Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(1):40-46
To analyze the quantity of cervical smears, also designated Papanicolaou tests, between 2006 and 2015 in all the Federal units of Brazil, as well as to verify the quantity of exams collected outside the recommended age range and the economic impact of such excess.
The data was collected from the Ministry of Health’s database called Sistema de Informação do Câncer do Colo de Útero (SISCOLO), which contains all the test results collected nationwide by the Unified Health System (SUS, in the Portuguese acronym). From that, the number of exams and the age range of thewomen who underwent them were analyzed; besides, these numbers were stratified according to the state of where the exam was performed. The quantity of exams collected outside the recommended age range was verified, and, so, the economic impact generated was noted.
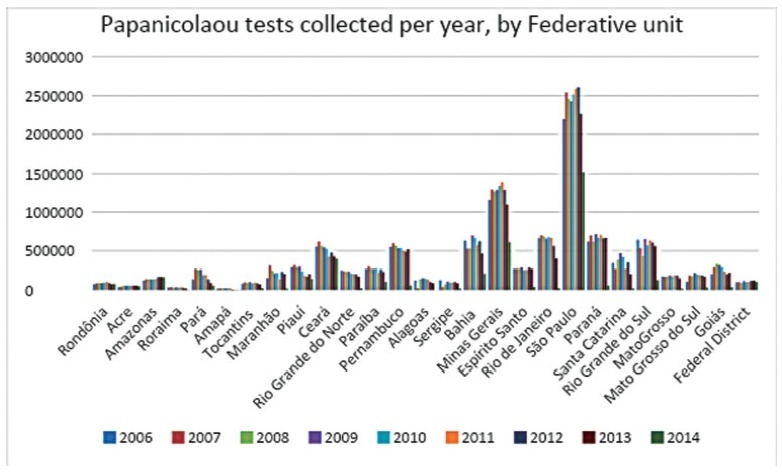
Between 2006and2015, 87,425,549Papanicolaoutestswere collected in Brazil. Of these, 20,215,052 testswere collected outside the age range recommended by the Brazilian Ministry of Health; this number corresponded to 23.12% of all exams. From such data, considering that each Pap smear collected by SUS generates a cost of BRL 7.30 to the government, according to the information in the Tabela SUS dated September 2018, there was a total charge of BRL 147,569,880 for tests collected outside the protocol.
In Brazil, according to the Ministry of Health’s protocol about the recommended practices on collecting Pap smears, whose newest edition dates of 2016, it is recommended that Pap smears are collected inwomen from a specific age range, inwhom the potential diagnosing advantages overcome the onus of overdiagnosis or of a lesion with great regression potential. However, such protocols have not been correctly followed, promoting more than 20 million tests in excess, and an exorbitant cost for the Brazilian public health system. It is relevant to take measures to correctly use the official protocol, reducing the patients risks, as well as the economic impact for SUS.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(2):79-85
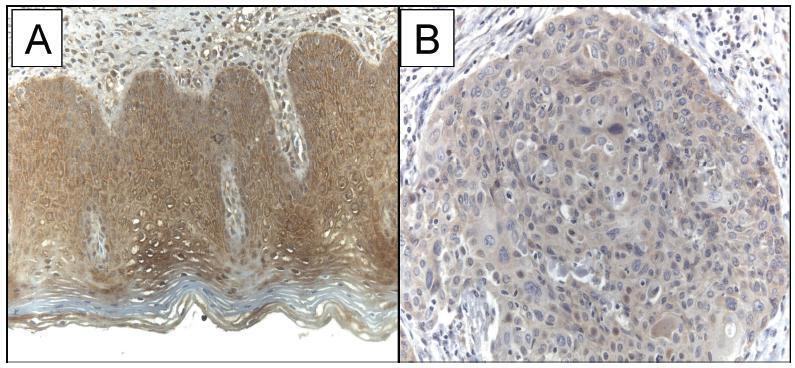
The current study evaluated the expression of WW domain-containing oxidoreductase (WWOX), its association with clinicopathological features and with p53, Ki-67 (cell proliferation) and CD31 (angiogenesis) expression in patients with invasive cervical squamous cell carcinoma (ICSCC). To the best of our knowledge, no other study has evaluated this association.
Women with IB stage-ICSCC (n = 20) and women with uterine leiomyoma (n = 20) were prospectively evaluated. Patients with ICSCC were submitted to type BC1 radical hysterectomy and pelvic lymphadenectomy. Patients in the control group underwent vaginal hysterectomy. Tissue samples were stained with hematoxylin and eosin for histological evaluation and protein expression was detected by immunohistochemistry studies.
The WWOX expression was significantly lower in the tumor compared with the expression in thebenign cervix (p = 0.019). TheWWOXexpressionwas inversely associated with the CD31 expression in the tumor samples (p = 0.018). There was no association betweentheWWOXexpression with the p53 expression (p = 0.464)or the Ki-67expression (p = 0.360) in the samples of invasive carcinoma of the cervix. There was no association between the WWOX expression and tumor size (p = 0.156), grade of differentiation (p = 0.914), presence of lymphatic vascular invasion (p = 0.155), parametrium involvement (p = 0.421) or pelvic lymph node metastasis (p = 0.310) in ICSCC tissue samples.
The results suggested that WWOX may be involved in ICSCC carcinogenesis, and this marker was associated with tumor angiogenesis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(1):41-46
To compare the diagnostic accuracy of the classic Meisels cytologic criteria and the Schneider secondary criteria relative to the hybrid capture method for diagnosing HPV infection.
This was a retrospective study performed at a public university hospital. A total of 41 patients with a cytologic diagnosis of HPV infection and 40 HPV-negative patients were selected for review of the cervical-vaginal smears seeking to classical and secondary criteria. A single pathologist reviewed the slides in search of the criteria. The classical and secondary cytologic criteria were compared with the hybrid capture for diagnosing HPV infection. Bartleti test was applied for the age analysis, and Fisher's exact test was used to compare proportions. The tests were considered significant when the probability of rejecting the null hypothesis was less than 5% (p < 0.05).
The Meisels criteria were less sensitive (34.0%) than the secondary Schneider criteria (57.5%) when compared with the hybrid capture (p < 0.0001), although the specificity of the former criteria was non-significantly higher (91.2% and 67.7%, respectively). In cases of moderate or intense inflammation, the sensitivity and specificity of the Schneider criteria were decreased, 33.3% and 50.0% respectively (p = 0.0115).
Compared with hybrid capture for diagnosis of HPV infection, the sensitivity of the secondary Schneider criteria was higher than the classical Meisels criteria.Moderate or intense inflammation reduces the sensitivity and specificity of the secondary Schneider criteria for diagnosing HPV infection using the hybrid capture as the gold standard.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(3):129-134
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000300002
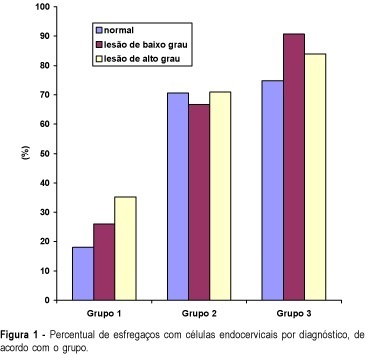
Purpose: to compare the performance of cervical canal and vaginal cul-de-sac samples for colpocytology testing, in order to diagnose cervical neoplasia. Methods: three sequential groups were constituted: group 1 - 10,048 women with ectocervix and cul-de-sac samples collected with the use of an Ayre spatula; group 2 - 3,847 women with ectocervix, cul-de-sac and cervical canal samples taken with an Ayre spatula and a cytobrush, and group 3 -- 4,059 women with ectocervix and cervical canal samples, using an Ayre spatula and a cytobrush. ANOVA (analysis of variance) and comparison of proportions were utilized for the statistical analysis. Results: the rates of abnormal tests in groups 2 (2.6%) and 3 (2.4%), including all squamous and glandular lesions, were significantly higher than in group 1 (2.0%). The diagnosis rates of low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (LGSIL) were not statistically different between the three groups (1.27, 1.25 and 1.07%). On the other hand, the diagnosis rates of high-grade squamous intraepithelial lesion (HGSIL) were statistically higher in groups 2 (0.81%) and 3 (0.77%) than in group 1 (0.54%). The difference between the rates of the second and the third groups did not present any statistical significance. Conclusions: the cervical canal sampling improves the performance of cytologic testing for the diagnosis of HGSIL, while cul-de-sac sampling does not change significantly the performance in diagnosing cervical neoplasia.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2000;22(2):65-70
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032000000200002
Purpose: to evaluate conization by the loop electrosurgical excision procedure (LEEP) for the diagnosis and treatment of cervical intraepithelial neoplasms (CIN), the importance of the margins and follow-up of these women. Methods: 95 women who underwent conization by LEEP for CIN and microinvasive carcinoma from January 1996 to December 1997 were evaluated. For statistical analysis, we used the kappa agreement coefficient and the tendency test of Cochran Armitage. Results: among 63 cases who underwent colposcopically directed biopsy before the conization, the cone presented the same grade of lesion in 20 and no residual disease in 8. The cone lesion presented a higher grade in 24 cases and one of them was a microinvasive carcinoma. Among the 25 women who underwent the cone biopsy with a previous biopsy suggestive of cervicitis or CIN 1, 56% had CIN 2 or 3 in the cone. Among the 32 women without previous biopsy, 15 had CIN 2 or 3, and four had microinvasive carcinoma in the cone. Regarding the margins of the cone, 25 cases presented some grade of CIN in the endocervical margins and 2/10 who underwent a second procedure presented residual disease on histological analysis. Among the 70 women with free cone margins, 2/4 who underwent a second procedure had residual disease on histological analysis. Conclusion: conization by LEEP without previous directed biopsy depends on the experience of the colposcopist. The second resection after LEEP for the diagnosis and treatment of CIN depends not only on the presence of disease in the cone margins but also on the follow-up. A second histological analysis is recommended in cases with microinvasive carcinoma and glandular lesion and affected margins.