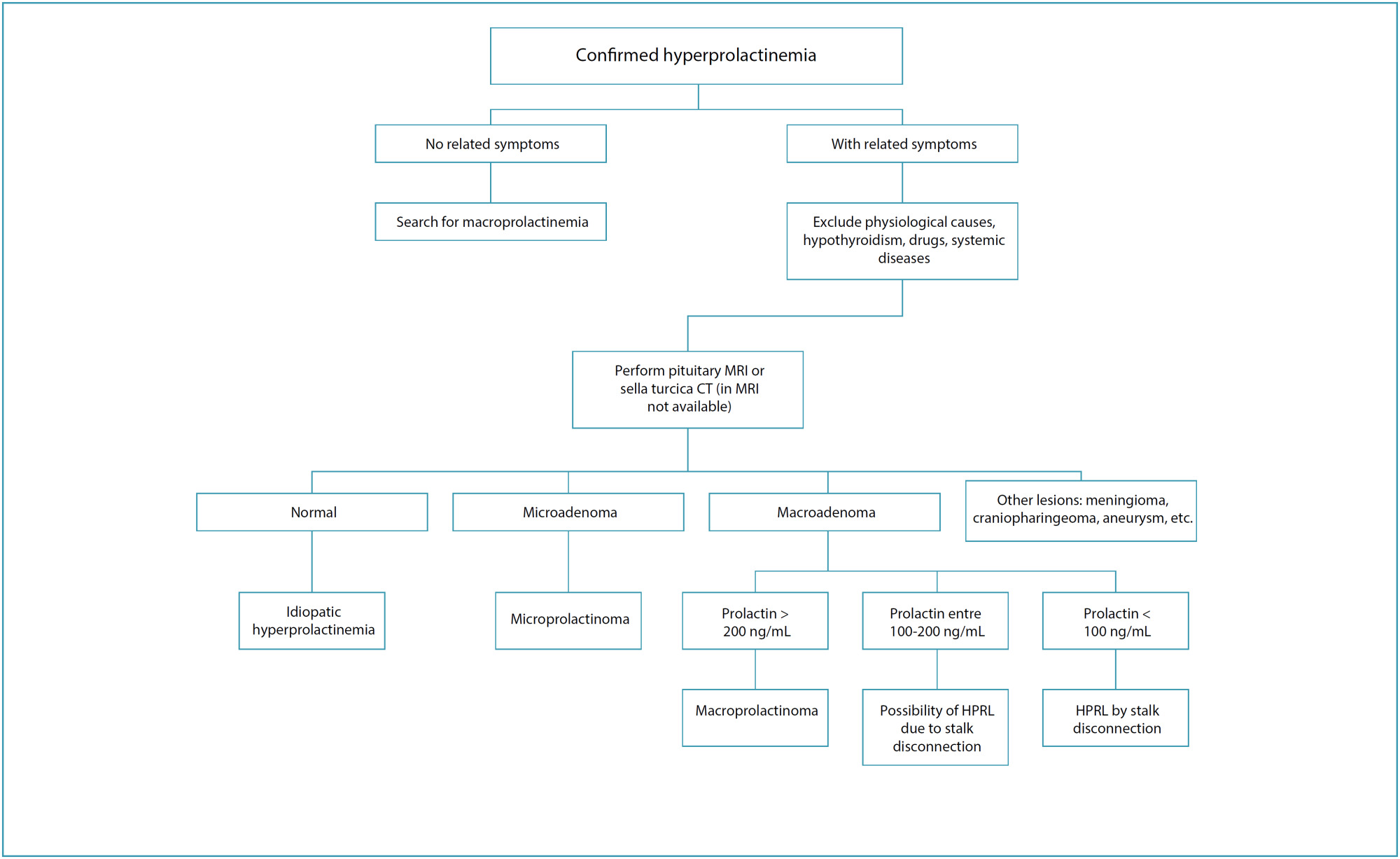
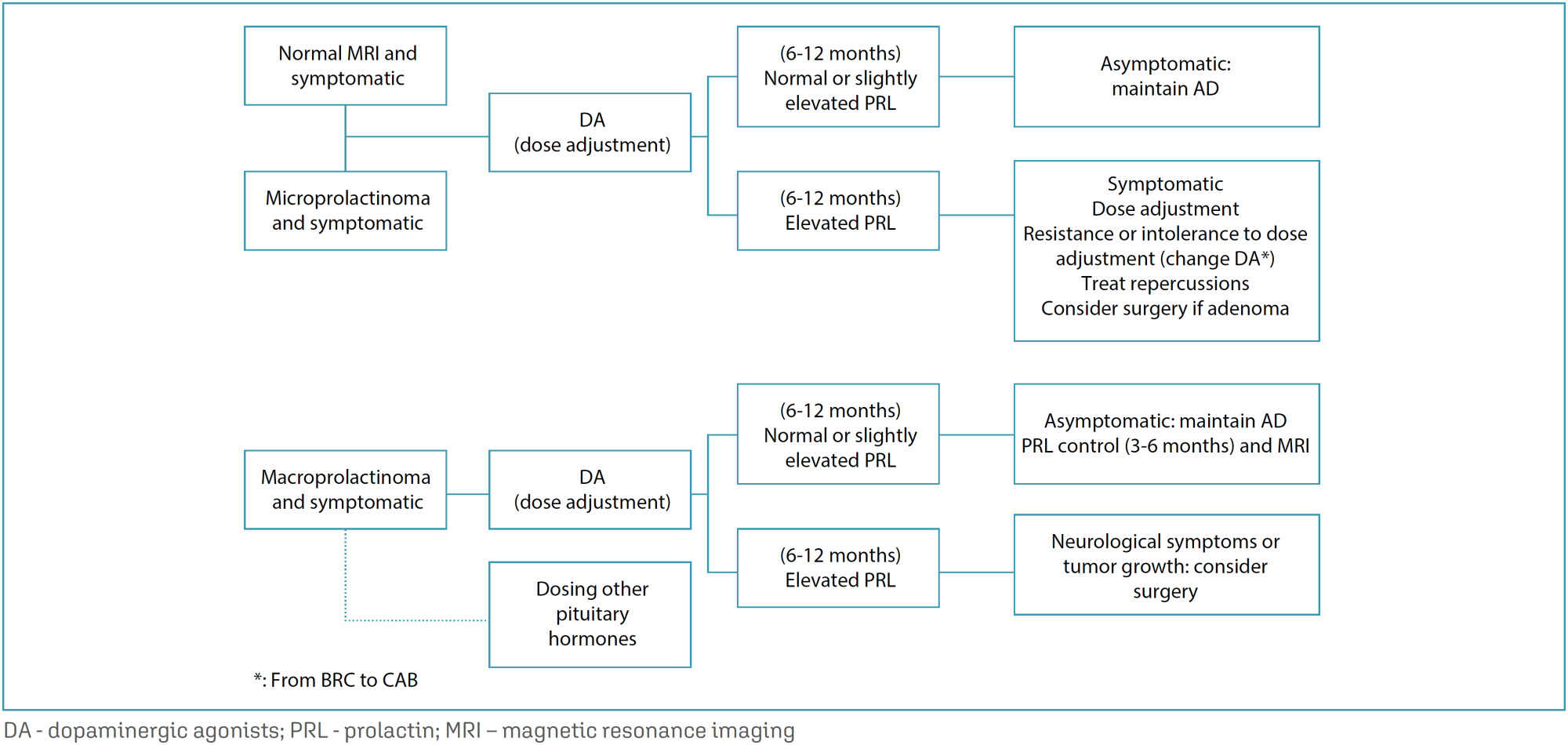
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT
Challenges and strategies in adolescent vaccination: Number 12 – 2024
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS12
11-14-2024
Summary
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTChallenges and strategies in adolescent vaccination: Number 12 – 2024
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS12
11-14-2024 -
Letter to the Editor
The gynecologist and cancer in women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo92
10-23-2024
Summary
Letter to the EditorThe gynecologist and cancer in women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo92
10-23-2024Views103Cervical cancer continues to claim an alarming number of victims around the world, especially among poor women. In Brazil, in 2022, an incidence of 16.3/100,000 women was recorded,() with a projection for 2023 of 17,010 new cases, corresponding to a rate of 15.38/100,000, representing 7% of tumors in women.In the Brazilian reality, where there is […]See more -
Original Article
Nipple-sparing mastectomy in young versus elderly patients
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo90
10-23-2024
Summary
Original ArticleNipple-sparing mastectomy in young versus elderly patients
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo90
10-23-2024Views117See moreAbstract
Objective:
In this study, we compared indications and outcomes of 115 young (< 40 years) versus 40 elderly (> 60 years) patients undergoing nipple-sparing mastectomy (NSM) as risk-reducing surgery or for breast cancer (BC) treatment.
Methods:
Between January 2004 and December 2018, young and elderly patients undergoing NSM with complete data from at least 6 months of follow-up were included.
Results:
BC treatment was the main indication for NSM, observed in 85(73.9%) young versus 33(82.5%) elderly patients, followed by risk-reducing surgery in 30(26.1%) young versus 7(17.5%) elderly patients. Complication rates did not differ between the age groups. At a median follow-up of 43 months, the overall recurrence rate was higher in the younger cohort (p = 0.04). However, when stratified into local, locoregional, contralateral, and distant metastasis, no statistical difference was observed. During the follow-up, only 2(1.7%) young patients died.
Conclusion:
Our findings elucidate a higher recurrence rate of breast cancer in younger patients undergoing NSM, which may correlate with the fact that age is an independent prognostic factor. High overall survival and low complication rates were evidenced in the two groups showing the safety of NSM for young and elderly patients.
-
Original Article
Access and adequacy of antenatal care in a city in Brazil during two phases of the COVID-19 pandemic
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo87
10-23-2024
Summary
Original ArticleAccess and adequacy of antenatal care in a city in Brazil during two phases of the COVID-19 pandemic
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo87
10-23-2024Views146Abstract
Objective:
To compare access and suitability of antenatal care between years 2020 and 2022 among postpartum individuals at a Hospital in Florianopolis, and evaluate factors associated with antenatal suitability.
Methods:
Observational, cross-sectional, and quantitative study carried out in 2022. Collected data were compared with the database of a previous similar study carried out in the same setting in 2020. Data were extracted from medical records and prenatal booklets, in addition to a face-to-face questionnaire. Adequacy was measured using the Carvalho and Novaes index and health access was qualitatively evaluated. Socio-demographic and antenatal variables were analyzed. A statistical significance level of 0.05 was considered. Open-ended questions were categorized for analysis.
Results:
395 postpartum individuals were included. Antenatal care was adequate for 48.6% in 2020 and 69.1% in 2022. Among the barriers to access, 56% reported difficulty in scheduling appointments and/or exams and 23% complained of reduced healthcare staff due to strikes, COVID-19, among others. Adequate antenatal care was associated with being pregnant in 2022, being referred to high-risk units (PNAR), and not reporting difficulties in access. Also, it was associated with twice the chance of investigation for gestational diabetes (GDM) and syphilis.
Conclusion:
The 2022 post-vaccination period showed higher antenatal adequacy. The main difficulty for postpartum individuals was scheduling appointments and/or exams. Having antenatal care in 2022, no reports of difficulty in access, and follow-up at a high-risk unit were associated with antenatal adequacy.
Key-words COVID-19Delivery of health careDiabetesGestationalpandemicsPostpartum periodPregnancyPrenatal caresurveys and questionnairesVaccinationSee more -
Original Article
The role of HIV as an independent risk factor to cervical HSIL recurrence
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo85
10-23-2024
Summary
Original ArticleThe role of HIV as an independent risk factor to cervical HSIL recurrence
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo85
10-23-2024Views190ABSTRACT
Objective:
To evaluate the role of being human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) positive for predicting the risk of recurrence in women with a cervical high grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HSIL) diagnosis.
Methods:
Retrospective observational case-control study, comprising HIV positive (case) and HIV negative (control) women in a 1:4 ratio. Women assisted by the Erasto Gaertner Hospital, between 2009-2018, with cervical HSIL diagnosis, submitted to treatment by Loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP), and with a minimum follow-up of 18 months, were included. The immunological status, number and time to recurrence were analyzed, with p<0.05 considered significant. In a second analysis, only patients with free margins were evaluated.
Results:
The sample consisted of 320 women (64 cases and 256 controls). Presence of HIV, CD4 levels <200 and detectable viral load (CV) were associated with high risk of recurrence, with odds ratio (OR) of 5.4 (p<0.001/95CI:2.8-10); 3.6 (p<0.001 /IC95:0.6-21.1) and 1.8 (p=0.039 /IC95:0.3-9.3), respectively. In the sample with free margins (n=271), this risk was also higher among seropositive patients, with OR 4.18 (p=0.001/95CI:1.8-9.2).
Conclusion:
HIV is an independent risk factor for cervical HSIL recurrence and reduced disease-free survival time. Glandular involvement, compromised margins, undetectable CV and CD4<200 also increase the risk of relapse.
Key-words Disease-free survivalElectrosurgeryExcision marginsHIV infectionsRecurrenceRisk factorsSquamous intraepithelial lesionsUterine cervical neoplasmsSee more -
Original Article
Assessment of risk factors associated with post-molar gestational trophoblastic neoplasia: a retrospective cohort
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo83
10-23-2024
Summary
Original ArticleAssessment of risk factors associated with post-molar gestational trophoblastic neoplasia: a retrospective cohort
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo83
10-23-2024Views116ABSTRACT
Objective:
Evaluate the risk factors for the development of post-molar gestational trophoblastic neoplasia.
Methods:
Retrospective cohort study with 320 women with gestational trophoblastic disease (GTD) followed in a tertiary hospital from January 2005 to January 2020. Data referring to the women’s sociodemographic profile, clinical, laboratory and treatment aspects and types of GTD were analyzed.
Results:
The mean age of women with the benign form was 26.4±8.6 years and with the malignant forms 26.9±8.5 years (p=0.536). Most women with malignant forms came from regions further away from reference center (p=0.012), had vesicle elimination at the time of diagnosis (p=0.028) and needed more than one uterine evacuation (p<0.001) when compared to the benign forms. There was no difference between laboratory tests in both forms. Being between 30 and 39 years old increased the chance of developing invasive mole by 2.5 (p=0.004; 95%CI:1.3–4.9) and coming from regions far from reference center by 4.01 (p=0.020; CI95%: 1.2-12.9). The women with the highest risk of malignant forms were those with the longest time of become normal on human gonadotrophic hormone (hCG) testing (each week the risk increases 1.3 times; p<0.001, 95%CI: 1.2-1.3).
Conclusion:
The prolonged hCG fall curve is the main indicator of an increased chance of GTN. Women from regions further away from reference center have a greater chance of developing malignant forms, probably due to the difficulty in accessing the reference center and, therefore, adequate follow-up that would allow early identification of more serious cases.
Key-words Gestational trophoblastic diseaseGestational trophoblastic neoplasmHydatidiform mole, invasiveSee more -
Original Article
Validation of Brazilian Version of the Sexual Desire Inventory 2 (SDI-2)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo78
10-23-2024
Summary
Original ArticleValidation of Brazilian Version of the Sexual Desire Inventory 2 (SDI-2)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo78
10-23-2024Views180ABSTRACT
Objective:
To traslate and validate of the Brazilian version of the SDI-2.
Methods:
This was a cross-sectional study. The cultural adaptation considered the stages of initial translation, synthesis of translations, evaluation by a committee of experts from different regions of Brazil, back-translation, and pre-test. The content validity and psychometric proprieties was assessed.
Results:
Ten specialists participated in the cultural adaptation of the SDI-2. The content validity showed a Content Validity Ratio (CVR) ≥ 0.75 (p = 0.05). A total of 674 subjects participated in the field study. The Exploratory Factorial Analysis (EFA) presented factor loads ≥ 0.445, and commonalities ≥ 0.40; and two dimensions represented 77% of the total variance explained. The Confirmatory Factorial Analysis CFA presented X2/df = 4.265; the Root Mean Square Error of Approximation RMSEA = 0.110; the Non-Normed Fit Index NNFI = 0.946; the Comparative Fit Index (CFI) = 0.963; the Goodness of Fit Index GFI = 0.986; and the Adjusted Goodness of Fit Index AGFI = 0.979 for a two-factor model. The coefficient values for the total SDI-2 score were 0.91 for Cronbach’s alpha, 0.91 for McDonald’s Omega, and 0.97 for the Greatest Lower Bound GLB coefficients. The invariance between sexes was 0.01 for the ΔCFI and ΔRMSEA, showing model stability for these two populations.
Conclusion:
The Brazilian version of the SDI-2 is self-report, valid, reliable and invariant across sex.
Key-words cross cultural comparisonLibidoPsychometricsSexual behaviorSexual desiresurveys and questionnairesSee more -
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT
Immunization in women’s lives: present and future
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS10
10-15-2024
Summary
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTImmunization in women’s lives: present and future
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS10
10-15-2024Views197See moreKey points
•The negative impact of infectious diseases and their immunoprevention during the different stages of a woman’s life requires a broad approach including adolescence, adulthood, pregnancy and the postmenopausal phase.
•Immunization of pregnant women should be a priority for the protection of the maternal-fetal dyad, especially in regions with high rates of infections preventable by immunization.
•Brazil has one of the most comprehensive vaccination programs in the world – the National Immunization Program (Programa Nacional de Imunizações, PNI) – that serves all age groups: newborns, children, adolescents, adults, pregnant women and older adults, as well as groups with special needs, such as adolescents, pregnant and older adult women.
•However, vaccination coverage remains below ideal for all available vaccines, especially among adolescents and pregnant women, and Febrasgo is committed to collaborating with the PNI to combat vaccine hesitancy.
•The gynecologist/obstetrician is the reference physician for women, therefore the access to information and updates regarding all vaccines recommended for their patients is extremely important for this professional, aiming at the greatest possible protection.
•The objective of this Febrasgo Position Statement is to bring an update to women’s vaccination schedule, covering some vaccines that are available, including new approved vaccines and those in the commercialization phase.
•This work is a compilation of the First Febrasgo Scientific Immunization Forum held in the city of São Paulo in October 2023 with the objective to update recommendations for vaccines in use and new innovative vaccines soon to be available.
Search
Search in:
Tag Cloud
Pregnancy (251)Breast neoplasms (104)Pregnancy complications (103)Risk factors (103)Menopause (87)Ultrasonography (83)Cesarean section (77)Prenatal care (71)Endometriosis (70)Obesity (60)Infertility (56)Quality of life (53)prenatal diagnosis (51)Women's health (48)Maternal mortality (45)Pregnant women (45)Breast (44)Postpartum period (44)Uterine cervical neoplasms (43)Prevalence (42)