- Recent Articles
- Most Citedi
- Most Visitedi
- Future Articles
-
Original Article04-12-1998
Chronic effects of acetylsacylic acid on pregnant rats
- Sílvia Espiridião,
- Renato Ajeje,
- Benjamin I. Kopelman,
- Manuel J. Simões,
- Joaquim Evêncio-Neto, [ … ],
- Luiz Kulay Júnior
Views99PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 2
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 9604
- Abstract Views: 777
- Social Media
- Shares, Likes & Comments: 1


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleChronic effects of acetylsacylic acid on pregnant rats
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(5):245-249
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000500003
- Sílvia Espiridião,
- Renato Ajeje,
- Benjamin I. Kopelman,
- Manuel J. Simões,
- Joaquim Evêncio-Neto,
- Luiz Kulay Júnior
Views99See moreThe purpose of the present study was to evaluate the effects of acetylsalicylic acid (ASA) on the pregnancy of female albino rats. We used 60 pregnant female rats which were divided into six groups of ten cache. All the animals received daily by gavage, from the 5th (day zero) until the 20th day of pregnancy, 1 ml of the following: Group I – only distilled water (control); Group II – 0.2% aqueous solution of carboxymethylcellulose (vehicle); Groups III, IV, V and VI – 1, 10, 100 and 400 mg/kg body weight respectively, of ASA diluted in 0.2% carboxymethylcellulose solution. The animals were weighed on days 0, 7, 14 and 20 of pregnancy. Our results showed that the animals treated with 100 mg of ASA presented a reduction in the number of live newborns. The animals treated with 400 mg/kg/day presented not only a reduction in the number of live newborns but also decrease in maternal, newborn and placental weight.
PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 2
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 9604
- Abstract Views: 777
- Social Media
- Shares, Likes & Comments: 1


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article04-12-1998
Glycosylated hemoglobin levels and cardiac abnormalities in fetuses of diabetic mothers
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(5):237-243
Views105PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 4
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 17097
- Abstract Views: 1114
- Captures
- Readers: 2
- Social Media
- Shares, Likes & Comments: 6


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleGlycosylated hemoglobin levels and cardiac abnormalities in fetuses of diabetic mothers
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(5):237-243
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000500002
Views105We analyze prospectively the existence of a relationship between the mother’s glycemic control, in the first half of pregnancy, and the occurrence of abnormal fetal cardiac abnormalities, in pregnant women with diabetes mellitus. In 127 pregnant women, the level of glycosylated hemoglobin was determined on the first visit during prenatal care. Nine patients had type I diabetes, 77 type II and 41 gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM). All mothers were submitted to detailed fetal echocardiography, during the 28th ± 4.127 week of gestation. In 31 (24.4%) of the 127 fetuses cardiac anomalies were detected. In 10 (7.87%) an isolated cardiac anomaly was identified. Mean HbA1c in the group of pregnant women without cardiac anomalies (5.64%) was statistically different from the group with anomalies (10.14%) (p<0.0001). The receiver-operator characteristic, representing the balance between sensitivity (92.83%) and specificity (98.92%) in the diagnosis of structural cardiac abnormalities, showed a cut-off point at the 7.5% HbA1c level. In nine of ten fetuses with structural cardiac anomalies, the maternal level of HbA1c was higher than 7.5%. The difference between means of the groups with and without myocardial hypertrophy diagnosed as isolated anomaly (MCHP) was not statistically significant, when considering both type II diabetes and GDM subgroups. In conclusion, levels of HbA1c higher than 7.5% were associated with most cases of echocardiographycally diagnosed structural cardiac anomalies. On the other hand, this test was not useful to discriminate conceptus with MCHP.
Key-words Diabetes mellitusFetusGlysosylated hemoglobin AMalformationsPregnancy complicationsUltrasonographySee morePlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 4
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 17097
- Abstract Views: 1114
- Captures
- Readers: 2
- Social Media
- Shares, Likes & Comments: 6


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
04-12-1998
RBGO: presente e futuro
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(5):235-235
Views56

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
RBGO: presente e futuro
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(5):235-235


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
04-12-1998
Estudo longitudinal das alterações hemodinâmicas e estruturas cardíacas em gestantes sem patologia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):225-225
Views80

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Estudo longitudinal das alterações hemodinâmicas e estruturas cardíacas em gestantes sem patologia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):225-225
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000400009
Views80Estudo Longitudinal das Alterações Hemodinâmicas e Estruturas Cardíacas em Gestantes sem Patologia[…]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
04-12-1998
Ultra-sonometria de calcâneo em mulheres pré e pós-menopáusicas comparação com densitometria óssea
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):225-225
Views100

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Ultra-sonometria de calcâneo em mulheres pré e pós-menopáusicas comparação com densitometria óssea
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):225-225
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000400010
Views100Ultra-Sonometria de Calcâneo em Mulheres Pré e Pós-Menopáusicas Comparação com Densitometria Óssea […]See more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Case Report04-12-1998
Necrotizing fasciitis of the breast: case report
- Marco Aurélio da Costa Silva,
- Jales Benevides Santana Filho,
- Ruffo de Freitas Júnior,
- Edgar Berquó Peleja,
- Rossana de Araújo Catão, [ … ],
- Luiz Fernando Jubé Ribeiro
Views160PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 1
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 94179
- Abstract Views: 963
- Captures
- Readers: 1


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Case ReportNecrotizing fasciitis of the breast: case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):221-224
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000400008
- Marco Aurélio da Costa Silva,
- Jales Benevides Santana Filho,
- Ruffo de Freitas Júnior,
- Edgar Berquó Peleja,
- Rossana de Araújo Catão,
- Luiz Fernando Jubé Ribeiro
Views160See moreA case of postsurgical necrotizing fasciitis is presented. A 68-year-old female patient was submitted to a lumpectomy for a big breast lipoma. After surgen there was an aggressive local infection, with extensive necrosis of the breast tissue, including the superficial and deep fasciae and also the skin over the breast. The gravity of the disease and the difficulties in its diagnosis due to the late skin necrosis are emphasized. Under such circunstances an early and aggressive approach is necessary.
PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 1
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 94179
- Abstract Views: 963
- Captures
- Readers: 1


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Case Report04-12-1998
Leiomyoma of the female urethra: a case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):217-219
Views122PlumX Metrics
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 28543
- Abstract Views: 1294
- Captures
- Readers: 1
- Social Media
- Shares, Likes & Comments: 1


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Case ReportLeiomyoma of the female urethra: a case report
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):217-219
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000400007
Views122See moreA case of urethral leiomyoma – a mass of approximately 5 cm in diameter – located on the anterior wall of the vaginal lower third is reported. The patient was submitted to a surgical tumor excision. Histopathological and immunohistochemical studies indicated leiomyoma, which is always a benign, unusual neoplasm, rarely relapsing after excision. Its pathogenesis and clinical features are also focused on.
PlumX Metrics
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 28543
- Abstract Views: 1294
- Captures
- Readers: 1
- Social Media
- Shares, Likes & Comments: 1


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article04-12-1998
Fine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) in the differential diagnosis of breast pathology
- Francisco José Candido dos Reis,
- Jurandyr Moreira de Andrade,
- Maria Angeles Sanches Llorach Velludo,
- Sérgio Alexandre de Oliveira,
- Ricardo Barbelli Feitosa, [ … ],
- Sérgio Bighetti
Views190

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleFine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) in the differential diagnosis of breast pathology
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 1998;20(4):209-213
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72031998000400006
- Francisco José Candido dos Reis,
- Jurandyr Moreira de Andrade,
- Maria Angeles Sanches Llorach Velludo,
- Sérgio Alexandre de Oliveira,
- Ricardo Barbelli Feitosa,
- Heitor Ricardo Cosiski Marana,
- Sérgio Bighetti
Views190See moreFine-needle aspiration cytology (FNAC) is a simple method and free from complications, among great value in mastology. Its accuracy can suffer the influence of several factors, among which we can highlight the experience of the physician who performs it. With the objective of verifying the effectiveness of FNAC performed by general gynecologists, 341 patients were studied concerning the relationship between the results of FNAC and the histology of the breast lesion. We obtained sensitivity of 70.87%, specificity of 70.58%, predictive positive value of 92.40%, predictive negative value of 89.36% and accuracy of 70.67%. We concluded that FNAC is of great value in handling breast lesions and can be appropriately performed by general gynecologists. The method, however, may lead to errors of diagnosis. We do not recommend, therefore, the use of the result of FNAC as a definitive diagnosis; instead this result must be interpreted in the context of the clinical diagnosis and mammography.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT03-01-2019
Increasing the Chances of Natural Conception: Opinion Statement from the the Brazilian Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics Associations – FEBRASGO Committee of Gynecological Endocrinology
- Bruno Ramalho de Carvalho
 ,
, - Ionara Diniz Evangelista Santos Barcelos,
- Sebastião Freitas de Medeiros,
- Cristina Laguna Benetti-Pinto,
- Daniela Angerame Yela, [ … ],
- Laura Olinda Bregieiro Fernandes Costa
Views467PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 2
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 988
- Abstract Views: 176
- Captures
- Readers: 39


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTIncreasing the Chances of Natural Conception: Opinion Statement from the the Brazilian Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics Associations – FEBRASGO Committee of Gynecological Endocrinology
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(3):183-190
- Bruno Ramalho de Carvalho
 ,
, - Ionara Diniz Evangelista Santos Barcelos,
- Sebastião Freitas de Medeiros,
- Cristina Laguna Benetti-Pinto,
- Daniela Angerame Yela,
- Andrea Prestes Nácul,
- Gustavo Arantes Rosa Maciel,
- José Maria Soares Júnior,
- Ana Carolina Japur de Sá Rosa e Silva,
- Laura Olinda Bregieiro Fernandes Costa
Views467See moreAbstract
Considering that myths and misconceptions regarding natural procreation spread rapidly in the era of easy access to information and to social networks, adequate counseling about natural fertility and spontaneous conception should be encouraged in any kind of health assistance. Despite the fact that there is no strong-powered evidence about any of the aspects related to natural fertility, literature on how to increase the chances of a spontaneous pregnancy is available. In the present article, the Brazilian Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics Associations (FEBRASGO, in the Portuguese acronym) Committee on Endocrine Gynecology provides suggestions to optimize counseling for non-infertile people attempting spontaneous conception.
PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 2
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 988
- Abstract Views: 176
- Captures
- Readers: 39


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Bruno Ramalho de Carvalho
-
Original Article11-01-2018
Do Food Intake and Food Cravings Change during the Menstrual Cycle of Young Women?
- Luciana Bronzi de Souza,
- Karine Anusca Martins,
- Mariana Morais Cordeiro,
- Ymárdila de Souza Rodrigues,
- Bruna Paola Murino Rafacho, [ … ],
- Rafael Aiello Bomfim
Views434PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 26
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 2911
- Abstract Views: 378
- Captures
- Readers: 233
- Mentions
- News Mentions: 1
- References: 1


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleDo Food Intake and Food Cravings Change during the Menstrual Cycle of Young Women?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(11):686-692
- Luciana Bronzi de Souza,
- Karine Anusca Martins,
- Mariana Morais Cordeiro,
- Ymárdila de Souza Rodrigues,
- Bruna Paola Murino Rafacho,
- Rafael Aiello Bomfim
Views434Abstract
Objective
The aim of the present study was to assess the anthropometric measures, food intake and food cravings during the menstrual cycle of undergraduate students of the faculty of nutrition.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was performed with 27 students from a public university in the state of Mato Grosso do Sul, Brazil, who had their food intake evaluated through a 24-hour food recall, their nutritional status evaluated based on anthropometric measures, and food cravings evaluated using the Food Desire Questionnaire. Data were collected during an evaluation in the follicular phase (between the 5th and the 9th day of the menstrual cycle) and another in the luteal phase (LP) (between the 20th and the 25th day of the menstrual cycle). For food intake variables, the analysis of variance (ANOVA) test was used, followed by the Tukey test. The Mann-Whitney test was used for the analysis of food cravings, considering a significance level of 5% (p< 0.05).
Results
The desire for foods rich in sugar, salt, and fat, such as chocolate, pastries, snacks and desserts were higher (p< 0.05) during the premenstrual period, although it did not reflect neither a higher energy intake nor an alteration in the distribution of macronutrients. A higher intake of carbohydrates, proteins, fibers, and calcium was observed during the LP; however, without statistical difference between the groups. There were no differences either in the intake of any food group or in the anthropometric measurements (p> 0.05).
Conclusion
Food cravings of nutrition students differed between the phases of the menstrual cycle; however, with no difference in food intake and in anthropometric measures.
Key-words Feeding behaviorfollicular phasefood intakeluteal phaseMenstrual cycleNutrition assessmentSee morePlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 26
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 2911
- Abstract Views: 378
- Captures
- Readers: 233
- Mentions
- News Mentions: 1
- References: 1


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 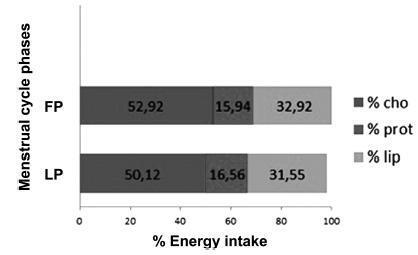
-
Review Article01-11-2023
Efficacy, Safety, and Acceptability of Misoprostol in the Treatment of Incomplete Miscarriage: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Thiago Menezes da Silva
 ,
, - Moema Alves Guerra de Araujo
 ,
, - Ana Carolina Zimmermann Simões
 ,
, - Ronnier de Oliveira
 ,
, - Kleyton Santos de Medeiros
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Ana Katherine Gonçalves

Views431

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleEfficacy, Safety, and Acceptability of Misoprostol in the Treatment of Incomplete Miscarriage: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(12):808-817
- Thiago Menezes da Silva
 ,
, - Moema Alves Guerra de Araujo
 ,
, - Ana Carolina Zimmermann Simões
 ,
, - Ronnier de Oliveira
 ,
, - Kleyton Santos de Medeiros
 ,
, - Ayane Cristine Sarmento
 ,
, - Robinson Dias de Medeiros
 ,
, - Ana Paula Ferreira Costa
 ,
, - Ana Katherine Gonçalves

Views431See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess the efficacy, safety, and acceptability of misoprostol in the treatment of incomplete miscarriage.
Data sources
The PubMed, Scopus, Embase, Web of Science, Cochrane Library, and Clinical Trials databases (clinicaltrials.gov) were searched for the relevant articles, and search strategies were developed using a combination of thematic Medical Subject Headings terms and text words. The last search was conducted on July 4, 2022. No language restrictions were applied.
Selection of studies
Randomized clinical trials with patients of gestational age up to 6/7 weeks with a diagnosis of incomplete abortion and who were managed with at least 1 of the 3 types of treatment studied were included. A total of 8,087 studies were screened.
Data collection
Data were synthesized using the statistical package Review Manager V.5.1 (The Cochrane Collaboration, Oxford, United Kingdom). For dichotomous outcomes, the odds ratio (OR) and 95% confidence interval (CI) were derived for each study. Heterogeneity between the trial results was evaluated using the standard test, I2 statistic.
Data synthesis
When comparing misoprostol with medical vacuum aspiration (MVA), the rate of complete abortion was higher in the MVA group (OR = 0.16; 95%CI = 0.07–0.36). Hemorrhage or heavy bleeding was more common in the misoprostol group (OR = 3.00; 95%CI = 1.96–4.59), but pain after treatment was more common in patients treated with MVA (OR = 0.65; 95%CI = 0.52–0.80). No statistically significant differences were observed in the general acceptability of the treatments.
Conclusion
Misoprostol has been determined as a safe option with good acceptance by patients.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 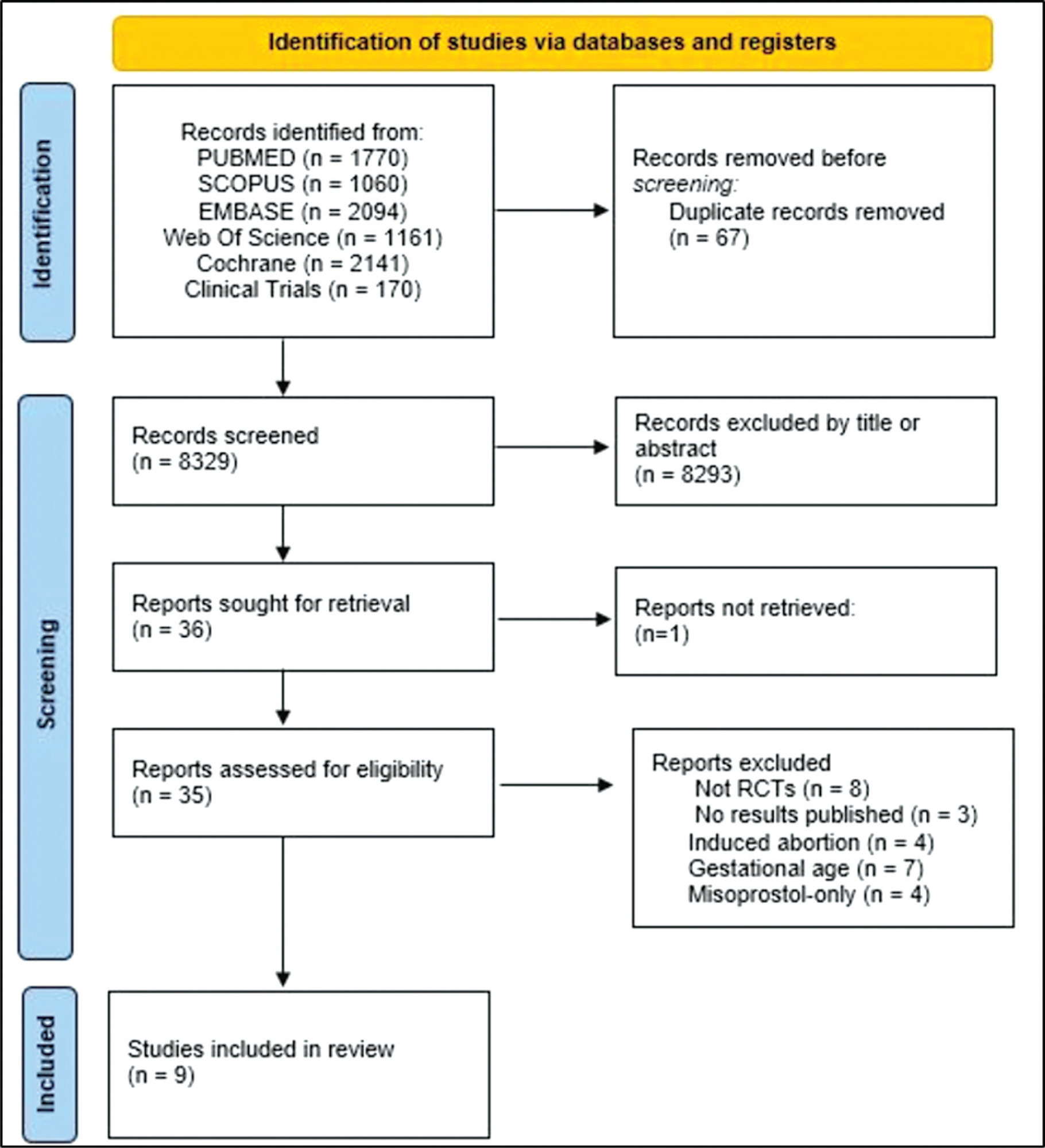
- Thiago Menezes da Silva
-
Review Article02-28-2022
Efficacy of Transversus Abdominis Plane Block in the Reduction of Pain and Opioid Requirement in Laparoscopic and Robot-assisted Hysterectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
- Claudia López-Ruiz
 ,
, - Jerutsa Catalina Orjuela
 ,
, - Diego Fernando Rojas-Gualdrón
 ,
, - Marcela Jimenez-Arango
 ,
, - José Fernando de los Ríos
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Claudia Vargas

Views448

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleEfficacy of Transversus Abdominis Plane Block in the Reduction of Pain and Opioid Requirement in Laparoscopic and Robot-assisted Hysterectomy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(1):55-66
- Claudia López-Ruiz
 ,
, - Jerutsa Catalina Orjuela
 ,
, - Diego Fernando Rojas-Gualdrón
 ,
, - Marcela Jimenez-Arango
 ,
, - José Fernando de los Ríos
 ,
, - Elsa Maria Vásquez-Trespalacios
 ,
, - Claudia Vargas

Views448Abstract
Objective
To summarize the available evidence of TAP Block in efficacy in laparoscopic or robotic hysterectomy.
Data Sources
We searched databases and gray literature for randomized controlled trials in which transversus abdominis plane (TAP) block was compared with placebo or with no treatment in patients who underwent laparoscopic or robot-assisted hysterectomy.
Method of Study
Selection Two researchers independently evaluated the eligibility of the selected articles. Tabulation, Integration, and Results Seven studies were selected, involving 518 patients. Early postoperative pain showed a difference in the mean mean difference (MD): – 1.17 (95% confidence interval [CI]: – 1.87-0.46) in pain scale scores (I2=68%), which was statistically significant in favor of using TAP block, but without clinical relevance; late postoperative pain: DM 0.001 (95%CI: – 0.43-0.44; I2=69%); opioid requirement: DM 0.36 (95%CI: – 0.94-1.68; I2=80%); and incidence of nausea and vomiting with a difference of 95%CI=- 0.11 (- 0.215-0.006) in favor of TAP.
Conclusion
With moderate strength of evidence, due to the high heterogeneity and imbalance in baseline characteristics among studies, the results indicate that TAP block should not be considered as a clinically relevant analgesic technique to improve postoperative pain in laparoscopic or robotic hysterectomy, despite statistical significance in early postoperative pain scale scores.
Key-words laparoscopic hysterectomyOpioidPainrobotic-assisted hysterectomytransversus abdominis plane blockSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 
- Claudia López-Ruiz
-
Review Article06-27-2022
Cognitive Behavioral Therapy in Endometriosis, Psychological Based Intervention: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(3):295-303
Views425

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleCognitive Behavioral Therapy in Endometriosis, Psychological Based Intervention: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(3):295-303
Views425Abstract
Introduction
Endometriosis is an inflammatory disease that affects women of reproductive age, causing pain and the possibility of infertility. Endometriosis was associated to low life quality and research shows the impact of endometriosis in several areas of life, justifying how these patients are more likely to develop depression, anxiety, and stress.
Objective
The aim of the present systematic review was to explore the field of psychology in endometriosis, identifying studies that used the cognitive behavioral therapy technique as a treatment for endometriosis and chronic pelvic pain.
Methods
The keywords used were Endometriosis and Behavioral Therapy; Behavioral Disciplines and Activities; Cognitive Behavioral Therapy; Mental Health; Psychological Techniques; Psychology; Psychotherapy; Mental Health Services; and the search was performed in the following databases: PubMed/Medline, Scielo, Lilacs, and Capes. The study followed the PRISMA guidelines and all studies whose intervention strategy used was related to cognitive-behavioral therapy were considered.
Results
Of the 129 articles found, only 5 were selected, and it was possible to identify that the psychological intervention whose approach brought cognitive-behavioral therapy techniques promoted a decrease in the sensation of pain, improvements in the scores of depression and stress, and significant changes in aspects of quality of life such as vitality, physical and social functioning, emotional well-being, control, and autonomy.
Conclusion
Cognitive-behavioral therapy can be very promising to take care of the emotional side of those who have endometriosis However, the present systematic review highlights the need to develop more structured studies with consistent, clear and replicablemethods to reach a psychological intervention protocol for patients who live with this gynecological-physical-emotional condition.
Key-words Chronic pelvic paincognitive behavioral therapyEndometriosispsychological interventionQuality of lifesystematic reviewsSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article08-26-2020
Tribulus Terrestris for Female Sexual Dysfunction: A Systematic Review
- Ana Luiza Cabrera Martimbianco
 ,
, - Rafael Leite Pacheco
 ,
, - Fábia Lima Vilarino
 ,
, - Carolina de Oliveira Cruz Latorraca
 ,
, - Maria Regina Torloni
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Rachel Riera

Views421PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 14
- Policy Citations: 1
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 1032
- Abstract Views: 272
- Captures
- Readers: 70


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleTribulus Terrestris for Female Sexual Dysfunction: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(7):427-435
- Ana Luiza Cabrera Martimbianco
 ,
, - Rafael Leite Pacheco
 ,
, - Fábia Lima Vilarino
 ,
, - Carolina de Oliveira Cruz Latorraca
 ,
, - Maria Regina Torloni
 ,
, - Rachel Riera

Views421See moreAbstract
Objective
We performed a systematic review to assess the effectiveness and safety of Tribulus terrestris to treat female sexual dysfunction (FSD).
Data sources
We performed unrestricted electronic searches in the MEDLINE, CENTRAL, EMBASE, LILACS, CINAHL, PsycINFO,WHO-ICTR, Clinicaltrials.gov and OpenGrey databases. Selection of studies We included any randomized controlled trials (RCTs) that compared T. terrestris versus inactive/active interventions. After the selection process, conducted by two reviewers, 5 RCTs (n = 279 participants) were included.
Data collection
Data extraction was performed by two reviewers with a preestablished data collection formulary.
Data synthesis
Due to lack of data and clinical heterogeneity, we could not perform meta-analyses. The risk of bias was assessed by the Cochrane Risk of Bias (RoB) tool, and the certainty of evidence was assessed with Grading of Recommendations, Assessment, Development and Evaluations (GRADE).
Results
After 1 to 3 months of treatment, premenopausal and postmenopausal women randomized to T. terrestris had a significant increase in sexual function scores. Three months of treatment with T. terrestris showed a significant increase in the serum testosterone levels of premenopausal women. There was no report of serious adverse events, and none of the studies assessed health-related quality of life. The certainty of the evidence was very low, whichmeans that we have very little confidence in the effect estimates, and future studies are likely to change these estimates.
Conclusion
MoreRCTs are needed to supportor refute the use of T. terrestris. The decision to use this intervention should be shared with the patients, and the uncertainties around its effects should be discussed in the clinical decision-making process. Number of Protocol registration in PROSPERO database: CRD42019121130
PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 14
- Policy Citations: 1
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 1032
- Abstract Views: 272
- Captures
- Readers: 70


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Ana Luiza Cabrera Martimbianco
-
Review Article06-01-2018
Guidelines for HPV-DNA Testing for Cervical Cancer Screening in Brazil
- Luiz Carlos Zeferino,
- Joana Bragança Bastos,
- Diama Bhadra Andrade Peixoto do Vale,
- Rita Maria Zanine,
- Yara Lucia Mendes Furtado de Melo, [ … ],
- Fábio Russomano
Views399PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 28
- Policy Citations: 1
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 3338
- Abstract Views: 1756
- Captures
- Readers: 106


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleGuidelines for HPV-DNA Testing for Cervical Cancer Screening in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):360-368
- Luiz Carlos Zeferino,
- Joana Bragança Bastos,
- Diama Bhadra Andrade Peixoto do Vale,
- Rita Maria Zanine,
- Yara Lucia Mendes Furtado de Melo,
- Walquíria Quida Salles Pereira Primo,
- Flávia de Miranda Corrêa,
- Isabel Cristina Chulvis do Val,
- Fábio Russomano
Views399See moreAbstract
Evidence-based clinical guidelines ensure best practice protocols are available in health care. There is a widespread use of human papillomavirus deoxyribonucleic acid (HPVDNA) tests in Brazil, regardless of the lack of official guidelines. On behalf of the Brazilian Association for the Lower Genital Tract Pathology and Colposcopy (ABPTGIC, in the Portuguese acronym), a team of reviewers searched for published evidence and developed a set of recommendations for the use of HPV-DNA tests in cervical cancer screening in Brazil. The product of this process was debated and consensus was sought by the participants. One concern of the authors was the inclusion of these tests in the assessment of women with cytologic atypia and women treated for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN). Testing for HPV is recommended in an organized screening scenario to identify women with precursor lesions or asymptomatic cervical cancer older than 30 years of age, and it can be performed every 5 years. It also has value after the cytology showing atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASC-US) or low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (LSILs) as a triage test for colposcopy, in the investigation of other cytological alterations when no abnormal findings are observed at colposcopy, seeking to exclude disease, or, further, after treatment of high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, to rule out residual disease.
PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 28
- Policy Citations: 1
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 3338
- Abstract Views: 1756
- Captures
- Readers: 106


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 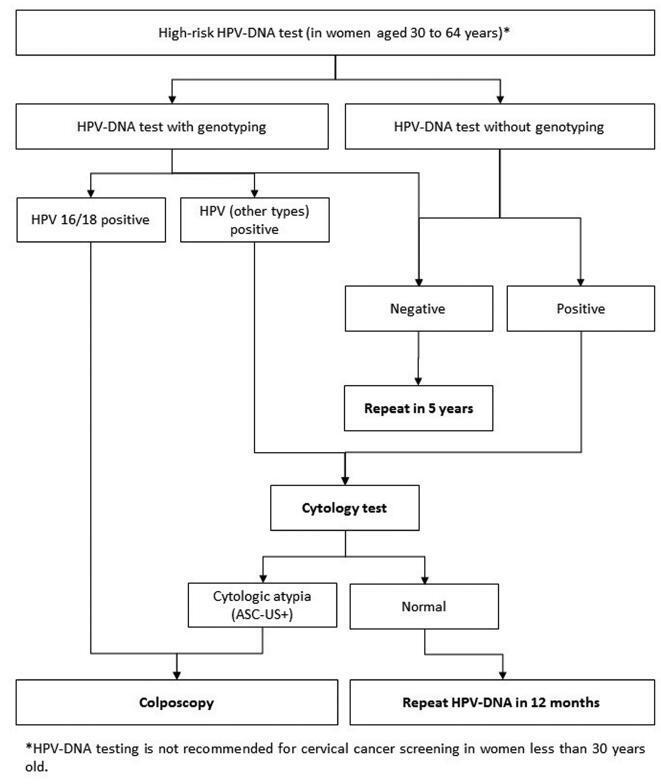
-
Original Article03-27-2020
Gestational Diabetes in the Population Served by Brazilian Public Health Care. Prevalence and Risk Factors
- Pâmela Antoniazzi dos Santos
 ,
, - José Mauro Madi
 ,
, - Emerson Rodrigues da Silva
 ,
, - Daiane de Oliveira Pereira Vergani
 ,
, - Breno Fauth de Araújo
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Rosa Maria Rahmi Garcia

Views368PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 24
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 1920
- Abstract Views: 773
- Captures
- Readers: 144


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleGestational Diabetes in the Population Served by Brazilian Public Health Care. Prevalence and Risk Factors
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(1):12-18
- Pâmela Antoniazzi dos Santos
 ,
, - José Mauro Madi
 ,
, - Emerson Rodrigues da Silva
 ,
, - Daiane de Oliveira Pereira Vergani
 ,
, - Breno Fauth de Araújo
 ,
, - Rosa Maria Rahmi Garcia

Views368See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess the prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus and the main associated risk factors in the population served by the Brazilian Unified Health System in the city of Caxias do Sul, state of Rio Grande do Sul.
Materials and Methods
A descriptive, cross-sectional and retrospective study was conducted. Maternal variables were collected from the medical records of all pregnant women treated at the basic health units in 2016. Hyperglycemia during pregnancy (pregestational diabetes, overt diabetes and gestational diabetes mellitus) was identified by analyzing the results of a 75-g oral glucose tolerance test, as recommended by the Brazilian Ministry of Health. Based on the data, the women were allocated into two groups: the gestational diabetes group and the no gestational diabetes group.
Results
The estimated prevalence of gestational diabetes among 2,313 pregnant women was of 5.4% (95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 4.56-6.45). Pregnant women with 3 or more pregnancies had twice the odds of having gestational diabetes compared with primiparous women (odds ratio [OR]=2.19; 95%CI: 1.42-3.37; p<0.001). Pregnant women aged 35 years or older had three times the odds of having gestational diabetes when compared with younger women (OR=3.01; 95%CI: 1.97-4.61; p<0.001). Overweight pregnant women were 84% more likely to develop gestational diabetes than those with a body mass index lower than 25 kg/m2 (OR =1.84; 95%CI: 1.25-2.71; p=0.002). A multivariable regression analysis showed that being overweight and being 35 years old or older were independent variables.
Conclusion
In this population, the prevalence of gestational diabetes mellitus was of 5.4%. Age and being overweight were predictive factors for gestational diabetes.
PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 24
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 1920
- Abstract Views: 773
- Captures
- Readers: 144


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Pâmela Antoniazzi dos Santos
-
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENT06-27-2019
Pre-eclampsia/Eclampsia
- José Carlos Peraçoli
 ,
, - Vera Therezinha Medeiros Borges,
- José Geraldo Lopes Ramos,
- Ricardo de Carvalho Cavalli,
- Sérgio Hofmeister de Almeida Martins Costa, [ … ],
- Edson Viera da Cunha Filho
Views119

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
FEBRASGO POSITION STATEMENTPre-eclampsia/Eclampsia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(5):318-332
- José Carlos Peraçoli
 ,
, - Vera Therezinha Medeiros Borges,
- José Geraldo Lopes Ramos,
- Ricardo de Carvalho Cavalli,
- Sérgio Hofmeister de Almeida Martins Costa,
- Leandro Gustavo de Oliveira,
- Francisco Lazaro Pereira de Souza,
- Henri Augusto Korkes,
- Ione Rodrigues Brum,
- Maria Laura Costa,
- Mário Dias Corrêa Junior,
- Nelson Sass,
- Angélica Lemos Debs Diniz,
- Caio Antonio de Campos Prado,
- Edson Viera da Cunha Filho
Views119See moreAbstract
Pre-eclampsia is a multifactorial and multisystemic disease specific to gestation. It is classically diagnosed by the presence of hypertension associated with proteinuria manifested in a previously normotensive pregnant woman after the 20th week of gestation. Pre-eclampsia is also considered in the absence of proteinuria if there is target organ damage. The present review takes a general approach focused on aspects of practical interest in the clinical and obstetric care of these women. Thus, it explores the still unknown etiology, current aspects of pathophysiology and of the diagnosis, the approach to disease prediction, its adverse outcomes and prevention. Management is based on general principles, on nonpharmacological and on pharmacological clinical treatment of severe or nonsevere situations with emphasis on the hypertensive crisis and eclampsia. Obstetric management is based on preeclampsia without or with signs of clinical and/or laboratory deterioration, stratification of gestational age


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - José Carlos Peraçoli
-
Systematic Review05-01-2017
Zika Virus Infection in Pregnant Women and Microcephaly
- Geraldo Duarte,
- Antonio Fernandes Moron,
- Artur Timerman,
- César Eduardo Fernandes,
- Corintio Mariani Neto, [ … ],
- Rossana Pulcineli Vieira Francisco
Views409PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 39
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 7532
- Abstract Views: 2120
- Captures
- Readers: 295
- Social Media
- Shares, Likes & Comments: 102


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Systematic ReviewZika Virus Infection in Pregnant Women and Microcephaly
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(5):235-248
- Geraldo Duarte,
- Antonio Fernandes Moron,
- Artur Timerman,
- César Eduardo Fernandes,
- Corintio Mariani Neto,
- Gutemberg Leão de Almeida Filho,
- Heron Werner Junior,
- Hilka Flavia Barra do Espírito Santo,
- João Alfredo Piffero Steibel,
- João Bortoletti Filho,
- Juvenal Barreto Borriello de Andrade,
- Marcelo Burlá,
- Marcos Felipe Silva de Sá,
- Newton Eduardo Busso,
- Paulo César Giraldo,
- Renato Augusto Moreira de Sá,
- Renato Passini Junior,
- Rosiane Mattar,
- Rossana Pulcineli Vieira Francisco
Views409Abstract
From the discovery of the Zika virus (ZIKV) in 1947 in Uganda (Africa), until its arrival in South America, it was not known that it would affect human reproductive life so severely. Today, damagetothe central nervous system is known to be multiple, and microcephaly is considered the tip of the iceberg. Microcephaly actually represents the epilogue of this infection’s devastating process on the central nervous system of embryos and fetuses. As a result of central nervous system aggression by the ZIKV, this infection brings the possibility of arthrogryposis, dysphagia, deafness and visual impairment. All of these changes of varying severity directly or indirectly compromise the future life of these children, and are already considered a congenital syndrome linked to the ZIKV. Diagnosis is one of the main difficulties in the approach of this infection. Considering the clinical part, it has manifestations common to infections by the dengue virus and the chikungunya fever, varying only in subjective intensities. The most frequent clinical variables are rash, febrile state, non-purulent conjunctivitis and arthralgia, among others. In terms of laboratory resources, there are also limitations to the subsidiary diagnosis. Molecular biology tests are based on polymerase chain reaction (PCR)with reverse transcriptase (RT) action, since the ZIKV is a ribonucleic acid (RNA) virus. The RT-PCR shows serum or plasma positivity for a short period of time, no more than five days after the onset of the signs and symptoms. The ZIKVurine test is positive for a longer period, up to 14 days. There are still no reliable techniques for the serological diagnosis of this infection. If there are no complications (meningoencephalitis or Guillain-Barré syndrome), further examination is unnecessary to assess systemic impairment. However, evidence is needed to rule out other infections that also cause rashes, such as dengue, chikungunya, syphilis, toxoplasmosis, cytomegalovirus, rubella, and herpes. There is no specific antiviral therapy against ZIKV, and the therapeutic approach to infected pregnant women is limited to the use of antipyretics and analgesics. Anti-inflammatory drugs should be avoided until the diagnosis of dengue is discarded. There is no need to modify the schedule of prenatal visits for pregnant women infected by ZIKV, but it is necessary to guarantee three ultrasound examinations during pregnancy for low-risk pregnancies, and monthly for pregnant women with confirmed ZIKV infection. Vaginal delivery and natural breastfeeding are advised.
Key-words arbovirus infectionsblindness/ etiologydeafness/ etiologymicrocephaly/ ultrasonographyPregnancy complicationsReal-time polymerase chain reactionZika virusSee morePlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 39
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 7532
- Abstract Views: 2120
- Captures
- Readers: 295
- Social Media
- Shares, Likes & Comments: 102


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 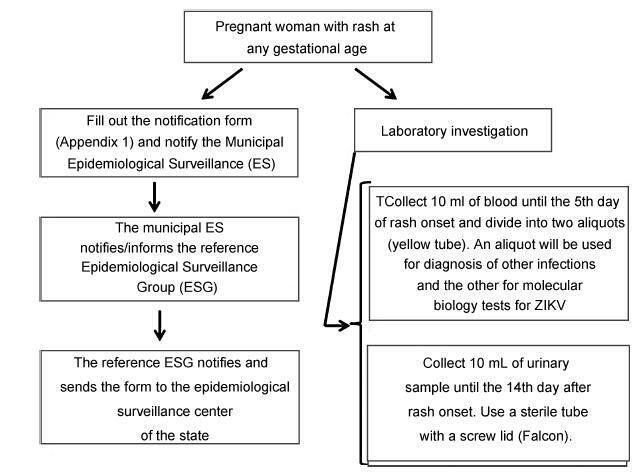
-
Original Article02-01-2019
Syphilis in Pregnancy: The Reality in a Public Hospital
- Rafael Garcia Torres,
- Ana Laura Neves Mendonça,
- Grazielle Cezarine Montes,
- Jacqueline Jácome Manzan,
- João Ulisses Ribeiro, [ … ],
- Marina Carvalho Paschoini

Views315PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 19
- Policy Citations: 1
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 2342
- Abstract Views: 376
- Captures
- Readers: 212


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleSyphilis in Pregnancy: The Reality in a Public Hospital
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2019;41(2):90-96
- Rafael Garcia Torres,
- Ana Laura Neves Mendonça,
- Grazielle Cezarine Montes,
- Jacqueline Jácome Manzan,
- João Ulisses Ribeiro,
- Marina Carvalho Paschoini

Views315See moreAbstract
Objective:
The present study assessed epidemiological and obstetrical data from pregnant women with syphilis at the Hospital de Clínicas of the Universidade Federal do Triângulo Mineiro (UFTM, in the Portuguese acronym), describing this disease during pregnancy and its vertical transmission for future healthcare actions.
Methods:
Records from pregnant women who had been admitted to the Obstetrics Department of the Hospital de Clínicas of the UFTM and were diagnosed with syphilis between 2007 and 2016 were reviewed. A standardized form was used to collect epidemiological, obstetric data and outcomes of congenital infection. The present research has been authorized by the Ethics Committee of the institution.
Results:
There were 268 women diagnosed with syphilis, with an average age of 23.6 years old. The majority of the patients were from Uberaba. Inadequate prenatal care was observed in 37.9% of the pregnant women. Only 34.2% of the patients completed the treatment according to the guidelines issued by the Ministry of Health of Brazil, and 19.8% of the partners of the patients underwent adequate syphilis treatment; 37 (13.8%) couples (patients and partners) underwent correct treatment. Regarding the obstetric outcomes, 4 (1.5%) patients had a miscarriage and 8 (3.4%) had fetal losses (from the fetal loss group, 7 had no adequate treatment); 61 (25.9%) patients had premature births – this prematurity has been significantly correlated to inadequate or incomplete treatment in 49 (27.9%) patients, compared with 12 (13.0%) patients with premature births and adequate treatment (p = 0.006). The average live newborn weight was 2,840 g; 25.3% had a birth weight < 2,500 g; 74.2% had congenital syphilis, a data with heavy correlation to inadequate or incomplete prenatal care, prematurity, and low birth weight.
Conclusion:
Public awareness policies on adequate prenatal care, intensification of serological screening, and early treatment of syphilis are needed, considering the rise of cases diagnosed during gestation and its potentially preventable deleterious consequences related to congenital transmission.
PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 19
- Policy Citations: 1
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 2342
- Abstract Views: 376
- Captures
- Readers: 212


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Editorial09-25-2020
COVID-19 and Maternal Death in Brazil: An Invisible Tragedy
- Marcos Nakamura-Pereira
 ,
, - Melania Maria Ramos Amorim
 ,
, - Rodolfo de Carvalho Pacagnella
 ,
, - Maira Libertad Soligo Takemoto
 ,
, - Fatima Cristina Cunha Penso
 , [ … ],
, [ … ], - Maria do Carmo Leal

Views245PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 32
- Policy Citations: 2
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 1855
- Captures
- Readers: 142
- Mentions
- News Mentions: 2


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
EditorialCOVID-19 and Maternal Death in Brazil: An Invisible Tragedy
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2020;42(8):445-447
- Marcos Nakamura-Pereira
 ,
, - Melania Maria Ramos Amorim
 ,
, - Rodolfo de Carvalho Pacagnella
 ,
, - Maira Libertad Soligo Takemoto
 ,
, - Fatima Cristina Cunha Penso
 ,
, - Jorge de Rezende-Filho
 ,
, - Maria do Carmo Leal

Views245The infection with the new severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2), which is responsible for causing the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19), became a devastating threat to the health of the world population and was declared a global pandemic by the World Health Organization (WHO) on March 11, 2020. Beginning in China at the end […]See morePlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 32
- Policy Citations: 2
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 1855
- Captures
- Readers: 142
- Mentions
- News Mentions: 2


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. - Marcos Nakamura-Pereira
-
Original Article01-01-2018
Premenstrual Syndrome Diagnosis: A Comparative Study between the Daily Record of Severity of Problems (DRSP) and the Premenstrual Symptoms Screening Tool (PSST)
- Aline Henz,
- Charles Francisco Ferreira,
- Carolina Leão Oderich,
- Carin Weirich Gallon,
- Juliana Rintondale Sodré de Castro, [ … ],
- Maria Celeste Osório Wender
Abstract
Original ArticlePremenstrual Syndrome Diagnosis: A Comparative Study between the Daily Record of Severity of Problems (DRSP) and the Premenstrual Symptoms Screening Tool (PSST)
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(1):20-25
- Aline Henz,
- Charles Francisco Ferreira,
- Carolina Leão Oderich,
- Carin Weirich Gallon,
- Juliana Rintondale Sodré de Castro,
- Maiara Conzatti,
- Marcelo Pio de Almeida Fleck,
- Maria Celeste Osório Wender
Views510Abstract
Objective
To validate the premenstrual symptoms screening tool (PSST) in relation to the daily record of severity of problems (DRSP) for premenstrual syndrome (PMS) and premenstrual dysphoric disorder (PMDD) diagnoses.
Methods
A cross-sectional study with 127 women (20 45 years) with PMS complaints. The women were evaluated in terms of weight, height and body mass index (BMI). After using the primary care evaluation of mental disorders (PRIME-MD) questionnaire to exclude the diagnosis of depression, the PSST was completed and the women were instructed to fill out the DRSP for two consecutive menstrual cycles. The agreement between the two questionnaires was assessed by the Kappa (k) and the prevalence-adjusted, bias-adjusted kappa (PABAK) values.
Results
Two-hundred and eighty-two women met the eligibility criteria and answered the PSST. The DRSP was completed for two cycles by 127 women. The percentages of women with PMS and PMDD diagnoses by the DRSP were 74.8% and 3.9% respectively; by PSST, the percentages were41.7% and 34.6% respectively. The number of patients considered “normal” (with symptoms below the threshold for the diagnosis of PMS) was similar in both questionnaires. There was no agreement (Kappa = 0.12) in the results of PMS/ PMDD diagnosis (the PABAK coefficient confirmed this result = 0.39). The PSST had a high sensitivity (79%) and a low specificity (33.3%) for PMS/PMDD diagnosis.
Conclusion
The PSST should be considered a diagnostic screening tool. Positive PMS/PMDD cases by PSST should be further evaluated by DRSP to confirm the diagnosis.
Key-words Diagnosispremenstrual dysphoric disorderPremenstrual syndromeQuestionnaireSigns and symptomsSee more

This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Original Article04-01-2017
Influence of Body Image in Women Undergoing Treatment for Breast Cancer
- Ana Carolina Lagos Prates,
- Ruffo Freitas-Junior,
- Mariana Ferreira Oliveira Prates,
- Márcia de Faria Veloso,
- Norami de Moura Barros
Views303PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 38
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 5472
- Abstract Views: 1237
- Captures
- Readers: 113
- Mentions
- News Mentions: 1


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Original ArticleInfluence of Body Image in Women Undergoing Treatment for Breast Cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(4):175-183
- Ana Carolina Lagos Prates,
- Ruffo Freitas-Junior,
- Mariana Ferreira Oliveira Prates,
- Márcia de Faria Veloso,
- Norami de Moura Barros
Views303See moreAbstract
Objective
The objective of this study was to investigate the self-esteem of women with and without breast cancer regarding their body image.
Methods
A quantitative, case-control study in which 90 women with breast cancer were evaluated in the case group, and 77 women without breast cancer in the control group. For data collection, the body satisfaction scale (BSS), a scale adapted and validated in Brazil, and the Rosenberg self-esteem questionnaire were used. For the statistical analysis of the data, the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences software (IBM-SPSS, Chicago, Il, US), version 16.0 was used.
Results
Compared with the women without breast cancer, those with breast cancer were more dissatisfied with body image related to appearance. Women undergoing neoadjuvant chemotherapy were more dissatisfied with their appearance compared with those with cancer who were not undergoing this treatment. Mastectomy also accounted for more dissatisfaction concerning appearance among women who underwent the procedure compared with the women who were submitted to breast-conserving therapy.
Conclusion
Women with breast cancer were more dissatisfied with their body image compared with those without breast cancer, particularly following mastectomy or during chemotherapy. The self-esteem was found to be negatively affected in patients who were dissatisfied with their body image.
PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 38
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 5472
- Abstract Views: 1237
- Captures
- Readers: 113
- Mentions
- News Mentions: 1


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. -
Review Article07-01-2017
Abnormal Uterine Bleeding
- Cristina Laguna Benetti-Pinto,
- Ana Carolina Japur de Sá Rosa-e-Silva,
- Daniela Angerame Yela,
- José Maria Soares Júnior
Views344PlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 38
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 12197
- Abstract Views: 4578
- Captures
- Readers: 363


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. Abstract
Review ArticleAbnormal Uterine Bleeding
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(7):358-368
- Cristina Laguna Benetti-Pinto,
- Ana Carolina Japur de Sá Rosa-e-Silva,
- Daniela Angerame Yela,
- José Maria Soares Júnior
Views344Abstract
Abnormal uterine bleeding is a frequent condition in Gynecology. It may impact physical, emotional sexual and professional aspects of the lives of women, impairing their quality of life. In cases of acute and severe bleeding, women may need urgent treatment with volumetric replacement and prescription of hemostatic substances. In some specific cases with more intense and prolonged bleeding, surgical treatment may be necessary. The objective of this chapter is to describe the main evidence on the treatment of women with abnormaluterinebleeding, both acuteand chronic.Didactically,thetreatmentoptions were based on the current International Federation of Gynecology and Obstetrics (FIGO) classification system (PALM-COEIN). The etiologies of PALM-COEIN are: uterine Polyp (P), Adenomyosis (A), Leiomyoma (L), precursor and Malignant lesions of the uterine body (M), Coagulopathies (C), Ovulatory dysfunction (O), Endometrial dysfunction (E), Iatrogenic (I), and Not yet classified (N). The articles were selected according to the recommendation grades of the PubMed, Cochrane and Embase databases, and those in which the main objective was the reduction of uterine menstrual bleeding were included. Only studies written in English were included. All editorial or complete papers that were not consistent with abnormal uterine bleeding, or studies in animal models, were excluded. The main objective of the treatment is the reduction of menstrual flow and morbidity and the improvement of quality of life. It is important to emphasize that the treatment in the acute phase aims to hemodynamically stabilize the patient and stop excessive bleeding, while the treatment in the chronic phase is based on correcting menstrual dysfunction according to its etiology and clinical manifestations. The treatment may be surgical or pharmacological, and thelatterisbasedmainlyonhormonaltherapy,anti-inflammatorydrugsandantifibrinolytics.
Key-words Abnormal uterine bleedingdysfunctional uterine bleedingheavy menstrual bleedingmenorrhagiaPALM-COEINSee morePlumX Metrics
- Citations
- Citation Indexes: 38
- Usage
- Full Text Views: 12197
- Abstract Views: 4578
- Captures
- Readers: 363


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited. 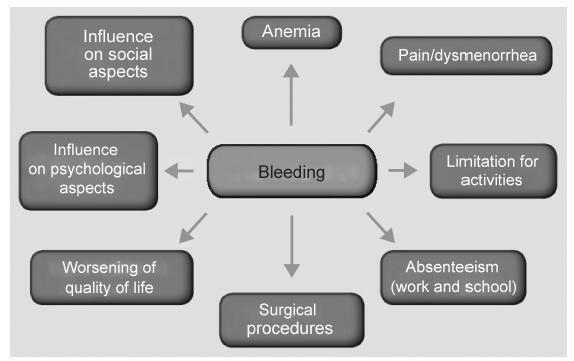
-
Original Article11-01-2018
Obstetric Outcomes among Syrian Refugees: A Comparative Study at a Tertiary Care Maternity Hospital in Turkey
- Sule Ozel,
- Selen Yaman,
- Hatice Kansu-Celik,
- Necati Hancerliogullari,
- Nurgul Balci, [ … ],
- Yaprak Engin-Ustun
Abstract
Original ArticleObstetric Outcomes among Syrian Refugees: A Comparative Study at a Tertiary Care Maternity Hospital in Turkey
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(11):673-679
- Sule Ozel,
- Selen Yaman,
- Hatice Kansu-Celik,
- Necati Hancerliogullari,
- Nurgul Balci,
- Yaprak Engin-Ustun
Views204See moreAbstract
Objective
The aim of this study was to analyze and compare obstetric and neonatal outcomes between Syrian refugees and ethnic Turkish women.
Methods
Retrospective, observational study. A total of 576 Syrian refugees and 576 ethnic Turkish women were included in this study, which was conducted between January 2015 and December 2015 at a tertiary maternity training hospital in Ankara, Turkey. The demographic characteristics, obstetric and neonatal outcomes were compared. The primary outcomes were pregnancy outcomes and cesarean rates between the groups
Results
The mean age was significantly lower in the refugee group (p< 0.001). Mean gravidity, proportion of adolescent pregnancies, proportion of pregnant women aged 12 to 19 years, and number of pregnancies at < 18 years were significantly higher among the refugee women (p< 0.001). Rates of antenatal follow-up, double testing, triple testing, gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) screening, and iron replacement therapy were significantly lower in the refugee group (p< 0.001). The primary Cesarean section rate was significantly lower in the refugee group (p= 0.034). Pregnancies in the refugee group were more complicated, with higher rates of preterm delivery (< 37 weeks), preterm premature rupture of membranes (PPROM), and low birth weight (< 2,500 g) when compared with the control group (4.2% versus 0.7%, p< 0.001; 1.6% versus 0.2%, p= 0.011; and 12% versus 5.8%, p< 0.001, respectively). Low education level (odds ratio [OR] = 1.7, 95% confidence interval [CI] = 0.5–0.1), and weight gain during pregnancy (OR = 1.7, 95% CI = 0.5–0.1) were found to be significant indicators for preterm birth/PPROM and low birthweight.
Conclusion
Syrian refugees had increased risks of certain adverse obstetric outcomes, including preterm delivery, PPROM, lower birth weight, and anemia. Several factors may influence these findings; thus, refugee women would benefit from more targeted care during pregnancy and childbirth.


This is an Open Access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original work is properly cited.
Search
Search in:
Tag Cloud
Pregnancy (252)Breast neoplasms (104)Pregnancy complications (104)Risk factors (103)Menopause (88)Ultrasonography (83)Cesarean section (78)Prenatal care (71)Endometriosis (70)Obesity (61)Infertility (57)Quality of life (55)prenatal diagnosis (51)Women's health (48)Maternal mortality (46)Postpartum period (46)Pregnant women (45)Breast (44)Prevalence (43)Uterine cervical neoplasms (43)

