Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2016;38(4):170-176
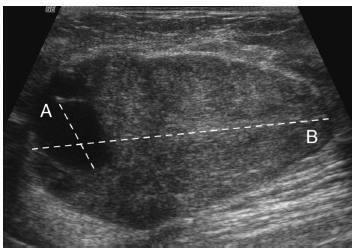
The objective of this study is to assess whether the largest cyst diameter is useful for BI-RADS ultrasonography classification of predominantly solid breast masses with an oval shape, circumscribed margins, and largest axis parallel to the skin, which, except for the cystic component, would be likely classified as benign.
This study received approval from the local institutional review board. From March 2009 to August 2014, we prospectively biopsied 170 breast masses from 164 women. We grouped the largest cyst and mass diameters according to histopathological diagnoses. We used Student's t-test, linear regression, and the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) for statistical assessment.
Histopathological examination revealed 143 (84%) benign and 27 (16%) malignant masses. The mean largest mass diameter was larger among malignant (mean standard deviation, 34.1 16.6 mm) than benign masses (24.7 16.7 mm) (P < 0.008). The mean largest cyst diameter was also larger among malignant (9.9 7.1 mm) than benign masses (4.6 3.6 mm) (P < 0.001). Agreement between measurements of the largest mass and cyst diameters was low (R2 = 0.26). AUC for the largest cyst diameter (0.78) was similar to the AUC for the largest mass diameter (0.69) ( p = 0.2). A largest cyst diameter < 3, 3 to < 11, and 11 mm had a positive predictive value of 0, 15, and 52%, respectively.
A largest cystic component < 3 mm identified within breast masses that show favorable characteristics may be considered clinically inconsequential in ultrasonography characterization. Conversely, masses with a largest cystic component 3 mm should be classified as BI-RADS-US category 4.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2008;30(4):171-176
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000400003
PURPOSE: the propose of this study was to analyze the clinical and laboratorial parameters of patients submitted to human assisted reproduction techniques with association of sperm processing techniques, in order to remove virus particles from semen samples of couples in which men was infected by human immunodeficiency virus (HIV). METHODS: it was assessed 11 intracytoplasmatic sperm injection (ICSI) cycles from couples whose men were HIV seropositive (HIV Group), and 35 cycles in which semen donors' samples were used in ICSI procedures (Control Group). Semen samples from Control Group were submitted to routine semen analysis, sperm wash and cryopreservation. The man from HIV Group received previous antibiotic therapy; the semen samples were analyzed routinely and prepared by sperm wash and density gradient method before cryopreservation. Those samples were evaluated to viral load and ICSI was performed when no HIV was detected. RESULTS: regards to semen analysis the groups were similar to sperm concentration and progressive motility. Nevertheless, the percentage of sperm with normal morphology were higher on Control Group (14.3%) than HIV (5.8%; p=0.002). On embryo parameters assessment, the normal fertilization (CT: 74.7% and HIV: 71.7; p=0.838, respectively) and good embryos rate (CT: 42.4% and HIV: 65.1%; p=0.312, respectively) were comparable. On the other hand, the Control Group presented better clinic results than HIV Group (ongoing pregnancy rate: 52.9% versus 12.5%; p=0.054, and implantation rate: 42.6 versus 10.4%; p=0.059, respectively), however the differences were not statistically significant. After delivery, no seroconversion was observed on mother and child. CONCLUSIONS: the association of sperm processing techniques in order to remove HIV from semen samples does not influence in laboratorial parameters of assisted reproduction techniques cycles. On the other hand, it has been demonstrated excellent results getting safety gametes to serodiscordant couples.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2007;29(4):171-174
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2023;45(4):171-178
To describe a reference curve for cervical length (CL) in mid-trimester twin gestations using transvaginal ultrasound (TVU) and to investigate whether short CL increases spontaneous preterm birth (sPTB) in asymptomatic twin pregnancies.
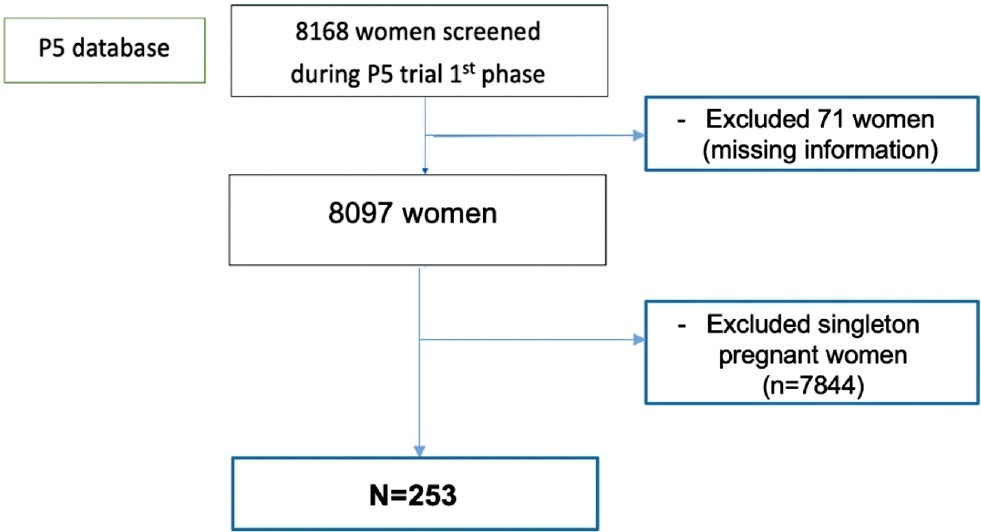
This was a prospective cohort study performed at 17 outpatient antenatal facilities of Brazil with women at 18 0/7 to 22 6/7 weeks of gestation who participated in a randomized clinical trial screening phase (P5 trial) between July 2015 and March 2019. TVU was performed to provide CL measurement in all screened women. Almost all women with CL ≤ 30 mm received vaginal progesterone 200mg/day and they were also randomized to receive cervical pessary or not. We considered data from the CL distribution among asymptomatic twin pregnancies and analyzed CL and its association with PTB generating receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curves and Kaplan-Meier curves.
A total of 253 pregnant women with twins were included in the distribution curve. The mean CL was 33.7 mm and median was 35.5mm. The 10th percentile was 17.8mm. We identified a PTB rate of 73.9% (187/253) with 33.6% of sPTB < 37 (85/253) and 15% (38/253) of sPTB < 34 weeks. The best cutoff point to predict sPTB < 37 was 24.15 mm. However, the ROC curve showed a poor performance (0.64). The Kaplan-Meier survival curves identified that only CL values ≤ 20mm were associated to sPTB < 34 weeks.
A cutoff point of CL ≤ 20 mm can be interesting point to identify short cervix in Brazilian twin pregnancies. However, in Brazilian asymptomatic twin pregnancies, CL does not show a good performance to predict PTB.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2009;31(4):171-176
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032009000400003
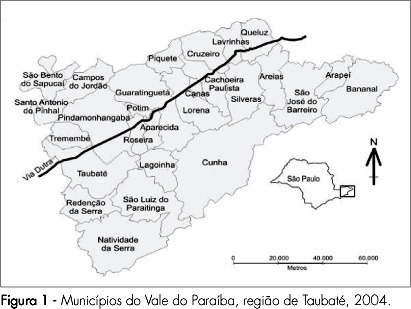
PURPOSE: to apply geoprocessing techniques for the spatial birth profile analysis of each municipality. METHODS: ecological and exploratory study, using data from the Health Information System about born alive babies in 2004, and using geoprocessing techniques. The spatial autocorrelations of the variables: cesarean section, mother's schooling, low birth weight, Apgar score at five minutes, prematurity, number of medical appointments and adolescent mothers, besides the map with the index of human development were estimated. For the detection of spatial events aggregates, Moran's I M statistics, through the program Terra View 3.13 (developed by INPE and available to the public) was used. Spatial maps with those variables were built, and Pearson's correlation coefficients, estimated. RESULTS: results have shown that the rate of born alive babies, from mothers with school level over primary school and from cesarean sections, presented a spatial pattern visually identifiable and significant spatial self-correlation. Low birth weight, prematurity, Apgar score, number of pre-natal appointments and adolescent mothers have presented a random spatial pattern, showing that, in this analysis scale, those markers have not discriminated the risk groups, despite their unquestionable predictive value for children's morbidity-mortality at individual level. There has been a positive correlation between cesarean section and schooling, and between cesarean section and human development index; and a negative correlation between adolescent mothers and human development index, with statistical significance (p<0.05). CONCLUSIONS: this methodology has allowed us to identify spatial clusters for the variables cesarean section and mother's schooling, besides deepening our knowledge on birth profile in the municipalities, presenting good potential on how to direct actions for specific areas.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(3):171-178
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006000300006
PURPOSE: postpartum anxiety (PPA) is highly prevalent and has important consequences on mother and newborn. The aim of the present study was to estimate the prevalence of PPA and its risk factors, in a sample of women attending a private setting. METHODS: a cross-sectional study was performed with 299 women, at a routine gynecological visit, from August 2000 to May 2003. The Spielberger State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAIT) and a questionnaire with sociodemographic data and obstetric data were used. Inclusion criteria were: women with no past or present history of depression, psychiatric treatment, alcohol or drug abuse and whose children were alive. The prevalences of PPA-trace and PPA-state, that evaluate characteristics of personality and transitory anxiety, respectively, were estimated with 95% confiance intervals (CI). Odds ratios and 95% CI were used to examine the association between PPA and exposure variables. Hypothesis testing was done by the chi2 test or chi2 test for linear trend, when categories were ordered. A p value < 0.05 was considered to be statistically significant. RESULTS: the prevalences of PPA-state and PPA-trace were 44.8% (CI 95%: 39.1 - 50.7) and 46.1% (CI 95%: 40.4 - 52.0, respectively). Formal agreement between scales was moderate (kappa = 0.55; p<0.001). By univariate analysis, lower mother income and presence of newborn complications were associated with PPA-state and PPA-trace. Lower maternal age and greater number of alive children were associated with PPA-trace and PPA-state, respectively. By multivariate analysis, PPA-trace and PPA-state were associated with higher mother income (OR:0.39; IC 95%: 0.21 - 0.74, p=0,005; OR:0.46; IC 95%: 0.24 - 0.87, p=0.02) and presence of complications in newborns (OR:2.15; IC 95%: 1.02 - 4.54, p=0.04) (OR:2.47; IC 95%: 1.16 - 5.25, p=0.02), respectively. PPA-trace was associated with greater maternal age (OR:0.34; IC 95%: 0.13 - 0.88, p=0.008), while PPA-state was associated with greater number of alive children (OR:1.82; IC 95%: 1.01 - 3.29, p=0.04). CONCLUSIONS: PPA was highly prevalent in this sample of women attending a private setting. Higher mother income and greater maternal age decrease the risk of AP, while presence of complications in newborns and greater number of alive children increase the risk.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2013;35(4):171-177
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000400007
PURPOSE: To evaluate changes in the venous axillary-subclavian and lymphatic systems of women with lymphedema after axillary lymphadenectomy for breast cancer treatment. METHODS: This was a case series involving 11 women with unilateral upper limb lymphedema after axillary lymphedenectomy for the treatment of breast cancer. The study was carried out in the Mastology Program of the Clinical Hospital of the Federal University of Goiás, Goiânia, GO, during the period between March 2010 and March 2011. Doppler velocimetry ultrasonography was used to detect the presence of venous changes in the subclavian and axillary veins. Lymphatic changes were evaluated by lymphoscintigraphy in both upper limbs. Fisher's exact test was used for the comparison between limbs. RESULTS: Subclavian vein flow volume in the upper limb with lymphedema was significantly different from that in the contralateral limb (p<0.001), 54.6% of the women had increased flow. In the axillary vein, 45.4% had increased flow and 45.4% had decreased flow, with a statistically significant difference (p<0.01) between limbs. Compared to the contralateral limb, significant lymphatic changes (p<0.05) were also found in the vessel route (not visualized), number of lymphatic vessels (none), axillary lymph nodes (absent) and dermal reflux (present). In the contralateral upper limb without lymphedema, no venous or lymphatic alterations were encountered. CONCLUSION: The women subjected to axillary lymphadenectomy for the treatment of breast cancer presented both venous and lymphatic changes in the upper limb with lymphedema.