-
Original Article04-25-2022
Histological and Immunohistochemical Characteristics for Hereditary Breast Cancer Risk in a Cohort of Brazilian Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(8):761-770
Abstract
Original ArticleHistological and Immunohistochemical Characteristics for Hereditary Breast Cancer Risk in a Cohort of Brazilian Women
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(8):761-770
Views213Abstract
Objective
The study aimed to characterize the clinical, histological, and immunohistochemical profile of women with invasive breast cancer, according to the risk for Hereditary Predisposition Breast and Ovarian Cancer Syndrome in a Brazilian population.
Methods
This is a retrospective study performed from a hospital-based cohort of 522 women, diagnosed with breast cancer treated at an oncology referral center in the Southeast region of Brazil, between 2014 and 2016.
Results
Among the 430 women diagnosed with invasive breast cancer who composed the study population, 127 (29.5%) were classified as at increased risk for hereditary predisposition to breast and ovarian cancer syndrome. There was a lower level of education in patients at increased risk (34.6%) when compared with those at usual risk (46.0%). Regarding tumor characteristics, women at increased risk had higher percentages of the disease diagnosed at an advanced stage (32.3%), and with tumors > 2cm (63.0%), with increased prevalence for both characteristics, when compared with those at usual risk. Furthermore, we found higher percentages of HG3 (43.3%) and Ki-67 ≥ 25% (64.6%) in women at increased risk, with prevalence being about twice as high in this group. The presence of triple-negative tumors was observed as 25.2% in women at increased risk and 6.0% in women at usual risk, with the prevalence of absence of biomarkers being 2.5 times higher among women in the increased risk group.
Conclusion
From the clinical criteria routinely used in the diagnosis of breast cancer, the care practice of genetic counseling for patients at increased risk of hereditary breast cancer in contexts such as Brazil is still scarce.
Key-words Breast cancerCohort studiesGenetic counselinghereditary breast and ovarian cancer syndromeImmunohistochemistrySee more -
Original Article04-20-2022
WhatsApp and Gynecologist-Patient Interaction: Development and Validation of a Questionnaire to Assess the Stress Perceived by the Doctor
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(5):497-502
Abstract
Original ArticleWhatsApp and Gynecologist-Patient Interaction: Development and Validation of a Questionnaire to Assess the Stress Perceived by the Doctor
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(5):497-502
Views136See moreAbstract
Objective
Construction and validation of the WhatsApp Stress Scale (WASS), a questionnaire designed for physicians that measures how the use of smartphones and related software communication applications affects the quality of life of gynecologists who use this tool to communicate with patients.
Methods
The present cross-sectional observational study analyzed 60 gynecologists according to weekly WhatsApp usage time for communication with patients and compared the data with the perception of the doctor on the use of this virtual interaction as a stressor. Physicians were equally divided into three groups:<2hours, 2 to 5 hours, and>5 hours. The authors created a questionnaire in Likert scale format. The study proceeded in three phases: development of the questionnaire items, pretesting, constructing, and validity and reliability testing using factor analysis, Cronbach α coefficient, and paired t-test.
Results
A 9-item instrument using a 5-point Likert scale was created and administered to the participants in 3 different times: T0, T1 (15minutes after the end of T0), and T2 (15 days later). All questionnaire items possessed adequate content validity indices and the internal consistency of the instrument was satisfactory (Cronbach α 0.935; 95% confidence interval [CI]: 0.744-0.989; p=0.0001). No statistically significant differences were observed in the responses between the rounds of testing, indicating good test-retest reliability. A positive association between the high frequency of WhatsApp usage for communication with patients and the stress perceived by the doctor was shown.
Conclusion
The WASS is a valid and reliable instrument for assessing the use of messaging applications to communicate with patients as a stressor perceived by gynecologists.
-
Original Article04-11-2022
Hematological Parameters to Predict the Severity of Hyperemesis Gravidarum and Ketonuria
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(5):458-466
Abstract
Original ArticleHematological Parameters to Predict the Severity of Hyperemesis Gravidarum and Ketonuria
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(5):458-466
Views264See moreAbstract
Objective
Hyperemesis gravidarum (HG) is a pregnancy complication that can progress with persistent nausea and vomiting. The aim of the present study is to evaluate the relationship between hematological parameters and HG.
Method
A total of 532 pregnant women with HG who were admitted to the Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology between March 2019 and February 2021, and 534 healthy pregnant women with characteristics similar to those of the case group were included in the study. The hematological parameters of both groups were compared. In addition, the hematological parametersof patients with HG according to the severity of ketonuria were compared.
Results
Themean age of the HG group (n=532) was 26.3 ± 4.1 years, and that of the control group (n=534) was 25.9 ± 4.8 years. Among patients with HG, 46% (n=249) had ketone(+), 33% (n=174), ketone(++), and 21% (n=109), ketone(+++). The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratio (PLR) were higher in the HG group than in the control group: 3.8 (2.8-5.8)/3.2 (2.6-4.0); p<0.001; and 135.2 ± 30.4/108.9 ± 62.2; p<0.001 respectively. The neutrophil count, NLR, and PLR were higher in the group with ketone(+++) than in the groups with ketone(+) or ketone(++): 7.6 ± 1.9/5.5 ± 2.4; p<0.001; 3.8(2.8-4.6)/2.9(2.3- 3.6); p<0.001; and 149.9 ± 48.0/135.9 ± 65.7; p<0.001 respectively. The mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH) level, the NLR, and the PLR were identified as independent predictors of the presence of HG and the level of ketone positivity in HG patients.
Conclusion
The NLR and PLR were high in patients with HG, suggesting the its inflammatory activity. They may be important markers associated with the presence and severity of HG.
-
Original Article04-08-2022
Estimate of Dietary Total Antioxidant Capacity of Pregnant Women and Associated Factors Estimativa da capacidade antioxidante total da dieta de gestantes e fatores associados
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):91-99
Abstract
Original ArticleEstimate of Dietary Total Antioxidant Capacity of Pregnant Women and Associated Factors Estimativa da capacidade antioxidante total da dieta de gestantes e fatores associados
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):91-99
Views133See moreAbstract
Objective
To investigate the dietary total antioxidant capacity (DTAC) of pregnant women, and associated factors.
Methods
Cross-sectional study conducted with 785 pregnant adult women attended in primary health care centers of Ribeirão Preto, state of São Paulo, Brazil. Two 24-hour dietary recalls were obtained, and the usual intake was estimated through the Multiple Source Method. The DTAC was estimated using the ferric reducing antioxidant power assay. The relationship between the higher DTAC estimate (≥ median of 4.3 mmol/day) and associated factorswas investigated usingadjusted logisticmodels with backward selection.
Results
In total, 25% of the pregnant women were classified as overweight, and 32% as obese. Themedian (P25, P75)DTAC was 4.3 (3.3-5.6)mmol/day. Through adjusted logistic regression models with backward selection, a higher chance of DTAC estimates above the median among pregnant womenaged ≥ 35 years old (2.01 [1.24-3.27])was verified when compared with younger pregnant women. Women with prepregnancy overweight (0.63 [0.45-0.89]) and obesity (0.59 [0.40-0.88]) presented a lower chance of DTAC estimates above the median when compared with eutrophic pregnant women. A higher DTAC estimate was positively associated with the use of dietary supplements (1.39 [1.03-1.88]), and negatively associated with total dietary energy (0.59 [0.42-0.85]).
Conclusion
The DTAC estimate over the median was associated with greater age, adequate body weight, use of dietary supplements, and lower energy intake.
-
Original Article04-08-2022
Levels and Predictors of Anxiety and Depression in Turkish PregnantWoman During the Covid-19 Pandemic
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):100-108
Abstract
Original ArticleLevels and Predictors of Anxiety and Depression in Turkish PregnantWoman During the Covid-19 Pandemic
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):100-108
Views188See moreAbstract
Objective
In addition to being a medical phenomenon, pandemics affect the individual and society on several levels and lead to disruptions. In the pandemic process, different groups in the population, including pregnant women as a defenseless group, are subjected to psychological threat. The present study aimed to determine the levels of anxiety and depression and related factors in pregnant women during the the coronavirus disease 2019 (Covid-19) pandemic.
Methods
The present cross-sectional study was conducted with 269 pregnant women through face-to-face interviews held in Istanbul, Turkey. Regarding the data collection tools, the Cronbach α reliability coefficient was of 0.90 for the Beck Anxiety Inventory, and of 0.85 for the Beck Depression Inventory.
Results
Among the participating pregnant women, 30.5% had mild, 17.5% had moderate, and 5.9% had severe anxiety symptoms, whereas 35.3% had mild, 16.7% had moderate, and 2.2% had severe depression symptoms. We found that those who were concerned about their health had 5.36 times (p=0.04) more risk of developing anxiety, and 4.82 times (p=0.01) more risk of developing depression than those who were not concerned. Those who had a history of psychiatric disease had 3.92 times (p=0.02) more risk of developing anxiety than those without it.
Conclusion
We determined that about half of the pregnant women included in the study had some degree of anxiety and depression during the COVID-19 pandemic. The risk factors for anxiety and depression among the pregnant women were determined as smoking, concerns about health and getting infectedwith the coronavirus, history of psychiatric disease, and undergoing regular antenatal care.
-
Original Article04-08-2022
Analysis of the Correlation/Agreement of Maternal-fetal Doppler Parameters in Normal and Growth-Restricted Fetuses
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):118-124
Abstract
Original ArticleAnalysis of the Correlation/Agreement of Maternal-fetal Doppler Parameters in Normal and Growth-Restricted Fetuses
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):118-124
Views191See moreAbstract
Objective
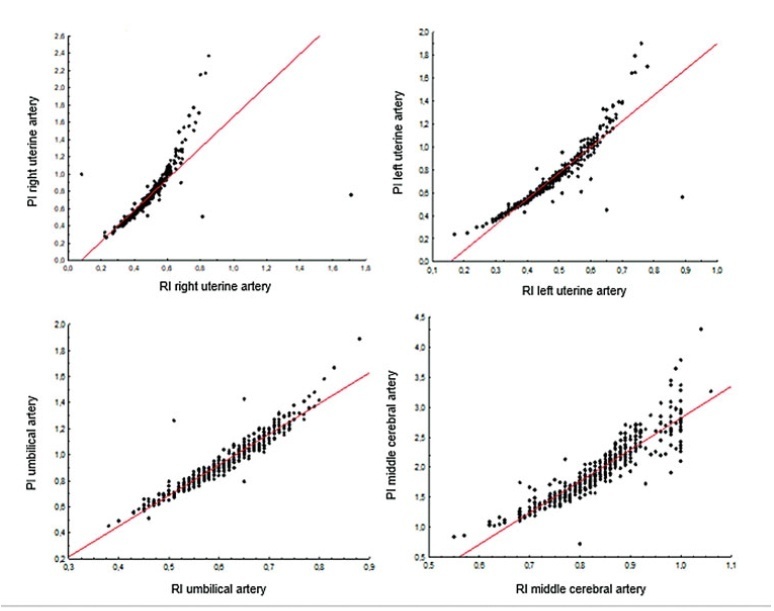
To assess the degree of correlation/agreement of maternal-fetal Doppler parameters between normal and growth-restricted fetuses (fetal growth restriction [FGR]).
Methods
The present observational and retrospective study included 274 singleton pregnancies. The following maternal-fetal Doppler parameters were assessed: uterine artery (UAt), umbilical artery (UA), middle cerebral artery (MCA), cerebroplacental ratio (CPR), and umbilical-cerebral ratio (U/C). The assessment of FGR was based on the Figueiras and Gratacós9 criteria. Spearman correlation coefficients were estimated to assess the correlation between resistance (RI) and pulsatility (PI) indices of Doppler parameters. The agreement between two Doppler parameters was assessed by the Kappa coefficient.
Results
In total, 502 Doppler examinations were included, and FGR was observed in 19 out of 274 fetuses. A strong correlation was observed between RI and PI of UAt, UA, and MCA in all of the samples (p<0.001). Of the 502 Doppler examinations, there was agreement between U/C and CPR percentiles for 480 (95.6%) and disagreement for 22 (4.4%), with Kappa coefficient of 0.26, thereby corresponding to weak agreement. Of the 68 cases with estimated fetal weight ≤ 9th percentile (small for gestational age [SGA]), there was agreement between U/C>1.0 and CPR<5th percentile in 61 (88.4%) and disagreement in 7 (5.8%) with Kappa coefficient of 0.49, thereby corresponding to moderate agreement.
Conclusion
Strong correlation was observed among RI and PI UAt, UA, and MCA Doppler examinations in the present study; however, weak agreement was observed between U/C and CPR in the normal and FGR fetuses. In SGA, U/C and CPR demonstrated moderate agreement.
-
Original Article04-08-2022
Expression of Endothelin-1 and Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase in Normal and Preeclamptic Placentae
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):125-132
Abstract
Original ArticleExpression of Endothelin-1 and Endothelial Nitric Oxide Synthase in Normal and Preeclamptic Placentae
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2022;44(2):125-132
Views174See moreAbstract
Objective
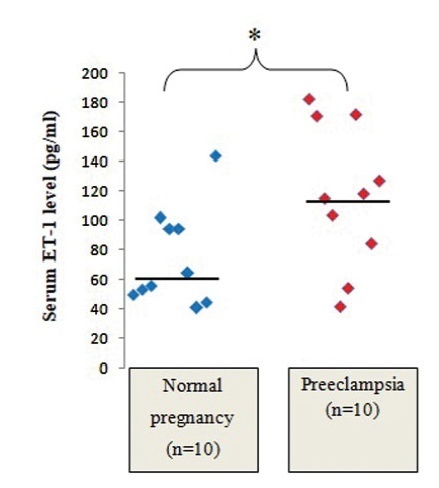
To investigate the expression of endothelin-1 (ET-1) and endothelial nitric oxide (NO) synthase (eNOS) in normal and preeclamptic (PE) placentae.
Methods
The present cross-sectional analytical study was performed in normal and PE primigravidae (n=10 in each group) who were admitted to the North Okkalapa General and Teaching Hospital from February 2019 to February 2020. Serum samples were collected immediately before delivery, and placental tissues were collected immediately after emergency or elective cesarean section. The expression of placental eNOS was measured by western blot, and the levels of ET-1 in placental tissue homogenates and in the serum were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).
Results
The PEgrouphadsignificantly higher serumlevelsof ET-1(median: 116.56 pg/mL; IQR: 89.14-159.62 pg/mL) than the normal group (median: 60.02 pg/mL; IQR: 50.89-94.37 pg/mL) (p<0.05). However, statistically significant differences were not observed in the levels of ET-1 in placental tissue homogenates between normal and PE placentae (median: 0.007 pg/μg of total protein; IQR: 0.002-0.0123 pg/μg of total protein; andmedian: 0.005 pg/μg of total protein; IQR: 0.003-0.016 pg/μg of total protein respectively). The median and IQR values of relative placental eNOS expression were significantly higher in the PE group than in the normal group (p<0.05). The serum levels of ET-1 level were not significantly correlated with placental ET-1 expression, and neither there was a significant correlation between placental ET-1 and eNOS expression in any of the groups.
Conclusion
The serum levels of ET-1 were significantly higher in PE pregnant women compared with normal pregnant women, while the ET-1 levels of placental tissue homogenates were not significantly different. Serum ET-1 rather than placental ET-1 might play a major role in the pathogenesis of PE.