You searched for:"Joelcio Francisco Abbade"
We found (8) results for your search.-
Vascular contraction of umbilical arteries of pregnant women with preeclampsia
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2024;46:e-rbgo2
Summary
Vascular contraction of umbilical arteries of pregnant women with preeclampsia
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2024;46:e-rbgo2
Views210See moreAbstract
Objective:
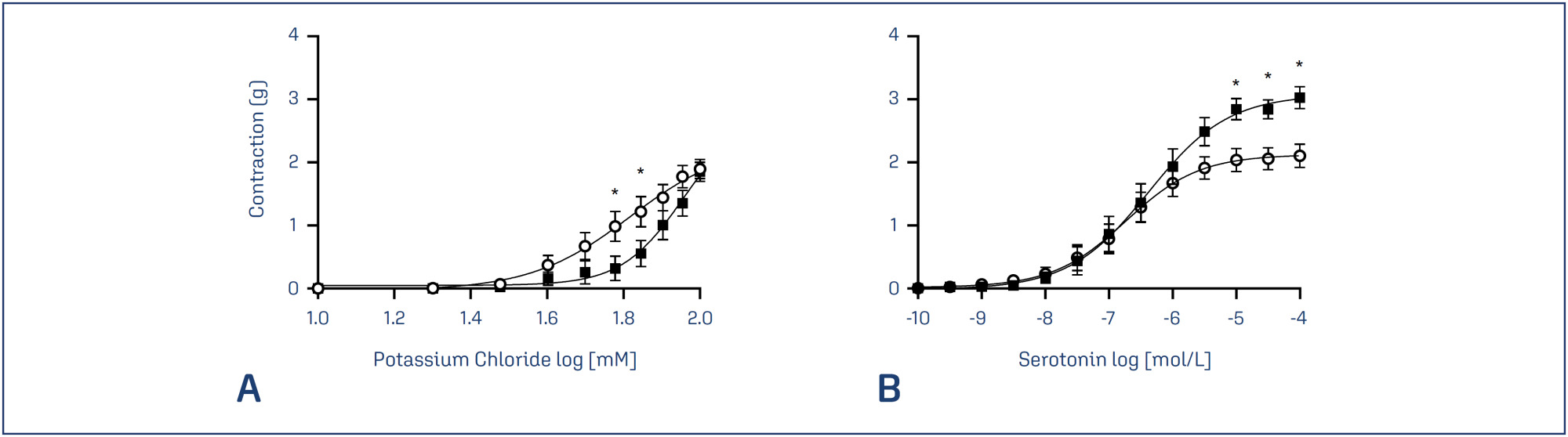
Potassium channels have an important role in the vascular adaptation during pregnancy and a reduction in the expression of adenosine triphosphate-sensitive potassium channels (Katp) has been linked to preeclampsia. Activation of Katp induces vasodilation; however, no previous study has been conducted to evaluate the effects of the inhibition of these channels in the contractility of preeclamptic arteries. Glibenclamide is an oral antihyperglycemic agent that inhibits Katp and has been widely used in vascular studies.
Methods:
To investigate the effects of the inhibition of Katp, umbilical arteries of preeclamptic women and women with healthy pregnancies were assessed by vascular contractility experiments, in the presence or absence of glibenclamide. The umbilical arteries were challenged with cumulative concentrations of potassium chloride (KCl) and serotonin.
Results:
There were no differences between the groups concerning the maternal age and gestational age of the patients. The percentage of smokers, caucasians and primiparae per group was also similar. On the other hand, blood pressure parameters were elevated in the preeclamptic group. In addition, the preeclamptic group presented a significantly higher body mass index. The newborns of both groups presented similar APGAR scores and weights.
Conclusion:
In the presence of glibenclamide, there was an increase in the KCl-induced contractions only in vessels from the PE group, showing a possible involvement of these channels in the disorder.
-
Original Article
Anthropometric characteristics of HIV/AIDS: pregnants and birth weight of theirs newborns
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2013;35(6):268-273
Summary
Original ArticleAnthropometric characteristics of HIV/AIDS: pregnants and birth weight of theirs newborns
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2013;35(6):268-273
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032013000600006
Views2See morePURPOSE: To describe the anthropometric and pregnancy characteristics of women with HIV/AIDS, assisted by the Brazilian National Health System and the birth weight of their newborns. METHODS: The participants were women assisted at public STD/AIDS clinics of the Municipal Health system of São Paulo. The anthropometric characteristics were evaluated by trained nutritionists and other information was obtained from the medical records. For comparison of the survey data to those of the general population, secondary maternal and pregnancy data were obtained from live birth certificates through the Live Birth Information System. Continuous variables were summarized as mean and standard deviation or as the 25th, 50th and 75th percentiles and minimum and maximum values. The other variables are presented as percentages. Means were compared by the Student’s t-test or Kruskal-Wallis test depending on the fulfillment of assumptions, with the decision based on the p value. RESULTS: We found the presence of inadequate maternal nutrition according to triceps skinfold (60.9%). The BMI/gestational age showed the presence of underweight (18.5%) and overweight or obesity (40%). There was no association between disease status (HIV or AIDS) and weight, height, and lean or fat mass. Mean newborn birth weight was lower than the value for the general population without infection or disease. The results of this study indicate the need to develop adapted curves to allow a more accurate nutritional assessment of this population group.
-
Original Article
Hyperthyroidism during pregnancy: maternal-fetal outcomes
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2008;30(9):452-458
Summary
Original ArticleHyperthyroidism during pregnancy: maternal-fetal outcomes
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2008;30(9):452-458
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000900005
Views1See morePURPOSE: to evaluate the experience of Hospital das Clínicas da Faculdade de Medicina de Botucatu da Universidade Estadual Paulista “Júlio de Mesquita Filho”, in the follow-up of pregnant women with hyperthyroidism. METHODS: Sixty patients, divided in groups with compensated hyperthyroidism (CHG=24) and with uncompensated hyperthyroidism (UHG=36) were retrospectively studied and compared concerning clinical-laboratorial characteristics and intercurrences. The t-Student test, contingency tables, multiple linear regression and multiple logistic regression with significance level at 5.0% were used. RESULTS: propylthiouracil (PTU) was used by 94.0% of UHG and by 42.0% of CHG (p<0.0001); maternal complications close to delivery have occurred in 20.6% of UHG and in 11.8% of CHG, and UHG presented three fetal deaths, influenced by the mother age, higher level of T4L (lT4L) and of PTU dose (PTUd) in the third trimester (p=0.007); restriction of intra-uterine growth, influenced by lT4L and PTUd in the third trimester has occurred in nine UHG and in three CHG cases, and oligoamnios has occurred in 12 patients (83.3% of UGH and 16.7% of CGH), influenced by age and lT4L in the third trimester (p=0.04); the gestational age at delivery was 34.4±4.6 weeks in UHG and 37.0±2.5 in CHG, influenced by the T4Ll in the third trimester (p<0.05). CONCLUSIONS: the UHG has presented less satisfactory results than CHG, influenced by high lT4L and PTUd in the third trimester, and by more advanced age of some pregnant women.
-
Original Article
Ming of the presence of schistocytes in blood smear of preeclamptic pregnat women
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2008;30(8):406-412
Summary
Original ArticleMing of the presence of schistocytes in blood smear of preeclamptic pregnat women
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2008;30(8):406-412
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032008000800006
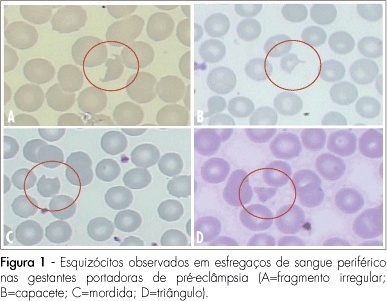
Views4See morePURPOSE: to evaluate the significance of schizocytes presence in peripheral blood smear of pregnant women with pre-eclampsia, identifying and correlating them with other markers of hemolysis and of the disease severity. METHODS: Seventh six glass slides of peripheral blood smear of pregnant women with pre-eclampsia have been evaluated. After the smear, the slides have been stained with Leishman’s dye and stored till they were examined with a Leica, model DLMB microscope, provided with the Qwin Lite 2.5 software that made it possible to record the images of selected fields in CD-ROM. Ten fields with approximately 100 erythrocytes were counted in each glass slide. Schizocytes (irregular fragment or helmet-shaped, bite-shaped or triangular) were considered as present, when their percentage was equal or higher than 0.2%, their presence being correlated with other hemolysis markers (hemoglobin, total bilirubin, lactic desidrogenasis and reticulocytes), pre-eclampsia markers (proteinuria and platelet number). The Statistical Package in Social Science for Windows (SPSS), 10.0 version has been used for statistical analysis, at p<0.05. RESULTS: schizocytes have been present in 31.6% of the pregnant women with pre-eclampsia. In most (75%) of the blood smears there have been three or four schizocytes. There has been no correlation between schizocyte presence and any other hemolysis marker, any pre-eclampsia marker or disease severity. CONCLUSIONS: schizocytes have been identified in a small number and in less than a third of the pregnant women with pre-eclampsia. There has been no correlation with other hemolysis marker parameters or with the disease severity. This way, the presence of schizocytes is not a marker of the clinical evolution of pre-eclampsia.
-
Original Article
Fetal macrosomia risk factors in pregnancies complicated by diabetes or daily hyperglycemia
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2005;27(10):580-587
Summary
Original ArticleFetal macrosomia risk factors in pregnancies complicated by diabetes or daily hyperglycemia
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2005;27(10):580-587
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032005001000003
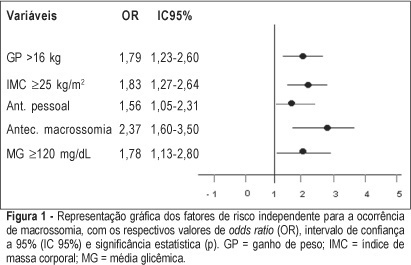
Views1See morePURPOSE: to identify risk factors for fetal macrosomia in pregnant women with diabetes or daily hyperglycemia. METHODS: retrospective study, control-case, including 803 pairs of mothers and newborns belonging to this specific population, divided into two groups – macrosomic (cases, n=242) and non-macrosomic (controls, n=561). Variables regarding age, parity, weight and body mass index (BMI), weight gain (WG), diabetes history, high blood pressure and tabagism, diabetes type and classification, and glycemic control indicators in the third trimester were compared. The means were evaluated by the F test and the categorized variables were submitted to univariate analysis using the chi² test. The significative results were included in the multiple regression model for the identification of macrosomia independent risk considering OR, 95% CI and p value. The statistical significance limit of 5% was established for all analyses. RESULTS: there was a significative association between macrosomia and WG >16 kg, BMI >25 kg/m², personal, obstetric and macrosomic history, classification in the Rudge groups (IB and IIA + IIB), glycemic mean (GM) >120 mg/dL and postprandial glycemic mean >130 mg/dL in the third trimester. In the multiple regression analysis, WG >16 kg (OR=1,79; 95% CI: 1,23-1.60), BMI >25 kg/m² (OR=1.83; 95% CI: 1.27-2.64), personal history of diabetes (OR=1.56; 95% CI: 1.05-2.31) and of macrosomia (OR=2.37; 95% CI: 1.60-3.50) and GM >120 mg/dL in the third trimester (OR=1.78; 95% CI: 1.13-2.80) confirmed to be independent risk factors for macrosomia in these pregnancies. CONCLUSION: WG >16 kg, BMI >25 kg/m², GM >120 mg/dL in the third trimester and personal history of macrosomia and diabetes were identified as risk factors for fetal macrosomia in pregnant women with diabetes or daily hyperglycemia.
-
Original Article
Blood pressure and heart rate evaluated by ABPM in primigravid women during labor and early puerperium
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2004;26(5):391-398
Summary
Original ArticleBlood pressure and heart rate evaluated by ABPM in primigravid women during labor and early puerperium
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2004;26(5):391-398
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000500008
Views2See moreOBJECTIVE: to analyze the maternal blood pressure and heart rate variation of primigravid women during labor and early puerperium. METHODS: sixty primigravid women were included in the study, and submitted to ambulatory blood pressure monitoring (ABPM) with SpaceLabs 90207 monitor during labor and the first 12 h of puerperium. The records of blood pressure and heart rate were done every 15 min during labor and every 30 min during the first 12 h of puerperium. Three periods during labor (until cervix dilated 7 cm, cervix dilated between 8 cm and total dilatation, and delivery period) and two during puerperium (first and twelfth hours), were analyzed. First of all the results were analyzed without considering the kind of analgesia used and then the patients were divided into three groups, according to the anesthetic technique: local, lumbar extradural or subarachnoid. Results were analyzed by one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and paired Student’s t-test for blood pressure and heart rate in each group during labor and puerperium. The nonpaired Student’s t-test was used to compare different groups. A p value < 0.05 was regarded as statistically significant. RESULTS: when the results were analyzed without considering the analgesic procedure, the values of systolic blood pressure during labor were significantly higher than in early puerperium. During labor, systolic blood pressure values were higher in the periods of later cervical dilatation and delivery than during early cervical dilatation. In the 12th h of puerperium the systolic blood pressure was lower than in the first hour. Diastolic blood pressure did not change during labor and was higher than in early puerperium. Heart rate increased during labor and decreased during puerperium. The systolic and diastolic blood pressure and heart rate were the same both in local or lumbar extradural anesthesia groups; however, in the subarachnoid group the systolic and diastolic blood pressure did not change during labor. CONCLUSIONS: labor increased systolic blood pressure and heart rate. During labor, systolic and diastolic blood pressure were higher than in early puerperium. Both blood pressure and heart rate significantly fell from the first to the 12th hour of puerperium. The different anesthetic techniques did not affect blood pressure or heart rate, as compared with the primigravid group when the anesthetic technique was not taken into consideration.
-
Original Article
Effect of Maternal Hemodynamic Alterations on the Product of Conception
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2001;23(3):147-151
Summary
Original ArticleEffect of Maternal Hemodynamic Alterations on the Product of Conception
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2001;23(3):147-151
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032001000300003
Views1See morePurpose: to evaluate maternal hemodynamic and cardiac structural changes during the three trimesters of pregnancy and to relate them to the weight/gestational age of the newborn. Methods: twenty-two healthy pregnant women were submitted to echocardiography for the study of cardiac output, mean arterial pressure, left atrium diameter, and peripheral resistance during three periods of pregnancy, i.e., before the 12th week and at the 26thand 36th weeks of pregnancy. Seventeen pregnant women gave birth to infants with adequate weight for gestational age, four gave birth to small for gestational age newborns and one gave birth to a large for gestational age infant. Results: among mothers of low weight newborns, cardiac output and left atrium diameter remained constant, mean arterial pressure showed a tendency to increase and peripheral resistance was significantly increased (28%), during the gestation. Among the mothers of adequate weight newborns there was an increase in cardiac output of 19% in the second trimester and 8% in the third. The left atrial diameter increased approximately 9% during the gestation, with maintenance of mean arterial pressure and a tendency to a decrease in peripheral resistance. Conclusion: the present results support an association between hemodynamic adaptation and weight newborn.
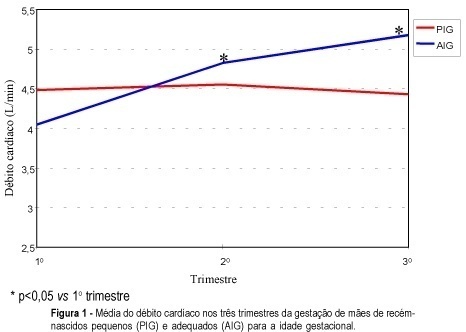
-
Original Article
The Trial of Labor After one Cesarean Section
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2002;24(3):161-166
Summary
Original ArticleThe Trial of Labor After one Cesarean Section
Rev Bras Ginecol Obstet. 2002;24(3):161-166
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032002000300003
Views0See morePurpose: to study trial of labor (TOL) for vaginal birth after one previous cesarean section. Methods: this is a retrospective cohort study that included 438 pregnant women with one previous cesarean section and their 450 newborns. They were divided into two groups – with and without TOL. The minimum sample size was 121 pregnant mothers per group. TOL was considered as an independent variable and vaginal birth and maternal and perinatal complication frequency as dependent variables. Both univariate and multivariate analyses were performed. The comparison of observed frequencies (%) was analyzed by the chi-squared test (chi²) with 5% significance, and linear regression from the odds ratio (OR) and confidence interval of 95% (CI95%). Results: TOL was used in 59.2% of vaginal deliveries. It was less used in women over 40 years (2.7% vs 6.7%) and in those with clinical or obstetrical diseases such as arterial hypertension (7.0%) and bleeding in the third trimester (0.3%). There was a higher risk for puerperal complications with cesarean deliveries (OR = 3.53, CI 95% = 1.57-7.93), independent of TOL. Perinatal mortality was dependent on neonatal weight and fetal malformations, not on TOL. Newborns from mothers not submitted to TOL were at a higher risk for developing breathing complications (OR = 1.92 CI 95% = 1.20-3.07). Conclusions: The results confirm that trial of labor after a previous cesarean section is a safe method – assisting vaginal delivery in 59.2% of births and not interfering with maternal and perinatal mortality. It is a treatment that should be stimulated.
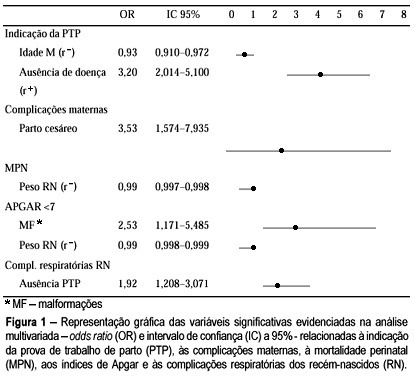
Search
Search in:
Tag Cloud
breast (42) breast cancer (42) breast neoplasms (95) Cesarean section (72) endometriosis (66) infertility (56) Maternal mortality (43) menopause (82) obesity (58) postpartum period (40) pregnancy (225) Pregnancy complications (99) Prenatal care (68) prenatal diagnosis (50) Prevalence (41) Quality of life (51) risk factors (94) ultrasonography (79) urinary incontinence (40) women's health (48)