- Recent Articles
- Most Citedi
- Most Visitedi
- Future Articles
-
10-10-2000
Preditores Clínicos, Histopatológicos e Curva de Regressão do beta-hcg para Tumor Trofoblástico Gestacional em Portadoras de Mola Hidatiforme Completa
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):119-119
Abstract
Preditores Clínicos, Histopatológicos e Curva de Regressão do beta-hcg para Tumor Trofoblástico Gestacional em Portadoras de Mola Hidatiforme Completa
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):119-119
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000200014
Views50Preditores Clínicos, Histopatológicos e Curva de Regressão do b-hcg para Tumor Trofoblástico Gestacional em Portadoras de Mola Hidatiforme Completa […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
10-10-2000
Bacteriúria após Drenagem Vesical no Pós-Operatório de Cirurgias Ginecológicas Vaginais: Comparação entre as Vias Transuretral e Suprapúbica
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):118-118
Abstract
Bacteriúria após Drenagem Vesical no Pós-Operatório de Cirurgias Ginecológicas Vaginais: Comparação entre as Vias Transuretral e Suprapúbica
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):118-118
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000200013
Views58Bacteriúria após Drenagem Vesical no Pós-Operatório de Cirurgias Ginecológicas Vaginais: Comparação entre as Vias Transuretral e Suprapúbica […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
10-10-2000
Avaliação do Risco de Parto Prematuro através da Autopalpação e da Monitorização Computadorizada da Contração Uterina
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):118-118
Abstract
Avaliação do Risco de Parto Prematuro através da Autopalpação e da Monitorização Computadorizada da Contração Uterina
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):118-118
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000200012
Views56Avaliação do Risco de Parto Prematuro através da Autopalpação e da Monitorização Computadorizada da Contração Uterina […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
10-10-2000
Estudo Transversal de Base Populacional de Mulheres Climatéricas Pré e Perimenopáusicas da Cidade de Passo Fundo
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):117-117
Abstract
Estudo Transversal de Base Populacional de Mulheres Climatéricas Pré e Perimenopáusicas da Cidade de Passo Fundo
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):117-117
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000200011
Views51Estudo Transversal de Base Populacional de Mulheres Climatéricas Pré e Perimenopáusicas da Cidade de Passo Fundo […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
10-10-2000
Estudo Transversal de Base Populacional de Mulheres Climatéricas Pré e Perimenopáusicas da Cidade de Passo Fundo
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):117-117
Abstract
Estudo Transversal de Base Populacional de Mulheres Climatéricas Pré e Perimenopáusicas da Cidade de Passo Fundo
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):117-117
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000200011
Views40Estudo Transversal de Base Populacional de Mulheres Climatéricas Pré e Perimenopáusicas da Cidade de Passo Fundo […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
10-10-2000
Estudo de Proteínas do Fluido Peritoneal pela Técnica de Eletroforese em Mulheres Inférteis com Endometriose
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):117-117
Abstract
Estudo de Proteínas do Fluido Peritoneal pela Técnica de Eletroforese em Mulheres Inférteis com Endometriose
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):117-117
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000200010
Views49Estudo de Proteínas do Fluido Peritoneal pela Técnica de Eletroforese em Mulheres Inférteis com Endometriose […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Case Report10-10-2000
Takayasu’s Arteritis and Pregnancy: a Case Report
- Mônica de Souza Visniewski Ximenes,
- Sinval Ferreira de Oliveira,
- Antônio Vieira Machado,
- Mário Dias Corrêa,
- Júlio César de Faria Couto
Abstract
Case ReportTakayasu’s Arteritis and Pregnancy: a Case Report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):113-116
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000200009
- Mônica de Souza Visniewski Ximenes,
- Sinval Ferreira de Oliveira,
- Antônio Vieira Machado,
- Mário Dias Corrêa,
- Júlio César de Faria Couto
Views67See moreTakayasu’s arteritis is an idiopathic occlusive inflammation of the aorta and its major branches. The disease shows a striking predilection for young women and thus is occasionally associated with pregnancy. The authors describe a case of a pregnant patient with Takayasu’s arteritis. The pregnancy was accompanied by a multidisciplinary group in a satisfactory way. There was only one hospitalization due to an exacerbation of the symptoms during the 32nd week of gestation, controlled by medical treatment. A vaginal delivery occurred at 37 weeks. A live infant weighing 2,750 g was delivered and the patient had an uncomplicated course.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article10-10-2000
Effects of Domperidone on Pregnant Albino Rats Pregnancy
- Arykerne Chamon do Carmo,
- Danilo Nagib Salomão Paulo,
- Ricardo Martins Oliveira-Filho,
- Manuel de Jesus Simões,
- Luiz Kulay Júnior
Views104

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleEffects of Domperidone on Pregnant Albino Rats Pregnancy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):107-111
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000200008
- Arykerne Chamon do Carmo,
- Danilo Nagib Salomão Paulo,
- Ricardo Martins Oliveira-Filho,
- Manuel de Jesus Simões,
- Luiz Kulay Júnior
Views104See morePurpose: the aim of the present work was to study the chronic action of the antiemetic domperidone on the pregnancy of albino rats. Methods: fifty albino, pregnant Wistar rats were randomly allocated to five groups: GI (control I) = intact rats; GII (control II) = rats receiving the drug vehicle (distilled water) by gavage at the same schedule of the experimental groups; rats in groups GIII, GIV and GV were treated with domperidone by gavage, 2, 6 and 12 mg/kg per day, respectively, divided into 4 daily doses, always in 1 ml of distilled water, from time zero up to the 20th day of pregnancy. The evolution of body weight gain was followed throughout and the animals were sacrificed at term (20th day) by deep ether anesthesia. Number of fetuses, placenta and implantation sites, placenta and fetus weight, fetal malformations and maternal and fetal mortality were evaluated. Results: we observed only intrauterine fetal mortality with 14, 26 and 32 in 74, 60 and 57 newborns of the groups III, IV and V, respectively. Conclusion: though the results of animal experimentation cannot directly be transposed to human conditions, this paper calls attention to the need for a safe judgement when prescribing domperidone to a first-trimester pregnant patient in order to reduce her emetic crises.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
-
Original Article07-20-2004
Search for human papillomavirus in samples of normal endometrial tissue and tissue with carcinoma by the PCR technique
- Edison Natal Fedrizzi,
- Newton Sérgio de Carvalho,
- Luisa Lina Villa,
- Irene Vieira de Souza,
- Ana Paula Martins Sebastião
Views125912

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleSearch for human papillomavirus in samples of normal endometrial tissue and tissue with carcinoma by the PCR technique
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(4):277-287
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000400003
- Edison Natal Fedrizzi,
- Newton Sérgio de Carvalho,
- Luisa Lina Villa,
- Irene Vieira de Souza,
- Ana Paula Martins Sebastião
Views125912See moreOBJECTIVE: to compare the prevalence of DNA of human papillomavirus (HPV), in samples of normal endometrial tissue, and tissue with endometrial carcinoma of women submitted to surgical treatment (hysterectomy), or between endometrial carcinoma and benign disease, through the PCR technique. METHODS: this is an observational control-case study where 100 women (50 with endometrial carcinoma and 50 with normal endometrial tissue) were analyzed for the detection of HPV DNA in samples of endometrial tissue kept in paraffin blocks by the PCR technique. The cases of endometrial carcinoma with uncertain primary site of the lesion as well as the cases with previous or current history of pre-neoplasic lesions or carcinoma of the lower genital tract were excluded. Variables as age, smoking habit, endometrial trophism, squamous differentiation and degree of tumor differentiation were also evaluated. RESULTS: the estimated relative risk of the presence of HPV in the endometrial carcinoma and in the normal endometrial tissue was the same. HPV was detected in 8% of the cases of carcinoma and 10% in the normal endometrial tissue. In spite of HPV having been 3.5 times more detected in women with smoking habit in the group without carcinoma, there was no statistical difference. The presence of HPV was also not correlated with the women’s age, endometrial trophism, squamous differentiation and degree of tumor differentiation. The HPV types 16 (5 cases) and 18 (4 cases) were the viruses most frequently found both in the normal endometrial tissue or in the tissue with carcinoma. No oncogenic low risk virus was detected in the samples. CONCLUSION: The same proportion of HPV is present in the endometrial tissue of women with endometrial cancer and with normal endometrium. It could not be demonstrated a possible correlation of DNA of HPV with the development of endometrial carcinoma.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT04-25-2024
Hyperprolactinemia in women: diagnostic approach
- Andrea Glezer
 ,
, - Heraldo Mendes Garmes
 ,
, - Leandro Kasuki
 ,
, - Manoel Martins
 ,
, - Paula Condé Lamparelli Elias
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Andrea Prestes Nácul

Views1202

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTHyperprolactinemia in women: diagnostic approach
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS04


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 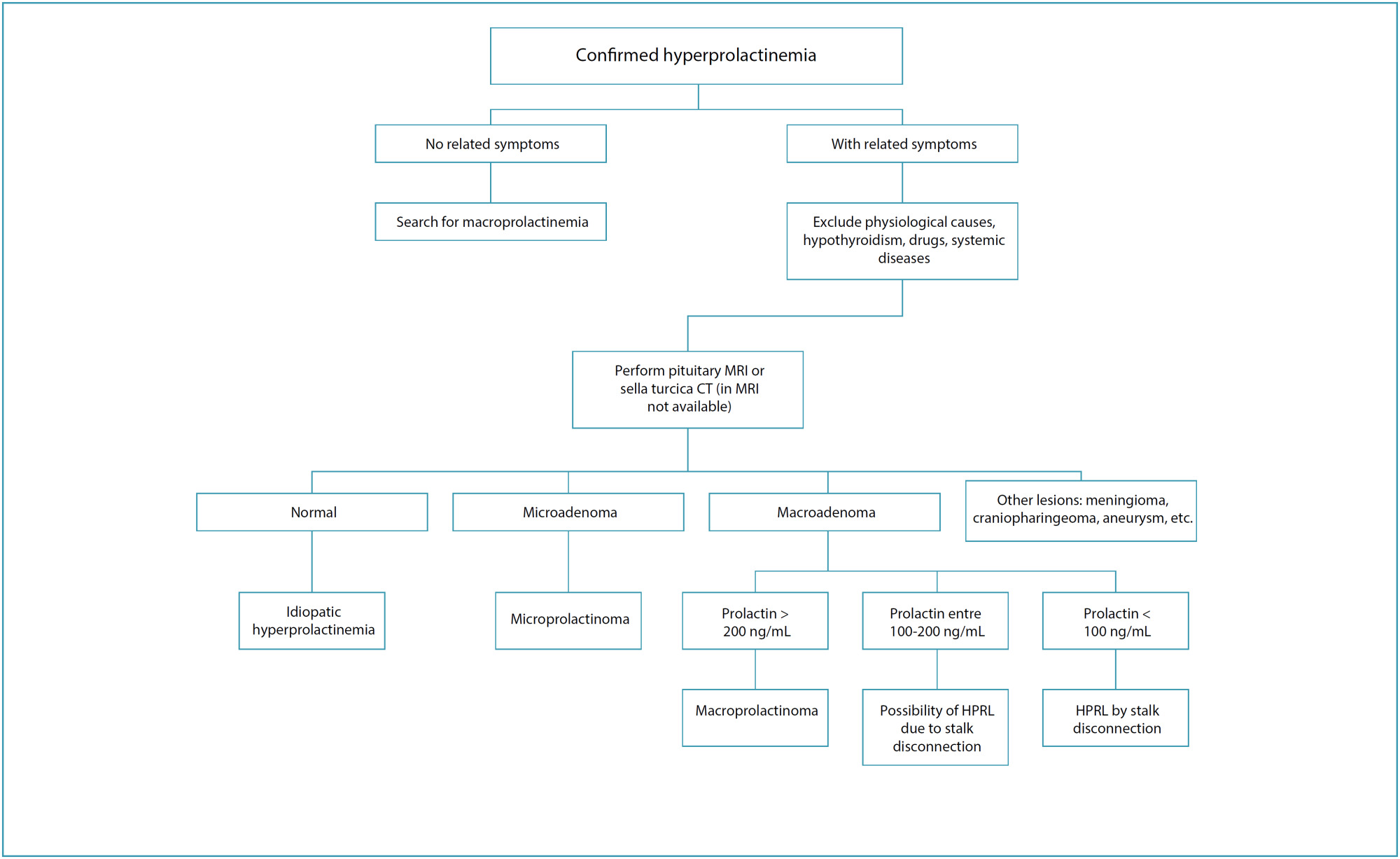
- Andrea Glezer
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT04-25-2024
Hyperprolactinemia in women: treatment
- Cristina Laguna Benetti-Pinto
 ,
, - Andrea Prestes Nácul
 ,
, - Ana Carolina Japur Rosa e Silva
 ,
, - Gustavo Arantes Rosa Maciel
 ,
, - Vania dos Santos Nunes Nogueira
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Andrea Glezer

Views1200

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTHyperprolactinemia in women: treatment
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS05


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 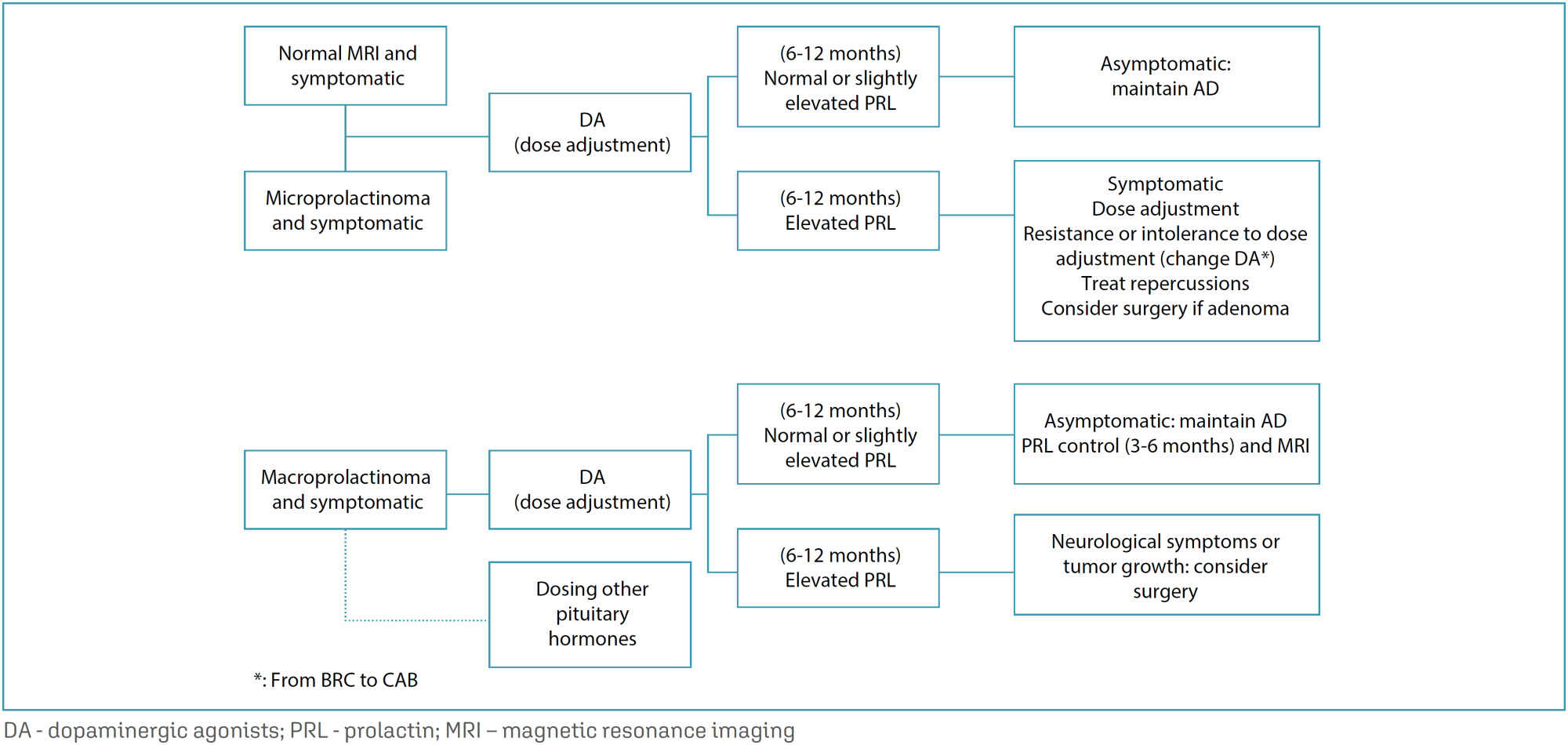
- Cristina Laguna Benetti-Pinto
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT00-00-2024
Breech birth care: Number 1 – 2024
- Álvaro Luiz Lage Alves
 ,
, - Alexandre Massao Nozaki
 ,
, - Carla Betina Andreucci Polido
 ,
, - Lucas Barbosa da Silva
 ,
, - Roxana Knobel

Views1004

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTBreech birth care: Number 1 – 2024
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgofps1


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Álvaro Luiz Lage Alves
-
Letter to the Editor04-09-2024
Letter to Editor: In response to existence of SARS-CoV-2 in the peritoneal fluid
- Gustavo Romero-Velez
 ,
, - Guillermo Ponce de Leon-Ballesteros
 ,
, - Juan Barajas-Gamboa
 ,
, - Jerry Dang
 ,
, - Andrew Strong
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Mathew Kroh

Abstract
Letter to the EditorLetter to Editor: In response to existence of SARS-CoV-2 in the peritoneal fluid
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgo24


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Gustavo Romero-Velez
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT04-02-2024
Use of hormones and risk of venous thromboembolism
- Venina Isabel Poço Viana Leme de Barros
 ,
, - André Luiz Malavasi Longo de Oliveira
 ,
, - Denis Jose do Nascimento
 ,
, - Eduardo Zlotnik
 ,
, - Marcelo Melzer Teruchkin
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Paulo Francisco Ramos Margarido

Views832

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTUse of hormones and risk of venous thromboembolism
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS02
- Venina Isabel Poço Viana Leme de Barros
 ,
, - André Luiz Malavasi Longo de Oliveira
 ,
, - Denis Jose do Nascimento
 ,
, - Eduardo Zlotnik
 ,
, - Marcelo Melzer Teruchkin
 ,
, - Marcos Arêas Marques
 ,
, - Paulo Francisco Ramos Margarido

Views832See moreKey points
•The risk of venous thromboembolism (VTE) is not increased in women using long-acting reversible contraceptive methods (LARCs) with progestogens.
•Oral contraceptives with levonorgestrel or norgestimate confer half the risk of VTE compared to oral contraceptives containing desogestrel, gestodene or drospirenone.
•Progestogen-only pills do not confer an increased risk of VTE.
•Women using transdermal contraceptive patches and combined oral contraceptives (COCs) are at an approximately eight times greater risk of VTE than non-users of hormonal contraceptives (HCs), corresponding to 9.7 events per 10,000 women/years.
•Vaginal rings increase the risk of VTE by 6.5 times compared to not using HC, corresponding to 7.8 events per 10,000 women/years.
•Several studies have demonstrated an increased risk of VTE in transgender individuals receiving hormone therapy (HT).
•Hormone therapy during menopause increases the risk of VTE by approximately two times, and this risk is increased by obesity, thrombophilia, age over 60 years, surgery and immobilization.
•The route of estrogen administration, the dosage and type of progestogen associated with estrogen may affect the risk of VTE in the climacteric.
•Combined estrogen-progesterone therapy increases the risk of VTE compared to estrogen monotherapy.
•Postmenopausal HT increases the risk of thrombosis at atypical sites.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Venina Isabel Poço Viana Leme de Barros
-
Editorial00-00-2024
The path to elimination: FEBRASGO 2023’s targeted strategies against cervical cancer in Brazil
- Agnaldo Lopes da Silva Filho
 ,
, - Cecilia Maria Roteli-Martins
 ,
, - Neila Maria de Góis Speck
 ,
, - Newton Sérgio de Carvalho
 ,
, - Eduardo Batista Cândido
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Júlio César Teixeira

Views820

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
EditorialThe path to elimination: FEBRASGO 2023’s targeted strategies against cervical cancer in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-rbgoedt2


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Agnaldo Lopes da Silva Filho
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT04-02-2024
Vulvovaginitis in pregnant women
- Geraldo Duarte
 ,
, - Iara Moreno Linhares
 ,
, - Regis Kreitchmann
 ,
, - Andréa da Rocha Tristão
 ,
, - Evelyn Traina
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Joelma Queiroz Andrade

Views786

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTVulvovaginitis in pregnant women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2024;46:e-FPS03
- Geraldo Duarte
 ,
, - Iara Moreno Linhares
 ,
, - Regis Kreitchmann
 ,
, - Andréa da Rocha Tristão
 ,
, - Evelyn Traina
 ,
, - Ivete Canti
 ,
, - Marcos Takimura
 ,
, - Joelma Queiroz Andrade

Views786See moreKey points
• The balanced vaginal microbiome is the main factor defending the vaginal environment against infections. Lactobacilli play a key role in this regard, maintaining the vaginal pH within the normal range (3.8 to 4.5).
•Hormonal and immune adaptations resulting from pregnancy influence changes in the vaginal microbiome during pregnancy.
•An altered vaginal microbiome predisposes to human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection.
•Bacterial vaginosis is the main clinical expression of an imbalanced vaginal microbiome.
•Vulvovaginal candidiasis depends more on the host’s conditions than on the etiological agent.
•Trichomonas vaginalis is a protozoan transmitted during sexual intercourse.
•The use of probiotics is not approved for use in pregnant women.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Geraldo Duarte
-
Review Article06-01-2018
Breastfeeding and the Benefits of Lactation for Women’s Health
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):354-359
Views477

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleBreastfeeding and the Benefits of Lactation for Women’s Health
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):354-359
Views477See moreAbstract
The offer of the maternal breast to the baby is an unquestionable right of mothers and their children, and all efforts should bemade to promote, follow and maintain exclusive breastfeeding for up to 6months and supplement it until the child completes 2 years of age. Many publications are available in the literature about the qualities of breast milk, its benefits and health repercussions, stimulating the practice of breastfeeding and supporting campaigns for its implementation. However, although it is widely known that breastfeeding is an important step in the reproductive process of women and its practice offers benefits to both mother and child, most of the available information highlights the benefits of breast milk for children, while mention of the effects of breastfeeding on the health of the mother is usually neglected. Thus, the objective of the present study is to highlight the multiple benefits of breastfeeding for the physical and emotional health of the nursing mother. The authors consulted articles published in the databases PubMed, Virtual Health Library andWeb of Science using the keywords breastfeeding, breast milk, lactation and maternal health.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article09-01-2017
Preeclampsia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(9):496-512
Views501

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticlePreeclampsia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(9):496-512
Views501Abstract
The authors review hypertensive disease during pregnancy with an academic and practical view, and using the best evidence available. This disease, which is the most important clinical disease in Brazilian pregnant women, may have its incidence reduced with prevention through the use of calcium and aspirin in pregnant women at risk. Previously, it was a disease that presented with hypertension with proteinuria, but it has now been classified with new clinical parameters besides proteinuria. Morbidity and mortality should be reduced in a continental country such as Brazil using protocols for the early treatment of complications by calculating severe outcomes in preeclampsia. The early treatment of acute hypertension, use of magnesium sulfate and early hospitalization in cases of preeclampsia are concepts to pursue the reduction of our pregnant women’s mortality.
Key-words HELLP syndromeHigh risk pregnancyPreeclampsiapregnancy arterial hypertensionPregnancy complicationsSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 
-
Review Article09-25-2020
Primary Dysmenorrhea: Assessment and Treatment
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(8):501-507
Views481

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticlePrimary Dysmenorrhea: Assessment and Treatment
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(8):501-507
Views481See moreAbstract
Primary dysmenorrhea is defined asmenstrual pain in the absence of pelvic disease. It is characterized by overproduction of prostaglandins by the endometrium, causing uterine hypercontractility that results in uterine muscle ischemia, hypoxia, and, subsequently, pain. It is the most common gynecological illness in women in their reproductive years and one of the most frequent causes of pelvic pain; however, it is underdiagnosed, undertreated, and even undervalued by women themselves, who accept it as part of themenstrual cycle. It hasmajor implications for quality of life, such as limitation of daily activities and psychological stress, being one of themain causes of school and work absenteeism. Its diagnosis is essentially clinical, based on the clinical history and normal physical examination. It is important to exclude secondary causes of dysmenorrhea. The treatment may have different approaches (pharmacological, nonpharmacological and surgical), but the first line of treatment is the use of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), and, in cases of women who want contraception, the use of hormonal contraceptives. Alternative treatments, such as topical heat, lifestyle modification, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, dietary supplements, acupuncture, and acupressure, may be an option in cases of conventional treatments’ contraindication. Surgical treatment is only indicated in rare cases of women with severe dysmenorrhea refractory to treatment.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article09-01-2018
Multiple Pregnancy: Epidemiology and Association with Maternal and Perinatal Morbidity
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):554-562
Views374

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleMultiple Pregnancy: Epidemiology and Association with Maternal and Perinatal Morbidity
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):554-562
Views374See moreAbstract
Twin pregnancy accounts for 2 to 4% of total births, with a prevalence ranging from 0.9 to 2.4% in Brazil. It is associated with worse maternal and perinatal outcomes. Many conditions, such as severe maternal morbidity (SMM) (potentially life-threatening conditions and maternal near-miss) and neonatal near-miss (NNM) still have not been properly investigated in the literature. The difficulty in determining the conditions associated with twin pregnancy probably lies in its relatively low occurrence and the need for larger population studies. The use of the whole population and of databases from large multicenter studies, therefore, may provide unprecedented results. Since it is a rare condition, it ismore easily evaluated using vital statistics from birth e-registries. Therefore, we have performed a literature review to identify the characteristics of twin pregnancy in Brazil and worldwide. Twin pregnancy has consistently been associated with SMM, maternal near-miss (MNM) and perinatal morbidity, with still worse results for the second twin, possibly due to some characteristics of the delivery, including safety and availability of appropriate obstetric care to women at a high risk of perinatal complications.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 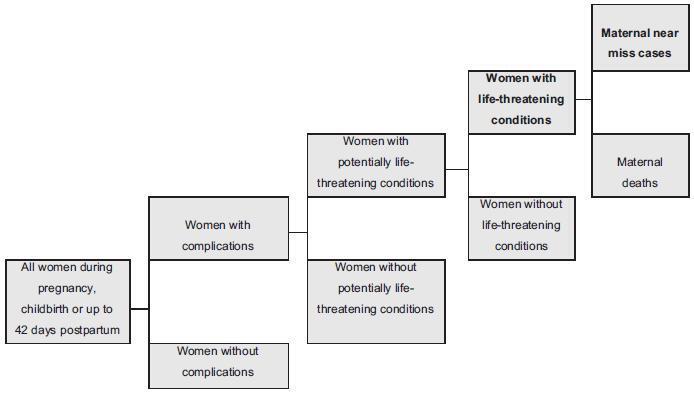
-
Review Article05-01-2018
Uterine Artery Doppler in Screening for Preeclampsia and Fetal Growth Restriction
- Marianna Amaral Pedroso,
- Kirsten Rebecca Palmer,
- Ryan James Hodges,
- Fabricio da Silva Costa,
- Daniel Lorber Rolnik
Views335

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleUterine Artery Doppler in Screening for Preeclampsia and Fetal Growth Restriction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(5):287-293
- Marianna Amaral Pedroso,
- Kirsten Rebecca Palmer,
- Ryan James Hodges,
- Fabricio da Silva Costa,
- Daniel Lorber Rolnik
Views335See moreAbstract
Objective
To perform a comprehensive review of the current evidence on the role of uterine artery Doppler, isolated or in combination with other markers, in screening for preeclampsia (PE) and fetal growth restriction (FGR) in the general population. The review included recently published large cohort studies and randomized trials.
Methods
A search of the literature was conducted usingMedline, PubMed, MeSH and ScienceDirect. Combinations of the search terms “preeclampsia,” “screening,” “prediction,” “Doppler,” “Doppler velocimetry,” “fetal growth restriction,” “small for gestational age” and “uterine artery” were used. Articles in English (excluding reviews) reporting the use of uterine artery Doppler in screening for PE and FGR were included.
Results
Thirty articles were included. As a single predictor, uterine artery Doppler detects less than 50% of the cases of PE and no more than 40% of the pregnancies affected by FGR. Logistic regression-based models that allow calculation of individual risk based on the combination of multiple markers, in turn, is able to detect ~ 75% of the cases of preterm PE and 55% of the pregnancies resulting in small for gestational age infants.
Conclusion
The use of uterine artery Doppler as a single predictive test for PE and FGR has poor accuracy. However, its combined use in predictive models is promising, being more accurate in detecting preterm PE than FGR.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article02-01-2016
Conservative Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
- Rafael Mendes Moroni,
- Pedro Sergio Magnani,
- Jorge Milhem Haddad,
- Rodrigo de Aquino Castro,
- Luiz Gustavo Oliveira Brito
Views305

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleConservative Treatment of Stress Urinary Incontinence: A Systematic Review with Meta-analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(2):97-111
- Rafael Mendes Moroni,
- Pedro Sergio Magnani,
- Jorge Milhem Haddad,
- Rodrigo de Aquino Castro,
- Luiz Gustavo Oliveira Brito
Views305See moreWe performed a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials that studied the conservative management of stress urinary incontinence (SUI). There were 1058 results after the initial searches, from which 37 studies were eligible according to previously determined inclusion criteria. For the primary outcomes, pelvic floor muscle training (PFMT) was more efficacious than no treatment in improving incontinence-specific quality of life (QoL) scales (SMD = [1]1.24SDs; CI 95% = [1]1.77 to [1]0.71SDs). However, its effect on pad tests was imprecise. Combining biofeedback with PFMT had an uncertain effect on QoL (MD = [1]4.4 points; CI 95% = [1]16.69 to 7.89 points), but better results on the pad test, although with elevated heterogeneity (MD = 0.9g; 95%CI = 0.71 to 1,10g); group PFMT was not less efficacious than individual treatment, and home PFMT was not consistently worse than supervised PFMT. Both intravaginal and superficial electrical stimulation (IES and SES) were better than no treatment for QoL and pad test. Vaginal cones had mixed results. The association of IES with PFMT may improve the efficacy of the latter for QoL and pad test, but the results of individual studies were not consistent. Thus, there is evidence of the use of PFMT on the treatment of SUI, with and without biofeedback.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 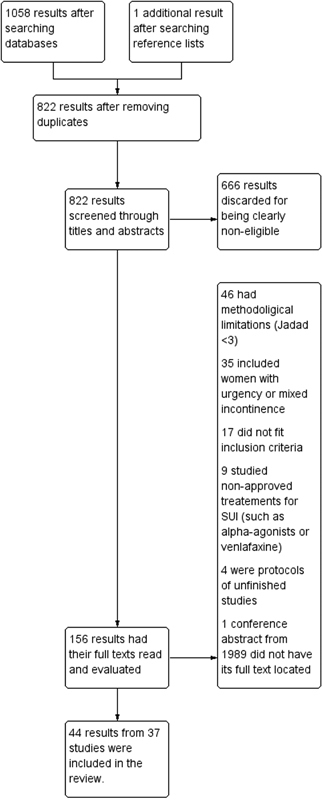
-
Review Article09-16-2019
Do Women have Adequate Knowledge about Pelvic Floor Dysfunctions? A Systematic Review
- Júlia Ferreira Fante,
- Thais Daniel Silva,
- Elaine Cristine Lemes Mateus-Vasconcelos,
- Cristine Homsi Jorge Ferreira,
- Luiz Gustavo Oliveira Brito

Views300

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleDo Women have Adequate Knowledge about Pelvic Floor Dysfunctions? A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(8):508-519
- Júlia Ferreira Fante,
- Thais Daniel Silva,
- Elaine Cristine Lemes Mateus-Vasconcelos,
- Cristine Homsi Jorge Ferreira,
- Luiz Gustavo Oliveira Brito

Views300See moreAbstract
Objective
We sought to investigate whether women present adequate knowledge of the main pelvic floor disorders (PFDs) (urinary incontinence – UI, fecal incontinence – FI, and pelvic organ prolapse – POP).
Data
sources A systematic review was performed in the MEDLINE, PEDro, CENTRAL, and Cochrane databases for publications from inception to April 2018. Selection of studies A total of 3,125 studies were reviewed. Meta-analysis was not possible due to the heterogeneity of primary outcomes and the diversity of instruments for measuring knowledge. The quality of the articles included in the analysis was evaluated with the Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) adapted for cross-sectional studies.
Data collection
Two authors performed data extraction into a standardized spreadsheet.
Data synthesis
Nineteen studies were included, comprising 11,512 women. About the methodological quality (NOS), most of the studies (n= 11) presented a total score of 6 out of 10. Validated questionnaires and designed pilot-tested forms were the most frequently used ways of assessing knowledge. Some studies were stratified by race, age, or group minorities. The most used questionnaire was the prolapse and incontinence knowledge questionnaire (PIKQ) (n= 5). Knowledge and/or awareness regarding PFD was low to moderate among the studies. Urinary incontinence was the most prevalent PFD investigated, and the most important risk factors associated with the lack of knowledge of the pelvic floor were: African-American ethnicity (n= 3), low educational level (n= 4), low access to information (n= 5) and socioeconomic status (n= 3).
Conclusion
Most women have a gap in the knowledge of pelvic floor muscle dysfunctions, do not understand their treatment options, and are not able to identify risk factors for these disorders.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article08-26-2020
Covid-19 and Pregnancy: An Overview
- Pedro Castro
 ,
, - Ana Paula Matos
 ,
, - Heron Werner
 ,
, - Flávia Paiva Lopes
 ,
, - Gabriele Tonni
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Edward Araujo Júnior

Views210

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleCovid-19 and Pregnancy: An Overview
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(7):420-426
- Pedro Castro
 ,
, - Ana Paula Matos
 ,
, - Heron Werner
 ,
, - Flávia Paiva Lopes
 ,
, - Gabriele Tonni
 ,
, - Edward Araujo Júnior

Views210See moreAbstract
Since the World Health Organization (WHO) declared coronavirus infection (COVID-19) a Public Health Emergency of International Concern in January 2020, there have been many concerns about pregnant women and the possible effects of this emergency with catastrophic outcomes inmany countries. Information on COVID-19 and pregnancy are scarce and spread throughout a fewcase series, with no more than 50 cases in total. The present review provides a brief analysis of COVID-19, pregnancy in the COVID-19 era, and the effects of COVID-19 on pregnancy.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Pedro Castro
Search
Search in:
Tag Cloud
Pregnancy (252)Breast neoplasms (104)Pregnancy complications (104)Risk factors (103)Menopause (88)Ultrasonography (83)Cesarean section (78)Prenatal care (71)Endometriosis (70)Obesity (61)Infertility (57)Quality of life (55)prenatal diagnosis (51)Women's health (48)Postpartum period (46)Maternal mortality (45)Pregnant women (45)Breast (44)Prevalence (43)Uterine cervical neoplasms (43)
