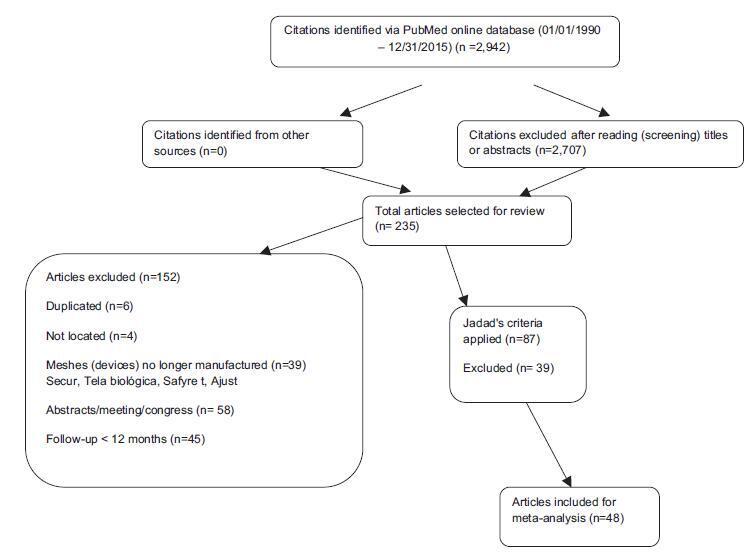
-
Review Article
Abortion in Cases of Zika Virus Congenital Infection
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(7):417-424
07-01-2018
Summary
Review ArticleAbortion in Cases of Zika Virus Congenital Infection
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(7):417-424
07-01-2018Views98See moreAbstract
The emergency in international public health caused by the Zika virus gave rise to the discussion about abortion in cases of congenital Zika virus syndrome (CZS). Therefore, we propose to carry out a bibliographic review on abortion in these cases. Five databases were searched using the following terms: abortion, miscarriage, and zika, with the interposition of the Boolean operator “AND.” In the selected literature, we found references to the lack of information concerning the risks and severity of CZS, to the great psychological distress suffered by pregnant women, and to the risk of unsafe abortions as a justification for abortion in cases of CZS. However, it is necessary to have available tests that could diagnose, in the first trimester of pregnancy, that the fetus has been affected by the virus, and that it may have important limitations, in order to subsidize the qualified discussion about abortion in these cases.
-
Review Article
Breastfeeding and the Benefits of Lactation for Women’s Health
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):354-359
06-01-2018
Summary
Review ArticleBreastfeeding and the Benefits of Lactation for Women’s Health
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):354-359
06-01-2018Views375See moreAbstract
The offer of the maternal breast to the baby is an unquestionable right of mothers and their children, and all efforts should bemade to promote, follow and maintain exclusive breastfeeding for up to 6months and supplement it until the child completes 2 years of age. Many publications are available in the literature about the qualities of breast milk, its benefits and health repercussions, stimulating the practice of breastfeeding and supporting campaigns for its implementation. However, although it is widely known that breastfeeding is an important step in the reproductive process of women and its practice offers benefits to both mother and child, most of the available information highlights the benefits of breast milk for children, while mention of the effects of breastfeeding on the health of the mother is usually neglected. Thus, the objective of the present study is to highlight the multiple benefits of breastfeeding for the physical and emotional health of the nursing mother. The authors consulted articles published in the databases PubMed, Virtual Health Library andWeb of Science using the keywords breastfeeding, breast milk, lactation and maternal health.
-
Review Article
Guidelines for HPV-DNA Testing for Cervical Cancer Screening in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):360-368
06-01-2018
Summary
Review ArticleGuidelines for HPV-DNA Testing for Cervical Cancer Screening in Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(6):360-368
06-01-2018Views270See moreAbstract
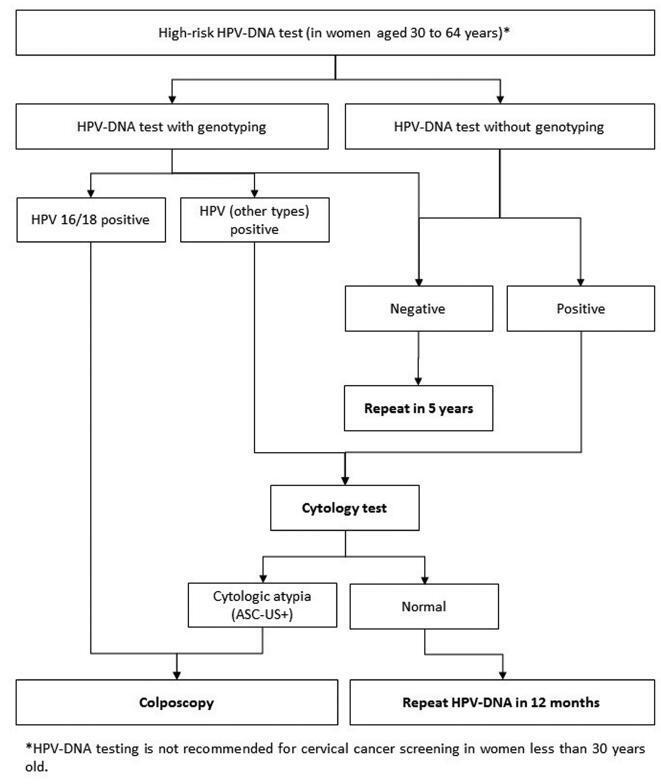
Evidence-based clinical guidelines ensure best practice protocols are available in health care. There is a widespread use of human papillomavirus deoxyribonucleic acid (HPVDNA) tests in Brazil, regardless of the lack of official guidelines. On behalf of the Brazilian Association for the Lower Genital Tract Pathology and Colposcopy (ABPTGIC, in the Portuguese acronym), a team of reviewers searched for published evidence and developed a set of recommendations for the use of HPV-DNA tests in cervical cancer screening in Brazil. The product of this process was debated and consensus was sought by the participants. One concern of the authors was the inclusion of these tests in the assessment of women with cytologic atypia and women treated for cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN). Testing for HPV is recommended in an organized screening scenario to identify women with precursor lesions or asymptomatic cervical cancer older than 30 years of age, and it can be performed every 5 years. It also has value after the cytology showing atypical squamous cells of undetermined significance (ASC-US) or low-grade squamous intraepithelial lesions (LSILs) as a triage test for colposcopy, in the investigation of other cytological alterations when no abnormal findings are observed at colposcopy, seeking to exclude disease, or, further, after treatment of high-grade cervical intraepithelial neoplasia, to rule out residual disease.
-
Review Article
Recommendations for the Use of Testosterone in Male Transgender*
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(5):275-280
05-01-2018
Summary
Review ArticleRecommendations for the Use of Testosterone in Male Transgender*
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(5):275-280
05-01-2018Views252See moreAbstract
Gender incongruence is defined as a condition in which an individual self-identifies and desires to have physical characteristics and social roles that connote the opposite biological sex. Gender dysphoria is when an individual displays the anxiety and/or depression disorders that result from the incongruity between the gender identity and the biological sex. The gender affirmation process must be performed by a multidisciplinary team. The main goal of the hormone treatment is to start the development of male physical characteristics by means of testosterone administration that may be offered to transgender men who are 18 years old or over. The use of testosterone is usually well tolerated and improves the quality of life. However, there is still lack of evidence regarding the effects and risks of the long-term use of this hormone. Many different pharmacological formulations have been used in the transsexualization process. The most commonly used formulation is the intramuscular testosterone esters in a short-term release injection, followed by testosterone cypionate or testosterone enanthate. In the majority of testosterone therapy protocols, the male physical characteristics can be seen in almost all users after 6 months of therapy, and themaximum virilization effects are usually achieved after 3 to 5 years of regular use of the hormone. To minimize risks, plasmatic testosterone levels should be kept within male physiological ranges (300 to 1,000 ng/dl) during hormonal treatment. It is recommended that transgender men under androgen therapy be monitored every 3 months during the 1st year of treatment and then, every 6 to 12 months.
-
Review Article
Uterine Artery Doppler in Screening for Preeclampsia and Fetal Growth Restriction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(5):287-293
05-01-2018
Summary
Review ArticleUterine Artery Doppler in Screening for Preeclampsia and Fetal Growth Restriction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(5):287-293
05-01-2018Views276See moreAbstract
Objective
To perform a comprehensive review of the current evidence on the role of uterine artery Doppler, isolated or in combination with other markers, in screening for preeclampsia (PE) and fetal growth restriction (FGR) in the general population. The review included recently published large cohort studies and randomized trials.
Methods
A search of the literature was conducted usingMedline, PubMed, MeSH and ScienceDirect. Combinations of the search terms “preeclampsia,” “screening,” “prediction,” “Doppler,” “Doppler velocimetry,” “fetal growth restriction,” “small for gestational age” and “uterine artery” were used. Articles in English (excluding reviews) reporting the use of uterine artery Doppler in screening for PE and FGR were included.
Results
Thirty articles were included. As a single predictor, uterine artery Doppler detects less than 50% of the cases of PE and no more than 40% of the pregnancies affected by FGR. Logistic regression-based models that allow calculation of individual risk based on the combination of multiple markers, in turn, is able to detect ~ 75% of the cases of preterm PE and 55% of the pregnancies resulting in small for gestational age infants.
Conclusion
The use of uterine artery Doppler as a single predictive test for PE and FGR has poor accuracy. However, its combined use in predictive models is promising, being more accurate in detecting preterm PE than FGR.
-
Review Article
A Critical Review on Obstetric Follow-up ofWomen Affected by Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(4):209-224
04-01-2018
Summary
Review ArticleA Critical Review on Obstetric Follow-up ofWomen Affected by Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2018;40(4):209-224
04-01-2018Views158See moreAbstract
Objective
To review the existing recommendations on the prenatal care of women with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE), based on currently available scientific evidence.
Methods
An integrative review was performed by two independent researchers, based on the literature available in the MEDLINE (via PubMed), EMBASE and The Cochrane Library databases, using the medical subject headings (MeSH) terms “systemic lupus erythematosus” AND “high-risk pregnancy” OR “prenatal care.” Studies published in English between 2007 and 2017 were included; experimental studies and case reports were excluded. In cases of disagreement regarding the inclusion of studies, a third senior researcher was consulted. Forty titles were initially identified; four duplicates were excluded. After reading the abstracts, 7 were further excluded and 29 were selected for a full-text evaluation.
Results
Systemic lupus erythematosus flares, preeclampsia, gestation loss, preterm birth, fetal growth restriction and neonatal lupus syndromes (mainly congenital heartblock) were the major complications described. The multidisciplinary team should adopt a specific monitoring, with particular therapeutic protocols. There are safe and effective drug options that should be prescribed for a good control of SLE activity.
Conclusion
Pregnant women with SLE present an increased risk for maternal complications, pregnancy loss and other adverse outcomes. The disease activity may worsen and, thereby, increase the risk of other maternal-fetal complications. Thus, maintaining an adequate control of disease activity and treating flares quickly should be a central goal during prenatal care.