Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(2):81-86
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000200005
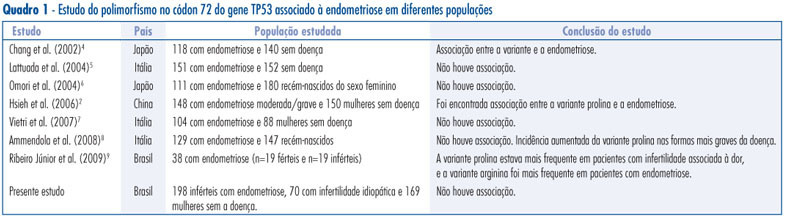
PURPOSE: to determine the prevalence of adverse gestational and neonatal outcomes in women with a positive screening and negative diagnosis for gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). METHODS: a retrospective descriptive cross-sectional study was conducted from 2000 to 2009 on 409 women with positive screening for GDM. The maternal variables studied were: age, body mass index, history of cesarean section, macrosomia or diabetes mellitus in a previous pregnancy and a personal or family history of diabetes mellitus and chronic arterial hypertension. The neonatal variables studied were: polyhydramnios, gestational age at birth, prematurity, cesarean delivery, large for gestational age (LGA) newborn, macrosomia, Apgar score, neonatal respiratory distress syndrome, hypoglycemia and hyperbilirubinemia. Uni- and multivariate descriptive analyses were first performed regarding risk factors and neonatal outcome and the prevalences and respective 95% confidence intervals were determined. RESULTS: the route of delivery was cesarian section in 255 cases (62.3%), preterm birth occurred in 14.2% of cases and 19.3% of the newborns were LGA. The risk factors correlated with LGA newborns were overweight or obesity, maternal age and a history of macrosomia in a previous pregnancy. CONCLUSIONS: a high rate of LGA newborns was observed in the population with positive risk factors or altered fasting glycemia on the occasion of the first prenatal visit, even when the glycemia curve was normal, with cesarean rates above those habitually observed in populations considered to be of low risk. Pregnant women with these characteristics represent a differential group.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(2):75-80
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000200004
PURPOSE: to determine the prevalence of lymphedema and its associated factors in breast cancer patients. METHODS: Two hundred and fifty women that had undergone more than six months of breast cancer treatment and were being treated at an oncology reference hospital in Juiz de Fora, Minas Gerais, Brazil. They were interviewed and submitted to physical evaluation. Data from the patients' medical records regarding the treatment of breast cancer, the extent of axillary intervention and the tumor were analyzed. Lymphedema was diagnosed when the difference between both upper limbs was 2 cm or more by perimetry. The groups of women with and without lymphedema were compared regarding the possible risk factors, and central tendency, dispersion, and prevalence were measured, with a significance level of 95%. RESULTS: One hundred and twelve women (44.8%) presented lymphedema. A significant difference was found between the groups of women with and without lymphedema regarding the median numbers of removed lymph nodes (p=0.02); presentation of superficial lymphatic thrombosis in the arm ipsilateral to the surgery (p<0.01); local application of radiotherapy, use of chemotherapy (p<0.01 for both); removal of the cuticles of the ipsilateral hand with pliers, and weightlifting after the treatment (p<0.01 and p=0.05, respectively). CONCLUSIONS: the association between lymphedema and the mentioned factors requires an interdisciplinary approach to this condition. It is of paramount importance that health teams and patients become aware of the prevention and treatment of lymphedema, a condition often undervalued.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(2):70-74
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000200003
OBJECTIVE: to correlate complaints of stress urinary incontinence and the results of a one-hour pad test in pre- and postmenopausal women. METHODS: cross-sectional study conducted on 60 postmenopausal volunteers divided into two groups: one consisting of 34 women with involuntary loss of urine due to stress incontinence and the other consisting of 26 women without involuntary loss of urine. A control group of 15 premenopausal women with normal menstrual cycles and no urinary complaints was also used. All women underwent clinical and laboratory analysis as well as the one-hour pad test. Patients were considered to be incontinent when sanitary pad weight post-test was more than 1 g. Data were submitted to descriptive statistics, parametric ANOVA, post-hoc Tukey test and Pearson's correlation. RESULTS: all postmenopausal women presented with stress urinary incontinence during the pad test, both those with urinary loss (4 g) and with no previous loss (3.5 g). A strong correlation was observed between urinary loss and time since menopause (r=0.8; p<0.01) and body mass index (r=0.7; p=0.01). Premenopausal women were continent during the pad test (0.4 g). CONCLUSIONS: the results of the one-hour pad test showed that all postmenopausal women exhibited stress urinary incontinence, including those without urine loss on effort. Urine loss was correlated with time since menopause and body mass index.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(2):65-69
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000200002
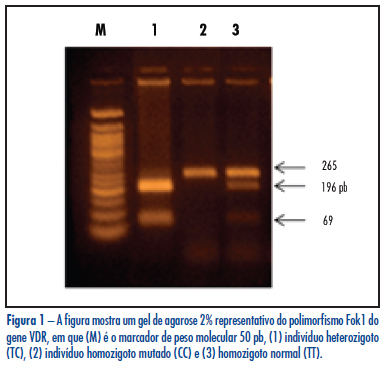
PURPOSE: to evaluate the frequency of VDR gene polymorphism Fok1 in infertile women with endometriosis and Control and its relation to the disease. METHODS: a case-control study that included 147 infertile women with endometriosis and 154 fertile women without endometriosis as Control. Fok1 polymorphism (rs10735810, T2C), which promotes a T/C exchange in exon 2 of the VDR gene, was identified by the polymerase chain reaction-restriction fragment length polymorphism (PCR-RFLP), that involves the combination of amplification by PCR and digestion with restriction endonuclease. The χ2 test was used to compare allele and genotype frequencies between groups. All p-values were two-tailed and a p-value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. RESULTS: the TT, TC and CC genotype frequencies of VDR Fok1 polymorphism were 44.2%, 46.9% and 8.9% in infertile women with endometriosis and 41.6%, 50% and 8.4% in the Control Group. No significant difference was found (p=0.8), even when the patients were subdivided according to the stage of endometriosis (p=0.3 for minimal and mild endometriosis and p=0.2 for moderate and severe endometriosis). Alleles T and C were present, respectively, in 67.6% and 32.3% of infertile women with endometriosis (p=0.8), in 63.5% and 36.5% of women with minimal/mild endometriosis (p=0.5), in 72.5% and 27.5% of women with moderate/severe endometriosis (p=0.2), and in 66.6% and 33.4% of the Control Group. No statistically significant difference was found among any groups and the Control. CONCLUSION: the results suggest that VDR gene polymorphism Fok1 does not confer genetic susceptibility to endometriosis-associated infertility in the Brazilian population.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(1):20-26
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000100003
PURPOSE: to evaluate associations between parental exposure to pesticides and births with congenital defects in São Francisco Valley, as well as the demographic profile and the defects found. METHODS: in this case-control study, each case (newborns with congenital defects) had two controls (healthy newborns). The subjects were born in the city of Petrolina, in São Francisco Valley, in 2009. The sample consisted of 42 cases and 84 controls. Data were gathered by a structured questionnaire adapted from Latin-American Collaborative Study of Congenital Malformations (ECLAMC), with the addition of questions related to exposure to pesticides, analysis of the medical records and contact with the hospital's pediatrician. The χ2 test was performed with a significance level of 5% to identify the variables with the greatest differences between case and control groups. Odds Ratio (OR) for the sample was calculated, as well as the OR obtained by logistic regression analysis, and finally, multivariate logistic regression analysis was performed. RESULTS: there was a greater exposure to pesticides during pregnancy in infants with congenital defects compared to healthy subjects. Increased risk was observed when at least one parent was exposed to pesticides (adjusted OR = 1.3; 95%CI = 0.4 - 3.9). The sociodemographic variables associated with congenital defects were: low school level, low weight, prematurity, young parents, chronic diseases, and physical factors. Multiple malformations and defects of the musculoskeletal and nervous systems were more frequently found. CONCLUSIONS: the present study suggests an association between exposure to pesticides and the occurrence of congenital defects, although the data were not significant.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(1):13-19
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000100002
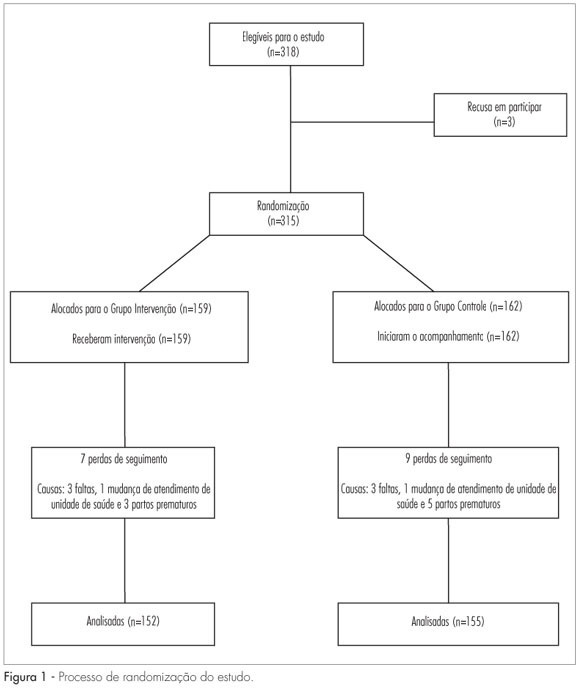
PURPOSE: to evaluate the impact of dietary counseling on controlling weight gain in pregnant women, who were served in a public health service facility. METHODS: the study was conducted at a known health unit located in the metropolitan region of the city of Porto Alegre, in Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil. Three hundred and fifteen pregnant women between the 10th and 29th week of gestation were randomized to Control and Intervention Groups. The Intervention Group received dietary counseling according to nutritional status, and pregnant women in the Control Group were instructed to follow the routine of the health service facility. Weight and height were measured, and the body mass index (BMI) was calculated. The pre-gestational nutritional status was determined according to the following BMI criteria: low weight (<18.5 kg/m²), eutrophy (18.5 to 24.9 kg/m²), overweight (25.0 to 29.9 kg/m²), and obesity (>30 kg/m²). The nutritional status during pregnancy was determined according to the BMI curve for gestational age adopted by the Health Ministry of Brazil. Data were analyzed by the relative risk and respective 95% confidence interval, and by the Student's t-test and χ2 test. Statistical significance was set at p<0.05. RESULTS: the assessment of nutritional status before pregnancy showed that 28.0% of the women were overweight and 4.1% were underweight. In the first and last interview during pregnancy, the rates of prevalence of excessive weight were 36.2 and 46.0%, respectively. The intervention proved to be effective in reducing the rate of weekly weight gain of pregnant women with excess weight (342.2 versus 420.2; p=0.015) and the prevalence of clinical complications (9.2 versus 24.85; p<0.001). CONCLUSIONS: dietary counseling was effective in decreasing the weight gain of pregnant women who were overweight and reducing clinical complications, such as gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, infant low weight, and prematurity in the Intervention Group.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2011;33(1):37-42
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032011000100006
PURPOSE: to evaluate the frequency of TP53 codon 72 polymorphism in infertile women with endometriosis, women with idiopathic infertility, controls and its relation to the disease. METHODS: a case-control study that included 198 infertile women with endometriosis, 70 women with idiopathic infertility and 169 fertile women without endometriosis as control. Detection of TP53 codon 72 gene polymorphism (rs1042522, Arg/C:Pro/G), that promotes a C/G exchange in the coding region of the gene, was performed by real time Polymerase Chain Reaction (PCR), using the TaqMan system of primers, that flank the implicated region and probes labeled with different fluorescent dyes, one for allele C and other for allele G. When two dyes were observed, the patient was considered to be heterozygous CG. In the presence of only one dye, the individual was considered to be homozygous CC or GG. The χ2 test was used to compare allele and genotype frequencies between groups. All p-values were two-tailed and a p-value <0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. RESULTS: we found no statistically significant difference in the distribution of TP53 codon 72 polymorphism genotypes CC, CG or GG (p=0.7) and alleles C or G (p=0.4) between infertile patients with endometriosis and controls (p=0.4), regardless of the stage of the disease. In relation to infertility, no statistically significant difference in the genotype or allele distribution (p=1.0 and p=0.9, respectively) was observed between idiopathic infertile women and controls. Considering the dominant inheritance model, again, no statistically significant difference was found even in the endometriosis (p=0.5) or the idiopathic infertility group (p=0.9) when compared to controls. Regarding the recessive inheritance model no statistically significant difference was found, with p=0.6 and p=1.0, respectively, for the endometriosis and idiopathic infertility groups. CONCLUSION: the results suggest that the TP53 codon 72 polymorphism does not confer genetic susceptibility to endometriosis and/or infertility in the Brazilian population, not even the severe form of the disease.