-
Review Article10-01-2018
Effect of the Air Filtration System Replacement on Embryo Quality in the Assisted Reproduction Laboratory
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(10):625-630
Abstract
Review ArticleEffect of the Air Filtration System Replacement on Embryo Quality in the Assisted Reproduction Laboratory
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(10):625-630
Views136See moreAbstract
Improving infrastructural conditions of the in vitro fertilization laboratory, such as the air quality, has profound positive effects on embryo culture. Poor environmental conditions reduce the rate of embryo formation and, therefore, of pregnancy. This review article presents important publications regarding the impact of air quality in human reproduction laboratories on embryo quality, pregnancy success, and live births. The studies demonstrate that the replacing the air filtration system improves significantly the environmental air quality, and, consequently, improves laboratory parameters, such as the fertilization rate, the number of blastocysts, the embryo implantation rate, and the number of live births. On the other hand, improving air quality decreases the number of abortions. Therefore, environmental parameters that improve embryo quality and increase healthy child birth ratesmust be themain targets for the assisted reproduction laboratory quality control.
-
Review Article09-01-2018
Multiple Pregnancy: Epidemiology and Association with Maternal and Perinatal Morbidity
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):554-562
Abstract
Review ArticleMultiple Pregnancy: Epidemiology and Association with Maternal and Perinatal Morbidity
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(9):554-562
Views359See moreAbstract
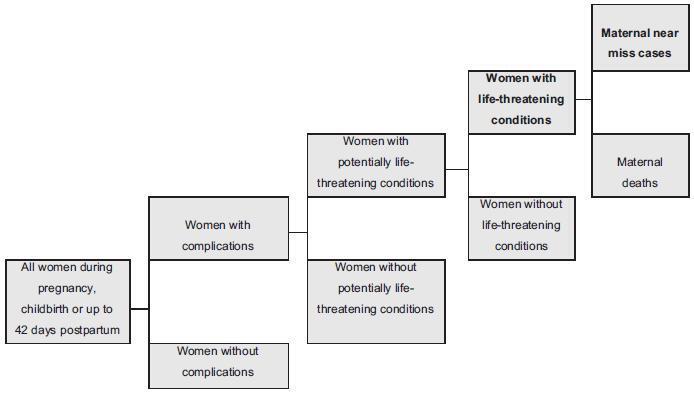
Twin pregnancy accounts for 2 to 4% of total births, with a prevalence ranging from 0.9 to 2.4% in Brazil. It is associated with worse maternal and perinatal outcomes. Many conditions, such as severe maternal morbidity (SMM) (potentially life-threatening conditions and maternal near-miss) and neonatal near-miss (NNM) still have not been properly investigated in the literature. The difficulty in determining the conditions associated with twin pregnancy probably lies in its relatively low occurrence and the need for larger population studies. The use of the whole population and of databases from large multicenter studies, therefore, may provide unprecedented results. Since it is a rare condition, it ismore easily evaluated using vital statistics from birth e-registries. Therefore, we have performed a literature review to identify the characteristics of twin pregnancy in Brazil and worldwide. Twin pregnancy has consistently been associated with SMM, maternal near-miss (MNM) and perinatal morbidity, with still worse results for the second twin, possibly due to some characteristics of the delivery, including safety and availability of appropriate obstetric care to women at a high risk of perinatal complications.
-
Review Article08-01-2018
Prenatal Care and Hypertensive Gestational Syndromes: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(8):471-476
Abstract
Review ArticlePrenatal Care and Hypertensive Gestational Syndromes: A Systematic Review
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(8):471-476
Views209See moreAbstract
Objective
Evaluate the influence of prenatal care on the occurrence of gestational hypertension.
Methods
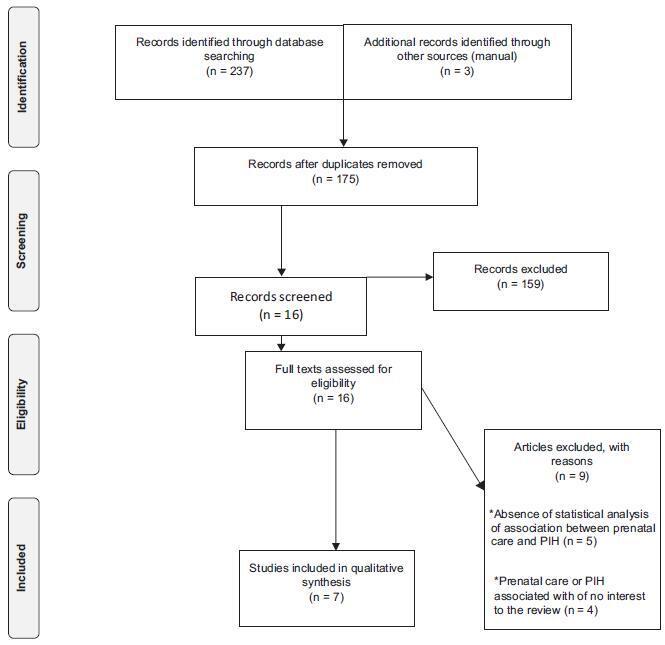
The Web of Science, Scopus, Pubmed, Cochrane and ClinicalTrials electronic databases were searched for articles published between January 1st, 2012 and December 31st, 2016. No language restrictions were imposed. The following keywords were used: prenatal care, medical assistance, prenatal education, pregnancy-induced hypertension. The preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses (PRISMA) checklist was employed. Two hundred and forty articles were identified during the initial search, but only seven met the inclusion criteria. This systematic review is registered with the international prospective register of systematic reviews (PROSPERO; #CRD42017064103).
Results
The seven studies hada lowriskof bias,withmethodological quality scores ranging fromsix to eight points. Five studies found a positive relationship between prenatal care and pregnancy-induced hypertension, whereas two studies found no significant association between the two variables. The divergence among the studies may have been due to the type of healthcare service at which the study was conducted and the sample size.
Conclusion
Although the studies analyzed differed with regard to methodological aspects, the findings demonstrate the importance of prenatal care during the gestational period as a prevention and health promotion measure.
-
Review Article07-01-2018
Abortion in Cases of Zika Virus Congenital Infection
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(7):417-424
Abstract
Review ArticleAbortion in Cases of Zika Virus Congenital Infection
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(7):417-424
Views120See moreAbstract
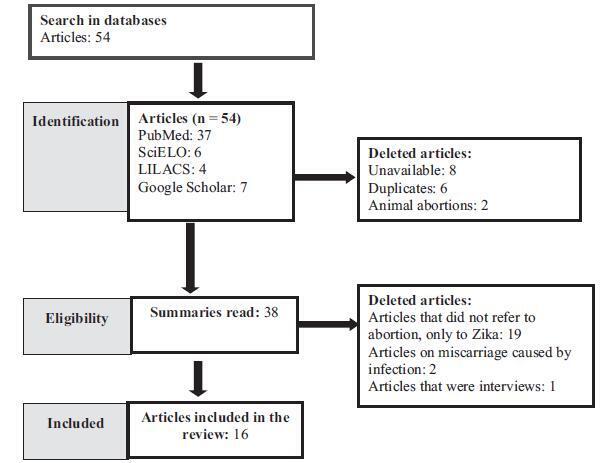
The emergency in international public health caused by the Zika virus gave rise to the discussion about abortion in cases of congenital Zika virus syndrome (CZS). Therefore, we propose to carry out a bibliographic review on abortion in these cases. Five databases were searched using the following terms: abortion, miscarriage, and zika, with the interposition of the Boolean operator “AND.” In the selected literature, we found references to the lack of information concerning the risks and severity of CZS, to the great psychological distress suffered by pregnant women, and to the risk of unsafe abortions as a justification for abortion in cases of CZS. However, it is necessary to have available tests that could diagnose, in the first trimester of pregnancy, that the fetus has been affected by the virus, and that it may have important limitations, in order to subsidize the qualified discussion about abortion in these cases.
-
Review Article06-01-2018
Breastfeeding and the Benefits of Lactation for Women’s Health
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):354-359
Abstract
Review ArticleBreastfeeding and the Benefits of Lactation for Women’s Health
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):354-359
Views456See moreAbstract
The offer of the maternal breast to the baby is an unquestionable right of mothers and their children, and all efforts should bemade to promote, follow and maintain exclusive breastfeeding for up to 6months and supplement it until the child completes 2 years of age. Many publications are available in the literature about the qualities of breast milk, its benefits and health repercussions, stimulating the practice of breastfeeding and supporting campaigns for its implementation. However, although it is widely known that breastfeeding is an important step in the reproductive process of women and its practice offers benefits to both mother and child, most of the available information highlights the benefits of breast milk for children, while mention of the effects of breastfeeding on the health of the mother is usually neglected. Thus, the objective of the present study is to highlight the multiple benefits of breastfeeding for the physical and emotional health of the nursing mother. The authors consulted articles published in the databases PubMed, Virtual Health Library andWeb of Science using the keywords breastfeeding, breast milk, lactation and maternal health.
-
Review Article06-01-2018
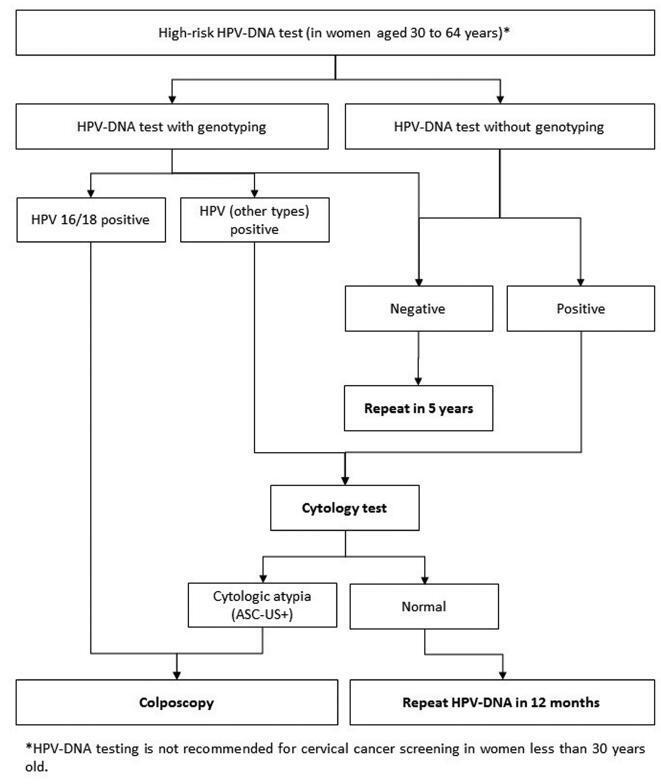
Guidelines for HPV-DNA Testing for Cervical Cancer Screening in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):360-368
Abstract
Review ArticleGuidelines for HPV-DNA Testing for Cervical Cancer Screening in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):360-368
Views329See moreAbstract
Evidence-based clinical guidelines ensure best practice protocols are available in health care. There is a widespread use of human papillomavirus deoxyribonucleic acid (HPVDNA) tests in Brazil, regardless of the lack of official guidelines. On behalf of the Brazilian Association for the Lower Genital Tract Pathology and Colposcopy (ABPTGIC, in the Portuguese acronym), a team of reviewers searched for published evidence and developed a set of recommendations for the use of HPV-DNA tests in cervical cancer screening in Brazil. The product of this process was debated and consensus was sought by the participants. One concern of the authors was the inclusion of these tests in the assessment of women with cytologic atypia and women treated for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN). Testing for HPV is recommended in an organized screening scenario to identify women with precursor lesions or asymptomatic cervical cancer older than 30 years of age, and it can be performed every 5 years. It also has value after the cytology showing atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASC-US) or low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (LSILs) as a triage test for colposcopy, in the investigation of other cytological alterations when no abnormal findings are observed at colposcopy, seeking to exclude disease, or, further, after treatment of high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, to rule out residual disease.