-
Original Article04-30-2025
Incidence of small-for-gestational-age newborns in pregnant women with COVID-19
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo20
Abstract
Original ArticleIncidence of small-for-gestational-age newborns in pregnant women with COVID-19
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo20
Views188Abstract
Objective:
This study aimed to assess the incidence of small for gestational age (SGA) newborns in pregnant women infected with COVID-19 and examine the associated neonatal outcomes.
Methods:
This study involved a secondary analysis of the REBRACO Network, a prospective cohort study conducted in 15 maternity hospitals in Brazil before the introduction of COVID-19 vaccination (February 2020 to February 2021). Demographic data of pregnant women tested for COVID-19 were analyzed, and fetal outcomes were compared between women with positive and negative COVID-19 results who had SGA fetuses.
Results:
A total of 729 symptomatic pregnant women with COVID-19 were included in the study. However, there were 248 participants with missing information regarding childbirth or loss of follow-up, and 107 participants without confirmatory tests for COVID-19. Among the remaining participants, 198 had confirmed COVID-19 and 176 tested negative. The incidence of SGA among women with COVID-19 was 22.4%, whereas the incidence among women who tested negative for COVID-19 was 14.8%. SGA newborns born to COVID-19 positive pregnant women were 1.6 times more likely to experience adverse outcomes (such as prematurity, stillbirth, neonatal death, and admission to a neonatal ICU) compared to non-SGA newborns [OR = 1.655 (1.145 – 2.394); P=0.017]. In SGA newborns of pregnant women with confirmed COVID-19 infection, mechanical ventilation use was found to be associated with the infection [OR = 0.692 (0.562 – 0.853); P=0.002].
Conclusion:
The higher incidence of SGA newborns and its stronger association with prematurity in pregnant women with confirmed COVID-19 infection suggest that COVID-19 infection is a significant factor contributing to neonatal morbidity and mortality.
Key-words coronavirus infectionsCOVID-19Infant, newbornInfant, small for gestational agematernal healthPregnancy complicationsSee more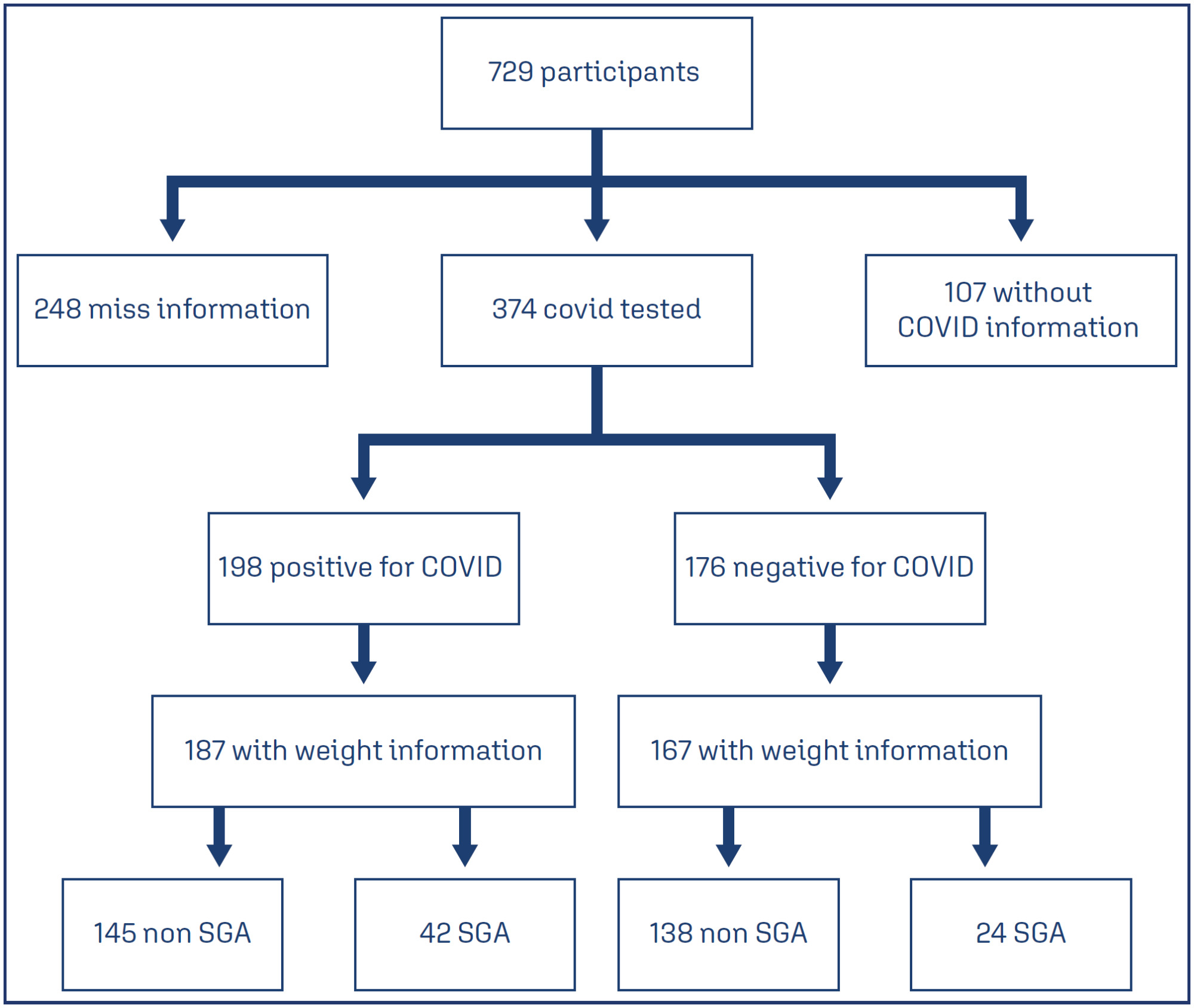
-
Original Article04-30-2025
An assessment of total antioxidant and oxidant parameters and their correlation with embryo quality in in-vitro fertilization patients
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo22
Abstract
Original ArticleAn assessment of total antioxidant and oxidant parameters and their correlation with embryo quality in in-vitro fertilization patients
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo22
Views223Abstract
Objective:
In vitro, fertilization is the primary treatment method for infertility. Follicular fluid analysis is an approach used to optimize the results of assisted reproductive techniques. Oxidative stress represents the imbalance between the production of reactive oxygen species and their detoxification. Total Antioxidant and Oxidant Status, and Oxidative Stress Index levels are the main oxidative stress markers. This study investigated the effects of oxidative stress markers on infertility etiology, embryo quality, and success of In vitro fertilization.
Methods:
Before enrolling in the ICSI-ET cycle, participants had their FSH and LH levels assessed on the second day of the cycle. The ovarian degrees of the participants were evaluated by transvaginal ultrasonography. Participants underwent controlled ovarian stimulation using the GnRH antagonist protocol. TV-USG and serial E2 measurements were performed at appropriate intervals to follow follicular development. Follicle sizes, quantity, and endometrial thickness were recorded. Total Antioxidant and Oxidant Status, and Oxidative analyses were conducted using Rel Assay Diagnostics Assay Kits.
Results:
The average number of total oocytes in the participants was 10.25±6.66, and the average of mature M2 stage oocytes was 6.71±3.72. The average number of fertilized oocytes was 4.65±2.81. Fertilization rates were calculated as approximately 54.75±25.58%. A statistically significant positive correlation was found between embryo quality and serum Total Antioxidant Status levels (p=0.004). Similarly, a significant positive correlation was observed between embryo quality and follicular Total Antioxidant Status values (r = 0.42, p = 0.01).
Conclusion:
This study concluded that oxidative stress markers affect certain stages of the IVF treatment process.
Key-words AntioxidantsFertilization in vitroFollicular fluidInfertilityOocytesOxidantsOxidative stressSee more
-
Original Article04-30-2025
Prevalence of antiphospholipid syndrome among women with recurrent pregnancy loss: a cohort study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo23
Abstract
Original ArticlePrevalence of antiphospholipid syndrome among women with recurrent pregnancy loss: a cohort study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo23
Views252Abstract
Objective:
This study aimed to evaluate the prevalence of antiphospholipid syndrome (APS) among women experiencing recurrent pregnancy loss (RPL).
Methods:
A cross-sectional was conducted, reviewing the medical records of 134 women with a history of two or more miscarriages, treated between January 2014 and May 2024 at a tertiary university center in Belo Horizonte, Brazil. APS screening was performed by assessing anticardiolipin (IgG and IgM), lupus anticoagulant, and anti-β2-glycoprotein-1 (IgG and IgM) antibodies, based on Sapporo criteria. All tests were performed during non-pregnant periods and at least 12 weeks after the last miscarriage.
Results:
The study included 134 women with a mean age of 33.8 ± 5.7 years. The number of prior miscarriages ranged from 2 to 11 per couple. Among the patients who presented the lupus anticoagulant, only two (1.49%) tested positive in two samples, as per revised Sapporo criteria. Considering IgG and IgM anticardiolipin antibodies, four patients (2.98%) tested positive in two samples according to old Sapporo criteria, with one patient having a positive IgG test in two samples, two having positive IgM in two samples and a single patient having both positive tests. None of the 56 patients tested positive for anti-β2-glycoprotein-1 antibodies in two samples.
Conclusion:
The prevalence of antiphospholipid antibodies, in line with revised Sapporo criteria, is low among Brazilian women with recurrent pregnancy loss, consistent with recent studies in literature. Ensuring the appropriateness of diagnostic criteria is crucial to avoid unnecessary treatment with platelet anticoagulants and heparin in this population.
Key-words Abortion, habitualAbortion, spontaneousAntibodiesAnticardiolipinAntiphospholipid syndromePrevalenceThrombophiliaSee more -
Original Article04-30-2025
Hysterectomy rates per resident in final year of training in teaching hospitals: an ecologic study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo24
Abstract
Original ArticleHysterectomy rates per resident in final year of training in teaching hospitals: an ecologic study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo24
Views243Abstract
Objective:
Analyze the hysterectomy rates per resident in graduation year in teaching hospitals in the state of São Paulo (Brazil).
Methods:
We selected teaching hospitals in the state of São Paulo and gathered information from two public databases to estimate the hysterectomy rates per resident in their final year of training between 2009 and 2019.
Results:
Between 2009 and 2019, there was a 37.5% increase in the number of residents in their final year of training, a 4.31% increase in the number of hysterectomies, and a drop in the hysterectomy rates per resident of 24.1%. The reduction of the rate of hysterectomy per resident was more pronounced for vaginal route (46.4%) followed by abdominal route (23.3%). The ratio of laparoscopic hysterectomy per resident increased 264% during the period, however, this route was used in only 7% of the surgeries in 2019.
Conclusions:
The hysterectomy rates per resident in their final year of training showed a notable reduction. This trend, particularly pronounced in vaginal and abdominal routes, signals a shift towards minimally invasive techniques.
Key-words Clinical competenceEducation, medicalHospitals, teachingHysterectomylearning curveMedical staff, hospitalPhysiciansStudents, medicalSurgical procedures, operativeSee more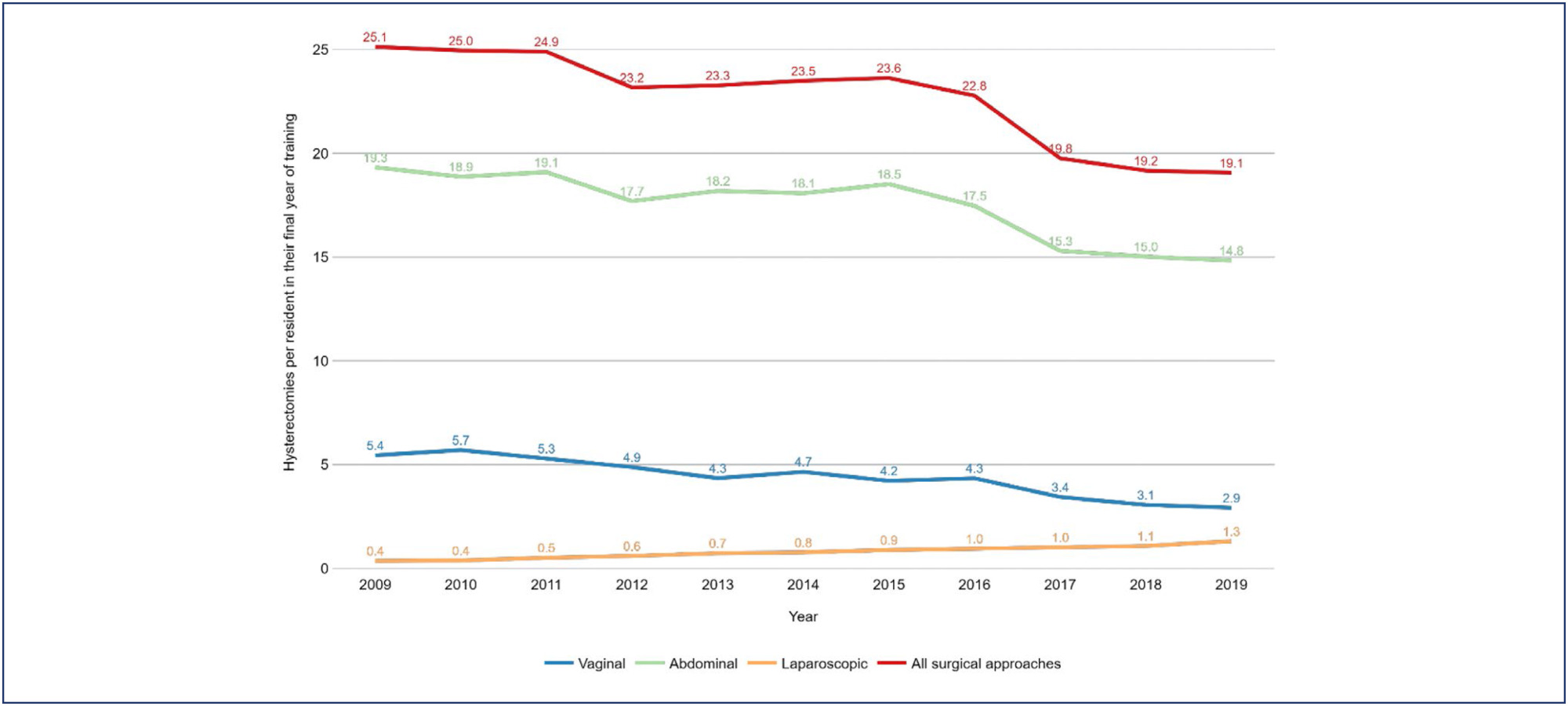
-
Original Article04-30-2025
Depression, anxiety, sexual function and quality of life in women with hyperprolactinemia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo7
Abstract
Original ArticleDepression, anxiety, sexual function and quality of life in women with hyperprolactinemia
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo7
Views170Abstract
Objective:
To evaluate anxiety, depression, sexual function and quality of life in women with hyperprolactinemia.
Methods:
Cross-sectional study with 80 women divided into two groups: 30 women with hyperprolactinemia (Study Group) followed and treated at the endocrine gynecology outpatient clinic and 50 women without hyperprolactinemia, with regular menstrual cycles (Control Group) followed at the family planning outpatient clinic of the State University of Campinas from June 2021 to October 2022. Sociodemographic characteristics, quality of life (SF-36 Questionnaire), sexual function (Female Sexual Function Index Questionnaire), depression (Beck Depression Inventory) and anxiety (Beck Anxiety Scale) were evaluated in both groups. Categorical variables were described as absolute frequency and percentage; numerical variables as mean and standard deviation. Comparison of numerical variables between two groups was performed by Mann-Whitney test, while categorical were compared by Chi-Square or Fisher's exact tests.
Results:
The mean age of women with hyperprolactinemia was 39.6±8.1 years and the Control Group was 31.2±9.5 years (p<0.001). There was no difference in anxiety scores (p=0.66), depression (p=0.08) and general sexual function (p=0.08) in both groups. However, women with hyperprolactinemia had lower scores in the domains of pain and arousal and worse functional capacity than Control Group (p<0.05).
Conclusion:
Women with hyperprolactinemia under treatment do not show any impairment in their anxiety, depression and sexual function when compared to women without hyperprolactinemia. However, analysis of quality of life showed that women with hyperprolactinemia have poor functional capacity.
Key-words AnxietyDepressionHyperpituitarismHyperprolactinemiaQuality of lifesexual functionsurveys and questionnairesSee more -
Original Article03-18-2025
Gastrin-releasing peptide receptor: a promising new biomarker to identify cervical precursor lesions and cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo4
Abstract
Original ArticleGastrin-releasing peptide receptor: a promising new biomarker to identify cervical precursor lesions and cancer
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo4
Views229Abstract
Objective:
This study aimed to verify the relation between gastrin-releasing peptide receptor (GRPR), oncogenic Human Papillomavirus (HPV) and cervical lesions severity.
Methods:
GRPR mRNA levels were evaluated in cervical cancer-derived cell lines and in primary keratinocytes expressing HPV16 oncogenes by RT-PCR. GRPR protein expression was assessed by immunohistochemistry in organotypic cell cultures derived from keratinocytes transduced with HPV16 oncogenes and in 208 cervical samples, including 59 non-neoplastic tissue, 28 cervical intraepithelial neoplasia grade 3 (CIN3), 44 squamous cell carcinomas (SCC) and 77 adenocarcinomas (ADC). Generic primers (GP5+/GP6+) were used to identify HPV infection in tissue samples. Experiments involving cell lines were analyzed through non-parametric tests (Kruskal Wallis), and Fisher's Exact Test for human tissues samples. All statistical tests were considered significant at p <0.05. Immunohistochemical evaluation was conducted independently and blindly by two observers (AD- LO). Any discordant findings were resolved through discussion to reach a consensus score.
Results:
GRPR mRNA levels were not increased in cells expressing HPV16 or HPV18 oncogenes. However, at the protein level, GRPR was upregulated in organotypic cell cultures containing HPV oncogenes. Besides, it was identified an association between GRPR expression and cervical lesion severity (p < 0.0001). The detection rate of high-risk HPV DNA was directly correlated with cervical disease. Nonetheless, HPV infection was not directly associated with GRPR in cervical samples.
Conclusion:
GRPR expression is highly predictive of cervical lesion severity, irrespective of HPV infection and might contribute to improving patient's therapeutic management as well as being used a marker of disease progression.
Key-words AdenocarcinomaCarcinoma, squamous cellGastrin-releasing peptide receptorHuman papillomavirusOncogenesPapillomavirus infectionsUterine cervical dysplasiaUterine cervical neoplasmsSee more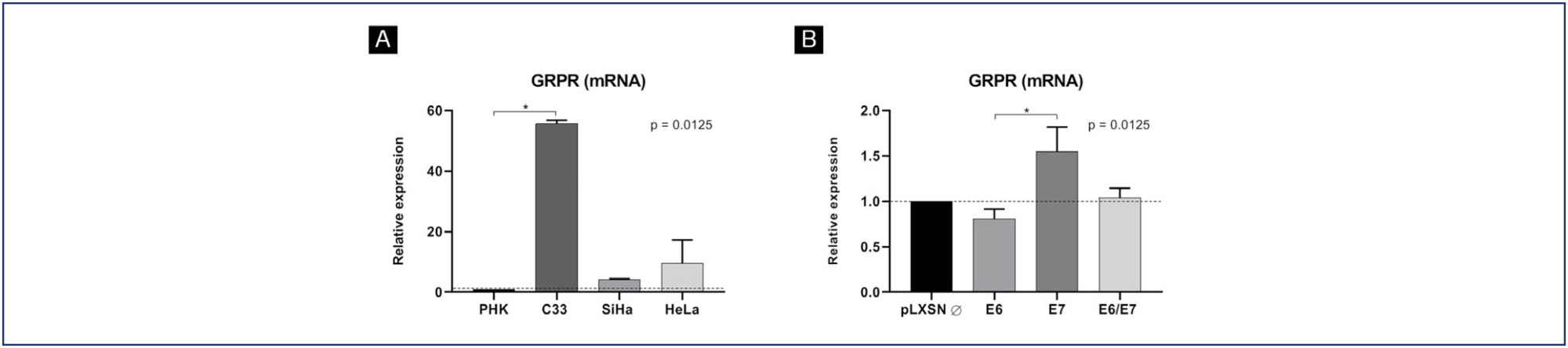
-
Original Article03-18-2025
Accurate evaluation of mode of delivery and labor progression with angle of progression: a prospective cross-sectional
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo5
Abstract
Original ArticleAccurate evaluation of mode of delivery and labor progression with angle of progression: a prospective cross-sectional
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo5
Views254See moreAbstract
Objective:
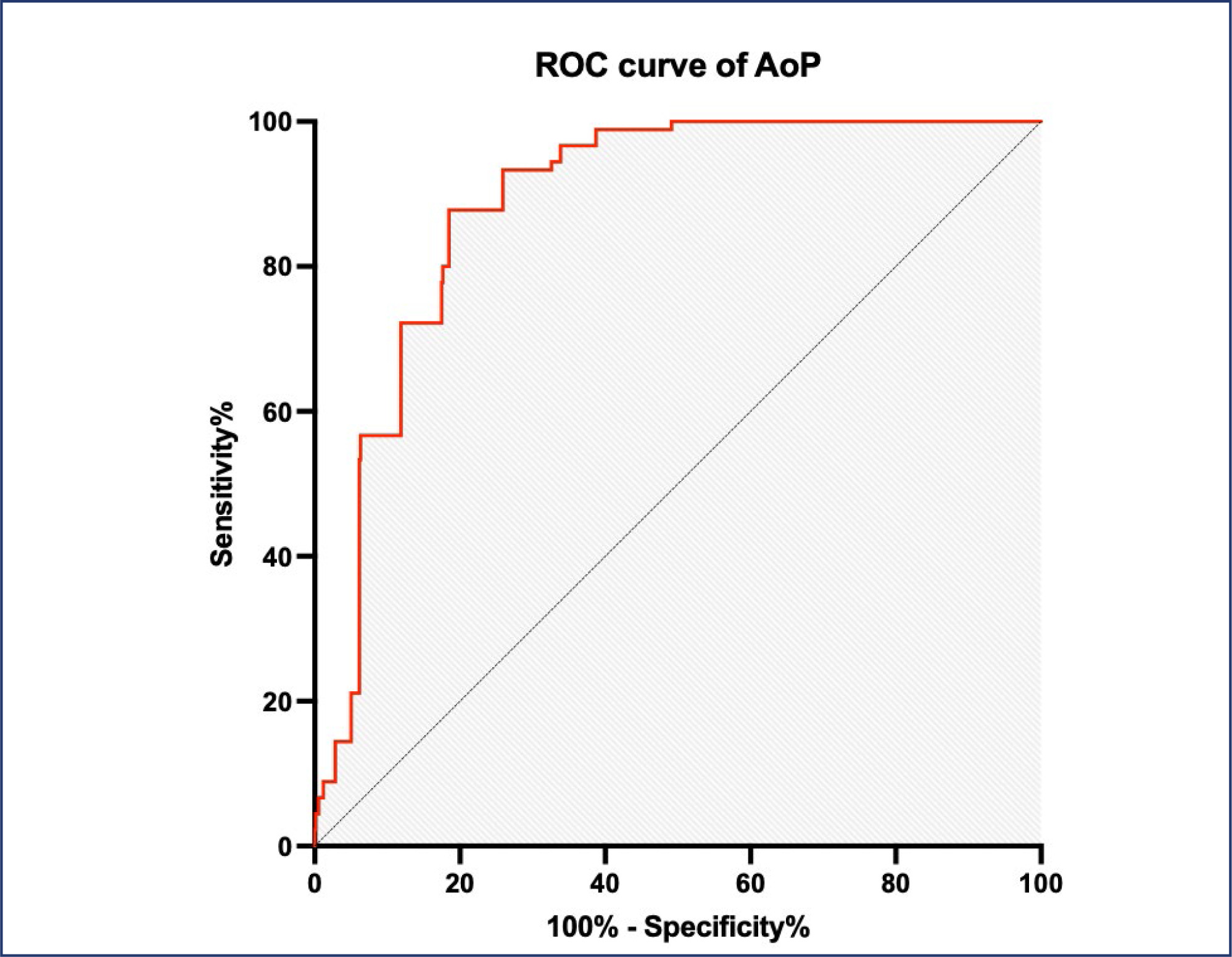
To determine the validity of the angle of progression (AoP) in predicting delivery mode among women in the second stage of labor.
Designs:
This prospective cohort study was conducted at the Obstetrics and Gynecology unit (OBGYN) of two hospitals in Vietnam. Transperineal ultrasound was performed for each woman to measure the progression angle in the second phase of labor.
Participants:
A total of 725 women with singleton pregnancies with cephalic presentation at term
Methods:
Transperineal ultrasound was used to measure the angle of progression in the second labor phase and to identify the delivery method.
Results:
The rate of vaginal birth in women with an AoP ≥ 120° on transperineal ultrasound was 70.2%. The optimal cutoff point of AOP ≥122° with sensitivity and specificity for vaginal birth were 87.8% and 80.7%, respectively the area under the ROC curve of 0.887 (p<0.0001). The study's sample size was restricted owing to deficiencies in resources and time.
Conclusion:
The likelihood of achieving spontaneous vaginal delivery can be predicted by the angle of progression measured with transperineal intrapartum ultrasonography during the second stage of labor in women.
-
Original Article03-18-2025
Effect of COVID-19 on Brazilian cesarean and prematurity rates: a cross-sectional study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo6
Abstract
Original ArticleEffect of COVID-19 on Brazilian cesarean and prematurity rates: a cross-sectional study
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2025;47:e-rbgo6
Views255See moreAbstract
Objective:
To investigate the relationship between prematurity and cesarean section rate in Brazil during the beginning of COVID-19 pandemic.
Methods:
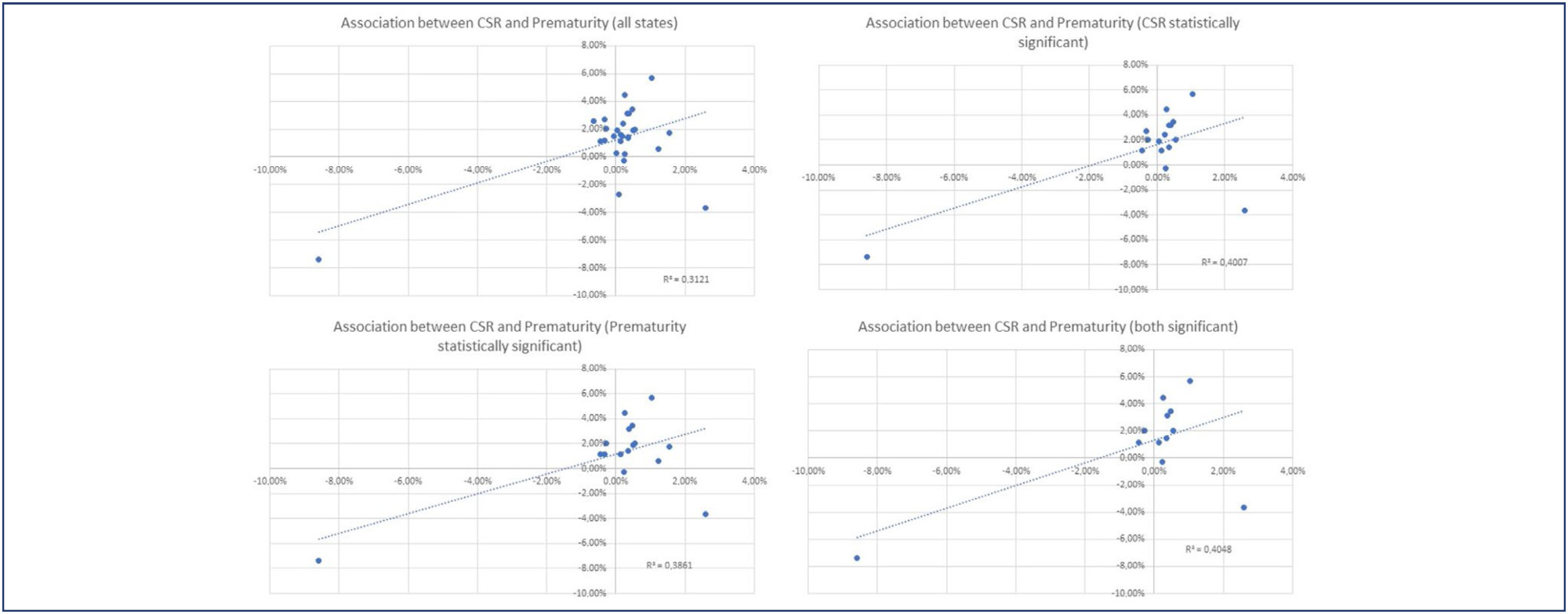
Utilizing the Robson Classification, this study analyzed data from the Brazilian Ministry of Health's Live Births Panel, comparing CSR) and group 10 (preterm deliveries) between 2019 (pre-pandemic) and 2021 (pandemic) in each of Brazilian states and the overall country. The prematurity and CSR were compared using prevalence ratio and confidence interval, and p-value was obtained. The variation of prematurity and CSR were compared through the coefficient of determination (R2).
Results:
A total of 5,522,910 deliveries were evaluated during the period. The CSR increased from 56.34% to 57.05% (p<0.01), and the frequency of preterm deliveries rose from 8.99% to 9.13% (p<0.01). The CSR increased in 23 States and decreased in 4 States, while the prematurity rate increased in 16 States and decreased in 10 States. A positive relationship between the increase of CSR and prematurity was observed during COVID-19, with an R2 value of 0.3121, suggesting a moderate association between these two variables.
Conclusion:
Between 2019 (pre-COVID-19 pandemic) and 2021 (the first full year of the COVID-19 pandemic), there was an increase in prematurity and CSR in Brazil. These increases were observed in most Brazilian states and may be correlated. However, it is impossible to establish a cause-effect relationship given the design of this study.