Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(11):643-651
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006001100003
PURPOSE: literature reports show that there are no conclusive data about the association between endometriosis and the concentrations of hormones involved in the control of reproduction. Thus, the present study was undertaken to determine FSH, LH, estradiol (E), progesterone (P), and histamine (Hi) concentrations in serum, peritoneal fluid and follicular fluid of women with and without endometriosis. METHODS: the extent of the disease was staged according to the revised American Fertility Society classification (1997). For the collection of serum and peritoneal fluid, 28 women with endometriosis undergoing diagnostic laparoscopy were selected (18 infertile women with endometriosis I-II and ten infertile women with endometriosis III-IV). For the control group, 21 fertile women undergoing laparoscopy for tubal sterilization were selected. Follicular fluid was obtained from 39 infertile women undergoing in vitro fertilization (21 women with endometriosis and 18 women without endometriosis). RESULTS: FSH and LH levels in serum, peritoneal fluid and follicular fluid did not differ significantly between groups. On the other hand, E and P concentrations in the peritoneal fluid were significantly lower in infertile women with endometriosis (E: 154.2±15.3 for stages I-II and 89.3 ng/mL±9.8 ng/mL for stages III-IV; P: 11.2±1.5 for stages I-II and 7.6 ng/mL±0.8 for stages III-IV) in comparison with control women (E: 289.1 ng/mL±30.1; P: 32.8±4.1 ng/mL) (Kruskal-Wallis/Dunn tests; p<0.05). In serum, estradiol and progesterone concentrations followed the same pattern. In the follicular fluid, E and Hi concentrations were significantly lower in women with endometriosis (E: 97.4±11.1 pg/mL; Hi: 6.6±0.9 ng/mL) in comparison to women without endometriosis (E: 237.5±28.5 pg/mL; Hi: 13.8±1.3 ng/mL) (Student t-test; p<0.05), while progesterone levels revealed no significant difference between groups. CONCLUSIONS: our results indicate ovary dysfunction in women with endometriosis, with reduction on E, P and Hi concentrations, which may contribute to the subfertility often associated with the disease.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(11):652-657
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006001100004
PURPOSE: to determine if the previous fertility history can predict current fertility status of a patient examined for couple’s infertility. METHODS: retrospective study involving semen analyses from 183 consecutive subfertile patients evaluated from September 2002 to March 2004. We excluded those patients who had undergone radio or chemotherapy, orchiectomy or vasectomy. Mean values of all analyses were used for patients with multiple semen analysis. Patients with more than 20x10(6) sperm/mL, motility higher than 50% and with normal strict sperm morphology higher than 14% were considered normal. Patients were divided into two groups, according to the fertility status: primary infertility (118 patients) and secondary infertility (65 patients). Data were analyzed according to the chi2 test and the Student t-test. RESULTS: no differences were detected in the mean age between patients with primary infertility, 37.3±6.3, and secondary infertility, 38.1±5.9; p=0.08. In the group of patients with primary infertility, 51.9% (61 patients) had a normal sperm concentration, 70.3% (83 patients) had normal sperm motility and 26.3% (31 patients) had normal sperm morphology. In the group of patients with secondary infertility, 53.8% (35 patients) had normal sperm concentration, 75.4% (49 patients) had normal sperm motility and 32.3% (21 patients) had normal sperm morphology. No significant differences were detected in sperm concentration (21.3x10(6)/mL versus 23.1x10(6)/mL; p=0.07), motility (45.2 versus 48.1%; p=0.08) and morphology (6.1 versus 6.4%; p=0.09) between groups of patients with primary and secondary infertility. CONCLUSIONS: semen analysis should be requested even in cases of prior male fertility. Physicians should not presume a patient to have a normal semen analysis based on his previous history of initiating a pregnancy.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(11):658-663
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006001100005
PURPOSE: to analyze breast tissue of postmenopausal women before and after six months of continuous combined estrogen-progestin replacement therapy (0.625 mg conjugated equine estrogens associated with 2.5 mg medroxyprogesterone acetate). METHODS: all patients were evaluated before treatment and considered eligible to receive the drug. The material was obtained from the upper outer left quadrant, through a percutaneous large-core breast biopsy. Epithelial density and nuclear volume on hematoxylin-eosin-stained plates were evaluated for the morphological study. Morphometry was graphically analyzed by optical microscopy (400X) after acquisition of image by a digital image-capturing system (Vidcap 32) and image analysis system (Imagelab 2000 Software®). RESULTS: after six months of estrogen-progestin replacement therapy, there was a significant increase in nuclear volume in late postmenopausal women (103.6 to 138.1 µm³). There was no difference in epithelial density with the treatment (before 0.08 and later 0.10). CONCLUSIONS: estrogen-progestin combined replacement therapy for six months induced an enhacement in nuclear volume of breast epithelial cells, suggesting an increase in their metabolic activity. However, it is important to emphasize that this finding was observed only in late postmenopausal women. The increased nuclear volume could precede other events that confirm the stimulation of cellular proliferation by these hormones.
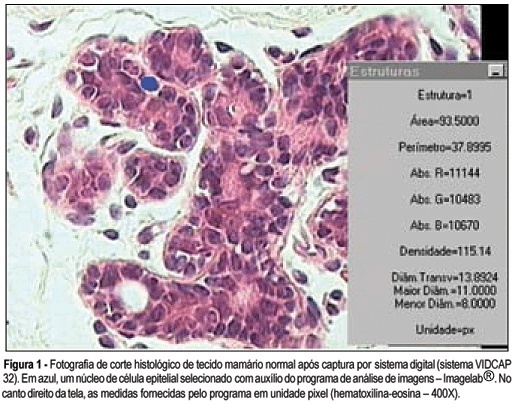
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(11):664-670
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006001100006
PURPOSE: to assess the role of ultrasonographic cervical length in predicting premature labor in patients presenting persistent uterine contractions and intact membranes. METHODS: a prospective observational cohort study was performed in 45 women admitted to our hospital between 22 and 34 weeks of gestation. Transvaginal sonographic evaluation of the cervix was performed once in the women who had completed a course of parenteral tocolysis. The cervical length was obtained according to criteria reported previously. Cervical sonographic findings were not used in diagnosis and management. Outcome variable was the occurrence of preterm delivery (<37 weeks). Statistical analysis consisted of univariate method with the purpose of determining the significant contribution of cervical length to the prediction of preterm delivery. The adopted significance level was 5% (p<0,05) and the confidence interval was 95% (95% CI). RESULTS: the incidence of preterm delivery was 51.11% (23/45). Cervical length was significantly associated with the outcome (p<0.0001). Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis showed that a cervical length of 20 mm was the best cutoff in predicting preterm delivery (sensitivity 86.9%; specificity 81.8%; positive predictive value 83.3%; negative predictive value 85.7%). The calculated area under the curve was 0.91 (95% CI: 0.79-0.97; p<0.0001). CONCLUSIONS: among women with persistent uterine contractions and intact membranes treated for preterm labor, a cervical length of less than 20 mm demonstrated a high likelihood of preterm birth. Transvaginal ultrasound may improve the accuracy of diagnosis in symptomatic women.
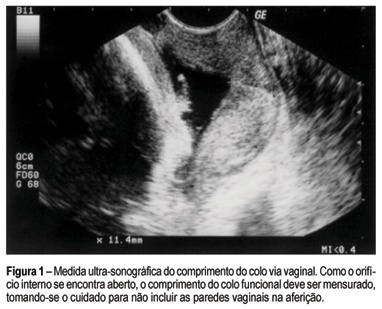
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(11):671-679
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006001100007
PURPOSE: to investigate the influence of the maternal mobility during the active phase of labor. METHODS: a prospective clinical trial was conducted through comparative analysis among a treatment group (n=50) and a control group (n=50), in the Obstetric Center of the Hospital Universitário da Universidade de São Paulo (USP). The inclusion criteria were: primigravidae with a single fetus on cephalic presentation, with 37 to 42 weeks of pregnancy, with two uterine contractions every ten minutes and with cervical dilatation until 4 cm, besides the agreement to sign the free and informed consent term. The evolution of labor for cesarean section was the exclusion criteria. The patients were assisted during the active phase of labor by the physiotherapist and encouraged for staying in vertical position and movement, according to each dilatation stage and fetus head progression. The control group had obstetric support without the presence of the physiotherapist; it was selected retrospectively, according to the same inclusion and exclusion criteria. RESULTS: 58 primigravidae between 15 and 37 years old were accompanied; 50 of them (86.2%) evolved to vaginal birth and eight (13.7%) evolved to cesarean section and were excluded. Among the patients who were accompanied, the mean of active phase was five hours and 16 minutes, while in the control group it was eight hours and 28 minutes (p<0.001). This difference was maintained in relation to the amniotic sac either whole or ragged. As for the cervix uterine evanescence, the treatment group showed a smaller period of active phase in association to a thin uterine cervix (p<0.001). In the treatment group, none of the patients used analgesics during the active phase, against 62% of the control group (p<0.001). In this group, all the patients used some kind of anesthesia for delivery; in the treatment group, among those who used anesthesia, 76% did it while the dilatation was 9 or 10 cm and 12% did not use any kind of anesthesia (p<0.05). The average weight of the newborns and the apgar did not show significant difference rates between the two groups. CONCLUSIONS: the good performance of maternal mobility has positive influences on the labor process: it increases the tolerance to pain, avoids the use of drugs during labor, improves the evolution of dilatation and reduces the duration of the active phase.

Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(10):575-580
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006001000002
PURPOSE: To determine the values of amniotic fluid in normal fetuses during the first trimester of pregnancy by three- and bi-dimensional ultrasonography. METHODS: In a prospective longitudinal study, 25 normal fetuses were evaluated from the 8th to the 11th week of gestation. Amniotic fluid volume was measured by endovaginal ultrasonography with the three- and two-dimensional modes. The two-dimensional study consisted of volumetric determination by mathematical calculation based on an ellipsoidal shape (constant 0.52) to obtain the amniotic sac and embryo volumes. In the three-dimensional study, the amniotic fluid volume was determined by the VOCAL technique using 6, 9, 15, and 30 degrees of rotation. The amniotic fluid volume obtained by 6-degree rotations was considered to be the final result. In both modes, amniotic fluid volume was obtained by subtracting the volume of the embryo from the volume of the amniotic sac. Data were analyzed statistically for variance (ANOVA), correlation and regression analysis. The level of significance was set at p < 0.05. RESULTS: The amniotic fluid volume as measured by two-dimensional ultrasonography increased from 5.45 to 39.52 cm³ in the range from the 8th to the 11th week (ANOVA - p < 0.05). There was a correlation between gestational age and amniotic fluid volume (p < 0.001, r² = 88.3%). In the three-dimensional study, the amniotic fluid volume increased from 5.7 to 42.9 cm³ in the range from the 8th to the 11th week (ANOVA - p < 0.05), and again a correlation between gestational age and amniotic fluid volume (p < 0.001, r² = 98.1%) was observed. CONCLUSION: an increase in amniotic fluid volume occurs during the first trimester of pregnancy, as determined by the two- and three-dimensional modes. In addition, we have demonstrated that the higher the gestational age, the larger the amniotic fluid volume.
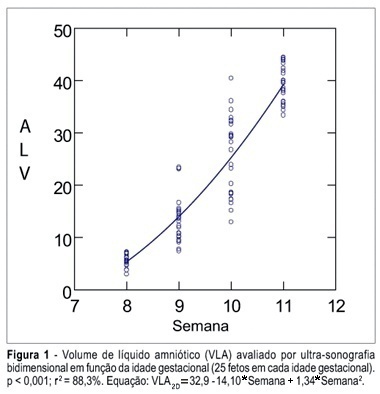
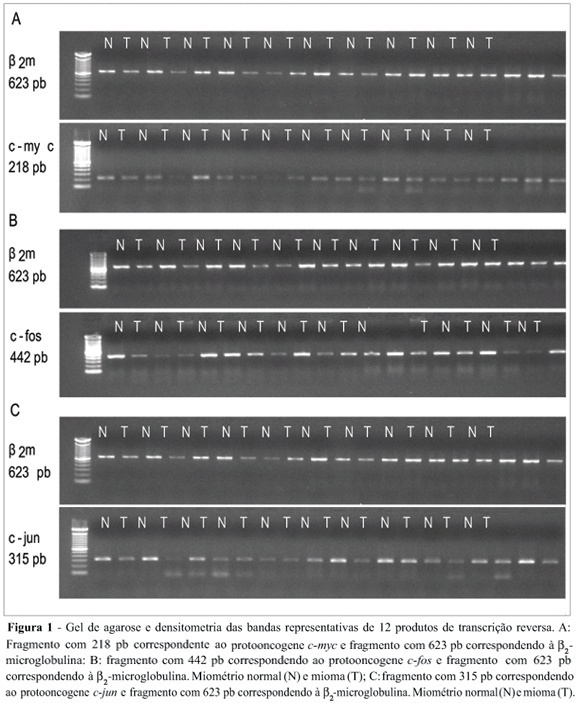
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(10):581-589
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006001000003
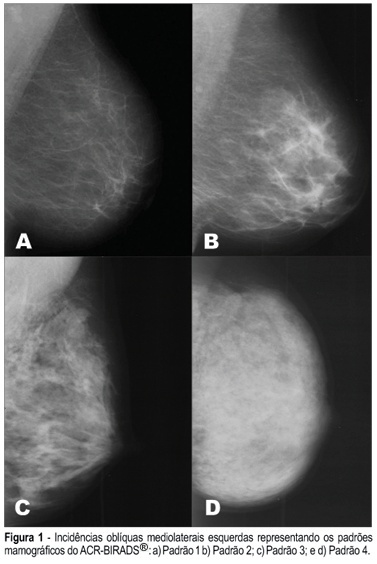
PURPOSE: To assess the presence of estrogen receptor gene polymorphisms HaeIII and MspI as well as clinical factors, and their possible associations with high mammographic density in post-menopausal women. METHODS: One hundred and fifteen post-menopausal women, not in use of hormonal therapy and without clinical or mammographic lesions were evaluated. Three independent observers have determined the mammographic density pattern based on the ACR-BIRADS® 2003 (two subjective and one objective evaluations - Adobe Photoshop 7.0 software). Oral swabs (Cytobrush) were obtained to extract DNA and the polymerase chain reaction - restriction fragment length polymorphism) was performed to assess the presence of polymorphisms in intron 1 and exon 1 from estrogen receptor gene (HaeIII and MspI). RESULTS: The HaeIII polymorphism was found in 43 (37.4%) of the 115 women, while MspI was found in 96 (83.5%) of them. There was a good agreement among determinations of the three observers with regard to mammographic density. Thirty-four (29.6%) women had dense breasts and eighty-one (70.4%) had non-dense breasts. CONCLUSION: The estrogen receptor gene polymorphism Haelll showed no association with mammographic density (Fisher = 0.712), while the association between estrogen receptor gene polymorphism Mspl and mammographic density was near significance (Fisher = 0.098). The associations among age, parity and body mass index revealed statistical significance.
Summary
Revista Brasileira de Ginecologia e Obstetrícia. 2006;28(10):590-595
DOI 10.1590/S0100-72032006001000004
Uterine myomas are common benign tumors of the female genital tract. The expression of growth factor signal transduction cascade components including the protooncogenes c-myc, c-fos, and c-jun seem to be involved in the development of myomas. PURPOSE: To compare the gene (mRNA) and protein expression of the protooncogenes c-fos, c-myc, and c-jun in human normal myometrium and leiomyoma. METHOD: A case-control study was performed. Samples were collected from 12 patients submitted to hysterectomy at the Hospital de Clínicas at Porto Alegre. The expression of the specific mRNA for c-myc, c-fos, c-jun, and beta-microglobulin was assessed through the RT-PCR technique, using specific primers to each gene. The protein expression of these protooncogenes was evaluated through the Western blot technique with specific antibodies. RESULTS: No statistically significant difference was observed in the gene expression for these protooncogenes between normal myometrium and leiomyoma (c-myc: 0,87 ± 0,08 vs 0,87 ± 0,08, p = 0,952; c-fos: 1,10 ± 0,17 vs 1,01 ± 0,11, p = 0,21; c-jun: 1,03 ± 0,12 vs 0,96 ± 0,09, p = 0,168, respectively). No statiscally significant difference was observed for the protein expression of these protooncogenes between normal myometrium and leiomyoma (c-myc: 1,36 ± 0,48 vs 1,53 ± 0,29, p = 0,569; c-fos: 8,85 ± 5,5 vs 6,56 ± 4,22, p = 0,434; e c-jun: 6,47 ± 3,04 vs 5,42 ± 2,03, p = 0,266, respectively). CONCLUSION: No difference was observed in the gene expression (transcription) nor in the protein expression (translation) of the protooncogenes c-myc, c-fos, and c-jun between leiomyoma and myometrium.