- Recent Articles
- Most Citedi
- Most Visitedi
- Future Articles
-
Review Article12-04-2024
Female genital tract microbiome: the influence of probiotics on assisted reproduction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo82
Views210

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleFemale genital tract microbiome: the influence of probiotics on assisted reproduction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo82
Views210Abstract
Assisted reproductive technology (ART) has been evolving since 1978, with the number of techniques performed increasing over the years. Despite continued advances, some couples continue to have difficulties getting pregnant, and it has recently been considered that the microbiome of the female genital tract (FGT) may influence embryo implantation and the establishment of pregnancy. This review aims to evaluate the role of probiotics on reproductive outcomes in infertile women on ART. A search throughout medical databases was performed, and six articles met the criteria. Five studies showed improvements in pregnancy rates, with only one demonstrating statistical significance. One article showed no improvement but reported a statistically significant reduction in the miscarriage rate in the probiotic group. Further research is needed to evaluate the true potential of probiotics, namely to assess whether they effectively modulate the FGT microbiome and if these changes are maintained over time.
Key-words Abortion, spontaneousEmbryo implantationGenitalia, femaleInfertility, femalePregnancy outcomePregnancy rateProbioticsReproductive techniques, assisted, MicrobiotaSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article12-04-2024
Prevalence and factors associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease among women with polycystic ovary syndrome
- Maria Elisa Franciscatto
 ,
, - Juliana Bosso Taniguchi
 ,
, - Raquel Wohlenberg
 ,
, - Isadora Luísa Riedi
 ,
, - Karen Oppermann

Views252

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticlePrevalence and factors associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease among women with polycystic ovary syndrome
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo81
- Maria Elisa Franciscatto
 ,
, - Juliana Bosso Taniguchi
 ,
, - Raquel Wohlenberg
 ,
, - Isadora Luísa Riedi
 ,
, - Karen Oppermann

Views252Abstract
Objective:
To verify the prevalence and factors associated with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) among women with Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS).
Methods:
A cross-sectional study was conducted with 53 patients with PCOS. The diagnosis of PCOS followed the Rotterdam criteria. The diagnosis of NAFLD was made through US showing hepatic steatosis, excluding significant alcohol consumption and chronic liver disease. The following variables were compared between the groups of women with and without NAFLD: age, race, anthropometric data, blood pressure levels, liver enzymes, glycemic and lipid profiles, total testosterone, presence of hirsutism, and metabolic syndrome (MS). Variables were compared between the groups using T-test, Mann-Whitney, and Chi-square tests.
Results:
Among 53 patients with PCOS, 50.9% had NAFLD. The NAFLD group had higher weight (p=0.003), BMI (p=0.001), waist circumference (p≤0.001), fasting glucose (p=0.021), HbA1C% (p=0.028), triglycerides (p=0.023), AST (p=0.004), ALT (p=0.001), higher prevalence of MS (p=0.004), and lower levels of HDL cholesterol (p=0.043). The other variables did not differ between the groups. Both groups were predominantly of caucasian race, and there was no significant difference in age.
Conclusion:
The prevalence of NAFLD among patients with PCOS was 50.9%. Metabolic and hepatic enzyme abnormalities were more prevalent in this group compared to the group without the disease. Obesity tripled the prevalence of NAFLD.
Key-words Alcohol drinkingHyperandrogenismmetabolic syndromenon-alcoholic fatty liver diseaseObesityPolycystic ovary syndromeWaist circumferenceSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Maria Elisa Franciscatto
-
Review Article12-04-2024
Zuranolone for postpartum depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis of two randomized studies
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo79
Views272

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleZuranolone for postpartum depression: a systematic review and meta-analysis of two randomized studies
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo79
Views272See moreAbstract
Objective:
To evaluate the maternal outcomes in women with postpartum depression using zuranolone, the first oral medication indicated to treat postpartum depression.
Methods:
We conducted a systematic search in September 2023, on Pubmed, Embase and Cochrane Trials. We included randomized controlled trials comparing the effectiveness and safety of zuranolone versus placebo in women with postpartum depression. No time or language restrictions were applied. 297 results were retrieved, of which 11 papers were selected and fully reviewed by two authors. Review Manager 5 was used for statistical analysis and Cochrane Risk-of-bias tool for randomized trials was applied for quality assessment.
Results:
We included 2 studies, with 346 women, of whom 174 (50.2%) were treated with zuranolone. Zuranolone was significantly associated to an improvement of Clinical Global Impression response rate; Hamilton Depression Rating Scale 15 days and 45-day remission, 3-day, 15-day, and 45-day symptom remission, and reduction in the dose of antidepressants. As for safety outcomes, it was noticed that zuranolone increases sedation risk, which can be dose related. No significant differences were found for other adverse events.
Conclusion:
These findings suggest that zuranolone might present a safe and effective medication for out-of-hospital treatment of PPD. Sedation effects need to be further assessed.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article12-04-2024
Self-medication among pregnant women in comparison to the general population: a scoping review of the main characteristics
- Gabriela Pereira
 ,
, - Cinthia Madeira de Souza
 ,
, - Amanda Canato Ferracini
 ,
, - Fernanda Garanhani Surita
 ,
, - Sherif Eltonsy
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Priscila Gava Mazzola

Views244

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleSelf-medication among pregnant women in comparison to the general population: a scoping review of the main characteristics
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo77
- Gabriela Pereira
 ,
, - Cinthia Madeira de Souza
 ,
, - Amanda Canato Ferracini
 ,
, - Fernanda Garanhani Surita
 ,
, - Sherif Eltonsy
 ,
, - Priscila Gava Mazzola

Views244Abstract
Objective:
An in-depth evaluation of the published evidence is needed on self-medication, specifically the evidence focusing on vulnerable groups, such as pregnant women. This scoping review aims to provide an overview of the differences in self-medication prevalence and study characteristics among different groups, while identifying gaps in the literature.
Methods:
A literature search was performed in PubMed and Web of Science, including articles published in the last 10 years for the pregnant women group (PWG) and the general population group (GPG). Data on study design, self-medication prevalence, medications used, and other variables were collected, tabulated, and summarized.
Results:
From 2888 screened articles, 75 were considered including 108,559 individuals. The self-medication (SM) in the PWG ranged from 2.6 to 72.4% and most studies had an SM prevalence between 21 and 50% and in the GPG, 32 from 50 studies had a SM prevalence higher than 50%. The reviewed studies varied considerably in methodology, requiring careful interpretation. While most of the studies assessed self-medication during the entire pregnancy, self-medication definition was often inconsistent between studies. Acetaminophen was the most used medication and headache was the most frequent symptom leading to self-medication initiation in the PWG.
Conclusions:
Self-medication among pregnant women showed a lower prevalence when compared to the general population. The medications used and symptoms reported were similar between groups. However, methodological differences must be carefully considered. Pregnant women should carefully follow their physicians’ advice before initiating self-medication to avoid preventable maternal and fetal adverse effects.
Key-words drug-related side effects and adverse reactionsMedication usePregnant womenSelf-medicationSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Gabriela Pereira
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT11-25-2024
Nonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency in women: diagnosis and treatment: Number 11 – 2024
- Andrea Prestes Nácul
 ,
, - Ana Carolina Japur Sá Rosa e Silva
 ,
, - Daniela Angerame Yela
 ,
, - Sebastião Freitas de Medeiros
 ,
, - José Maria Soares Júnior
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Cristina Laguna Benetti-Pinto

Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTNonclassic congenital adrenal hyperplasia due to 21-hydroxylase deficiency in women: diagnosis and treatment: Number 11 – 2024
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS11
- Andrea Prestes Nácul
 ,
, - Ana Carolina Japur Sá Rosa e Silva
 ,
, - Daniela Angerame Yela
 ,
, - Sebastião Freitas de Medeiros
 ,
, - José Maria Soares Júnior
 ,
, - Gabriela Pravatta Rezende Antoniassi
 ,
, - Lia Cruz da Costa Damásio
 ,
, - Técia Maria de Oliveira Maranhão
 ,
, - Gustavo Arantes Rosa Maciel
 ,
, - Cristina Laguna Benetti-Pinto



This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Andrea Prestes Nácul
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT11-14-2024
Challenges and strategies in adolescent vaccination: Number 12 – 2024
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS12
Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTChallenges and strategies in adolescent vaccination: Number 12 – 2024
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS12


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Letter to the Editor10-23-2024
The gynecologist and cancer in women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo92
Views136

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Letter to the EditorThe gynecologist and cancer in women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo92
Views136Cervical cancer continues to claim an alarming number of victims around the world, especially among poor women. In Brazil, in 2022, an incidence of 16.3/100,000 women was recorded,() with a projection for 2023 of 17,010 new cases, corresponding to a rate of 15.38/100,000, representing 7% of tumors in women.In the Brazilian reality, where there is […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article10-23-2024
Nipple-sparing mastectomy in young versus elderly patients
- Antônio Luiz Frasson
 ,
, - Isabela Miranda
 ,
, - Betina Vollbrecht
 ,
, - Carolina Malhone
 ,
, - Ana Beatriz Falcone
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Martina Lichtenfels

Abstract
Original ArticleNipple-sparing mastectomy in young versus elderly patients
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo90
- Antônio Luiz Frasson
 ,
, - Isabela Miranda
 ,
, - Betina Vollbrecht
 ,
, - Carolina Malhone
 ,
, - Ana Beatriz Falcone
 ,
, - Fernanda Barbosa
 ,
, - Francisco Pimentel Cavalcante
 ,
, - Martina Lichtenfels

Views160See moreAbstract
Objective:
In this study, we compared indications and outcomes of 115 young (< 40 years) versus 40 elderly (> 60 years) patients undergoing nipple-sparing mastectomy (NSM) as risk-reducing surgery or for breast cancer (BC) treatment.
Methods:
Between January 2004 and December 2018, young and elderly patients undergoing NSM with complete data from at least 6 months of follow-up were included.
Results:
BC treatment was the main indication for NSM, observed in 85(73.9%) young versus 33(82.5%) elderly patients, followed by risk-reducing surgery in 30(26.1%) young versus 7(17.5%) elderly patients. Complication rates did not differ between the age groups. At a median follow-up of 43 months, the overall recurrence rate was higher in the younger cohort (p = 0.04). However, when stratified into local, locoregional, contralateral, and distant metastasis, no statistical difference was observed. During the follow-up, only 2(1.7%) young patients died.
Conclusion:
Our findings elucidate a higher recurrence rate of breast cancer in younger patients undergoing NSM, which may correlate with the fact that age is an independent prognostic factor. High overall survival and low complication rates were evidenced in the two groups showing the safety of NSM for young and elderly patients.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Antônio Luiz Frasson
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT04-25-2024
Hyperprolactinemia in women: treatment
- Cristina Laguna Benetti-Pinto
 ,
, - Andrea Prestes Nácul
 ,
, - Ana Carolina Japur Rosa e Silva
 ,
, - Gustavo Arantes Rosa Maciel
 ,
, - Vania dos Santos Nunes Nogueira
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Andrea Glezer

Views1170

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTHyperprolactinemia in women: treatment
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS05


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 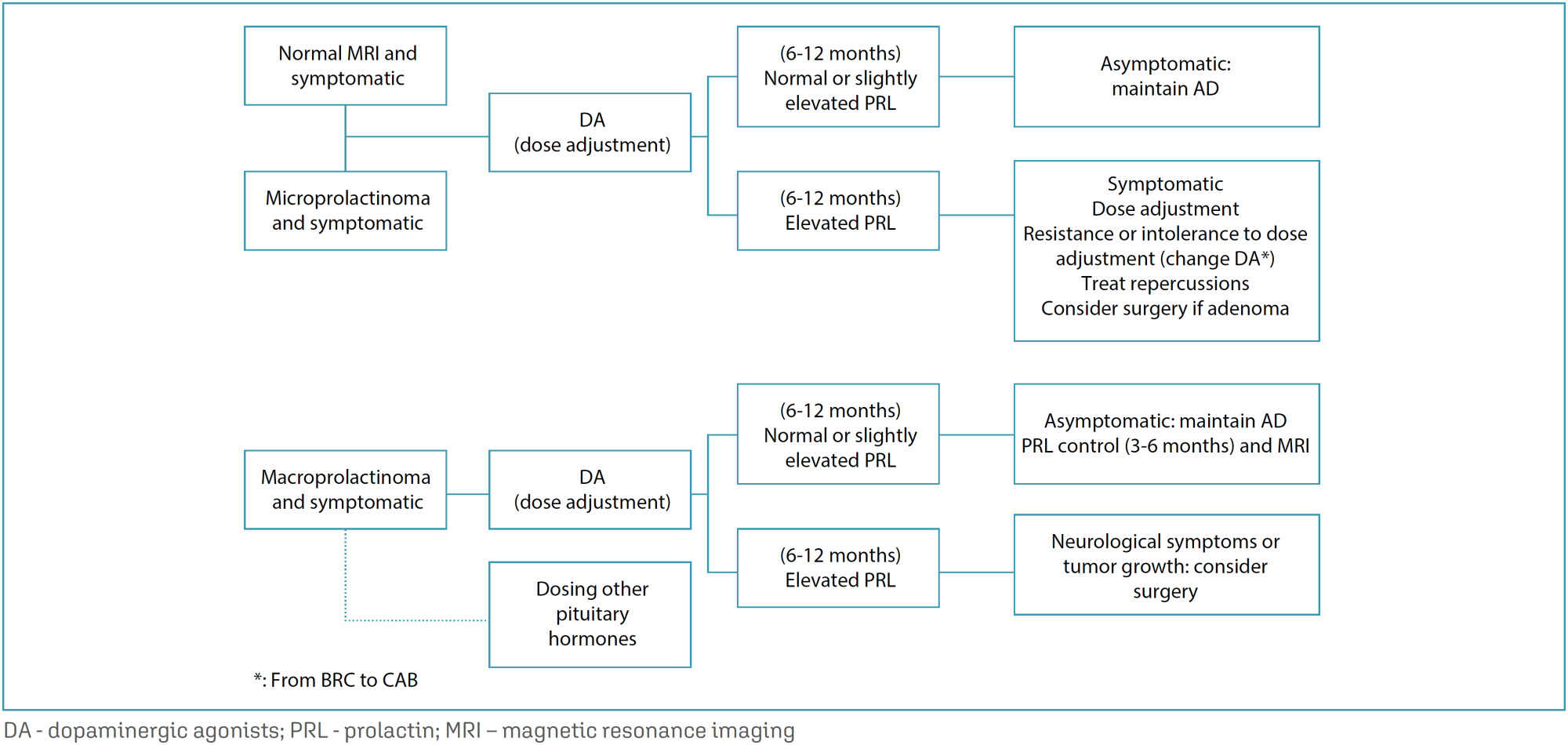
- Cristina Laguna Benetti-Pinto
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT04-25-2024
Hyperprolactinemia in women: diagnostic approach
- Andrea Glezer
 ,
, - Heraldo Mendes Garmes
 ,
, - Leandro Kasuki
 ,
, - Manoel Martins
 ,
, - Paula Condé Lamparelli Elias
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Andrea Prestes Nácul

Views1165

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTHyperprolactinemia in women: diagnostic approach
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS04


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 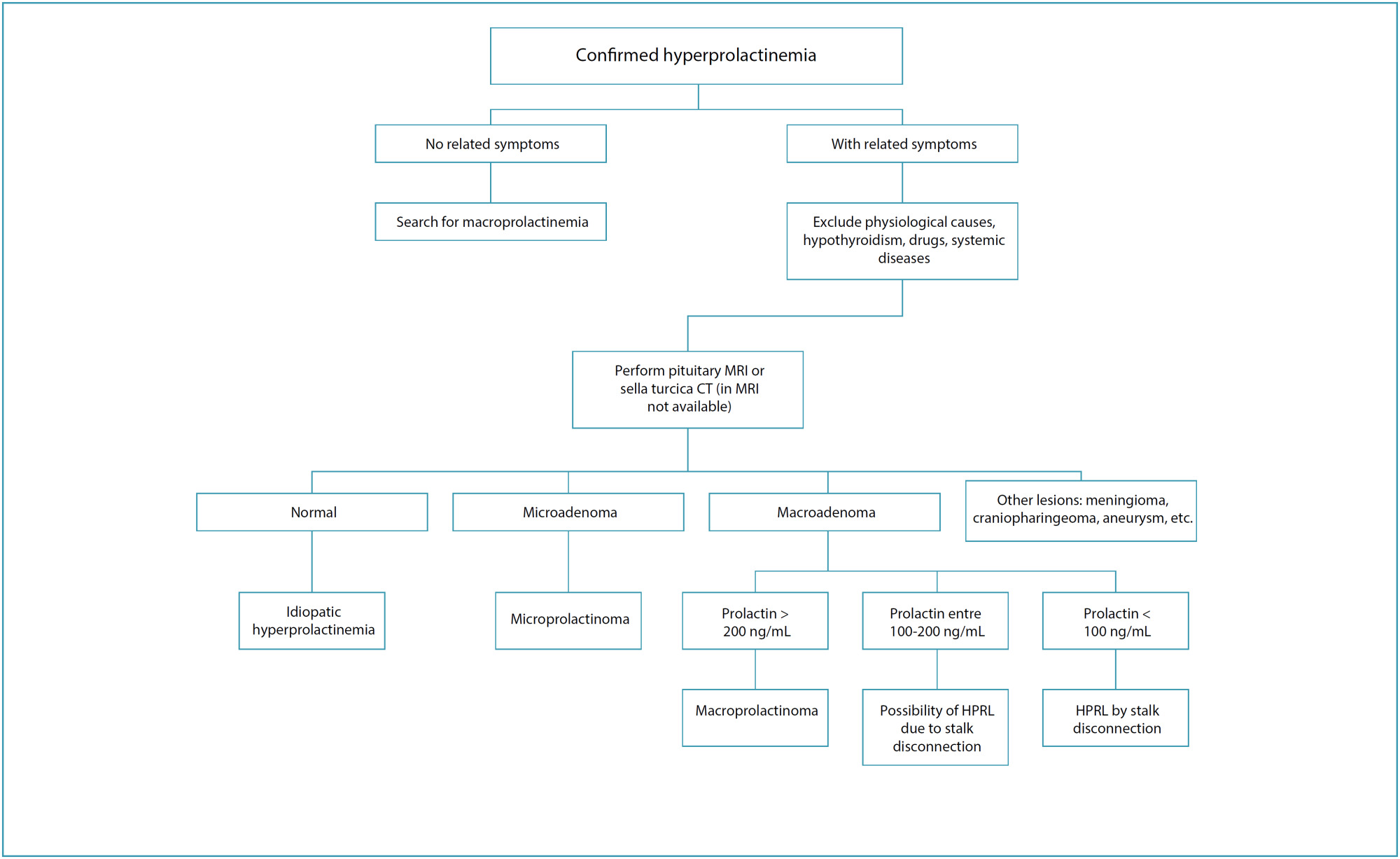
- Andrea Glezer
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT00-00-2024
Breech birth care: Number 1 – 2024
- Álvaro Luiz Lage Alves
 ,
, - Alexandre Massao Nozaki
 ,
, - Carla Betina Andreucci Polido
 ,
, - Lucas Barbosa da Silva
 ,
, - Roxana Knobel

Views977

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTBreech birth care: Number 1 – 2024
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgofps1


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Álvaro Luiz Lage Alves
-
Letter to the Editor04-09-2024
Letter to Editor: In response to existence of SARS-CoV-2 in the peritoneal fluid
- Gustavo Romero-Velez
 ,
, - Guillermo Ponce de Leon-Ballesteros
 ,
, - Juan Barajas-Gamboa
 ,
, - Jerry Dang
 ,
, - Andrew Strong
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Mathew Kroh

Abstract
Letter to the EditorLetter to Editor: In response to existence of SARS-CoV-2 in the peritoneal fluid
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo24


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Gustavo Romero-Velez
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT04-02-2024
Use of hormones and risk of venous thromboembolism
- Venina Isabel Poço Viana Leme de Barros
 ,
, - André Luiz Malavasi Longo de Oliveira
 ,
, - Denis Jose do Nascimento
 ,
, - Eduardo Zlotnik
 ,
, - Marcelo Melzer Teruchkin
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Paulo Francisco Ramos Margarido

Views797

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTUse of hormones and risk of venous thromboembolism
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS02
- Venina Isabel Poço Viana Leme de Barros
 ,
, - André Luiz Malavasi Longo de Oliveira
 ,
, - Denis Jose do Nascimento
 ,
, - Eduardo Zlotnik
 ,
, - Marcelo Melzer Teruchkin
 ,
, - Marcos Arêas Marques
 ,
, - Paulo Francisco Ramos Margarido

Views797See moreKey points
•The risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) is not increased in women using long-acting reversible contraceptive methods (LARCs) with progestogens.
•Oral contraceptives with levonorgestrel or norgestimate confer half the risk of VTE compared to oral contraceptives containing desogestrel, gestodene or drospirenone.
•Progestogen-only pills do not confer an increased risk of VTE.
•Women using transdermal contraceptive patches and combined oral contraceptives (COCs) are at an approximately eight times greater risk of VTE than non-users of hormonal contraceptives (HCs), corresponding to 9.7 events per 10,000 women/years.
•Vaginal rings increase the risk of VTE by 6.5 times compared to not using HC, corresponding to 7.8 events per 10,000 women/years.
•Several studies have demonstrated an increased risk of VTE in transgender individuals receiving hormone therapy (HT).
•Hormone therapy during menopause increases the risk of VTE by approximately two times, and this risk is increased by obesity, thrombophilia, age over 60 years, surgery and immobilization.
•The route of estrogen administration, the dosage and type of progestogen associated with estrogen may affect the risk of VTE in the climacteric.
•Combined estrogen-progesterone therapy increases the risk of VTE compared to estrogen monotherapy.
•Postmenopausal HT increases the risk of thrombosis at atypical sites.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Venina Isabel Poço Viana Leme de Barros
-
Editorial00-00-2024
The path to elimination: FEBRASGO 2023’s targeted strategies against cervical cancer in Brazil
- Agnaldo Lopes da Silva Filho
 ,
, - Cecilia Maria Roteli-Martins
 ,
, - Neila Maria de Góis Speck
 ,
, - Newton Sérgio de Carvalho
 ,
, - Eduardo Batista Cândido
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Júlio César Teixeira

Views793

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
EditorialThe path to elimination: FEBRASGO 2023’s targeted strategies against cervical cancer in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgoedt2


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Agnaldo Lopes da Silva Filho
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT04-02-2024
Vulvovaginitis in pregnant women
- Geraldo Duarte
 ,
, - Iara Moreno Linhares
 ,
, - Regis Kreitchmann
 ,
, - Andréa da Rocha Tristão
 ,
, - Evelyn Traina
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Joelma Queiroz Andrade

Views747

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTVulvovaginitis in pregnant women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS03
- Geraldo Duarte
 ,
, - Iara Moreno Linhares
 ,
, - Regis Kreitchmann
 ,
, - Andréa da Rocha Tristão
 ,
, - Evelyn Traina
 ,
, - Ivete Canti
 ,
, - Marcos Takimura
 ,
, - Joelma Queiroz Andrade

Views747See moreKey points
• The balanced vaginal microbiome is the main factor defending the vaginal environment against infections. Lactobacilli play a key role in this regard, maintaining the vaginal pH within the normal range (3.8 to 4.5).
•Hormonal and immune adaptations resulting from pregnancy influence changes in the vaginal microbiome during pregnancy.
•An altered vaginal microbiome predisposes to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection.
•Bacterial vaginosis is the main clinical expression of an imbalanced vaginal microbiome.
•Vulvovaginal candidiasis depends more on the host’s conditions than on the etiological agent.
•Trichomonas vaginalis is a protozoan transmitted during sexual intercourse.
•The use of probiotics is not approved for use in pregnant women.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Geraldo Duarte
-
Original Article00-00-2024
Early and late-onset preeclampsia: effects of DDAH2 polymorphisms on ADMA levels and association with DDAH2 haplotypes
- Fernanda Santos Mendes
 ,
, - Marcelo Rizzatti Luizon
 ,
, - Ana Cristina dos Santos Lopes
 ,
, - Daniela Alves Pereira
 ,
, - Fernanda Cristina Gontijo Evangelista
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Patrícia Nessralla Alpoim

Views615

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleEarly and late-onset preeclampsia: effects of DDAH2 polymorphisms on ADMA levels and association with DDAH2 haplotypes
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo19
- Fernanda Santos Mendes
 ,
, - Marcelo Rizzatti Luizon
 ,
, - Ana Cristina dos Santos Lopes
 ,
, - Daniela Alves Pereira
 ,
, - Fernanda Cristina Gontijo Evangelista
 ,
, - Lara Carvalho Godoi
 ,
, - Luci Maria Dusse
 ,
, - Patrícia Nessralla Alpoim

Views615Abstract
Objective:
To examine whether the DDAH2 promoter polymorphisms -1415G/A (rs2272592), -1151A/C (rs805304) and -449G/C (rs805305), and their haplotypes, are associated with PE compared with normotensive pregnant women, and whether they affect ADMA levels in these groups.
Methods:
A total of 208 pregnant women were included in the study and classified as early-onset (N=57) or late-onset PE (N =49), and as normotensive pregnant women (N = 102).
Results:
Pregnant with early-onset PE carrying the GC and GG genotypes for the DDAH2 -449G/C polymorphism had increased ADMA levels (P=0.01). No association of DDAH2 polymorphisms with PE in single-locus analysis was found. However, the G-C-G haplotype was associated with the risk for late-onset PE.
Conclusion:
It is suggested that DDAH2 polymorphisms could affect ADMA levels in PE, and that DDAH2 haplotypes may affect the risk for PE.
Key-words Asymmetric dimethylarginineDimethylarginine dimethylaminohydrolase 2 geneGenotypeHaplotypesNitric Oxide SynthaseNitric Oxide Synthase Type III/ geneticsPolymorphism, geneticPre-eclampsiaPregnant womenSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Fernanda Santos Mendes
-
Review Article01-23-2022
Efficacy of Hormonal and Nonhormonal Approaches to Vaginal Atrophy and Sexual Dysfunctions in Postmenopausal Women: A Systematic Review
- Ayane Cristine Alves Sarmento
 ,
, - Ana Paula Ferreira Costa
 ,
, - Juliana Lírio
 ,
, - José Eleutério Jr
 ,
, - Pedro Vieira Baptista
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Ana Katherine Gonçalves

Views313

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleEfficacy of Hormonal and Nonhormonal Approaches to Vaginal Atrophy and Sexual Dysfunctions in Postmenopausal Women: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(10):986-994
- Ayane Cristine Alves Sarmento
 ,
, - Ana Paula Ferreira Costa
 ,
, - Juliana Lírio
 ,
, - José Eleutério Jr
 ,
, - Pedro Vieira Baptista
 ,
, - Ana Katherine Gonçalves

Views313See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the efficacy of the hormonal and nonhormonal approaches to symptoms of sexual dysfunction and vaginal atrophy in postmenopausal women.
Data Sources
We conducted a search on the PubMed, Embase, Scopus, Web of Science, SciELO, the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL), and Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL) databases, as well as on clinical trial databases. We analyzed studies published between 1996 and May 30, 2020. No language restrictions were applied.
Selection of Studies
We selected randomized clinical trials that evaluated the treatment of sexual dysfunction in postmenopausal women.
Data Collection
Three authors (ACAS, APFC, and JL) reviewed each article based on its title and abstract. Relevant data were subsequently taken from the full-text article. Any discrepancies during the review were resolved by consensus between all the listed authors.
Data Synthesis
A total of 55 studies were included in the systematic review. The approaches tested to treat sexual dysfunction were as follows: lubricants and moisturizers (18 studies); phytoestrogens (14 studies); dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA; 8 studies); ospemifene (5 studies); vaginal testosterone (4 studies); pelvic floor muscle exercises (2 studies); oxytocin (2 studies); vaginal CO2 laser (2 studies); lidocaine (1 study); and vitamin E vaginal suppository (1 study).
Conclusion
We identified literature that lacks coherence in terms of the proposed treatments and selected outcome measures. Despite the great diversity in treatment modalities and outcome measures, the present systematic review can shed light on potential targets for the treatment, which is deemed necessary for sexual dysfunction, assuming that most randomized trials were evaluated with a low risk of bias according to the Cochrane Collaboration risk of bias tool. The present review is registered with the International Prospective Register of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO; CRD42018100488).


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Ayane Cristine Alves Sarmento
-
Review Article09-29-2022
Management Strategies for Sexuality Complaints after Gynecologic Cancer: A Systematic Review
- Luciane Machado Pizetta
 ,
, - Augusto da Cunha Reis
 ,
, - Mirian Picinini Méxas
 ,
, - Vanessa de Almeida Guimarães
 ,
, - Carmen Lucia de Paula

Views162

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleManagement Strategies for Sexuality Complaints after Gynecologic Cancer: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(10):962-971
- Luciane Machado Pizetta
 ,
, - Augusto da Cunha Reis
 ,
, - Mirian Picinini Méxas
 ,
, - Vanessa de Almeida Guimarães
 ,
, - Carmen Lucia de Paula

Views162See moreAbstract
Objective
To explore the main sexuality complaints of gynecologic cancer survivors after treatment and to identify the care strategies provided.
Data Source
Searches were conducted in six electronic databases: Scopus, Web of Science, LILACS, MEDLINE, PsychINFO, and EMBASE.
Study Selection
Articles published between 2010 and 2020 were selected and the following descriptors were used in the English language: female genital neoplasms and gynaecological cancer. The methodological quality of the studies used the Mixed Methods Appraisal Tool (MMAT).
Data Collection
The primary data extracted were: names of the authors, year of publication, country of origin, objective and type of study, data collection instrument, sample size and age range, types of cancer, and symptoms affected with the strategies adopted.
Data Summary
A total of 34 out of 2,536 screened articles were included. The main strategies found for patient care were patient-clinician communication, practices for sexuality care, individualized care plan, multiprofessional team support, and development of rehabilitation programs. For sexuality care, the most common practices are pelvic physiotherapy sessions and the use of vaginal gels and moisturizers.
Conclusion
The main complaints identified in the scientific literature were low libido and lack of interest in sexual activity, vaginal dryness, pain during sexual intercourse, and stenosis. Different care strategies may be adopted, such as follow-up with a multidisciplinary health team and sexual health rehabilitation programs, which could minimize these symptoms and ensure the quality of life of patients.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Luciane Machado Pizetta
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT03-24-2022
Abnormal uterine bleeding and chronic iron deficiency: Number 11 – December 2022
- Venina Viana de Barros
 ,
, - Eliane Azeka Hase
 ,
, - Cristiano Caetano Salazar
 ,
, - Ana Maria Kondo Igai
 ,
, - Fernanda Andrade Orsi
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Paulo Francisco Ramos Margarido

Views216

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTAbnormal uterine bleeding and chronic iron deficiency: Number 11 – December 2022
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(12):1161-1168


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Venina Viana de Barros
-
Review Article05-23-2022
Non-pharmacological Interventions for Improving Sleep Quality During Pregnancy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- Daiane Sofia Morais Paulino
 ,
, - Carolina Bicudo Borrelli
 ,
, - Débora Bicudo Faria-Schützer
 ,
, - Luiz Gustavo Oliveira Brito
 ,
, - Fernanda Garanhani Surita

Views230

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleNon-pharmacological Interventions for Improving Sleep Quality During Pregnancy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(8):776-784
- Daiane Sofia Morais Paulino
 ,
, - Carolina Bicudo Borrelli
 ,
, - Débora Bicudo Faria-Schützer
 ,
, - Luiz Gustavo Oliveira Brito
 ,
, - Fernanda Garanhani Surita

Views230Abstract
Objective
To investigate the effect of non-pharmacological interventions to improve sleep quality during pregnancy.
Data sources
A search was made in the NCBI/PubMed, ClinicalTrials.gov, Embase, BVS, and Web of Science databases. There were no limitations regarding language, sample size, and type of non-pharmacological intervention. We have included prospective clinical trials between July 2014 and July 2019.
Selection of studies
This study was registered in the Prospective International Registration of Systematic Reviews (PROSPERO) database was performed. Publication bias was also assessed with funnel plots. the primary outcome was the total score in the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) before and after intervention. Risk of bias and the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development, and Evaluation (GRADE) criteria were used for assessing methodological quality. From the 28 retrieved studies, we have selected 8 for qualitative analysis and 6 for meta-analysis.
Data collection
Two independent reviewers performed the study selection. In the case of disagreement, a third senior reviewer was consulted. The study was initially assessed based on the title, followed by abstract. Lastly, the full text was assessed to be included.
Data Synthesis
A significant improvement on the sleep quality (PSQI score) was observed when all interventions were grouped (MD = -3.03, 95%CI -4.15 to -1.92, n= 623, i2= 84%, p< 0.001). Analysis by subgroup (music listening: MD = -1.96, 95% CI -3.27 to -0.65, n= 207, i2= 67%, p= 0.003 and other interventions: MD = -3.66, 95% CI -4.93 to -2.40, n= 416, i2 = 80%, p< 0.001) showed an improvement, with high heterogeneity. Risk of bias has shown performance and detection bias for almost studies, and GRADE evidence was very low for all analyzed variables.
Conclusion
Non-pharmacological interventions—listening to music, physical exercise, relaxation exercises, lettuce seed, sleep hygiene, and acupressure—are effective for improving sleep quality during pregnancy.
Key-words Meta-analysisnon-pharmacological interventionsPregnant womensleep qualitysystematic reviewSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Daiane Sofia Morais Paulino
-
Original Article07-07-2022
Increment of Maternal Mortality Among Admissions for Childbirth in Low-risk Pregnant Women in Brazil: Effect of COVID-19 Pandemic?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(8):740-745
Views154PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 4
- Policy Citations: 1
- Captures
- Readers: 60
- Social Media
- Shares, Likes & Comments: 2


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleIncrement of Maternal Mortality Among Admissions for Childbirth in Low-risk Pregnant Women in Brazil: Effect of COVID-19 Pandemic?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(8):740-745
Views154See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess the possible impact of the COVID-19 pandemic on maternal mortality among admissions for childbirth in 2020 in relation of the last 10 years.
Methods
An ecological study with pregnant women who underwent hospital births at the Brazilian unified public health service (SUS, in the Portuguese acronym) in Brazil from 2010 to 2020. The mortality among admissions for childbirth was obtained based on the number of admissions for childbirth with reported death as outcome divided by the total number of admissions. The underlying gestational risk and route of delivery were considered based on the national surveillance system. The average mortality for the period between 2010 and 2019 (baseline) was compared with the rate of deaths in 2020 (1st pandemic year); the rate ratio was interpreted as the risk of death in 2020 in relation to the average of the previous period (RR), with 95% confidence intervals (CIs).
Results
In 2020, the 1st year of the COVID-19 pandemic, 1,821,775 pregnant women were hospitalized for childbirth and 651 deaths were reported, which represents 8.7% of the total hospitalizations and 11.3% of maternal deaths between 2010 and 2020. There was an increase in maternal mortality after births in 2020 compared with the average for the period between 2010 and 2019, specially in low-risk pregnancies, both in vaginal (RR = 1.60; 95%CI:1.39–1.85) and cesarean births (RR = 1.18; 95%CI:1.04–1.34).
Conclusion
Maternal mortality among admissions for childbirth according to SUS data increased in 2020 compared with the average between 2010 and 2019, with an increment of 40% in low-risk pregnancies. The increase was of 18% after cesarean section and of 60% after vaginal delivery.
PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 4
- Policy Citations: 1
- Captures
- Readers: 60
- Social Media
- Shares, Likes & Comments: 2


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article10-18-2021
Placental Findings in Preterm and Term Preeclampsia: An Integrative Review of the Literature
- Luciana Pietro
 ,
, - José Paulo de Siqueira Guida
 ,
, - Guilherme de Moraes Nobrega
 ,
, - Arthur Antolini-Tavares
 ,
, - Maria Laura Costa

Views223

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticlePlacental Findings in Preterm and Term Preeclampsia: An Integrative Review of the Literature
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(7):560-569
- Luciana Pietro
 ,
, - José Paulo de Siqueira Guida
 ,
, - Guilherme de Moraes Nobrega
 ,
, - Arthur Antolini-Tavares
 ,
, - Maria Laura Costa

Views223Abstract
Introduction
Preeclampsia (PE) is a pregnancy complication associated with increased maternal and perinatal morbidity and mortality. The disease presents with recent onset hypertension (after 20 weeks of gestation) and proteinuria, and can progress to multiple organ dysfunction, with worse outcomes among early onset preeclampsia (EOP) cases (<34 weeks). The placenta is considered the root cause of PE; it represents the interface between the mother and the fetus, and acts as a macromembrane between the two circulations, due to its villous and vascular structures. Therefore, in pathological conditions, macroscopic and microscopic evaluation can provide clinically useful information that can confirm diagnosis and enlighten about outcomes and future therapeutic benefit.
Objective
To perform an integrative review of the literature on pathological placental findings associated to preeclampsia (comparing EOP and late onset preeclampsia [LOP]) and its impacts on clinical manifestations.
Results:
Cases of EOP presented worse maternal and perinatal outcomes, and pathophysiological and anatomopathological findings were different between EOP and LOP placentas, with less placental perfusion, greater placental pathological changes with less villous volume (villous hypoplasia), greater amount of trophoblastic debris, syncytial nodules, microcalcification, villous infarcts, decidual arteriolopathy in EOP placentas when compared with LOP placentas. Clinically, the use of low doses of aspirin has been shown to be effective in preventing PE, as well asmagnesium sulfate in preventing seizures in cases of severe features.
Conclusion
The anatomopathological characteristics between EOP and LOP are significantly different, with large morphological changes in cases of EOP, such as
Key-words anatomopathological characteristicsmaternal mortality and morbidityPlacentapreeclampsia early onsetpreeclampsia late onsetSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Luciana Pietro
-
Case Report06-18-2021
Uterine Rescue in High-Risk Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia Treated with EMA-CO by Uterine Arteries Embolization due to Arteriovenous Malformations
- Arlley Cleverson Belo da Silva
 ,
, - Jurandir Piassi Passos
 ,
, - Roney Cesar Signorini Filho
 ,
, - Antonio Braga
 ,
, - Rosiane Mattar
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Sue Yazaki Sun

Views180

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Case ReportUterine Rescue in High-Risk Gestational Trophoblastic Neoplasia Treated with EMA-CO by Uterine Arteries Embolization due to Arteriovenous Malformations
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(4):323-328
- Arlley Cleverson Belo da Silva
 ,
, - Jurandir Piassi Passos
 ,
, - Roney Cesar Signorini Filho
 ,
, - Antonio Braga
 ,
, - Rosiane Mattar
 ,
, - Sue Yazaki Sun

Views180Abstract
Complete hydatidiform mole (CHM) is a rare type of pregnancy, in which 15 to 20% of the cases may develop into gestational trophoblastic neoplasia (GTN). The diagnostic of GTN must be done as early as possible through weekly surveillance of serum hCG after uterine evacuation.We report the case of 23-year-old primigravida, with CHM but without surveillance of hCG after uterine evacuation. Two months later, the patient presented to the emergency with vaginal bleeding and was referred to the Centro de Doenças Trofoblásticas do Hospital São Paulo. She was diagnosed with high risk GTN stage/score III:7 as per The International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics/World Health Organization (FIGO/WHO). The sonographic examination revealed enlarged uterus with a heterogeneous mass constituted of multiple large vessels invading and causing disarrangement of the myometrium. The patient evolved with progressive worsening of vaginal bleeding after chemotherapy with etoposide, methotrexate, actinomycin D, cyclophosphamide and vincristine (EMA-CO) regimen. She underwent blood transfusion and embolization of uterine arteries due to severe vaginal hemorrhage episodes, with complete control of bleeding. The hCG reached a negative value after the third cycle, and there was a complete regression of the anomalous vascularization of the uterus as well as full recovery of the uterine anatomy. The treatment in a reference center was essential for the appropriate management, especially regarding the uterine arteries embolization trough percutaneous femoral
Key-words EMA-CO protocolGestational trophoblastic diseaseGestational trophoblastic neoplasiaHigh risk pregnancyUterine artery embolizationSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Arlley Cleverson Belo da Silva
-
Review Article06-03-2022
Relation between Selenium and Female Fertility: A Systematic Review
- Luiz Gustavo Lima
 ,
, - André Amaro Mamédio dos Santos
 ,
, - Tiago Daniel Gueiber
 ,
, - Ricardo Zanetti Gomes
 ,
, - Camila Marinelli Martins
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Andrielle Cristina Chaikoski

Views266

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleRelation between Selenium and Female Fertility: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(7):701-709
- Luiz Gustavo Lima
 ,
, - André Amaro Mamédio dos Santos
 ,
, - Tiago Daniel Gueiber
 ,
, - Ricardo Zanetti Gomes
 ,
, - Camila Marinelli Martins
 ,
, - Andrielle Cristina Chaikoski

Views266See moreAbstract
Objective
To analyze the influence of selenium in female fertility.
Conclusion
Selenium supplementation is promising in women with this micronutrient deficiency to promote improvement of the reproductive efficiency and prevent damage to the pregnancy. Further studies on this theme are still required.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Luiz Gustavo Lima
Search
Search in:
Tag Cloud
Pregnancy (252)Breast neoplasms (104)Pregnancy complications (104)Risk factors (103)Menopause (88)Ultrasonography (83)Cesarean section (78)Prenatal care (71)Endometriosis (70)Obesity (61)Infertility (57)Quality of life (55)prenatal diagnosis (51)Women's health (48)Postpartum period (46)Maternal mortality (45)Pregnant women (45)Breast (44)Prevalence (43)Uterine cervical neoplasms (43)

