Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(2):131-138
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000200008
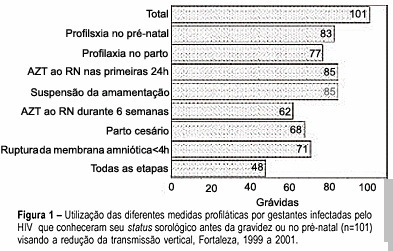
PURPOSE: to analyze the management for reduction of HIV transmission from mother to infant in infected pregnant women who delivered in public maternity hospitals of the municipality of Fortaleza, Ceará, from 1999 to 2001. METHODS: a descriptive study where data of SINASC, SINAN and LACEN data bank systems were cross-checked looking for HIV-infected pregnant women, followed by an active search for complementary information on the subject through medical records of the maternity hospitals. RESULTS: a hundred and thirty-eight pregnant women infected with HIV were identified. It was observed that 35.5% knew their serum status before pregnancy and 48.6% (67/138) were diagnosed during the prenatal visits. Of those 101 women that knew their serum status before or during pregnancy, only 47.5% followed all steps of prophylaxis, including the management of the newborns. The previous knowledge of the serum status was found to be significantly related to following the correct steps of prophylaxis (p<0.001). CONCLUSIONS: an increasing number of women who had no access to the different strategies for the reduction of vertical transmission were found in Fortaleza, Ceará, especially among those who became pregnant without knowing their serum status. Continuous awareness and training are very important for all health care providers involved in attending the pregnant women for the application of correct management in order to reduce HIV transmission from mother to infant.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(2):147-151
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000200010
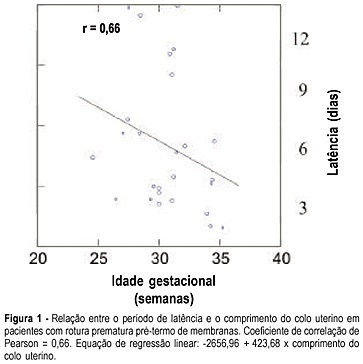
PURPOSE: to assess the length of the uterine cervix by transvaginal ultrasonography in pregnant women with preterm premature rupture of membranes. METHODS: the study group (Ge) consisted of 26 pregnant women with gestational age between 24 and 36 weeks and the control group (Gc) of 49 clinically normal patients at the same gestational age. The patients were evaluated between the 24th to 28th, 28th to 32th and 32th to 36th weeks. The groups were divided into subgroups Ge24-28, Ge28-32, Ge32-36 and Gc24-28, Gc28-32, Gc32-36, according to the study or control group. The cervix length was measured by transvaginal ultrasonography as the linear distance between the internal and external cervical os. RESULTS: we observed significant differences in cervix length between Ge24-28 and Gc24-28 groups whose values were, respectively, 24.3 and 33.0 mm (p=0.04), and between Ge32-36 and Gc32-36, 20.1 and 28.0 mm, respectively (p=0.005). The latency periods of Ge24-28, Ge28-32 and Ge32-36 were, respectively, seven, five and three days, showing a positive correlation with cervix length (r=0.66) and a negative correlation with gestational age (r=-0.27). CONCLUSIONS: the length of the uterine cervix varied with the gestational age when premature preterm rupture of the membranes was detected, with the length being shorter in the study group than in the control group betweeen the 24th and 28th and 32th and 36th weeks. In addition, it was demonstrated that, the shorter the cervix length, the shorter the latency time, with a reduction in the latency period with increasing gestational age at the time of rupture.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(2):89-96
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000200002
PURPOSE: to evaluate knowledge, opinion and practice of gynecologists/obstetricians regarding induction of abortion. Method: a pretested, structured questionnaire was sent to gynecologists/obstetricians affiliated to FEBRASGO. They were asked to answer and return the questionnaire in a self-addressed, prepaid envelope, without identification of the respondent so as to preserve anonymity. Knowledge about the legal situation of abortion in Brazil, opinion about it and practice if confronted with abortion requests were questioned. RESULTS: approximately 90% of the respondents believed that abortion is legal for pregnancy resulting from rape or in case of risk to a woman's life and for 31.8% in case of severe fetal malformation. In their opinion abortion should be permitted in the case that pregnancy is a risk for a woman's life (79.3%), fetal malformation (77.0%) and after rape (76.6%), added to 9.9% who expressed that abortion should be permitted in all circumstances. Two thirds wrongly thought that a judicial order is required to practice a legal abortion and only 27.4% knew that a written request by the woman is required. Confronted with unwanted pregnancy, 77.6% of female gynecologists/obstetricians and 79.9% of partners of male respondents had an abortion, 40% would help a client and 48.5% a relative in the same situation. CONCLUSION: gynecologists/obstetricians lack knowledge on the legal situation of abortion although their opinion and practice are favorable.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(2):97-102
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000200003
PURPOSE: to correlate the type of cervical lesion diagnosed by Pap smear with CD4 cell counts and HIV-RNA viral load in HIV-positive patients. METHODS: one hundred and fifteen HIV patients were evaluated retrospectively in the present study, during the period from January 2002 to April 2003, at a university hospital. Eighty-three patients presented cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) in Pap smear, in comparison with thirty-two with no lesions. Patients were divided into three groups, according to CD4 counts: CD4 more than 500 cells/mm³, between 200 and 500 cells/mm³, and less than 200 cells/mm³, and other three groups, according to HIV viral load: less than 10,000 HIV-RNA copies/mL, between 10,000 and 100,000 HIV-RNA copies/mL, or more than 100,000 HIV-RNA copies/mL. Correlation was investigated by the Fisher test. RESULTS: of the eighty-three patients with CIN, 73% presented CD4 counts less than 500 cells/mm³. In all CD4 groups, more than 50% of the patients presented CIN. According to the viral load, 71.7% of the patients with less than 10,000 HIV-RNA copies/mL presented CIN I, compared with 11.3% that showed CIN III. In the group with higher viral load (>100.000 HIV-RNA copies/mL), 61.5% showed CIN I and 30.8% presented CIN III. CONCLUSION: association between viral load and CIN was established (p=0.013), which was not observed with CD4 cell counts and CIN. Concomitant cervicovaginal infection was considered a potential confounding factor.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(1):15-20
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000100003
PURPOSE: to analyze the values of Doppler ultrasound for blood flow velocity in the ductus venosus between the 10th and the 14th week of gestation, during the different phases of the cardiac cycle: ventricular systole (wave S), ventricular diastole (wave D), atrial systole (wave a), and angle-independent indexes. METHODS: Doppler was used in this prospective cross-sectional study to examine 276 single pregnancies. Fetus malformations, abnormal nuchal translucency, and women with clinical pathologies were excluded. A Toshiba SSH-140 ultrasound equipment was used. The derivation of Doppler frequency spectra was carried out according to standardized measurement procedures: less than 30ºinsonation angle and 50-70 Hz high-pass filter. The ductus venosus was identified in a median sagittal and ventral plane with the presence of color aliasing due to increase in blood flow velocity. The sample volume (1-2 mm³) was placed immediately at the origin of the ductus venosus. At least three clearly and subsequent waves were available for measurement of standard values. The Levene test and the Bonferroni method were used for statistical analysis. RESULTS: increase in blood flow velocity from 29 cm/s to 37 cm/s (p=0.013) was observed during ventricular systole between the 10th and the 14th week of gestation. Similarly, increase in blood flow velocity was recorded during the ventricular diastole (from 25 cm/s to 32 cm/s, p=0.026). There were no changes in wave a, pulsatility index, and S/a ratio in this period. CONCLUSION: the reference ranges established by this study may serve as the basis for Doppler ultrasound follow-up in a normal patient population. Further studies are required to determine the validity of these parameters and, in particular, for the fetus at risk.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(1):21-29
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000100004
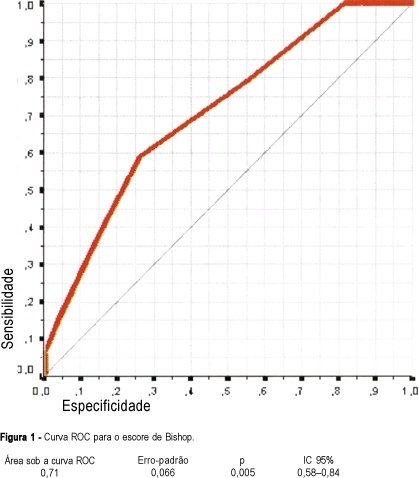
PURPOSE: to determine the main factors associated with vaginal delivery in high-risk pregnant women submitted to labor induction with vaginal misoprostol (50 µg). METHODS: this is a secondary analysis of an open nonrandomized clinical trial that included 61 high-risk pregnant women admitted at the "Maternidade-Escola Assis Chateaubriand", Fortaleza (Ceará). All women had singleton pregnancies with alive fetuses, gestational age >37 weeks and Bishop scores <7. Misoprostol was vaginally administered at doses of 50 µg every 6 h for a maximum of four doses. Univariate and multiple logistic regression analyses were performed to determine association between vaginal delivery (dependent variable) and independent variables (predictive), and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves were constructed for parity and Bishop scores. RESULTS: parity (one or more previous deliveries), Bishop scores >4 and interval induction to delivery <6 h were significantly associated with vaginal delivery, while tachysystole reduced the probability of vaginal delivery. A multivariate stepwise logistic regression was then performed to evaluate each of these as independent predictors. Parity (OR = 5.41, 95% CI = 4.18-6.64) and Bishop score >4 (OR = 3.30, 95% CI = 2.15-4.45) were significant independent predictors for vaginal delivery. In the ROC curve for parity and Bishop score, sensitivity of 63.2% and positive predictive value of 100% were found. The area under the ROC curve was 86.8%, significantly higher than 50% (p=0.023). CONCLUSIONS: the most important predictive factors for vaginal delivery after induction with misoprostol were parity and Bishop score. These characteristics should be considered when choosing schemes and doses of misoprostol for cervical ripening and labor induction.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2004;26(1):37-42
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032004000100006
PURPOSE: to evaluate the accuracy of directional vacuum-assisted biopsy (mammotomy), guided by ultrasonography, in the diagnosis of nonpalpable breast lesion, as compared with excision biopsy, and to evaluate the therapeutic value of mammotomy in nonpalpable benign lesions. METHODS: 114 patients, who presented nonpalpable breast lesion, visible on ultrasonography, were included. The patients were referred to complementary ultrasonographic evaluation due to mastalgia or earlier found mammographic alteration. All were submitted to mammotomy guided by ultrasonography using Mammotome® (Biopsys, Irvine, Califórnia), with a 11 gauge needle. The excision biopsy was performed with previous puncture of those patients who presented residual lesion after the mammotomy, that is, 88 patients. To evaluate comparatively the mammotomy results with those of excision biopsy, the sensitivity and specificity rates, positive and negative predictive values, and the agreement proportion were calculated. Not only the sensibilities, but also the specificities and the agreement proportions of both examinations were compared through Wald statistics, using a model for classified data. RESULTS: of 114 patients, 88 were submitted to excision biopsy. The remaining 26 did not show post-mammotomy lesions visible on ultrasonography, and for one year they were without alterations on the bi-annual mammographic and ultrasonographic examinations. The diameter of those lesions was less than 1.5 cm. Among the 88 patients that underwent excision biopsy, 69 (78,4%) showed benign and 19 (21,6%), malignant lesions. Mammotomy diagnosed 16 of the malignant lesions, with three false-negative and no false-positive results. The false results occurred in the first cases, showing the existence of a learning curve of the method, or due to technical difficulty such as the blurring of ultrasonographic image by bleeding. The sensitivity and specificity were 84,2% and 100%, respectively, with 100% positive predictive and 95,8% predictive negative values. The mammotomy accuracy was 96,6%. Complications were rare: two cases of hematomas, none of them needing surgical drainage; a case of vasovagal reflex not allowing the conclusion of the examination. The cosmetic results were very favorable due to small incisions (3 mm) and to the smaller amount of excised tissue. CONCLUSION: mammotomy guided by ultrasonography showed to be a diagnostic method with high accuracy, and it may be used as therapy for benign, smaller than 1.5 cm lesions.