 36th week of gestation, an elective cesarean section was performed. The perioperative period transfusions were guided by rotational thromboelastometry (ROTEM) monitoring. The procedure was performed under general anesthesia and videolaryngoscopy-assisted intubation. The patient was hemodynamically stable, without significant bleeding, and was transferred to the intensive care unit. The platelet count eventually decreased and a splenectomy was performed. Regional anesthesia may be contraindicated, and general anesthesia is associated with an increased risk of airway hemorrhage due to traumatic injury during the tracheal intubation and of hemorrhage associated with the surgical procedure. A multidisciplinary approach is essential in high-risk cases.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(12):800-802
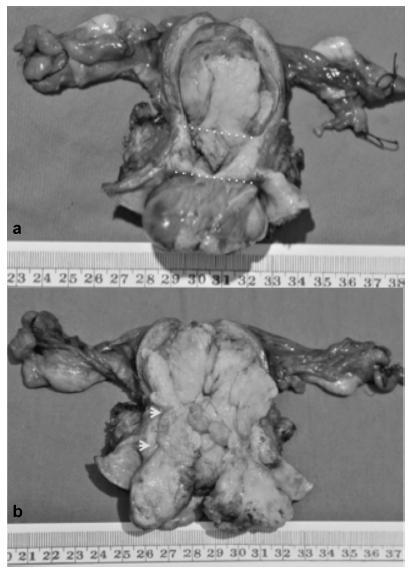
To describe a case of radiation-induced uterine carcinosarcoma 6 years after a cervical squamous cell carcinoma treatment, which imposed some diagnostic and management challenges.
A 57-year-old woman with a history of pelvic chemoradiotherapy ~ 6.5 years before the event described in this study, following an International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) stage IIB cervical cancer, presented with a cervical mass, involving the uterine cavity, the cervical canal and the upper two thirds of the vagina. The biopsy showed a poorly differentiated carcinoma, and a positron emission tomography (PET) scan excluded distant metastasis, although it was unable to define the origin of the tumor as either a new primary malignancy of the endometrium/cervix or as a cervical recurrence. Surgical staging procedure was performed, and the diagnosis was endometrial carcinosarcoma, FIGO stage IIB. The patient was not able to complete the adjuvant therapy, and the progression of the disease was remarkable.
The present case highlights one of the less common but more serious consequences of radiotherapy for cervical cancer, which has an increasing incidence in younger women, raising concerns about the long-termconsequences of its management.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(10):647-649
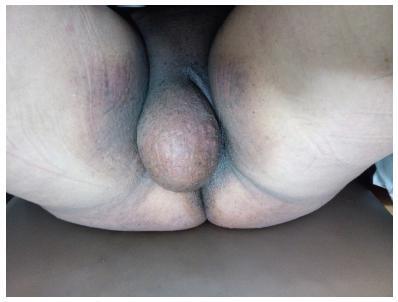
The present study is a case report of vulvar lipoma. The vulva is a rare site for the development of lipomas, and the aim of the study is to determine if the current imaging modalities can diagnose lipomas correctly. A 43-year-old patient presented with a painless, slowly progressive, oval, mobile and non-tender right vulvar mass compressing the vagina and totally covering the introitus. Both the ultrasonography and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) exams suggested the diagnosis of lipoma. Surgical excision was performed, and the histopathological examination of the mass confirmed a lipoma.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(10):642-646
Transverse vaginal septum is a rare female genital tract anomaly, and little is described about its surgical treatment. We report the case of a patient who wished to preserve hymenal integrity due to social and cultural beliefs. We performed a vaginoscopic resection of the septum under laparoscopic view, followed by the introduction of a Foley catheter in the vagina, thus preserving the hymen. After 12 months of follow-up, no septal closure was present, and the menstrual flow was effective. Vaginoscopic hysteroscopy is an effectivemethod of vaginal septum resection, even in cases in which hymenal integrity must be preserved due to social and cultural beliefs.