-
Original Article06-18-2021
Is there a Role for Antenatal Corticosteroids in Term Infants before Elective Cesarean Section?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(4):283-290
Abstract
Original ArticleIs there a Role for Antenatal Corticosteroids in Term Infants before Elective Cesarean Section?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(4):283-290
Views169See moreAbstract
Objective
Cesarean section (CS) delivery, especially without previous labor, is associated with worse neonatal respiratory outcomes. Some studies comparing neonatal outcomes between term infants exposed and not exposed to antenatal corticosteroids (ACS) before elective CS revealed that ACS appears to decrease the risk of respiratory distress syndrome (RDS), transient tachypnea of the neonate (TTN), admission to the neonatal intensive care unit (NICU), and the length of stay in the NICU.
Methods
The present retrospective cohort study aimed to compare neonatal outcomes in infants born trough term elective CS exposed and not exposed to ACS. Outcomes included neonatal morbidity at birth, neonatal respiratory morbidity, and general neonatal morbidity. Maternal demographic characteristics and obstetric data were analyzed as possible confounders.
Results
A total of 334 newborns met the inclusion criteria. One third of the population study (n=129; 38.6%) received ACS. The present study found that the likelihood for RDS (odds ratio [OR]=1.250; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.454-3.442), transient TTN (OR=1.,623; 95%CI: 0.556-4.739), and NIUC admission (OR=2.155; 95%CI: 0.474-9.788) was higher in the ACS exposed group, although with no statistical significance. When adjusting for gestational age and arterial hypertension, the likelihood for RDS (OR=0,732; 95%CI: 0.240-2.232), TTN (OR=0.959; 95%CI: 0.297--3.091), and NIUC admission (OR=0,852; 95%CI: 0.161-4.520) become lower in the ACS exposed group.
Conclusion
Our findings highlight the known association between CS-related respiratory morbidity and gestational age, supporting recent guidelines that advocate postponing elective CSs until 39 weeks of gestational age.
-
Original Article06-18-2021
Continuation Rates of the 52-mg Levonorgestrel-releasing Intrauterine System according to the Primary Reason for its Use
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(4):291-296
Abstract
Original ArticleContinuation Rates of the 52-mg Levonorgestrel-releasing Intrauterine System according to the Primary Reason for its Use
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(4):291-296
Views166Abstract
Objective
To evaluate whether continuation rates with the 52-mg levonorgestrelreleasing intrauterine system (LNG-IUS) up to 5 years after placement differed between women using the method exclusively for contraception and those using the device for medical reasons alone.
Methods
A retrospective cohort study was conducted in a family planning clinic with 5,034 LNG-IUS users: 4,287 using the method exclusively for contraception and 747 for medical reasons alone. The continuation rate at 1 to 5 years of use was calculated by life table analysis.
Results
Initially, the continuation rate was significantly higher in the contraception group: 85.8 versus 83.4 and 77.4 versus 76.0 per 100 women-years in the 1st and 2nd years of use, respectively. There were more discontinuations due to bleeding/spotting in the medical reasons group in the first two years. The discontinuation rate according to reason for use was not significantly different from the third to the fifth year of use. No women discontinued due to amenorrhea in either group.
Conclusion
The continuation rate was significantly higher in the contraception group in the first two years of use. Amenorrhea was not a reason for discontinuation in either group, suggesting that counselling in this respect was adequate. Nevertheless, counselling could perhaps have been better with regards to the expected long period of bleeding and spotting in the first two years after placement.
Key-words Amenorrheableeding and spottingcontinuation ratecounsellingindication for uselevonorgestrel IUSSee more -
Original Article06-02-2021
Evaluation of the Blood Level of Adiponectin in Pregnant Adolescents
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(6):429-435
Abstract
Original ArticleEvaluation of the Blood Level of Adiponectin in Pregnant Adolescents
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(6):429-435
Views150See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate serum levels of adiponectin in pregnant adolescents between 30 and 36 weeks of gestation.
Method:
A prospective cross-sectional study enrolled 67 normal pregnant women between 30 and 36 weeks of gestation and eutrophic (body mass index [BMI]: 18.5-25 kg/m2), of which 36 were adolescents (< 20 years old) and 31 adults (≥ 20 years old). Serum adiponectin levels were determined by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The t-student or Mann-Whitney tests were used for intergroup comparison.
Results
Pregnant adolescents showed significantly higher serum adiponectin concentrations comparedwith pregnant adults (p=0.04). No differences were observed in adiponectin levels in younger pregnant adolescents (< 16 years old) compared with older pregnant adolescents (≥ 16 years old). Adiponectin values were divided into 3 subgroups:<3,000 ng/mL, between 3,000 and 5,000 ng/mL, and>5,000 ng/mL. Birthweight was significantly higher in women>5,000 ng/mL when compared with<3,000 ng/mL in the adolescent group. No association between pregestational adiponectin levels and BMI, gestational weight gain, and gestational age was observed; however, there was a positive relation with birthweight (p=0.0239).
Conclusion
Serum adiponectin values in pregnant adolescents between 30 and 36 weeks of gestation were higher compared with pregnant adults; however, no differences between younger and older pregnant adolescents were observed.
-
Original Article05-24-2021
Disease Progression and Obstetric Outcomes of Women with Multiple Sclerosis at a Reference Center in Northeastern Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):165-171
Abstract
Original ArticleDisease Progression and Obstetric Outcomes of Women with Multiple Sclerosis at a Reference Center in Northeastern Brazil
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):165-171
Views221See moreAbstract
Objective
To describe the obstetric outcomes of patients withmultiple sclerosis (MS) and the impact of pregnancy and the postpartum period on the progression of the disease.
Methods
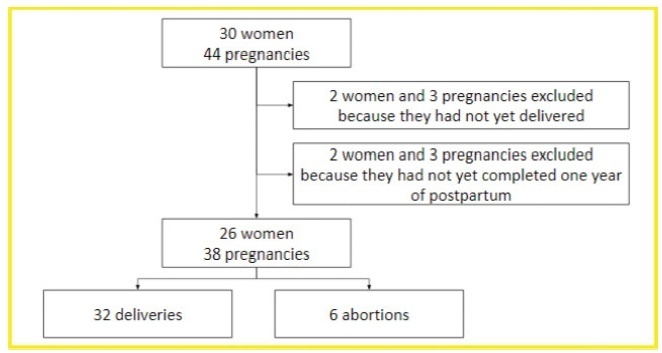
A case series study performed between December 2019 and February 2020, reporting pregnancies occurred between 1996 and 2019. The subjects included were women with MS undergoing follow-up at an MS referral center in Northeastern Brazil, and who had at least one pregnancy after the onset of MS symptoms, or who had their first relapse in the first year after delivery.
Results
In total, 26 women and 38 pregnancies were analyzed - 32 of them resulted in delivery, and the remaining 6, in miscarriages. There was a significant increase in the prevalence of relapse during the postpartum period when compared with the gestational period. In 16 (42.1%) of the pregnancies, there was exposure to diseasemodifying therapies (DMTs) - 14 (36.8%), to interferon β, and 2 (5.3%), to fingolimod. Higher rates of abortion, prematurity and low birth weight were reported in the group was exposed to DMT when compared with the one who was not.
Conclusion
In the sample of the present study, there was a significant increase in the rate of MS relapse during the postpartum period when compared with the gestational period. Additionally, it seems that exposure to DMTs during pregnancy may affect the obstetric outcomes of the patients.
-
Original Article05-24-2021
Postplacental Placement of Intrauterine Devices: Acceptability, Reasons for Refusal and Proposals to Increase its Use
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):172-177
Abstract
Original ArticlePostplacental Placement of Intrauterine Devices: Acceptability, Reasons for Refusal and Proposals to Increase its Use
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):172-177
Views232See moreAbstract
Objective
To evaluate the acceptability of postplacental placement of intrauterine devices (PPIUD), reasons for refusal and suggested policies to increase its use.
Methods
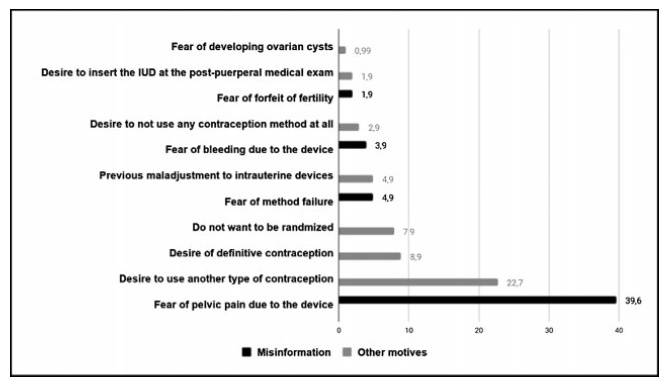
Cross-sectional study conducted at the Women Hospital of the Universidade de Campinas, Campinas, SP, Brazil. Postplacental placement of intrauterine devices was offered to women admitted in labor who did not present infections, uterinemalformation, twin pregnancy, preterm birth, and were at least 18 years old. In case of refusal, the parturient was asked to give their reasons and the answers were classified as misinformation about contraception or other reasons. The following were considered misinformation: fear of pain, bleeding, contraception failure and future infertility. Bivariate analysis was performed.
Results
Amongst 241 invited women, the refusal rate was of 41.9%. Misinformation corresponded to 50.5% of all refusals, and the reasons were: fear of pain (39.9%); fear of contraception failure (4.9%); fear of bleeding (3.9%); fear of future infertility (1.9%); other reasons for refusal were 49.5%. Parturients aged between 18 and 27 years old refused the PPIUD more frequently due to misinformation (67.4%), and older parturients (between 28 and 43 years old) refused frequently due to other reasons (63.6%) (p=0.002). Themean age of those who declined the PPIUD due to misinformation was 27.3 ± 6.4 years old, while those who declined for other reasons had a mean age of 29.9 ± 5.9 years old (p=0.017).
Conclusion
The refusal of the PPIUD was high, especially amongst young women and due to misinformation. It is necessary to develop educative measures during antenatal care to counsel women about contraception, reproductive health and consequences of unintended pregnancy.
-
Original Article05-24-2021
Awareness about Vulvovaginal Aesthetics Procedures among Medical Students and Health Professionals in Saudi Arabia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):178-184
Abstract
Original ArticleAwareness about Vulvovaginal Aesthetics Procedures among Medical Students and Health Professionals in Saudi Arabia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):178-184
Views166Abstract
Objective
The present study aimed to explore the opinion and ethical consideration of vulvovaginal aesthetics procedures (VVAPs) among health professionals and medical students in Saudi Arabia.
Methods
This is a cross-sectional study performed between January 2020 and April 2020. Data was collected through electronic media, WhatsApp, and emails. The results were analyzed by applying the Students t-test, and correlations were considered significant if they presented a p-value<0.05.
Results
There is significant demand to educate doctors, health professionals, medical students, and gynecologists for the VVAPs to have a solid foundation, justified indications, and knowledge about various aesthetic options. Although female doctors, medical students, young doctors, and gynecologists have more knowledge about VVAPs, all health professionals ought to be aware of recent trends in vulvovaginal aesthetics (VVA). The present analysis determined that VVA should be under the domain of gynecologists, rather than under that of plastic surgeons, general surgeons, and cosmetologists. Themajority of the participants considered that vaginal rejuvenation, “G-spot” augmentation, clitoral surgery, and hymenoplasty are not justifiable on medical grounds.
Conclusion
The decision to opt for different techniques for vaginal tightening and revitalization should be taken very carefully, utilizing the shared decision-making approach. Ethical aspects and moral considerations are important key factors before embarking in the VVAPs purely for cosmetic reasons. Further research is required to determine the sexual, psychological, and body image outcomes for women who underwent elective VVAPs. Moreover, medical educators must consider VVAPs as part of the undergraduate and postgraduate medical curriculum.
Key-words aesthetic gynecologyawareness about aesthetic surgery among health professionalsSexual and reproductive healthvulvovaginal aesthetics proceduresvulvovaginal cosmetic proceduresSee more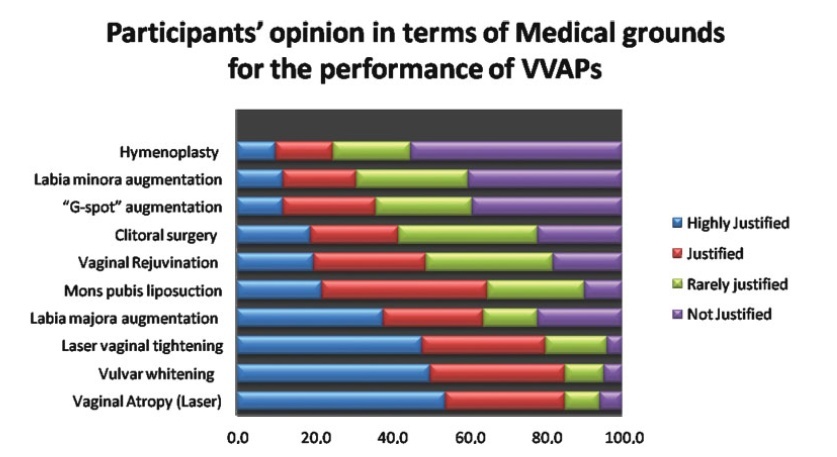
-
Original Article05-24-2021
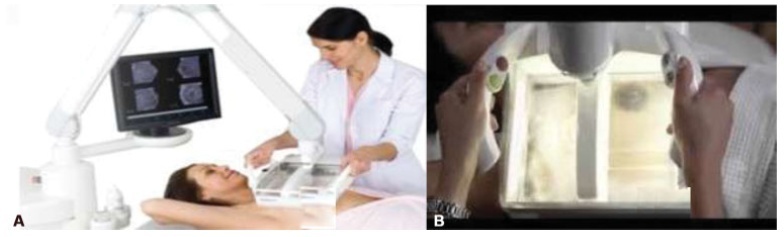
Comparison of Automated Breast Ultrasound and Hand-Held Breast Ultrasound in the Screening of Dense Breasts
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):190-199
Abstract
Original ArticleComparison of Automated Breast Ultrasound and Hand-Held Breast Ultrasound in the Screening of Dense Breasts
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):190-199
Views256See moreAbstract
Objective
To compare hand-held breast ultrasound (HHBUS) and automated breast ultrasound (ABUS) as screening tool for cancer.
Methods
A cross-sectional study in patients with mammographically dense breasts was conducted, and both HHBUS and ABUS were performed. Hand-held breast ultrasound was acquired by radiologists and ABUS by mammography technicians and analyzed by breast radiologists. We evaluated the Breast Imaging Reporting and
Data System
(BI-RADS) classification of the exam and of the lesion, as well as the amount of time required to perform and read each exam. The statistical analysis employed was measures of central tendency and dispersion, frequencies, Student t test, and a univariate logistic regression, through the odds ratio and its respective 95% confidence interval, and with p<0.05 considered of statistical significance.
Results
Atotal of 440 patientswere evaluated. Regarding lesions,HHBUS detected 15 (7.7%) BI-RADS 2, 175 (89.3%) BI-RADS 3, and 6 (3%) BI-RADS 4, with 3 being confirmed by biopsy as invasive ductal carcinomas (IDCs), and 3 false-positives. Automated breast ultrasound identified 12 (12.9%) BI-RADS 2, 75 (80.7%) BI-RADS 3, and 6 (6.4%) BI-RADS 4, including 3 lesions detected by HHBUS and confirmed as IDCs, in addition to 1 invasive lobular carcinoma and 2 high-risk lesions not detected by HHBUS. The amount of time required for the radiologist to read the ABUS was statistically inferior compared with the time required to read the HHBUS (p<0.001). The overall concordance was 80.9%. A total of 219 lesions were detected, from those 70 lesions by both methods, 126 only by HHBUS (84.9% not suspicious by ABUS) and 23 only by ABUS.
Conclusion
Compared with HHBUS, ABUS allowed adequate sonographic study in supplemental screening for breast cancer in heterogeneously dense and extremely dense breasts.
-
Original Article05-24-2021
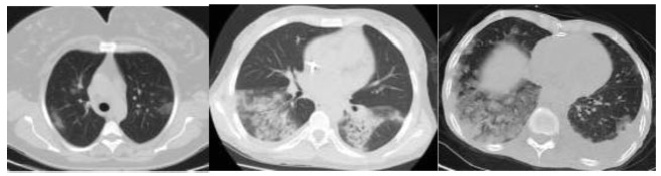
Comparison of Laboratory and Radiological Findings of Pregnant and Non-PregnantWomen with Covid-19
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):200-206
Abstract
Original ArticleComparison of Laboratory and Radiological Findings of Pregnant and Non-PregnantWomen with Covid-19
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(3):200-206
Views144See moreAbstract
Objective
Covid-19 became a pandemic, and researchers have not been able to establish a treatment algorithm. The pregnant population is also another concern for health care professionals. There are physiological changes related to pregnancy that result in different laboratory levels, radiological findings and disease progression. The goal of the present article is to determine whether the laboratory results and radiological findings were different in non-pregnant women (NPWs) of reproductive age and pregnant women (PWs) diagnosed with the Covid-19 infection.
Methods
Out of 34 patients, 15 (44.11%) PWs and 19 (55.8%) NPWs were included in the study. Age, comorbidities, complaints, vitals, respiratory rates, computed tomography (CT) findings and stages, as well as laboratory parameters, were recorded from the hospital database.
Results
Themean age of the PWs was of 27.6 ± 0.99 years, and that of the NPWs was of 37.63 ± 2.00; when agewas compared between the groups, a statistically significant difference (p=0.001) was found. The mean systolic blood pressure of the PWs was of 116.53 ± 11.35, and that of the NPWs was of 125.53 ± 13.00, and their difference was statistically significant (p=0.05). The difference in the minimum respiratory rates of the patients was also statistically significant (p=0.05). The platelet levels observed among the PWs with Covid-19 were lower than those of the NPWs (185.40 ± 39.09 x 109/mcL and 232.00 ± 71.04 x 109/mcL respectively; p=0.05). The mean D-dimer value of the PWs was lower in comparison to that of the NPWs (p<0.05).
Conclusion
The laboratory findings and imaging studiesmay differ between pregnant and non-pregnant populations. It is important to properly interpret these studies. Future studies with a higher number of patients are required to confirm these preliminary data.