Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(7):303-309
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005012
To identify spatial patterns of neonatal mortality distribution in the micro regions of São Paulo State and verify the role of avoidable causes in the composition of this health indicator.
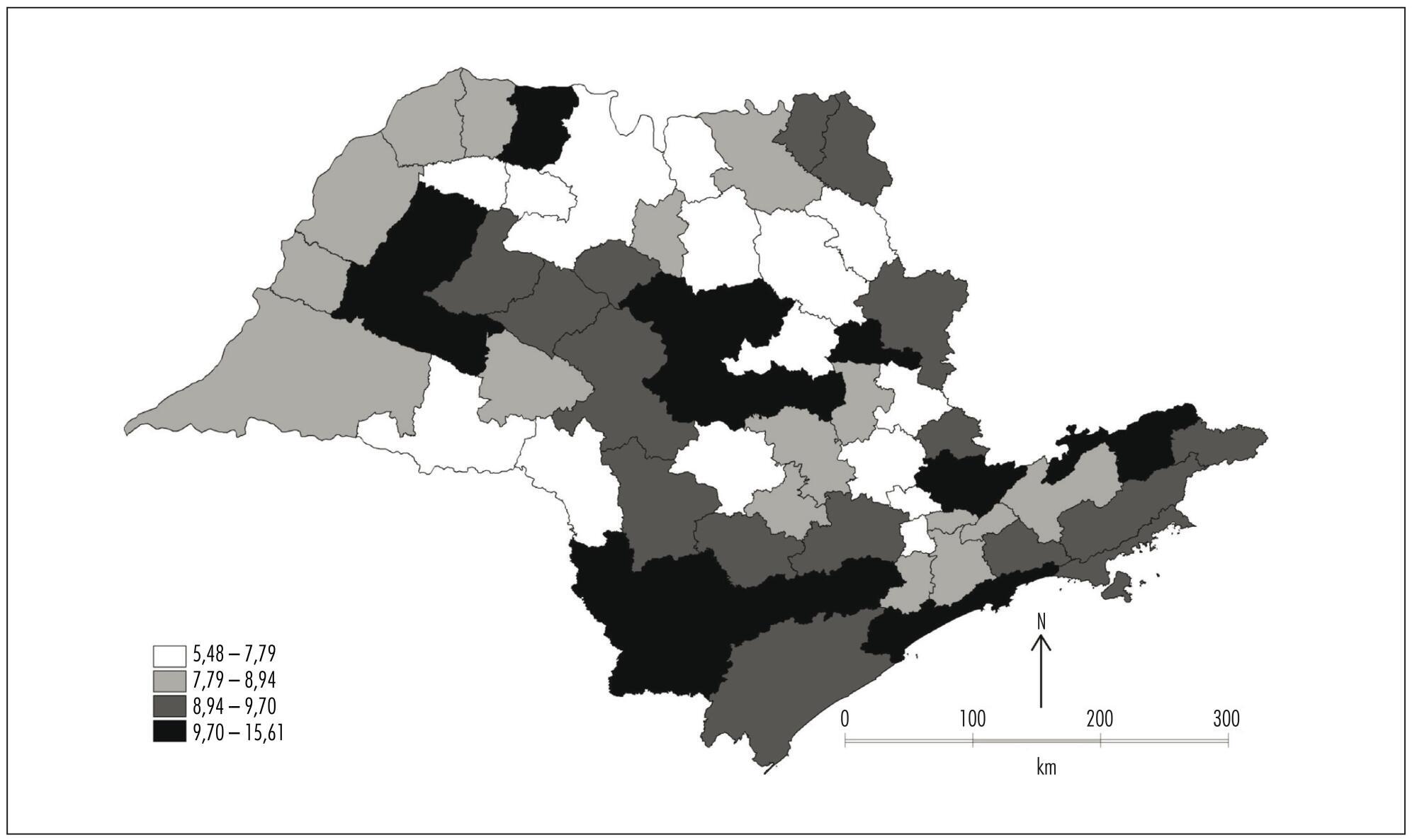
This ecological exploratory study used neonatal mortality information obtained from Information System and Information Technology Department of the Brazilian National Healthcare System (DATASUS) in the period between the years 2007 and 2011. The digital set of micro regions of São Paulo State was obtained from Instituto Brasileiro de Geografia e Estatística (IBGE). Moran Indexes were calculated for the neonatal mortality total rate and rate from avoidable causes; thematic maps were constructed with these rates, as well as the difference between them; and the Box Map was built.
The overall neonatal mortality rate was 8.42/1,000 live births and neonatal mortality rate from avoidable causes of 6.19/1,000 live births. Moran coefficients (I) for these rates were significant (p-value<0.05) - for the total rate of neonatal mortality I=0.11 and for mortality from preventable causes I=0.19 -, and neonatal deaths were concentrated in southwest region and the Vale do Paraíba. If preventable causes were abolished, there would be a significant reduction in the average rate of overall neonatal mortality, from 8.42 to 2.23 deaths/1,000 live births, representing a decline of 73%.
This study demonstrated that neonatal mortality rate would be close to the rates of developed countries if avoidable causes were abolished.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(7):310-314
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140005008
The objective of this study was to investigate the relationship between overactive bladder syndrome and anxiety in older women.
Of the 198 older women who were invited, 29 were excluded and 166 were then divided into two groups according to the Advanced Questionnaire of Overactive Bladder (OAB-V8): one group with overactive bladder symptoms (OAB-V8≥8) and the other without the symptoms of an overactive bladder (OAB-V8<8). The purpose was to conduct a frequency analysis and to investigate the relation of the social demographic data and anxiety in the two groups. The Beck Anxiety Inventory (BAI) was used to evaluate the level of anxiety. The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test was used to determine the distribution of the data. The differences between the two groups for the continuous variables were analyzed by the Mann-Whitney U test, the differences for the categorical variables were analyzed by the Chi-Square test and the association between the continuous variables was analyzed by the Spearman Correlation test. The tests were two-tailed with a confidence level of 5%.
Overall, the frequency of an overactive bladder was present in 117 (70.5%) of the participants. The body mass index (BMI) of the group with overactive bladder symptoms was significantly higher than the BMI of those without these symptoms (p=0.001). A higher prevalence of mild, moderate and severe anxiety was observed among older women with overactive bladder symptoms. In addition, the overactive bladder symptoms group presented a positive low correlation with anxiety symptoms (r=0.345) and with BMI (r=0.281). There was a small correlation between BMI and anxiety symptoms (r=0.164).
Overactive bladder syndrome was prevalent among older women and the existence of these symptoms was linked to the presence of mild, moderate and/or severe anxiety symptoms.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(7):320-327
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140004998
Apresentar a adaptação transcultural para o português da Escala de Atitudes em Relação ao Ganho de Peso na Gestação.
Essa escala, que contém afirmações que expressavam diferentes atitudes de gestantes em relação ao seu próprio ganho de peso, foi desenvolvida para determinar se as atitudes em relação ao corpo afetariam o ganho de peso durante a gestação. Os procedimentos foram: tradução, retrotradução, avaliação da compreensão, elaboração de versão final, aplicação da escala em 180 gestantes (média 29,6 anos e idade gestacional 25,7 semanas) e análise psicométrica.
Constatou-se equivalência satisfatória entre as versões inglês-português e boa consistência interna (Alpha de Cronbach 0,7). A análise fatorial exploratória sugeriu quatro subescalas com variância total explicada de 51,4%.
A escala se demonstrou válida e pode ser utilizada em estudos com gestantes no Brasil para avaliação de atitudes em relação ao ganho de peso e detecção e prevenção de comportamentos disfuncionais durante a gestação.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(7):320-327
DOI 10.1590/SO100-720320140004998
To present the cross-cultural adaptation to Brazilian Portuguese language of the Pregnancy and Weight Gain Attitude Scale.
This scale was developed in order to verify whether attitude toward thinness affects weight gain during pregnancy and contains statements that express different attitudes of pregnant women regarding their own weight gain. The procedures were: translation, back translation, comprehension evaluation, preparation of a final version, application of the scale to 180 pregnant women (mean age=29.6, gestational age=25.7 weeks) and psychometric analysis.
Satisfactory equivalence between the versions and satisfactory internal consistency (Cronbach's alpha 0.7) were detected. The exploratory factor analysis suggested four subscales with 51.4% total variance explained.
The scale proved to be valid and can be used in studies with pregnant women in Brazil to assess attitudes toward weight gain and to detect and prevent dysfunctional behaviors during pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(6):237-243
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140005010
To assess the determinants of late stage in women with cervical cancer in Brazil.
A cross-sectional study of secondary basis. Women with invasive cervical cancer enrolled in the Cancer Hospital Registry between January 2000 and December 2009 were included. Late clinical stage (≥IIB) was the outcome considered. The following variables were studied: age at diagnosis, race or ethnicity, years of education, marital status, alcohol consumption, smoking status, place of residence, year of diagnosis, initial treatment received, and status after the first treatment. Odds ratio (OR) with 95% confidence intervals (95%CI) and a logistic regression model were used. P values<0.05 were considered statistically significant.
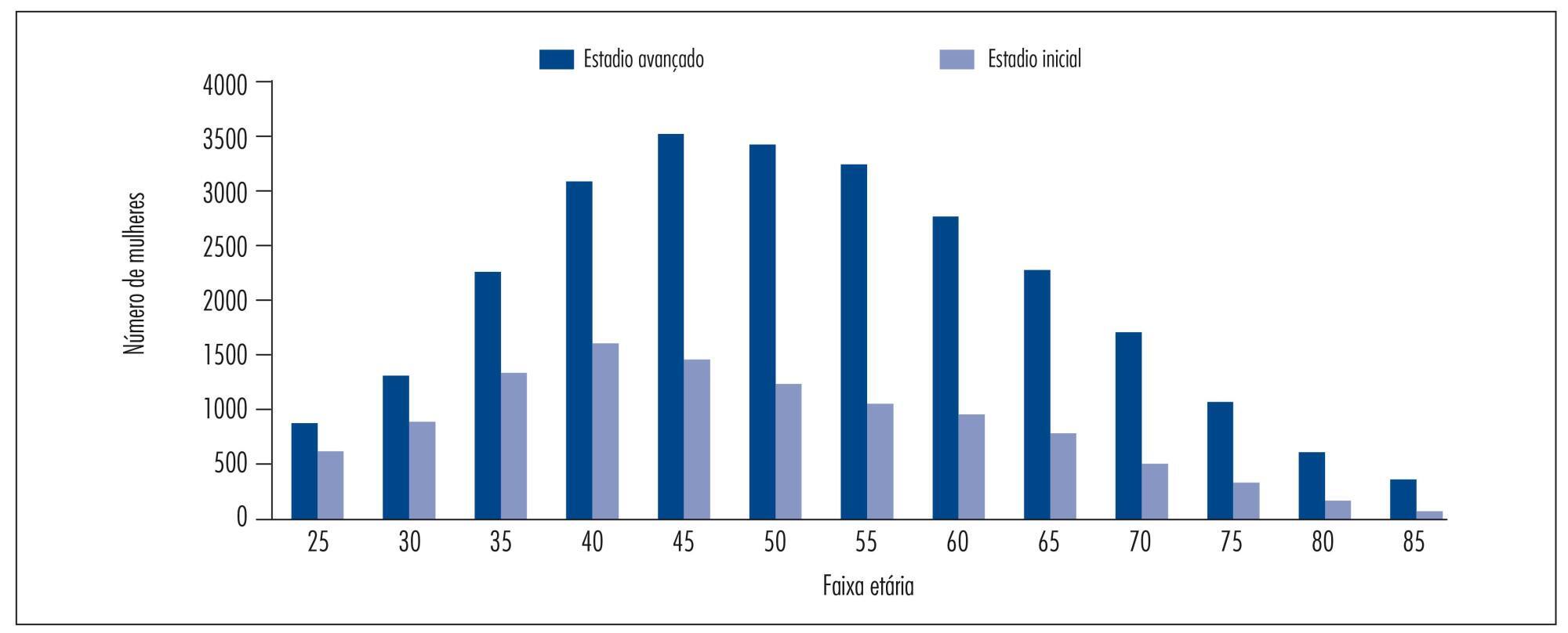
37,638 cases were included, with a mean age of 52.4±14.1 years. Late clinical stages were observed in 70.6% of cases and were associated with the presence of squamous cell carcinoma (OR=1.8; 95%CI 1.7-2.0), age ≥50 years (OR=1.5; 95%CI 1.4-1.6), living with a partner (OR=1.3; 95%CI 1.2-1.4), black skin color (OR=1.2; 95%CI 1.1-1.4), and low educational level (OR=1.2; 95%CI 1.1-1.3).
In Brazil, the diagnosis of cervical cancer is a delayed event. Although the main factor associated with late stage of cervical cancer identified in this study is a biological factors (histological type) and, consequently, not eligible for intervention, it was confirmed that socioeconomic disparities in the country are associated with late stage disease.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(6):244-250
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140005004
This study investigated short-term changes in body composition, handgrip strength, and presence of lymphedema in women who underwent breast cancer surgery.
Ninety-five women participated in a cross-sectional study, divided into two groups: Control (n=46), with healthy women, and Experimental (n=49), with women six months after breast cancer surgery . The Experimental Group was subdivided into right total mastectomy (RTM, n=15), left total mastectomy (LTM, n=11), right quadrant (RQ, n=13), and left quadrant (LQ, n=10). It was also redistributed among women with presence (n=10) or absence (n=39) of lymphedema. Presence of lymphedema, handgrip strength, and body composition were assessed.
Trunk lean mass and handgrip strength were decreased in the Experimental Group. Total lean mass was increased in the LTM compared to RTM or LQ. Left handgrip strength in LTM was decreased compared to RTM and RQ and in LQ compared to RTM and RQ. Finally, total lean mass, trunk fat mass, trunk lean mass, right and left arm lean mass were increased in women with lymphedema.
Breast cancer survivors have changes in their body composition and in handgrip strength six months after surgery; however, the interaction between the type of surgery and its impact is unclear. Furthermore, women who developed lymphedema in this period showed more significant changes in the body composition, but they were not enough to cause impairment in handgrip strength.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(6):251-258
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140004976
To assess the effects of a soy dietary supplement on the main biomarkers of cardiovascular health in postmenopausal women compared with the effects of low-dose hormone therapy (HT) and placebo.
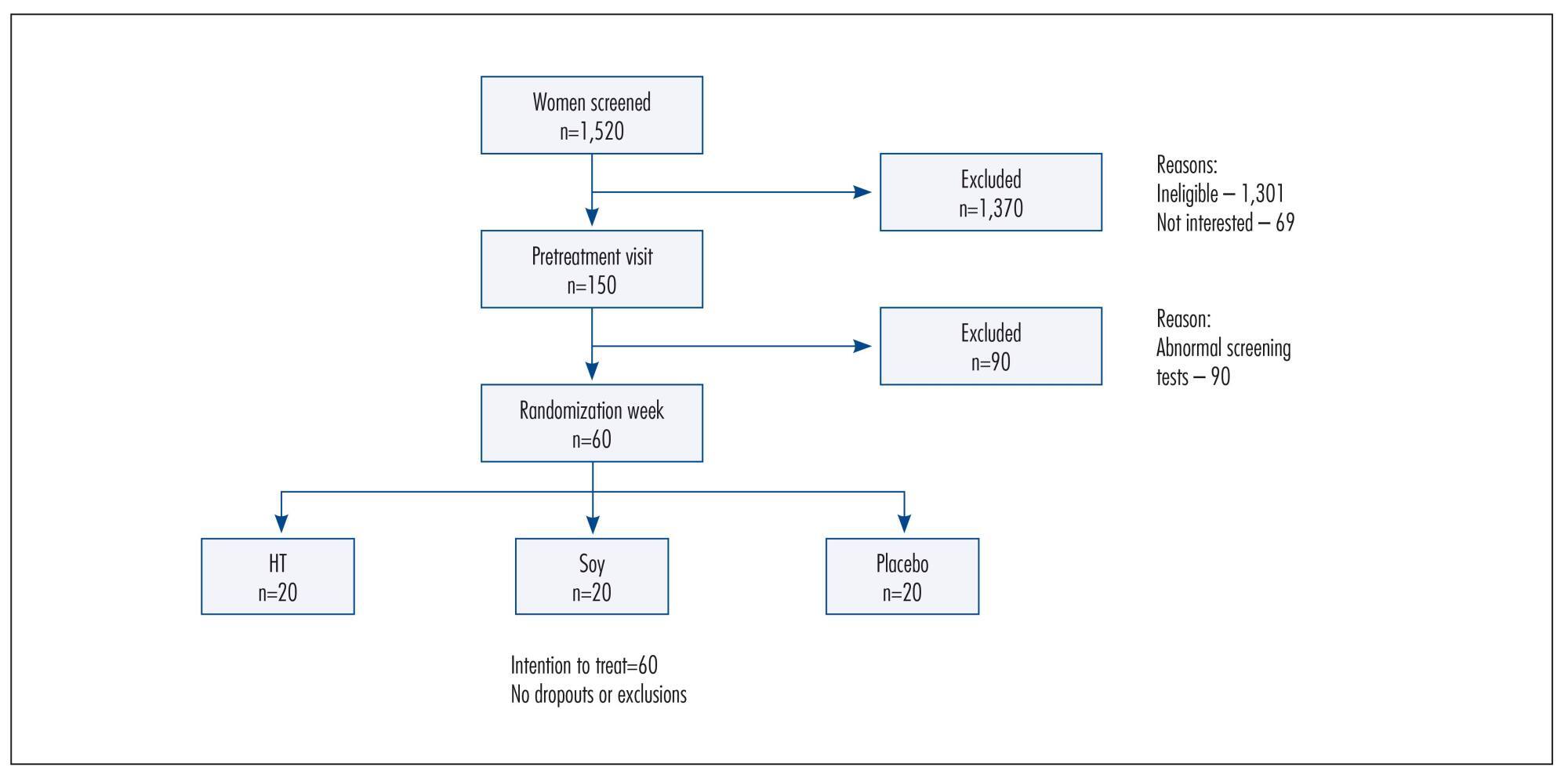
Double-blind, randomized and controlled intention-to-treat trial. Sixty healthy postmenopausal women, aged 40-60 years, 4.1 years mean time since menopause were recruited and randomly assigned to 3 groups: a soy dietary supplement group (isoflavone 90mg), a low-dose HT group (estradiol 1 mg plus noretisterone 0.5 mg) and a placebo group. Lipid profile, glucose level, body mass index, blood pressure and abdominal/hip ratio were evaluated in all the participants at baseline and after 16 weeks. Statistical analyses were performed using the χ2 test, Fisher's exact test, Kruskal-Wallis non-parametric test, analysis of variance (ANOVA), paired Student's t-test and Wilcoxon test.
After a 16-week intervention period, total cholesterol decreased 11.3% and LDL-cholesterol decreased 18.6% in the HT group, but both did not change in the soy dietary supplement and placebo groups. Values for triglycerides, HDL-cholesterol, glucose level, body mass index, blood pressure and abdominal/hip ratio did not change over time in any of the three groups.
The use of dietary soy supplement did not show any significant favorable effect on cardiovascular health biomarkers compared with HT. Clinical Trial Registry: The trial is registered at the Brazilian Clinical Trials Registry (Registro Brasileiro de Ensaios Clínicos - ReBEC), number RBR-76mm75.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2014;36(6):259-263
DOI 10.1590/S0100-720320140004812
To analyze the factors related to route of delivery in patients with pre-eclampsia.
A retrospective analytical study was conducted from January 2009 to January 2011, during which 250 medical records of patients diagnosed with pre-eclampsia who gave birth to live fetuses with a gestational age of 28 weeks or more were selected. The variables evaluated were: maternal age (19 years, 20−34 years and over 35 full years), gestational age at delivery (28−37 weeks and more than 37 weeks), parity (primiparous or multiparous), previous cesarean section, history of pre-eclampsia or chronic hypertension, current diagnosis of mild or severe pre-eclampsia, and birth weight of the newborn. The information was transcribed to a questionnaire based on the variables being investigated. The chi-square test was applied to identify the relationship between the variables, with the level of significance set at p<0.05, and the Odds Ratio (OR) was calculated only for the variables showing a statistically significant difference in order to determine the odds for the patient to be submitted to a cesarean section.
In this study, we observed a 78.4% rate of cesarean delivery, with 54.1% of the patients submitted to the procedure having a gestational age of 28 to 37 weeks (OR=3.1; p<0.01). Patients with a history of pre-eclampsia were 2.5 times more likely to have cesarean delivery (OR=2.5; p<0.02). All patients who had had a previous cesarean were submitted to cesarean delivery in the current pregnancy (p<0.01). Pregnant women with severe pre-eclampsia were 3.3 times more likely to progress to cesarean delivery than those with mild pre-eclampsia (OR=3.3; p<0.01).
After individual analysis, only gestational age and a diagnosis of severe pre-eclampsia showed significant differences, representing risk factors for this type of delivery.