-
Original Article01-12-2021
Association of Overweight and Consistent Anovulation among Infertile Women with Regular Menstrual Cycle: A Case-control Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(11):834-839
Abstract
Original ArticleAssociation of Overweight and Consistent Anovulation among Infertile Women with Regular Menstrual Cycle: A Case-control Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(11):834-839
Views219See moreAbstract
Objective
It has been suggested that excess body weight could represent a risk factor for infertility outcomes. The present study aimed to evaluate the association of overweight and anovulation among infertile women with regular menstrual cycles.
Methods
We conducted a retrospective case-control study with consistently anovulatory patients undergoing assisted reproduction treatment. The patients were stratified into normal weight (body mass index [BMI]: 18.5-24.9kg/m2) and overweight (BMI: 25.0- 29.9kg/m2).Those with polycystic ovary syndrome or obesity were excluded. The groups were matched for age, duration of infertility, prolactin, follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), thydroid stimulating hormone (TSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), and estradiol levels.
Results
Overweight was significantly associated with anovulation, when using the World Health Organization (WHO) criteria for anovulation: progesterone levels>5.65 ng/ml and ultrasonography evidence of follicle collapse (odds ratio [OR]: 2.69; 95% confidence interval [CI95%]: 1.04-6.98).
Conclusion
Body mass index above the normal range jeopardizes ovulation among non-obese infertile women with regular menstrual cycles.
-
Original Article01-12-2021
Teleoncology Orientation of Low-Income Breast Cancer Patients during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Feasibility and Patient Satisfaction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(11):840-846
Abstract
Original ArticleTeleoncology Orientation of Low-Income Breast Cancer Patients during the COVID-19 Pandemic: Feasibility and Patient Satisfaction
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(11):840-846
Views211See moreAbstract
Objective
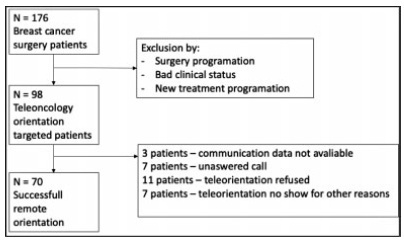
The present study aims to assess the feasibility and patient satisfaction of teleoncology orientation in a vulnerable population of breast cancer patients assessed in a government health system during the coronavirus pandemic in 2020.
Methods
Eligible patients received an invitation to receive remote care to minimize exposure to an environment in which the risk of respiratory infection was present. The means of communication was telephone through an application that allows free conversation with no charge. An anonymous-response questionnaire based on a Likert-type scale was sent through a cell phone application or e-mail directly to each patient or close relative of the patient immediately after teleconsultation. Responses to the questions, which addressed utility, facility, interface quality, interaction quality, reliability, satisfaction, and interest in future evaluation, were compiled and analyzed.
Results
A total of 176 eligible patients scheduled for consultation were evaluated and 98 were included. Seventy (71.4%) successfully undertook the teleorientation. The questionnaire was submitted by 43 (61.4%) patients. The overall teleoncology orientation was classified as very positive by 41 (95.3%) patients. Specifically, regarding the questionnaire items, 43 (100%) patients scored 4 or 5 (agreed that the teleconsultation was beneficial) concerning the facility, followed by 42 (97.2%) for the interface quality, 41 (95.3%) for both utility and interaction quality, 40 (93%) for satisfaction and interest in future evaluation, and, finally, 39 (90.6%) for reliability.
Conclusion
Teleoncology orientation of low-income breast cancer patients is most feasible and leads to high patient satisfaction.
-
Original Article01-12-2021
Prevalence of Urinary Incontinence in CrossFit Practitioners before and during the COVID-19 Quarantine and its Relationship with Training Level: An Observational Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(11):847-852
Abstract
Original ArticlePrevalence of Urinary Incontinence in CrossFit Practitioners before and during the COVID-19 Quarantine and its Relationship with Training Level: An Observational Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(11):847-852
Views196See moreAbstract
Objective
To compare the prevalence of urinary incontinence (UI) before and during the COVID-19 quarantine in CrossFit women and their relationship with training level.
Methods
A cross-sectional study was performed among 197 women practicing CrossFit. The inclusion criteria were nulliparous women, between 18 and 45 years old, who had trained, before quarantine, in accredited gyms. The exclusion criteria were not following the COVID-19 prevention protocols and having UI on other occasions than just sport. An online questionnaire was emailed containing questions about frequency, duration, and intensity of training and data related to the COVID-19 pandemic. The participants were invited to answer whether they were infected with COVID-19 and what treatment/recommendation they have followed. Whether UI stopped among participants, they were asked about the possible reasons why this happened. The training intensity was categorized as “the same,” “decreased” or “increased.”
Results
The mean age of the participants was 32 years old and most (98.5%) could practice CrossFit during the pandemic. There was a decrease in training intensity in 64% of the respondents. Exercises with their own body weight, such as air squat (98.2%), were the most performed. Urinary incontinence was reported by 32% of the participants before the COVID-19 pandemic, and by only 14% of them during the pandemic (odds ratio [OR]=0.32 [0.19-0.53]; p<0.01; univariate analysis). Practitioners reported that the reason possibly related to UI improvement was the reduction of training intensity and not performing doubleunder exercise.
Conclusion
The reduction in the intensity of CrossFit training during the COVID-19 quarantine decreased the prevalence of UI among female athletes.

-
Original Article12-17-2021
The Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Depression and Sexual Function: Are Pregnant Women Affected More Adversely?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(10):765-774
Abstract
Original ArticleThe Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Depression and Sexual Function: Are Pregnant Women Affected More Adversely?
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(10):765-774
Views210See moreAbstract
Objective
To investigate depression and sexual function among pregnant and nonpregnant women throughout the COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods
A total of 188 women, 96 pregnant and 92 non-pregnant were included. The Beck Depression Inventory (BDI) and the Arizona Sexual Experience Scale (ASEX) were applied to the participants after obtaining sociodemographic data.
Results
The depression scores of pregnant and non-pregnant women were similar (p = 0.846). We found that the depression scores were significantly higher among the group of participants who have lower economic status (p = 0.046). Moreover, the depression score was significantly higher among women who lost their income during the pandemic (p = 0.027). The score on the ASEX was significantly higher, and sexual dysfunction was more prevalent among women who have lower levels of schooling and income (p < 0.05). Likewise, the ASEX scores were significantly higher (p = 0.019) among the group who experienced greater income loss throughout the pandemic. Upon comparing the pregnant and non-pregnant groups, we detected that sexual dysfunction had a significantly higher rate among pregnant women (p < 0.001).
Conclusion
In times of global crisis, such as the current pandemic, low-income families have an increased risk of experiencing depression and sexual dysfunction. When we compared pregnant women with non-pregnant women, depression scores were similar, but pregnant women were at a 6.2 times higher risk of developing sexual dysfunction.
-
Original Article12-17-2021
Investigating the Relationship between Childbirth Type and Breastfeeding Pattern Based on the LATCH Scoring System in Breastfeeding Mothers
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(10):728-735
Abstract
Original ArticleInvestigating the Relationship between Childbirth Type and Breastfeeding Pattern Based on the LATCH Scoring System in Breastfeeding Mothers
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(10):728-735
Views225See moreAbstract
Objective
The role of breast milk in the physical and mental health of infants and in the prevention of infant death is widely known. The benefits of breastfeeding for mothers and infants have been proven, but several factors can affect breastfeeding. Childbirth is one of the most influential factors. The present study aimed to investigate the effect of the type of delivery (natural childbirth and cesarean section) on breastfeeding based on the latch, audible swallowing, type of nipple, comfort, hold (LATCH) scoring system.
Methods
The present cross-sectional observational study was performed using the census method among women who referred to Afzalipour Hospital for delivery in May 2020; the breastfeeding pattern was completed by observation and the in-case information, by LATCH checklist. Data were analyzed using the Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, United States) software, version 19.0, analysis of variance (ANOVA), and the Chi-squared statistical test.
Results
Out of a total of 254 deliveries (127 natural childbirths and 127 cesarean deliveries), there was no statistically significant difference between the 2 study groups in terms of age, maternal employment status, and infant weight, but there was a statistically significant relationship between the type of delivery, the maternal level of schooling, and the appearance, pulse, grimace, activity, and respiration (Apgar) score in the first minute. The mean score of breastfeeding patterns among the natural childbirth group (9.33) was higher than that of the cesarean section group (7.21).
Conclusion
The type of delivery affects the mother’s performance during breastfeeding, and mothers submitted to cesarean sections need more support and help in breastfeeding.
-
Original Article12-17-2021
Thyroid Function of Pregnant Women and Perinatal Outcomes in North Macedonia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(10):736-742
Abstract
Original ArticleThyroid Function of Pregnant Women and Perinatal Outcomes in North Macedonia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(10):736-742
Views151See moreAbstract
Objective
Thyroid diseases are the second most common endocrine disorders in the reproductive period of women. They can be associated with intrauterine growth restriction (IUGR), preterm delivery, low Apgar score, low birthweight (LBW) or fetal death. The aim of the present study is to explore thyroid dysfunction and its relationship with some poor perinatal outcomes (Apgar Score, low birthweight, and preterm delivery).
Methods
Dried blood spot samples from 358 healthy pregnant women were analyzed for thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), total thyroxine (TT4), and thyroglobulin (Tg). Neonatal data were collected upon delivery. Four groups were formed based on thyroid function tests (TFTs).
Results
Of the 358 tested women, 218 (60.72%) were euthyroid. Isolated hypo thyroxinemia was present in 132 women (36.76%), subclinical hyperthyroidism in 7 women (1.94%), and overt hypothyroidism in 1 (0.28%). The perinatal outcomes IUGR (p = 0.028) and Apgar score 1 minute (p = 0.015) were significantly different between thyroid function test [TFT]-distinct groups. In the multiple regression analysis, TT4 showed a statistically significant inverse predictive impact on LBW (p < 0.0001), but a positive impact of Tg on LBW (p = 0.0351).
Conclusion
Thyroid hormones alone do not have a direct impact on neonatal outcomes, but the percentage of their participation in the total process cannot be neglected. Based on the regression analysis, we can conclude that TT4 and Tg can be used as predictors of neonatal outcome, expressed through birthweight and Apgar score. The present study aims to contribute to determine whether a test for thyroid status should become routine screening during pregnancy.
-
Original Article12-17-2021
The Assessment of Vitamin D Levels in Pregnant Women is not Associated to Fetal Growth Restriction: A Cross Sectional Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(10):743-748
Abstract
Original ArticleThe Assessment of Vitamin D Levels in Pregnant Women is not Associated to Fetal Growth Restriction: A Cross Sectional Study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(10):743-748
Views276See moreAbstract
Objective
To assess maternal serum levels of vitamin D in fetuses appropriate for gestational age (AGA), small for gestational age (SGA), and with fetal growth restriction (FGR) according to estimated fetal weight (EFW).
Methods
This cross-sectional study included 87 pregnant women between 26 and 36 weeks of gestation: 38 in the AGA group, 24 in the SGA group, and 25 in the FGR group. Maternal serum vitamin D levels were assessed using the chemiluminescence method. The Fisher exact test was used to compare the results between the groups.
Results
The mean ± standard deviation (SD) of maternal age (years) and body mass index (kg/m2) in the AGA, SGA, and FGR groups were 25.26 8.40 / 26.57 ± 4.37; 25.04 ± 8.44 / 26.09 ± 3.94; and 25.48 ± 7.52 / 26.24 ± 4.66, respectively (p > 0.05). The maternal serum vitamin D levels (mean ± SD) of the AGA, SGA, and FGR groups were 22.47 ± 8.35 ng/mL, 24.80 ± 10.76 ng/mL, and 23.61 ± 9.98 ng/mL, respectively, but without significant differences between the groups (p = 0.672).
Conclusion
Maternal serum vitamin D levels did not present significant differences among pregnant women with AGA, SGA, or FGR fetuses between 26 and 36 weeks of gestation according to EFW.
-
Original Article12-17-2021
Improving Implantation Rate in 2nd ICSI Cycle through Ovarian Stimulation with FSH and LH in GNRH Antagonist Regimen
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(10):749-758
Abstract
Original ArticleImproving Implantation Rate in 2nd ICSI Cycle through Ovarian Stimulation with FSH and LH in GNRH Antagonist Regimen
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2021;43(10):749-758
Views204Abstract
Objective
To investigate whether patients with a previous recombinant follicle stimulating hormone (rFSH)-stimulated cycle would have improved outcomes with rFSH + recombinant luteinizing hormone (rLH) stimulation in the following cycle.
Methods
For the present retrospective case-control study, 228 cycles performed in 114 patients undergoing intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) between 2015 and 2018 in an in vitro fertilization (IVF) center were evaluated. Controlled ovarian stimulation (COS) was achieved with rFSH (Gonal-f, Serono, Geneva, Switzerland) in the first ICSI cycle (rFSH group), and with rFSH and rLH (Pergoveris, Merck Serono S.p.A, Bari, Italy) in the second cycle (rFSH + rLH group). The ICSI outcomes were compared among the groups.
Results
Higher estradiol levels, oocyte yield, day-3 high-quality embryos rate and implantation rate, and a lower miscarriage rate were observed in the rFSH + rLH group compared with the rFSH group. In patients < 35 years old, the implantation rate was higher in the rFSH + rLH group compared with the rFSH group. In patients ≥ 35 years old, higher estradiol levels, oocyte yield, day-3 high-quality embryos rate, and implantation rate were observed in the rFSH + rLH group. In patients with ≤ 4 retrieved oocytes, oocyte yield, mature oocytes rate, normal cleavage speed, implantation rate, and miscarriage rate were improved in the rFSH + rLH group. In patients with ≥ 5 retrieved oocytes, higher estradiol levels, oocyte yield, and implantation rate were observed in the rFSH + rLH group.
Conclusion
Ovarian stimulation with luteinizing hormone (LH) supplementation results in higher implantation rates, independent of maternal age and response to COS when compared with previous cycles stimulated with rFSH only. Improvements were also observed for ICSI outcomes and miscarriage after stratification by age and retrieved oocytes.
Key-words Follicle stimulating hormoneintracytoplasmic sperm injection implantationLuteinizing hormoneOvarian stimulationSee more


