Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(8):376-383
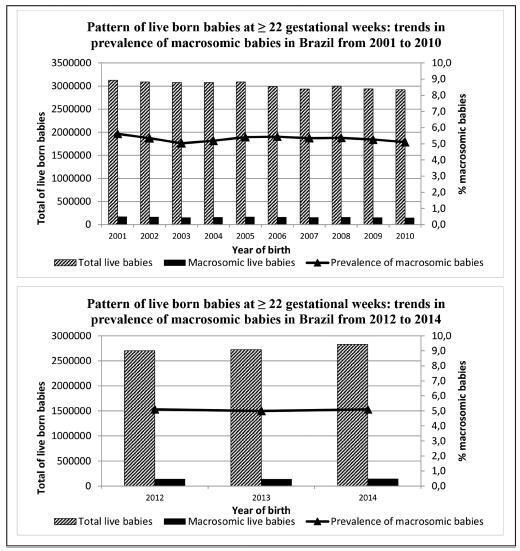
To describe the trends in the prevalence of macrosomia (birth weight ± 4,000 g) according to gestational age in Brazil in the periods of 2001-2010 and 2012-2014.
Ecological study with data from the Brazilian Live Birth Information System (SINASC, in the Portuguese acronym) regarding singleton live newborns born from 22 gestational weeks. The trends in Brazil as a whole and in each of its five regions were analyzed according to preterm (22-36 gestational weeks) and term (37-42 gestational weeks) strata. Annual Percent Changes (APCs) based on the Prais-Winsten method and their respective 95% confidence intervals (CIs) were used to verify statistically significant changes in 2001-2010.
In Brazil, the prevalence of macrosomic births was of 5.3% (2001-2010) and 5.1% (2012-2014). The rates were systematically higher in the North and Northeast Regions both in the preterm and in term strata. In the preterm stratum, the North Region presented the highest variation in the prevalence of macrosomia (+137.5%) when comparing 2001 (0.8%) to 2010 (1.9%). In the term stratum, downward trends were observed in Brazil as a whole and in every region. The trends for 2012-2014 were more heterogeneous, with the prevalence systematically higher than that observed for 2001-2010. The APC in the preterm stratum (2001-2010) showed a statistically significant trend change in the North (APC: 15.4%; 95%CI: 0.6-32.3) and South (APC: 13.5%; 95%CI: 4.8-22.9) regions. In the term stratum, the change occurred only in the North region (APC:-1.5%; 95%CI: -2.5--0.5).
The prevalence of macrosomic births in Brazil was higher than 5.0%. Macrosomia has potentially negative health implications for both children and adults, and deserves close attention in the public health agenda in Brazil, as well as further support for investigation and intervention.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(8):384-396
To identify the prevalence of anemia and its relation to food insecurity (FI) and other determinants in pregnant women.
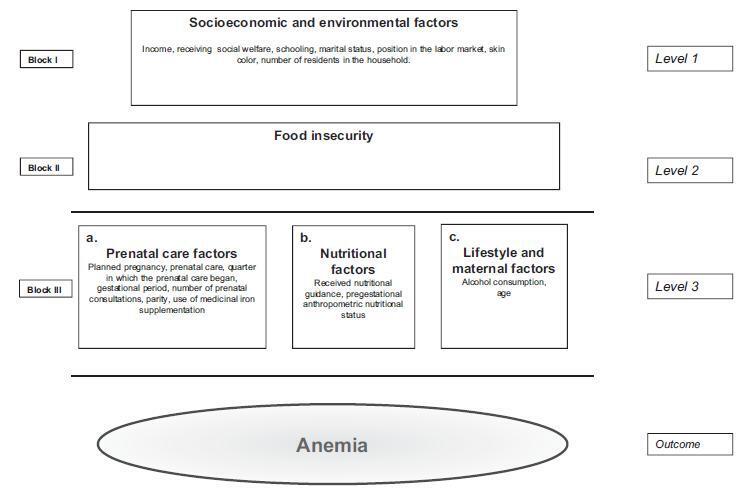
A cross-sectional, cohort-nested study, with the participation of 245 pregnant women who were cared for at Family Health Units in the municipality of Santo Antônio de Jesus, Bahia, Brazil. The participants underwent blood tests for hemoglobin levels, anthropometric examinations, and answered a structured questionnaire. The hemoglobin (Hb) parameter (Hb < 11 g/dL) was used for the classification of the diagnosis of anemia. Food insecurity was evaluated using the North American short-scale food insecurity assessment. Logistic regression was adopted for the statistical analyses, based on a hierarchical conceptual model that enabled the measurement of the decomposition of the total effect of its non-mediated and mediated components using the proposed hierarchical levels.
The prevalence of anemia in the studied population was of 21.8%, and the average hemoglobin was 12.06 g/dL (standard deviation [SD]: 1.27). Food insecurity was identified in 28.16% of the pregnant women. The average maternal age was 25.82 years (SD: 5.94). After ranking, the variables positively associated with anemia remained significant: FI (odds ratio [OR] =3.63; 95% confidence interval [95%CI]: 1.77-7.45); not undergoing prenatal care (OR = 5.15;95%CI: 1.43-18.50); multiparity (OR = 2.27;95%CI: 1.02-5.05); and non-supplementation of iron medication (OR = 2.45; 95%CI: 1.04-5.76). The results also indicated that the socioeconomic and environmental factors were largely mediated by food insecurity and factors regarding prenatal care.
In the present study, the chance of occurrence of anemia in pregnant women was significantly higher,mainly among women: in situations of food insecurity, not undergoing prenatal care, not having received iron supplements, and who are multiparous.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(7):350-357
The aim of this study was to evaluate the overall and type-specific prevalence of human papillomavirus (HPV) infection among females living in riverside communities in the state of Pará, in the Eastern Brazilian Amazon. These communities are inhabited by low-income people, and are accessible only by small boats. Cervical cytology and risk factors for HPV infection were also assessed.
Cervical samples from 353 women of selected communities were collected both for Papanicolau (Pap) test and HPV detection. Conventional polymerase chain reaction (PCR) and real-time PCR were used to assess the overall and type-specific prevalence of HPV-16 and HPV-18, the main oncogenic types worldwide. Epidemiological questionnaires were used for the assessment of the risk factors for HPV infection.
The mean age of the participants was 37 years (standard deviation [SD] ± 13.7). Most were married or with a fixed sexual partner (79%), and had a low educational level (80%) and family monthly income (< U$ 250; 53%). Overall, HPV prevalence was 16.4% (n = 58), with 8 cases of HPV-16 (2.3%) and 5 of HPV-18 (1.4%). Almost 70% of the women surveyed had never undergone the Pap test. Abnormal cytology results were found in 27.5% (n = 97) of the samples, with higher rates of HPV infection according to the severity of the lesions (p = 0.026).
The infections by HPV-16 and HPV-18 were not predominant in our study, despite the high prevalence of overall HPV infection. Nevertheless, the oncogenic potential of these types and the low coverage of the Pap test among women from riverside communities demonstrate a potential risk for the development of cervical lesions and their progression to cervical cancer, since the access to these communities is difficult and, in most cases, these women do not have access to primary care and public health services.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(7):344-349
To evaluate the trends in definitive contraception in a ten-year interval comprising the years 2002 and 2012.
Retrospective analysis of the tubal sterilization performed in our service in 2002 and2012,analyzingthedemographiccharacteristics,personalhistory,previouscontraceptive method, definite contraception technique, effectiveness and complications.
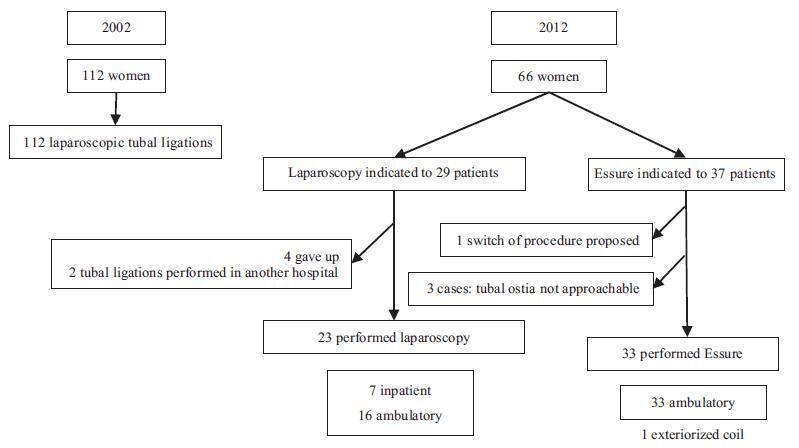
Definitive contraception was performed in 112 women in 2002 (group 1) and in 60 women in 2012 (group 2). The groups were homogeneous regarding age, parity, educational level and personal history. The number of women older than 40 years choosing a definitive method was more frequent in group 1, 49.1% (n = 55); for group 2, the rate was 34.8% (n = 23) (p = 0.04). The time between the last delivery and the procedure was 11.6±6.2 and 7.9±6.4 years (p = 0.014) in 2002 against 2012 respectively. In 2002, all patients performed tubal ligation by laparoscopic inpatient regime. In 2012, the bilateral placement of the Essure (Bayer Corporation, Whippany, NJ, US) device was suggested to 56.1% (n = 37) of the patients, while laparoscopy was suggested to 43.9% (n = 29) of them. All women who underwent laparoscopic sterilization had the procedure successfully completed using silastic rings. The overall bilateral device placement rate for the Essure was 91.6%, with only one complication reported. All Essure procedures were performed in an outpatient setting; for the laparoscopy, this rate was 79% (n = 15). No intentional pregnancies occurred until this date.
There is a trend in the decrease in definitive contraception over the years in our institution, maybe as a result of the development of long-acting reversible contraceptives. The hysteroscopic procedure has become a frequent option, as it is performed in an office setting without anesthesia, being a well-tolerated, minimal invasive method.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(7):337-343
Vitamin D deficiency is associated with various diseases. Prevalent in Brazil, it can result from inadequate lifestyle habits.
To demonstrate that postmenopausal women with vitamin D deficiency have worse quality of health, expressed as worse quality of life, lower levels of physical activity, and worse nutritional profile.
Postmenopausal women answered questionnaires about physical activity and quality of life, provided a 24-hour food record, and had serum vitamin D levels measured.
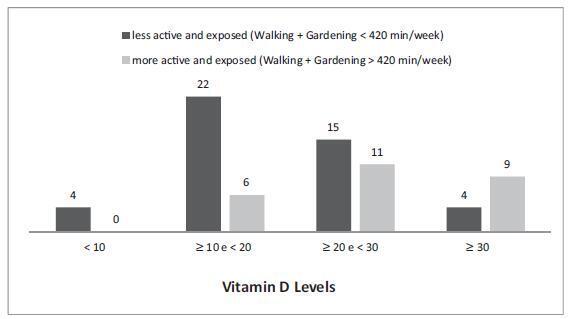
Among the more active women, those who perform a daily average of one hour of physical activity had vitamin D levels above 20 ng/mL (76.9%), and those, which expose themselves to sunlight, had vitamin D levels above 30 ng/mL (34.6%). Meanwhile the percentages for the women who are less physically active and less exposed to sunlight were 42.2% and 8.9% respectively. Being more active and more exposed to sunlight resulted in a lower fat percentage. Serum vitamin D levels were not correlated with quality of life.
Walking and gardening increased serum vitamin D levels and decreased the percentage of body fat. The limitations of the study prevented the impact of 25hidroxyvitamin D on the quality of life and nutritional aspects of the women from being evaluated.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(7):330-336
To assess the impact of pre-pregnancy obesity (body mass index [BMI] ≥30 kg/m2) on the gestational and perinatal outcomes.
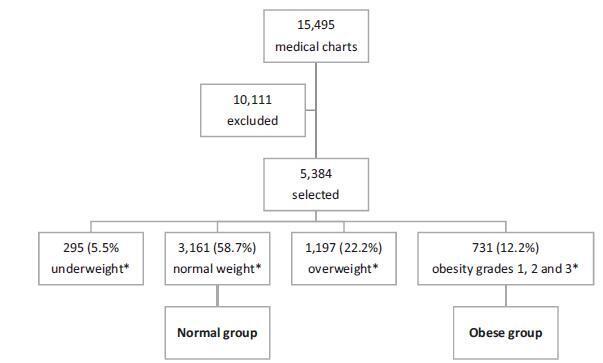
Retrospective cohort study of 731 pregnant women with a BMI ≥30 kg/m2 at the first prenatal care visit, comparing them with 3,161 women with a BMI between 18.5 kg/m2 and 24.9 kg/m2. Maternal and neonatal variables were assessed. Statistical analyses reporting the demographic features of the pregnant women (obese and normal) were performed with descriptive statistics followed by two-sided independent Student’s t tests for the continuous variables, and the chi-squared (χ2) test, or Fisher’s exact test, for the categorical variables. We performed a multiple linear regression analysis of newborn body weight based on the mother’s BMI, adjusted by maternal age, hyperglycemic disorders, hypertensive disorders, and cesarean deliveries to analyze the relationships among these variables. All analyses were performed with the R (R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria) for Windows software, version 3.1.0. A value of p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Obesity was associated with older age [OR 9.8 (7.8-12.2); p < 0.01], hyperglycemic disorders [OR 6.5 (4.8-8.9); p < 0.01], hypertensive disorders [OR 7.6 (6.1-9.5); p < 0.01], caesarean deliveries [OR 2.5 (2.1-3.0); p < 0.01], fetal macrosomia [OR 2.9 (2.3-3.6); p < 0.01] and umbilical cord pH [OR 2.1 (1.4-2.9); p < 0.01). Conversely, no association was observed with the duration of labor, bleeding during labor, Apgar scores at 1 and 5 minutes after birth, gestational age, stillbirth and early neonatal mortality, congenital malformations, and maternal and fetal injury.
We observed that pre-pregnancy obesity was associated with maternal age, hyperglycemic disorders, hypertension syndrome, cesarean deliveries, fetal macrosomia, and fetal acidosis.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(7):322-329
Considering the physical, mental and behavioral problems related to fetal alcohol exposure, prenatal clinical guides suggest a brief evaluation of alcohol consumption during pregnancy to detect alcohol intake and to adjust interventions, if required. Even if any alcohol use should be considered risky during pregnancy, identifying women with alcohol use disorders is important because they could need a more specific intervention than simple advice to abstain. Most screening tests have been developed and validated in male populations and focused on the long-term consequences of heavy alcohol use, so they might be inappropriate to assess consumption in pregnant women.
To analyze the internal reliability and validity of the alcohol screening instruments Alcohol Use Disorders Identification Test (AUDIT), Alcohol Use Disorders IdentificationTest- Consumption (AUDIT-C), Tolerance, Worried, Eye-Opener, Amnesia and Cut-Down (TWEAK), Rapid Alcohol Problems Screen - Quantity Frequency (RAPSQF) and Tolerance, Annoyed, Cut-Down and Eye-Opener (T-ACE) to identify alcohol use disorders in pregnant women.
A total of 641 puerperal women were personally interviewed during the 48 hours after delivery. The receiver operating characteristics (ROC) curves and the sensitivity and specificity of each instrument using different cut-off points were analyzed.
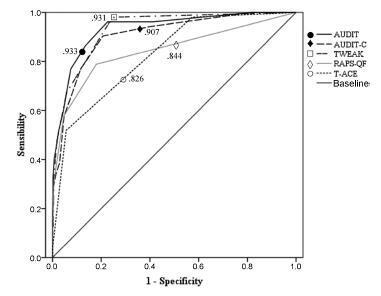
All instruments showed areas under the ROC curves above 0.80. Larger areas were found for the TWEAK and the AUDIT. The TWEAK, the T-ACE and the AUDIT-C showed higher sensitivity, while the AUDIT and the RAPS-QF showed higher specificity. Reliability (internal consistency) was low for all instruments, improving when optimal cut-off points were used, especially for the AUDIT, the AUDIT-C and the RAPS-QF.
In other cultural contexts, studies have concluded that T-ACE and TWEAK are the best instruments to assess pregnant women. In contrast, our results evidenced the low reliability of those instruments and a better performance of the AUDIT in this population.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2017;39(7):317-321
This study aimed to evaluate and validate the qualitative human chorionic gonadotropin β subunit (β-hCG) test of the vaginal fluid washings of pregnant women with premature rupture of fetal membranes (PROM).
Cross-sectional study of pregnant women between gestational weeks 24 and 39 who underwent consultations in one of our institutions. They were divided into two groups: group A (pregnant women clinically diagnosed with PROM) and group B (pregnant women without loss of amniotic liquid). The patients were subjected to a vaginal fluid washing with 3 mL of saline solution, which was aspirated subsequently with the same syringe. The solution was immediately sent to the laboratory to perform the vaginal β-hCG test with cut-off points of 10 mIU/mL (β-hCG-10) and/or 25 mIU/mL (β-hCG-25).
The β-hCG-10 test of the vaginal secretion was performed in 128 cases. The chi-squared test with Yates’ correction showed a statistically significant difference between the 2 groups (p = 0.0225). The sensibility, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), and accuracy parameters were 77.1%, 43.6%, 52.3%; 70.4%; and 58.6% respectively. The β-hCG-25 test of the vaginal washing was performed in 49 cases. The analysis by Fisher’s exact test showed a statistically significant difference between the groups (p = 0.0175). The sensibility, specificity, PPV, NPV, and accuracy parameters were 44.4%, 87.1%, 66.6%; 72.9%; and 71.4% respectively.
The β-hCG-25 test showed better accuracy for the diagnosis of PROM, and can corroborate the early diagnosis of PROM because it is a simple and quick exam.