Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 06-01-2018;40(6):360-368
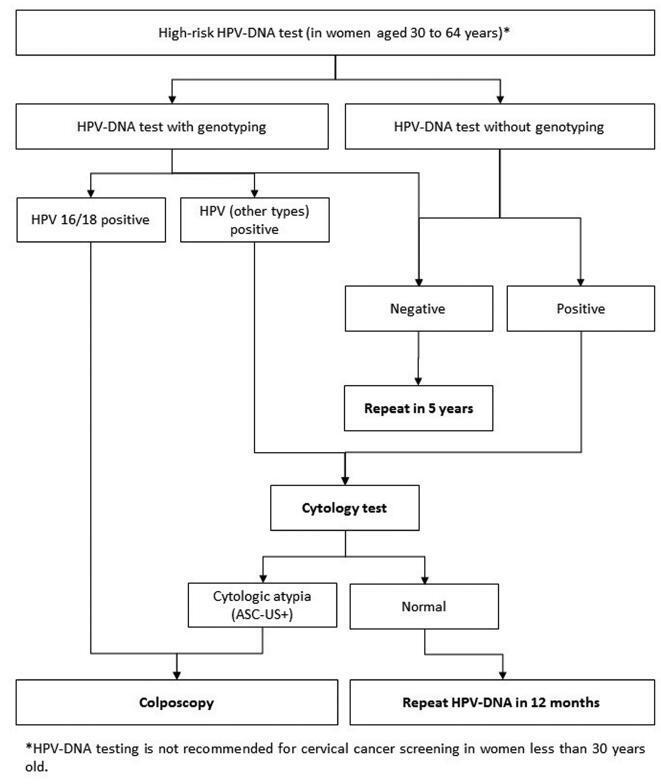
Evidence-based clinical guidelines ensure best practice protocols are available in health care. There is a widespread use of human papillomavirus deoxyribonucleic acid (HPVDNA) tests in Brazil, regardless of the lack of official guidelines. On behalf of the Brazilian Association for the Lower Genital Tract Pathology and Colposcopy (ABPTGIC, in the Portuguese acronym), a team of reviewers searched for published evidence and developed a set of recommendations for the use of HPV-DNA tests in cervical cancer screening in Brazil. The product of this process was debated and consensus was sought by the participants. One concern of the authors was the inclusion of these tests in the assessment of women with cytologic atypia and women treated for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN). Testing for HPV is recommended in an organized screening scenario to identify women with precursor lesions or asymptomatic cervical cancer older than 30 years of age, and it can be performed every 5 years. It also has value after the cytology showing atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASC-US) or low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (LSILs) as a triage test for colposcopy, in the investigation of other cytological alterations when no abnormal findings are observed at colposcopy, seeking to exclude disease, or, further, after treatment of high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, to rule out residual disease.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 09-01-2017;39(9):480-487
To evaluate the coverage of the Papanicolaou test in Brazil and the associated factors.
Cross-sectional study based on data from the Brazilian Health Survey 2013 comprising the proportion of 25- to 64-year-old women who had undergone a Papanicolaou test within the previous 3 years, categorized by sociodemographic variables and access to healthcare services.
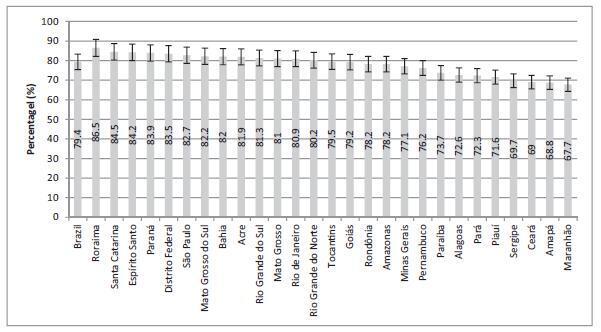
The screening coverage in Brazil was of 79.4% (95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 78.4-80.3), showing significant differences between the different states of the country, with the highest rate in the state of Roraima (86.5; 95%CI: 83.5-89.4), and the lowestone in the state ofMaranhão (67.7; 95%CI: 61.3-74.0).Undergoing the test was significantlymore frequent amongmarriedwomen (83.6%; 95%CI: 82.4-84.8), those with higher educational levels (88.7%; 95%CI: 87.0-90.5), of white ethnicity (82.6%; 95%CI: 81.3-83.9) and who reside in urban areas (80.1%; 95%CI: 79.1-81.2). Those who had undergone the test more than three years prior to the survey and the ones who had never undergone it were associated with a lower level of education, being of black or brown ethnicity, single or divorced, and rural dwellers.
The coverage of cervical cancer screening in Brazil is below the recommended rate and presents regional and sociodemographic disparities.